Abstract
Wuzi Yanzong prescription (WYP), as a classical prescription for male infertility with kidney essence deficiency, is composed of Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii), Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae), Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) and Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis). It has been used for hundreds of years in the treatment of male infertility, known as “the first prescription of ancient and modern seeds”, with convincing clinical evidence. At present, more than 100 chemical compounds have been isolated from WYP, including polysaccharide, fatty acids, flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, organic acids, alkaloids, terpenoids, etc. Pharmacological and clinical studies show that WYP has an obvious effect on reproductive system diseases, especially male infertility, which has a very wide application prospect. It also has effects on the nervous system, inhibiting liver injury, lowering blood sugar and blood lipid, anti-aging, improving immunity, resisting hypoxia and fatigue effects. This study reviewed the chemical constituents, quality control, pharmacology, and clinical application of WYP. There is no doubt about the clinical value of WYP, but its quality control system is not perfect, pharmacological mechanism is not fully explained, and clinical applications need to be reevaluated. Therefore, the follow-up researches should proceed from the theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and clinical applications, further explain the theoretical connotation, reveal the mechanism of action, and provide the basis for the secondary development of classic famous prescriptions. In addition, WYP is mostly used in combination with western medicines besides being used alone. Whether it can improve the efficacy and reduce side effects will also be a meaningful research direction in the future.
Keywords: quality control, pharmacology, clinical applications, chemical constituents, Wuzi Yanzong prescription, review
1. INTRODUCTION
Infertility and subfertility affect a significant proportion of humanity. According to World Health Organization (WHO) and European Association of Urology (EAU), about 15% of couples do not achieve pregnancy within one year and seek medical treatment for infertility. One in every four couples in developing countries had been found to be affected by infertility1Infertility will become the third major disease affecting human health after cancer and cardiovascular disease. The incidence rate of infertility caused by male factors is 30% to 50%. Male fertility can be impaired as a result of semen abnormality, spermatogenesis dysfunction, vas deferens obstruction and other systemic factors (such as high altitude, high temperature, super intensity work and radiation work, etc.).2 The most common reason is oligoasthenospermia, with an incidence rate of about 75% and a trend of increasing year by year. At present, the treatment of male infertility by Western Medicine mainly includes primary diseases, semen drugs, assisted reproductive technology, etc., but the therapeutic effect is limited and can’t solve the problem of male infertility fundamentally. However, the theory of TCM believes that male infertility with abnormal semen and few weak sperm is often caused by insufficient kidney essence, and should take the method of nourishing kidney and improving essence. With the main effect of tonifying kidney and essence, WYP is favored by ancient and modern doctors. It has unique advantages in the treatment of infertility, and has become a new research direction of infertility and adjuvant treatment.
WYP also known as Wuzi pill (五子丸) and Wuzi Bushen pill (五子补肾丸), being firstly detailed recorded in Shesheng Zhongmiao Fang (摄生众妙方) of the Ming Dynasty, as a classical prescription for male infertility with kidney essence deficiency, is composed of Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii), Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae), Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii), Cheqianzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii). It is recognized as “the first prescription of ancient and modern seeds”. “Wu” (五) means composed of five drugs, “Zi” (子) means that all drugs are seeds, “Yan” (衍) means breed offspring. The whole prescription and its medicines are shown in Figure 1. Among them, Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) and Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) are Monarch drugs, which can nourish the Yin of liver and kidney and make its essence and blood sufficient. Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) and Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) are Minister drugs, which not only supplement the kidney essence, but also have the effect of consolidating essence. Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) as Adjuvant drug, its property is cold. It can release the fire of the bladder and prevent the essence of the kidney from leaking out. The compatibility of five seeds can not only tonify kidney Yin, but also tonify kidney Yang, so as to play the role of tonifying kidney and benefiting essence.3,4
Figure 1. Composition and interpretation of Wuzi Yanzong prescription.
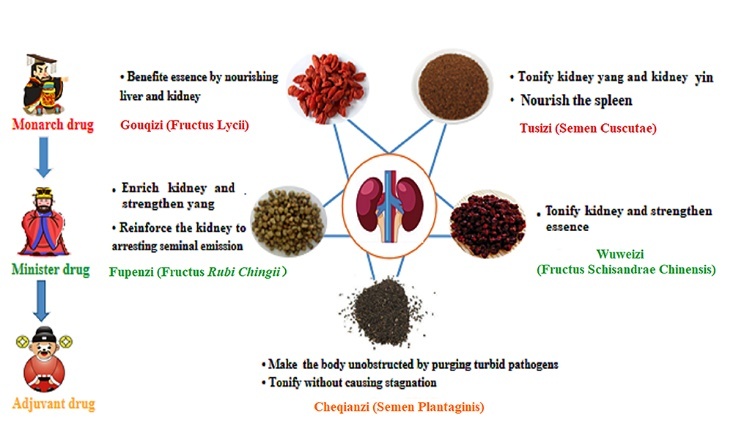
Now, WYP is often used to treat oligozoospermia and asthenospermia of male infertility. In addition, the combination of Chinese and Western medicine can be used to treatoligozoospermia or azoospermia caused by primary spermatogenesis dysfunction. Based on the theory of TCM, it is found that WYP also can prevent and treat Alzheimer disease, aging, neuroendocrine network disorders related diseases, neural tube malformations and other diseases. In recent years, with the rapid development of experimental technology, some achievements have been made in the study of the effective components, basic research, clinical research and mechanism of WYP. However, these studies are still in the exploratory stage, lacking breakthrough and leaving many unclear issues to further explore.
In this review, we not only analyze the chemical composition, quality control, pharmacology and clinical application of WYP, but also discuss the limitations of the current researches, in order to promote the basic research and modern development of it and serve the clinic better.
2. CHEMICAL CONSTITUENTS
2.1. Chemical constituents of single drug in Wuzi Yanzong prescription
WYP is composed of Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii), dried fructus of Lycium barbarum L. Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae), dried semen of Cuscuta australis R.Br. or Cuscuta chinensis Lam. Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), dried fructus of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii), dried fructus of Rubus chingii Hu. Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis), dried semen of Plantago asiatica L. or Plantago depressa Willd.
At present, there are few studies on chemical constituents of WYP, mainly focusing on single drug (Table 1). The main active ingredient of Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) are flavonoids, which can improve the endocrine of germ cells and inhibit the apoptosis of spermatogenic cells. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide is the main effective component of Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii), which can promote the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells in vitro and protect the development of germ cells. The main component of Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) are terpenoids, which has obvious antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Lignans and triterpenoids are the main active components in Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), which have antitumor and antioxidant activities. The main components of Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) are flavonoids and phenylethanol glycosides, which have antioxidant activity and protect the male reproductive system.5
Table 1.
