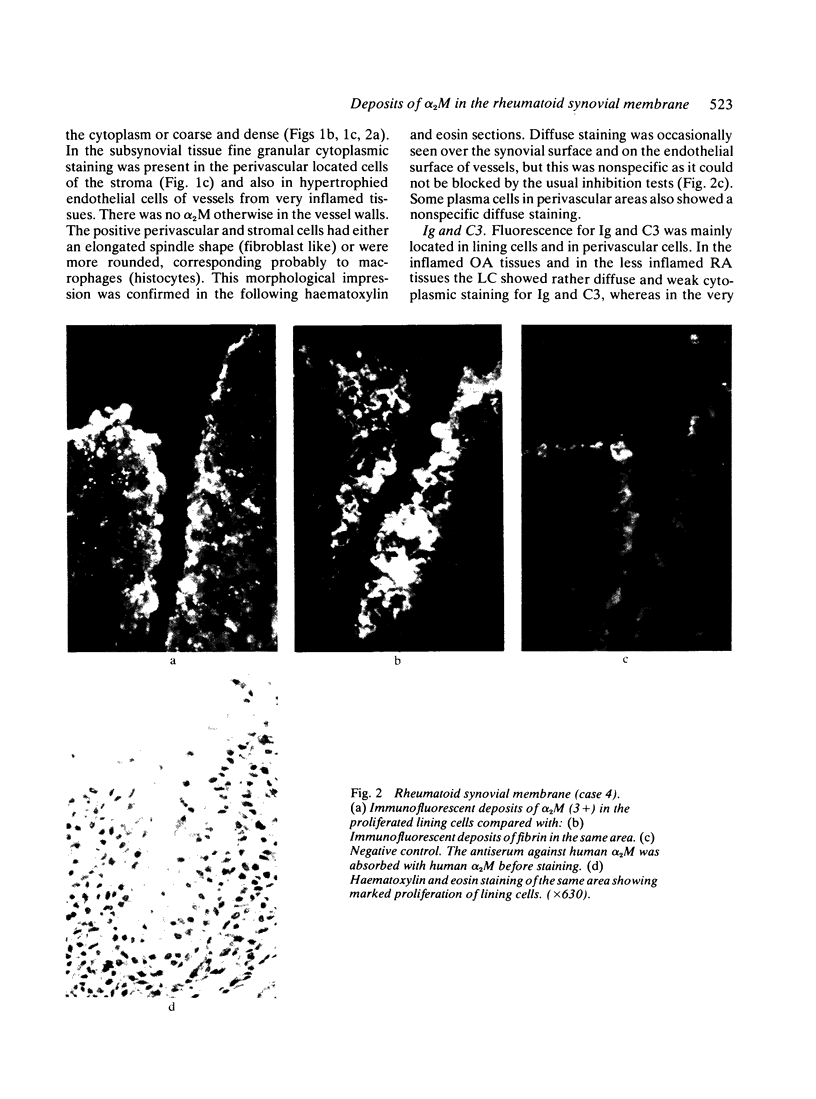
Abstract
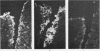
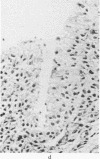
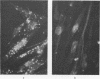
Synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, osteoarthritis, and having menisectomies was examined by immunofluorescence for deposits of alpha-2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M). In inflammed tissues, alpha 2M was found in the synovial lining cells and in perivascular cells. The amount of alpha 2M correlated with the degree of inflammation. Similarly, free lining cells obtained by trypsination of the intact synovial membrane contained identical inclusions. alpha 2M was not detected in the menisectomy cases and in the less inflammatory osteoarthritic specimens. In-vitro studies demonstrated uptake of alpha 2M-trypsin complexes but not of native alpha 2M by most of the cultured synovial cells whether they came from rheumatoid patients or controls. The internalised complexes disappeared within 12 hours of culture. The results suggest that alpha 2M-proteinase complexes formed in the joint are taken up by phagocytic and perivascular cells in a similar way to immune complexes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Evidence for the presence of a complex of collagenase with alpha2-macroglobulin in human rheumatoid synovial fluid: a possible regulatory mechanism of collagenase activity in vivo. J Biochem. 1973 Apr;73(4):897–900. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarris B. J., Fraser J. R., Moran C. J., Muirden K. D. Rheumatoid synovial cells from intact joints. Morphology, growth, and polykaryocytosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Aug;36(4):293–301. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarris B. J., Fraser J. R. On the pericellular zone of some mammalian cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jan;49(1):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Russell R. G., Robinson D. R. Production of collagenase and prostaglandins by isolated adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh-Phadke K., Nanda S., Lee K. Macrophage factor that induces neutral protease secretion by normal rabbit chondrocytes. Studies of some properties and effects on metabolism of chondrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER J. R., CATT K. J. Human synovial-cell culture use of a new method in a study of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1961 Dec 30;2(7218):1437–1439. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., McCall J. F. Culture of synovial cells in vitro. Notes on isolation and propagation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Jul;24(4):351–359. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrand O., Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Immunofluorescence studies for immunoglobulins and complement C3 in synovial joint membranes in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):422–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Mosher D., Vaheri A. Cultured human monocytes synthesize and secrete alpha2-macroglobulin. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1580–1589. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUSCOMBE M. Acid phosphatase and catheptic activity in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Nature. 1963 Mar 9;197:1010–1010. doi: 10.1038/1971010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavergne M., Raynaud M. Préparation et propriétés de l'alpha2-macroglobuline de cheval. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Jul;119(1):27–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Wing D. A. Synthesis and secretion of alpha2-macroglobulin by cultured human fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):462–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirden K. D. Lysosomal enzymes in synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis. Relationship to joint damage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):265–271. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Laurell C. B. The disappearance of enzyme-inhibitor complexes from the circulation of man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jul;51(1):87–92. doi: 10.1042/cs0510087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M., Anderson W., Gallo M. Localization of serum-derived alpha 2 macroglobulin in cultured cells and decrease after Moloney sarcoma virus transformation. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L., Berger D. Activation of macrophages to produce neutral proteinases by endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin-trypsin complexes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Nov;28(5):427–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]