Chemical constituents of single drug in Wuzi Yanzong prescription
| Chemical component | Source | Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 41 | 6 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | - | 7 | |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 14 | 8 | |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 16 | 9 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | 11, including flavonoids, flavonols and their glycosides | 10-11 | |
| Polysaccharides | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | Including neutral heteropolysaccharide, H3 acid polysaccharide | 6 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | It's made up of six monosaccharides | 12 | |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | The polysaccharide content is 85.56%, which is composed of rhamnose, galactose, arabinose and glucose | 13 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | It contains 10%-30% arabinose, xylose, mannose and galactose (5.6:9.4:1.3:1) | 10-11 | |
| Phenylethanoid glycosides | Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | 20,it is composed of caffeic acid, phenyl glycogen and glycogen | 10-11 |
| Iridoids | Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | 22 | 10-11 |
| Steroids | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 6, β-sitosterol, carotenoside, 7-α-hydroxy sitosterol, rape oleosterol, stigmastol, △ 5-oatmasterol | 6 |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 6 | 9,14 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | - | 10 | |
| Terpenoids | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 9 | 6 |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 9 | 8 | |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 19 | 14 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | - | 10 | |
| Alkaloids | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 4 | 6 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Betaine | 15 | |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 7 | 14 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | - | 10,12 | |
| Amino acid | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 15 | 6 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | 18 | 12 | |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 16 | 16 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | - | 11 | |
| Acids | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 18 | 6 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | 18%-22% | 17 | |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 14 | 8 | |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 8 | 14 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | 5 | 18 | |
| Trace elements | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Zn, Pb, Sn, etc. | 6 |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | K, Ca, Zn, Fe, etc. | 8 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | Fe, Mg, Al, Zn, etc. | 11 | |
| Lignans | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | 29 | 6 |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 31 (8%) | 8 | |
| Volatile components | Cuscutae Semen | 11 | 6 |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | 5%-6% | 16 | |
| Coumarins | Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | 4, including esculetin, esculin, imperatorin, hexacosylp-coumarate | 14 |
| Others | Cuscutae Semen | Thymine, arbutin, etc. | 19 |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Vitamins, 4-desmethylsterols, 4-methylsterols, 4'4-dimethylsterols, taurine, etc. | 12 | |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | neoisostegane, plaunol, gedunin, merulinic acid A, etc. | 8 | |
| Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) | butyl dosocanoate, pentacosanol, liballino, 1H-2-indenone, etc. | 9 | |
| Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) | Protein, Plantaginic Acid, Adenine, β-sitosterol, etc. | 18 |
2.2. Chemical constituents of Wuzi Yanzong prescription
The five drugs of WYP are seeds or fruits of plants, which are rich in fatty acids. Tan et al 20used GC-MS to determine 19 kinds of fatty acids in WYP, including 9 saturated fatty acids and 10 unsaturated fatty acids. With the development of modern analytical techniques, UPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS was used to make the constituents of WYP more clear and comprehensible. A total of 106 compounds of WYP were identified or tentatively identified, including 35 flavonoids, 34 phenylpropanoids, 17 organic acids, 8 alkaloids, 11 terpenoids and 1 miscellaneous ingredient. Among them, 14 ingredients from Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii), 10 ingredients from Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) (fried), 33 ingredients from Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii), 37 ingredients from Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) (steamed), and 20 ingredients from Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) (fried with salt). Abromine, nicotinic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, taurine, quinic acid, atropine, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, scopoletin, rutin, esculin, apigenin, hesperidin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, isorhamnetin and schisandrin were unambiguously identified with available standards.21 The structures of main components of WYP were shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Structures of main components of Wuzi Yanzong prescription.
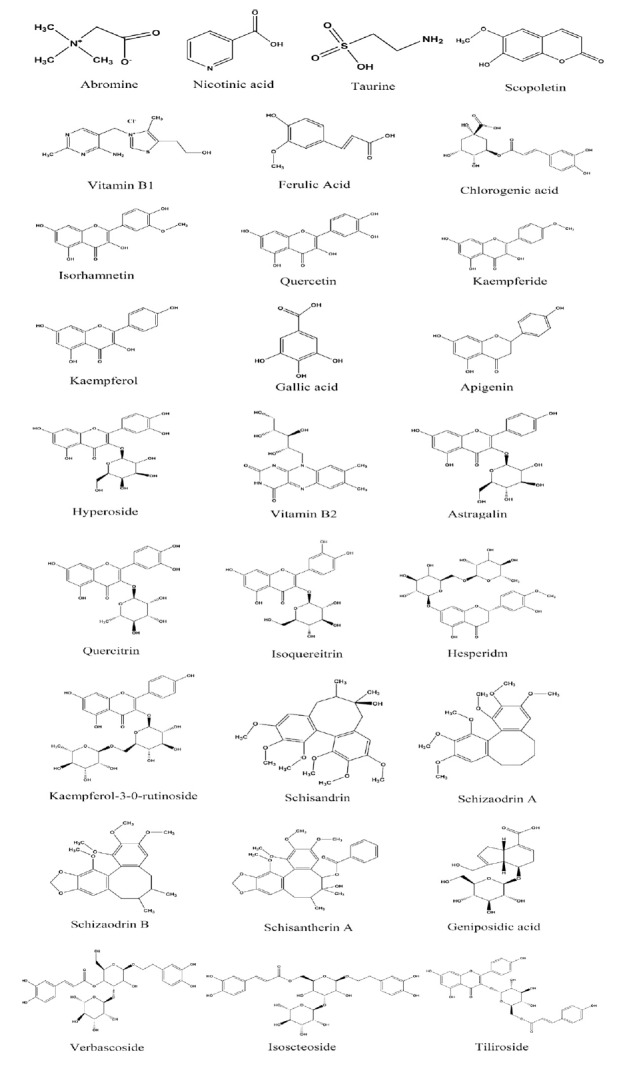
In addition, Yan et al 22 analyzed WYP by network pharmacology, the effective components of WYP in the treatment of infertility, the effective components of WYP are mainly steroids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, alcohols and alkaloids. Among them, the content of steroids 42%-48%, phenylpropanoids 11%-15%, flavonoids 12%-14%, alcohols 9%-12%, and alkaloids 15%, which provides a theoretical basis for the researches and clinical application of its active ingredients.
3. QUALITY CONTROL
Chinese patent medicines with WYP as prescription include pill, tablet, capsule, soft capsule, oral liquid and granule. In order to ensure the safety, effectiveness and stability of WYP, it is particularly important to establish scientific and comprehensive quality control methods. With the rapid development of modern technology, accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple chemical components in Chinese polyherbal formula has been achieved, which provides a powerful methods for its quality control. This manuscript systematically summarizes the research progress of chemical analysis methods of WYP.
3.1. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) qualitative identification
TLC is a low-cost method for rapid qualitative analysis and identification by detecting the main or characteristic components of herbs. There are many TLC studies on WYP, such as Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 Edition), Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun, Zhong Yao Cheng Fang Zhi Ji, and so on (Table 2). However, there are few chemical components involved, most of them are tested separately for individual components of a certain medicine.
Table 2.
TLC identification of Wuzi Yanzong prescription
| Dosage form | Control ingredients and medicinal materials | Developing solvent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wuzi Yanzong Wan | Scopoletin | Petroleum ether (30-60)-ethyl formate-formic acid (20:20:0.1) | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020) |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), Schisandrin | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate (6:4) | ||
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Ethyl acetate-trichloromethane-formic acid (3:2:1) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun | |
| Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | Petroleum ether (30-60)-butyl acetate-butanone-methyl alcohol-water (15:25:3:7:1) | ||
| Schisandrin A | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate (9:1) | ||
| Gallic acid | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate-formic acid (6:3:1) | ||
| Wuzi Yanzong Pian | Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate-formic acid (5:5:3) | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020) |
| Scopoletin | Petroleum ether (30-60)-ethyl formate-formic acid (20:20:0.1) | ||
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis), Gomisin A | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate (6:4) | ||
| Wuzi Yanzong Ruanjiaonang | Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Petroleum ether (60-90)-ethyl acetate-formic acid (13:5:1) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun |
| Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae) | Methylbenzene-ethyl acetate-formic acid (5:5:3) | ||
| Schisandrin A, Schisandrin | Petroleum ether (30-60)-ethyl acetate-formic acid (15:5:1) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun | |
| Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Acetate-trichloromethane-formic acid (2:3:0.1) | ||
| Quercetin | Acetate-trichloromethane-formic acid (26:13:5) | ||
| Wuzi Yanzong Jiaonang | Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Trichloromethane-ethyl acetate-benzene-formic acid (5:6:3:1) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun |
| Wuweizi (Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis) | Petroleum ethe (30-60)-ethyl acetate-formic acid (15:5:1) | ||
| Wuzi Yanzong Koufuye | Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii) | Trichloromethane-ethyl acetate-benzene-formic acid (5:6:3:1) | Zhong Yao Cheng Fang Zhi Ji |
Notes: TLC: thin layer chromatography.
3.2. HPLC quantitative analysis
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the most commonly methods for quantitative and qualitative analysis of chemical components in herbs. Previous literature reports mainly determined the content of single components such as betaine, hyperoside, kaempferin, schisandrin, schisandrin A, and schisandrin B, etc. With the introduction of advanced technologies and methods, the quality evaluation of WYP has been significantly improved (Table 3). However, more quantitative control methods for the effective ingredients need to be established to reflect the overall characteristics and internal quality of WYP.
Table 3.
HPLC methods developped for quantitative determination of Wuzi Yanzong prescription
| Dosage form | Determination of components | Detection method (wavelength) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wuzi Yanzong Wan | Hyperoside, Gomisin A | HPLC (360, 250 nm) | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020) |
| Hyperoside, Kaempferide, Schisandrin, Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B | HPLC/PDA (360, 250 nm) | 23 | |
| Hyperoside, Quercitrin, kaempferol-3-rutinoside, Schisandrin, Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B | HPLC/PDA (254 nm) | 24 | |
| Betaine | HPLC (192 nm) | 25 | |
| Scopoletin | HPLC-FLD (343 nm,458 nm) | 26 | |
| Wuzi Yanzong Pian | Hyperoside, Gomisin A | HPLC (360,250 nm) | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020) |
| Schisandrin A | HPLC (230 nm) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun | |
| Wuzi Yanzong Jiaonang | Schisandrin | HPLC (254 nm) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun |
| Wuzi Yanzong Keli | Rutin | HPLC (254 nm) | Xin Yao Zhuan Zheng Biao Zhun |
Notes: HPLC: high performance liquid chromatography; PDA: photo-diode array.
3.3. Fingerprint or specific chromatogram analysis
In order to control the quality of WYP more effectively and control its internal quality from the perspective of multi drug and multi-component systematization, many researches have established the fingerprint of WYP (Table 4), identified the characteristic components, and matched with the fingerprint of single herbal medicine to obtain exclusive and overall comprehensive characteristic information. It can reflect the internal quality of WYP and the overall difference of preparation technology, provide a scientific, simple and feasible evaluation method for the qualitative and quantitative identification of WYP. However, further studies such as quantitative and structural determination are needed to control the quality of compounds more comprehensively.
Table 4.
HPLC methods developed for fingerprint or specific chromatogram analysis of Wuzi Yanzong prescription
| Dosage form | Detection Method (Wavelength) | Total chromatographic peak number | Chromatographic peak identification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuzi Yanzong Wan | HPLC (250 nm) | 5 | Hyperoside, Verbascoside, Kaempferide, Schisandrin | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020) |
| HPLC (254 nm) | 18 | Hyperoside, Isoquercitrin, Kaempferol, Verbascoside, Astragalin, Gomisin A | 27 | |
| HPLC-DAD (254 nm) | 24 | Gallic acid, geniposidic acid, Chlorogenic acid, Hyperoside, Isoquercitrin, Verbascoside, Kaempferol-3-rutinoside, Isoverbascoside | 28 | |
| HPLC/PDA (360, 250 nm) | 11 | Chlorogenic acid, Hyperoside, Quercetin, Kaempferide,Verbascoside, Astragalin, Schisandrin, Gomisin A, Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B | 23 | |
| HPLC/PDA (254 nm) | 10 | Chlorogenic acid, Hyperoside, Verbascoside, Kaempferol, Schisandrin, Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B, Astragalin, Quercetin | 29 |
Notes: HPLC: high performance liquid chromatography; HPLC-DAD: high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection; HPLC/PDA: high-performance liquid chromatography- photo-diode array.
3.4. Other methods
Wei et al 20 used GC-MS qualitatively and quantitatively to determine the contents of 19 fatty acids in WYP. Based on previous studies, it is speculated that fatty acid may be the basis for the partial pharmacological effects. Multi index comprehensive quality controlwill become the trend of quality evaluation. Since Quantitative analysis of multicomponents by single-marker (QAMS) was put forward, it has been recognized by many scholars. He et al 24 simultaneously determined Schisandrin, Hyperoside, quercitrin, kaempferol-3-o-rutinoside, schisandrin A and schisandrin B in WYP. This method can significantly reduce the cost of detection, improve the efficiency of analysis and test. Dong et al 27 determined the contents of hyperoside, isoquercitrin, verbascoside, astragalin, kaempferol and schisandrin A by QAMS, and established HPLC fingerprint, which provides an accurate and scientific evaluation mode for the quality control of WYP.
4. PHARMACOLOGY
4.1. Effects on reproductive system
4.1.1 Effects on the male reproductive system
The strength of male fertility is intently associated to spermatogenic function and sperm quality. WYP can promote spermatogenesis, improve sperm quality and protect the integrity of sperm structure and function by repairing the damage of spermatogenic cells and Sertoli cells, resisting excessive oxidative stress, inhibiting the decrease of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) and alleviating the damage of mitochondrial microstructure to improve the reproductive function. The effects on the male reproductive system of WYP have been summarized in Table 5.
Table 5.
Effects on the male reproductive system of Wuzi Yanzong prescription
| Pharmacological activity | Testing subject | Dosage | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effects on spermatogenesis | Oxidative damage of testis in mice | 2, 4 g·kg-1·d-1,35 d | Significantly antagonize the testicular oxidative injury and spermatogenic cell apoptosis induced by cyclophosphamide | 30 |
| Mice with oligospermia | 1.56 g·kg-1·d-1, 14 d | Regulate the meiosis of spermatogenic cells, homologous recombination of testis, renin-angiotensin recombination of testis, renin-angiotensin system, cholesterol metabolism pathway and others,so as to repair the blocking of testicular spermatogenesis,by affecting the gene expression of testis tissue in mice with oligospermia | 31 | |
| AT1KO mouse | 5.8 g/kg, 2 times a day | Has a positive regulatory effect on the sex hormone levels of male AT1+/- mice, increasing the levels of GnRH and FSH, and the degree of improvement is positively correlated with the intervention time, improving the reproductive function of male mice | 32 | |
| Testicular tissue of rats with kidney essence deficiency | 0.01 mL/g, 30 d | Can reduce the apoptosis of spermatogenic cells in rat testis by inhibiting Bax and promoting the expression of Bcl-2 protein | 33 | |
| Effects on sperm quality | Rat with oligospermia | 1.96 g·kg-1·d-1, 60 d | Can correct HPG secretion disorder and improve sperm quality | 34 |
| Effects on Sertoli cells | Mouse Testis TM4 Sertoli Cells | 12.0 g/kg, 2 times a day, 7 d | Serum can improve the secretory function of TM4 Sertoli cells by regulating the levels of ROS and autophagy | 35 |
| Human testicular support cell line TM4 cells | 0.2, 1.0, 5.0 mg/mL | Can improve oxidative stress injury of testicular support cells and inhibit cell apoptosis | 36 | |
| Heat stress model of rat Sertoli cells | 20 g/L | Can reduce the generation of reactive oxygen species and the expression of heat shock protein 70 to protect heat stress | 37 | |
| Effects on sperm mitochondria | Rats with Oligoasthenozoospermia | 1, 2, 4 g·kg-1·d-1, 28 d | Can inhibit the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), improve the quality of spermatozoa, and reduce the apoptosis rate of spermatogenic cells (including spermatozoa) | 38 |
| Rats with Oligoasthenozoospermia | 4.0g·kg-1·d-1, 28 d | Can down-regulate the expression of Bax,VDAC1 and CypD proteins in rat testicular tissue, inhibit the over-opening of mPTP, and prevent the germ cell apoptosis caused by the activation of Caspase protein family | 39 |
Notes: GnRH: gonadotropin-releasing hormone; HPG: human pituitary gonadotropin; TM4: testicular Sertolicells of normalmice; ROS: reactive oxygen species; MPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore; CypD: cyclophilin D; VDAC1: voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1.
4.1.2 Effects on the female reproductive system
It is found that WYP also has a corresponding regulatory effect on the female reproductive system. It can up regulate the expression of S100A11 gene decreased by GnRHa long case COH, improve endometrial receptivity, and improve mouse pregnancy rate and embryo im-plantation rate.40 Studies have shown that total flavonoids of Cuscutae Semen (TFSC) can significantly restore the ovarian function of rats with premature ovarian failure, increase the ovarian weight and number of follicles, improve the estrogen level, and have obvious curative effect on premature ovarian failure.41 TFSC can also increase the contents of serum E2 and FSH in letrozole induced polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) model rats.42
4.2. Effect on nervous system
The theory of TCM believes that an important way to treat encephalopathy is to invigorate the kidney, replenish the essence and fill the marrow. WYP also plays a more important role in the field of nerve, and might be a useful agent for prevention and treatment of neuroinflammatory disease. WYP might act to suppress neuroinflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide stimulated rat astrocytes via NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling cascades.43 It could also improve neurological function, regulate Rho/ROCK signaling pathway, reduce nerve tissue damage, inhibit the expression of inflammatory protein, promote the expression of anti-inflammatory macrophage cells and anti-inflammatory factor, and reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice.44,45 WYP can reduce inflammatory factors interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and affect the expression of IL-4, improve the aggravation of inflammatory response in the brain, repair the damaged myelin sheath, promote myelin regeneration, and then improve the demyelination of cuprizone induced model.46 WYP can improve the cognitive and learning status of patients with Parkinson's disease,47 mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease by inhibiting the apoptosis of neural tube cells,48 promoting the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells.49 Besides, WYP has the effect of preventing neural tube defects (NTDs), and better than folic acid (FA). Its mechanism may be to up-regulate the expression levels of glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and inhibit oxidative stress response.50
4.3. Effect on urinary system
Urinary system is composed of kidney, ureter, bladder and urethra. The main function of it is to generate and excrete urine and excrete metabolic end products, regulate water and salt metabolism and maintain acid-base balance of body fluids.51 Diseases of urinary system can not only be caused by diseases of other systems, but also affect other systems and even the whole body. However, its specific diseases such as glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis and renal failure are mainly related to the kidney. Pharmacological studies have shown that WYP can improve the abnormal urination,52 nephromegaly and abnormal indexes of kidney and prostate in rats, and has a significant regulatory effect on urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (CRE).53 However,Fupenzi (Fructus Rubi Chingii) has significant urinary contraction effect, and the effect of salt products is better. It can significantly improve aldosterone (ALD), urine volume and renal index in adenine induced polyuria model rats with kidney Yang deficiency.54 Some scholars also found that kaempferol can inhibit apoptosis, inhibit inflammatory response and protect renal function.55,56 Isorhamnetin inhibits NF-κB over activation, reduce the level of inflammatory factors to reduce proteinuria.57
4.4. Other pharmacological effects
Modern researches also found that WYP also has the functions of inhibiting liver damage, lowering blood sugar and blood lipids, anti-aging, improving immunity, resisting hypoxia and fatigue, etc. WYP can regulate the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in serum, SOD and malon-dialdehyde (MDA) in liver tissue, and had a good protective effects on liver injury caused by cyclophosphamide (CTX).58,59 WYP can reduce the secretion of inflammatory factors, inhibit Rho signal pathway, improve the neurological function score of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice, delay the onset time of EAE, and regulate the body immunity.47 It can also regulate serum immunoglobulin G, IL-6, IL-2 and promote the balance of T lymphocyte network, improve the immune function of kidney essence deficiency rats.60 WYP can significantly increase the activity of SOD and GSH-Px, reduce the content of MDA, alleviate the oxidative damage caused by D-galactose, inhibit the abnormal activity of polyol pathway in lens tissue of diabetic cataract mice, improve the opacity of lens in diabetic cataract mice.61 Through swimming test and survival time test under anoxic condition in mice, WYP can significantly prolong the swimming time, enhance the anoxic tolerance time and enhance the immune function of mice, etc.62 In addition, WYP can regulate tumor energy metabolism through SIRT1 signal pathway, so as to play a role in the treatment of tumor related fatigue (CRF).63
5. CLINICAL APPLICATION
5.1. Reproductive system
5.1.1 Treatment of male reproductive system diseases
Clinical studies have found that WYP can reduce the levels of DNA fragmentation index (DFI) and ROS in semen, improve SOD activity and improve sperm DNA damage.64 By observing the patient’s TCM symptoms, sperm concentration, forward movement sperm rate, and normal sperm morphology rate, and comparing the therapeutic effects of taking WYP, vitamin C and vitamin E on male infertility patients, the result showed that WYP can significantly improve male infertility. The quality of semen in patients with symptom, and the improvement of semen parameters is significantly better than the effect of vitamin C combined with vitamin E treatment.65 WYP combined with Jinshuibao capsule can significantly improve semen volume, sperm density, grade a sperm motility, (a + b) sperm motility and sperm motility. It also can improve the level of serum hormone and the success rate of spouse pregnancy.66 Yang et al 67 compared the efficacy and safety of WYP and Qilin pill (麒麟丸) in the treatment of idiopathic oligoasthenospermia according to the method of randomized double-blind parallel control study, and found that both WYP and Qilin pill can significantly improve sperm quality, regulate sex hormone level, present the efficacy law of time effect improvement, without obvious adverse reactions, and medication safety. Li et al 68 found that in infertile patients with oligospermia and asthenospermia, the sperm motility was significantly increased and the levels of caspase 3 and caspase 8 in semen and sperm were decreased after continuous use of WYP for 2 months. Tan et al 69 used WYP to treat poor semen liquefaction, the result showed that the contents of prostate-specific antigen and acid phosphatase in the seminal plasma of the patients were significantly increased, the semen liquefaction time was shortened, and the semen quality was improved.
5.1.2 Treatment of female reproductive system diseases
Clinical studies have shown that WYP not only has significant curative effect on male reproductive system diseases, but also has a certain conditioning effect on female reproductive system. Zhang et al 70 treated 86 cases of adolescent dysfunctional uterine bleeding with Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pill (加味五子衍宗丸). Among them, 64 cases were cured, 19 cases were improved and 3 cases were not cured. The total effective rate was 96.51%. Sun et al 71 used WYP to treat infertility patients with ovulation disorder. WYP can effectively improve the symptoms of kidney deficiency and essence deficiency, improve the level of sex hormone secretion and luteal function, and improve the endometrial receptivity and pregnancy rate of patients with infertility caused by kidney deficiency and essence deficiency symptom pattern and luteal insufficiency (LPD). It has high safety and is worthy of clinical promotion.72 Modified Wuziyanzong pill can regulate HPOA axis, improve luteal function, improve hormone level, reduce the score of kidney deficiency and essence deficiency symptom pattern, and improve endometrial receptivity, so as to improve pregnancy rate. Its clinical effect is better than that of Western Medicine.73 WYP combined with clomiphene citrate in the treatment of infertility can improve the ovulation of patients and alleviate clinical symptoms. It has high safety and is worthy of clinical application.74 WYP combined with clomiphene citrate capsule can improve the ovulation rate, pregnancy rate, endometrial thickness, basal body temperature (BBT) distribution and cervical mucus score (CMS) of patients with ovulatory infertility, and the scoring effect is better than that of TCM alone or western medicine alone.75
5.2. Nervous system
Li et al 76 found that Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pill can improve the ability of image free recall, pointing memory and associative learning of patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to varying degrees, and significantly reduce the hippocampal index and temporal angle width, indicating that it can improve the memory ability of patients and delay hippocampal atrophy. Zhang et al 17 found that after 12 weeks of treatment with Wuzi Yanzong decoction combined with donepezil, the total effective rate, MCI and mini mental state examination scores were significantly higher than those with donepezil alone.
5.3. Urinary system
In recent years, studies have found that WYP also has a certain effect on urinary system diseases. Female urinary incontinence and infantile enuresis belong to the category of “urinary incontinence” and “enuresis” in TCM. The pathogenesis is mostly kidney deficiency, resulting in kidney Qi deficiency, ineffective intake and storage, and the bladder loses its restraint ability. The main treatment methods are warming and tonifying kidney Yang, fixing and shrinking urine, strengthening spleen and tonifying lung. Pan et al 77 used Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pills to treat female urinary incontinence. After a course of medication, the patient had normal urination and no urinary incontinence. Compound Wuzi oral liquid can significantly reduce the clinical symptoms of frequent micturition and urgency in women with urethral symptom pattern, and improve the level of estrogen.78 Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊) combined with WYP is effective in the treatment of immunoglobulin A nephropathy proteinuria damp heat symptom pattern.79 In addition, WYP has good curative effect on enuresis, frequent urination and nephrotic symptom pattern in children.80
5.4. Others system
WYP is still used in the treatment of stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with deficiency of lung and kidney Qi (Yang),81 and has certain curative effect on recurrent oral ulcer, alopecia areata, primary thrombocytopenic Pura and other diseases.82 Based on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist program intervention, Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pill was given to the patients with poor kidney deficiency symptom pattern with low ovarian response by cycle and stage. It can regulate the level of endocrine hormones, promote follicular development, improve ovarian reserve function, increase the number of ovums, improve the quality of ovums, improve the pregnancy outcome, and increase the chances of successful assisted pregnancy with autonomous rail rapid transit, but it is worthy of further study.83 WYP combined with clomiphene citrate capsule can improve the ovulation rate, pregnancy rate, endometrial thickness, BBT distribution and CMS in patients with ovulatory infertility. It is better than using Chinese medicine or Western Medicine alone.75 In addition, the combination of WYP and compound glycyrrhizic acid S injection can significantly improve the liver function and clinical symptoms of lung cancer, gastric cancer and breast cancer chemotherapy induced liver injury, and is better than the injection alone.84
6. DISCUSSION
WYP as a classic famous prescription for nourishing kidney and producing essence. It has been used in the symptom patterns of Yang phlegm infertility, spermatorrhea and premature ejaculation caused by kidney essence deficiency for thousands of years and is still widely used today. Its composition is scientific and the curative effect is definite. It has a significant effect on reproductive system diseases, especially male infertility, as well as neurological diseases and endocrine system diseases. This article reviews its chemical composition, quality control, pharmacology and clinical application. We found that WYP had the value of further development and utilization, but the production practice and clinical application showed that there were still some problems in the development and utilization of WYP.
First of all, WYP was first recorded in the 1985 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China. As a traditional pill, its preparation process is simple. At present, a series of preparations have been developed on the basis of WYP. However, we found that WYP produced by different companies has great differences in properties, specifications, usage, dosage and content of active ingredients, which inevitably lead to the phenomenon of “different effects of the same drug”. In order to improve the quality of WYP, it is recommended to fully consider the nature of raw materials, processes and the principle of facilities in the production to promote the technological innovation of the preparation of WYP. At the same time, it is necessary to introduce relevant indicators such as biological potency, effective component index, biomarkers and other related indicators into quality control and quality evaluation of WYP, construct the quality evaluation method of WYP based on efficacy, further improve the existing quality evaluation system, ensure the quality of WYP, and make it better serve the clinical.
Pharmacodynamic researches of WYP are still in the basic stage, and the researches on its target and related molecular mechanism are mostly single perspective or level. Hyperoside, Verbascoside, Gomisin A, Schisandrin A, Schisandrin B and Kaempferol have good protective effects on central nervous system diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, depression, cerebral ischemia and glioma, especially on neurodegenerative diseases.85 Quercetin has a certain protective function on the reproductive system and can protect the structure and function of testicular tissue and maintain normal.86 Kaempferol has the functions of anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, prevention and treatment of diabetes, atherosclerosis and inhibition of protein kinase.87 The mechanism mainly includes regulating the activity of proinflammatory enzymes and controlling the expression of inflammation related genes.88 Stigmasterol and β-Sitosterol have many functions such as reducing blood lipid, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, regulating growth and hormone like functions.89 After oxidation, they will be transformed into estrogen like substances in the body, which will improve the level of sex hormones in the plasma, which is beneficial to the development of the body's reproductive system, enhance the body's reproductive ability, and reduce the level of reproductive steroid hormones in the plasma.90 In addition, based on network pharmacology, Yan et al 22concluded that the pharmacodynamic compounds of WYP in the treatment of infertility, impotence and premature ejaculation are steroids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, alcohols and alkaloids, which provides a theoretical basis for its active ingredient research and clinical application. Modern scientific research requires us not only to use a variety of modern technology to explore the changes of effective substances of it, but also to study its compatibility significance from the theory of TCM, understand the special relationship between individual herbs and the whole prescription in terms of nature, taste, meridian tropism and efficacy, carry out the researches on material basis and mechanism of action, provide scientific proof for the main efficacy of WYP, and make it glow with new brilliance.
With the deepening of modern research, the clinical application of WYP has become more and more extensive. It has a significant effect on a variety of diseases such as reproductive system, urinary system and nervous system, especially reproductive system diseases. WYP is mainly used to treat male infertility caused by oligospermia and asthenospermia, it is not suitable for all male infertility. It should be reasonably on the basis of symptom pattern identification and treatment. Most literatures mainly focus on clinical efficacy, lack of in-depth study on the mechanism of male infertility, and most of them use modified WYP or combination drugs. The specific medicinal ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms of WYP have not been studied. Meanwhile, Tusizi (Semen Cuscutae), Wuweizi (Fructus Schis-andrae Chinensis), and Cheqianzi (Semen Plantaginis) have a wide variety of four herbs, and they are widely distributed, and there is no uniform medication standard. The specific modified drugs and dose changes are also uncertain, which brings many unknown factors to clinical research. Therefore, it is still an arduous task to establish a standardized mechanism for the treatment of male infertility. In addition, WYP is also used in the treatment of female urinary incontinence, alopecia areata, purpura and other diseases, but they are mostly case reports, lack of large sample of clinical randomized trial data, its effectiveness needs to be further verified.
7. CONCLUSIONS
WYP as a classic prescription for nourishing kidney and producing essence. Its composition is scientific and the curative effect is definite. On the one hand, with the expansion of clinical application, it has the value of further development and utilization. On the other hand, it also exposed some problems that need further research. It is very important to study the chemical components for the identification of material basis of efficacy and the exploration of its mechanism. There are few studies on the multiplicity of new preparations, new processes, effective components, effective parts, compatibility and combination, therapeutic approaches and targets of WYP, the researches in related fields should be further strengthened. In addition, WYP is mostly used in combination with western medicines besides being used alone. Whether it can improve the efficacy and reduce side effects will also be a meaningful research direction in the future.
Contributor Information
Changjiang HU, Email: 654460129@qq.com.
Yongxiang GAO, Email: China.drgaoyx@cdutcm.edu.cn.
Reference
- 1. Mascarenhas MN, Flaxman SR, Boerma T, Vanderpoel S, Stevens GA. National, regional, and global trends in infertility prevalence since 1990: a systematic analysis of 277 health surveys. PLoS Med 2012; 9: e1001356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Tang W, Hu DX. Application and progress of stem cells in male infertility. Di San Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2019; 41:1897-901. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Li L, Wang TS. Historical changes and modern pharmacological research of Wuziyanzong pill. Zhong Yi Yao Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2018; 30: 608-11. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Han DC. Representative prescription for tonifying kidney-Wuziyanzong pill. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2017; 22: 26. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Xu HJ, Liu Q, Guo YL, Gao F, Li M, Wei PF. Research progress of Wuzi Yanzong pill in the treatment of male infertility oligoasthenospermia. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 22: 149-53. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wang YY, Wang L, Qi YX, Liu Q, Zhang YQ. Research progress on chemical constituents of Cuscutae Semen. Shandong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 44: 705-12. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Zhang F, Guo S, Qian DW, Zhang X, Zhang WH, Duan JA. Research and development status and prospect analysis of multiple types of small molecule chemicals in Lycium barbarum. Zhong Cao Yao 2016; 39: 2917-21. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bai WY, Wang HE, Wang BY, Yu HS, Li Z. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Schisandra chinensis. Zhong Cheng Yao 2019; 41: 2177-83. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Cheng D, Li J, Zhou B, Zhen PW. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Rubi Fructus. Zhong Yao Cai 2012; 35: 1873-76. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Li CC, Gong SX, Xu J, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Semen Plantaginis and prediction analysis of quality markers. Zhong Cao Yao 2018; 49: 1233-46. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Xu S, Xu WF, Liang XL, Wu XJ, Jin PF. Research progress on chemical constituents and biological activities of Semen Plantaginis. Xi Bei Yao Xue Za Zhi 2019; 34: 567-70. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Fu WH, Yu M. Research progress of Gouqizi (Fructus Lycii). Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2017; 17: 104. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Li SS, Qi YL, Hua M, Sun YS. Separation, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis. Shi Pin Gong Ye 2018; 39: 233-7. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Cui L, Zheng ZQ. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Rubi Fructus. Quan Ke Kou Qiang Yi Xue Dian Zi Za Zhi 2020; 7: 192+6. [Google Scholar]
- 15. Zhang Q, Chen W, Zhao J, Xi W. Functional constituents and antioxidant activities of eight Chinese native goji genotypes. Food Chem 2016; 200: 230-6.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yang Q, Qu XB, Li H, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Schisandra chinensis. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 35: 626-8. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Zhang HH, Huang JP, Li W, et al. Evaluation of Wuzi Yanzong decoction in the treatment of mild cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease with kidney deficiency and marrow reduction. Zhejiang Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2016; 26: 998-1001. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Xie M, Yang SS, Wang LL, Li L, Wang XY. Research progress of Plantaginis Semen. Heilongjiang Yi Yao 2015; 28: 474-6. [Google Scholar]
- 19. Xiang SX, He ZS, Ye Y. Four furan lignans from Cuscuta chinensis. Chin J Chem 2010; 19: 282-5. [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tan W, Huang XH, Fu TT, Qiu WZ, Min CY, Wang CJ. Analysis of fatty acids in Wuzi Yanzong pills by GC-MS. Xian Dai Yi Yuan 2016; 16: 1186-8 + 91. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Zou DX, Wang JF, Zhang B, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in Wuzi-Yanzong-Wan by UPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS. Molecules 2015; 20: 21373-404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yan JN, Hu C, Meng XL. Pharmacodynamic mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill based on network pharmacology. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu 2020; 22: 2294-310. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Zhou JL, Liu W, Tan CM, Zhu Ming, Ma SC. Study on quality control standard of Wuzi Yanzong pills. Zhong Guo Yao Xue Za Zhi 2015; 50: 125-130. [Google Scholar]
- 24. He CX, Yuan D, He YM, et al. Application of multiple evaluation method in quality control of Wuzi Yanzong pills. Zhong Cao Yao 2017; 48: 3754-9. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Cai JA. Determination of betaine in Wuzi Yanzong pills by HPLC. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi Za Zhi 2011; 18: 57-8. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhou JL, Liu W, Chen BL, Zhu M. Determination of scopoletin in Gouqizi and Wuziyanzong pills by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Ying Yong Yao Xue 2015; 32: 482-6. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Dong QJ, Zhou Y, Feng W, et al. Application of fingerprint combined with multiple evaluation method in quality evaluation of Wuzi Yanzong pills. Zhong Yao Cai 2019; 42: 579-83. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Dong QJ, Wang XG, Niu LY, Feng W. Study on fingerprints of Wuzi Yanzong prescription-medicinal materials based on peak pattern matching. Zhong Cao Yao 2017; 48: 1153-8. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Liu W, Zhou JL, Chen BL, Zhu M. Study on HPLC fingerprint of Wuzi yanzong Pills. Yi Xue Dao Bao 2014; 33: 1360-4. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Liu MM, Zhang CC, Jia LL, et al. Protective effect of Wuzi Yanzong recipe on oxidative damage of testis in mice induced by cyclophosphamide. Zhong Cheng Yao 2013; 35: 2591-7. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Meng XD, Zhao CJ, Zhao X, et al. Effect of Wuzi Yanzong Wan on testicular gene expression profile of mice with oligospermia. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 13: 1653-60. [Google Scholar]
- 32. Zou Y, Zhao FF, Li H, et al. Intervention of Wuzi Yanzong pills on the reproductive function of AT1KO male mice. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 54: 97-100. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Liao YJ, Zhang X, Ao MY, Hu CJ, Chen ZM, Xu RC. Effect of prescription on spermatogenic cell apoptosis in rats after preparation of drug salt contained in Wuziyanzong pill. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2021; 27: 1-7. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yan RH, Huo JF, Dong AG, Wang YH, Liang Q. Comparative study on the effect of reproductive nutrition capsule and Wuzi Yanzong pill on reproductive function of drug-induced oligospermia model. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2015; 33: 1215-7+99. [Google Scholar]
- 35. Cui TW, Liu BX, Qin M, Zhang XP, Gao YX. The effect of Wuzi Yanzong pills containing serum on the secretory function and autophagy of mouse Sertoli cells. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2107; 32: 549-52. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Yin JL, Xu Y, Wu B. The effect of Wuzi Yanzong compound on oxidative stress injury and apoptosis of testicular Sertoli cells. Zhong Hua Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2013; 19: 257-61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Liu SJ, Chen YC, Hu SQ, Li CR, Guo J. Protective effect and mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill on testis of heat stressed rats. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 43: 386-92. [Google Scholar]
- 38. Li L, Dai Ni, Na S, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pills on experimental oligoasthenospermia rats. Zhong Hua Nan Ke Xue Za Zhi 2016; 22: 827- 33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Liu HJ, Wu DL, Tong XH, Li L, Wang TS. Mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pills interfering with mitochondrial permeability transition pore to inhibit sperm apoptosis. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2020; 26: 34-9. [Google Scholar]
- 40. Chen Y, Fu ZY, Zhang YG, Peng JL. Wuzi Yanzong Wan regulates the S100A11 gene during implantation in GnRHa controlled hyperovulation mice. Zhong Yi Yao Dao Bao 2014; 20: 14-7. [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wang YX, Ma N, Zhong XM, Cui R, Miao ZL. Study on the effect of total flavonoids of Cuscuta on ovarian function in rats with premature ovarian failure. Yi Xue Zong Shu 2019; 25: 2695-9. [Google Scholar]
- 42. Miao MS, Peng MF, Yan XL, et al. The effect of total flavonoids of Cuscuta on the rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome induced by letrozole. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2109; 25: 17-23. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Zeng KW, Zhang T, Fu H, Liu GX, Wang XM. Modified Wu-Zi-Yan-Zong prescription, a traditional Chinese polyherbal formula, suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory processes in rat astrocytes via NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2012; 19: 122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Zhang RN, Chai Z, Fan HJ, et al. Study on the prevention and treatment effects of Wuzi Yanzong pills on mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and its mechanism. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2018; 33: 1316-9. [Google Scholar]
- 45. Sun MY, Fan HJ, Chai Z, et al. Effect of Wuziyanzong Wan on neurotrophic factor secreted by astrocytes in demyelinating mice. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2021; 62:712-6. [Google Scholar]
- 46. Liu X, Sun MY, Xue JY, Li YR, Fan HJ, Chai Z. Inhibitory effect of Wuziyanzong pill on inflammatory response in demyelinating model. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2021; 36: 2904-8. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Li YL, Fan HJ, Chai Z, et al. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of Wuzi Yanzong pills on Parkinson's disease mice. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 35: 3623-6. [Google Scholar]
- 48. Li RX, Fan HJ, Cai Z, et al. Effects of Wuzi Yanzong pills (五子衍宗丸) on the apoptotic pathway of neural tube defects cell model. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2019; 60: 1134-41. [Google Scholar]
- 49. Song FJ, Zeng KW, Yu Q, Song YX, Tu PF, Wang XM. Study of modified Wuzi-Yanzong prescription's effect on gene expression profile of SAMP8 mice brain based on gene microarray. Zhong Guo Yao Xue Za Zhi 2015; 50: 1874-9. [Google Scholar]
- 50. Yang CJ, Fan HJ, Chai Z, et al. Mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill in preventing neural tube malformation. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021; 27: 1887-91. [Google Scholar]
- 51. Chen WC, Tan LH, Li L. Analysis of patent information of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of urinary system diseases in China. Zhong Guo Fa Ming Yu Zhuan Li 2021; 18: 44-9. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Bae S, Lee KW, Jeong HC, et al. Effects of a combination of herbal extracts [modified Ojayeonjonghwan (Wuzi Yanzong wan)] on partial urethral obstruction-induced detrusor overactivity in rats: impact on the nitric oxide pathway and oxidative stress. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019; 19: 64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Ge ZY, Jin L, He FJ, Dong XX, Li HK, Liu JX. Experimental study of Wuziyanzong pill on oligospermia model rats. Sheng Zhi Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010; 19: 224-7. [Google Scholar]
- 54. Zhang X, Liao YJ, Yang Z, Chen ZM, Li WB, Hu CJ. Study on the changes of chemical components and pharmacodynamics of Rubi Fructus before and after salt preparation. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2020; 31: 82-4. [Google Scholar]
- 55. Wu QM, Ni HX, Lu X, Yuan X, Luo YY, Jin YM. Kaempferol delays kidney injury in mice with spontaneous obesity type 2 dia-betes mellitus. Xin Nao Xin Guan Bing Fang Zhi 2017; 17: 19-22. [Google Scholar]
- 56. Tang LH, Fang C, Wang HR, Tang SG. Protective effects of kaempferol on renal function and histopathological damage in rats with diabetic nephropathy induced by high glucose. Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 34: 1041-6. [Google Scholar]
- 57. Qiu SJ. The protective effect and mechanism of ISO rhamnin on diabetic rats. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017: 35-46. [Google Scholar]
- 58. Han GF, Zhang CC, Chen X, Chen YQ, Yuan D, Zhao HX. Extraction of total polysaccharides from Wuzi Yanzong prescription and its protective effect on liver injury. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2017; 28: 549-51. [Google Scholar]
- 59. Liu ZC, Zhao HX, Chen X, Liu GY, Yuan D, Zhang CC. Protective effect and mechanism of Wuzi-Yanzong prescription against the liver injury induced by cyclophosphamide. Zhong Guo Quan Ke Yi Xue 2017; 20: 3426-30. [Google Scholar]
- 60. Yang Z, Zhang X, Hu CJ. The effect of Wuzi Yanzong pills on the immune function of rats with kidney essence deficiency after being prepared with salt. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2019; 30: 2134-7. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Zhu XD, Wang Y. Effect of Wuzi Yanzong pill on lens oxidative damage and polyol pathway in diabetic cataract mice. Zhong Yi Yan Jiu 2013; 26: 66-9. [Google Scholar]
- 62. Yuan Y, Wang XH. The effect of Wuzi Yanzong pills on anti-fatigue and hypoxia tolerance in mice. Yao Xue Shi Jian Za Zhi 2008; 26: 430-1. [Google Scholar]
- 63. Fu TT, Li J, Wang CJ, Tan W. Study on the mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong pill interfering with SIRT1 signal pathway to regulate tumor related fatigue. Zhong Yao Cai 2017; 40: 2657-62. [Google Scholar]
- 64. Li JJ, Dong L, Tan K, Yu Yan, Yu XJ, Yang F. Clinical study on improving sperm DNA integrity damage by tonifying the kidney and activating blood circulation. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Yi Yao 2021; 17: 79-83. [Google Scholar]
- 65. Li H, Yu XJ, Yang F, Dong L, Tan K, Li JJ. Clinical study on 64 cases of male infertility treated with Wuzi Yanzong pill. Zhong Guo Xing Ke Xue 2020; 29: 123-6. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Yu WH, Zhan JF, Chen R. Clinical study of Jinshuibao capsule and Wuziyanzong pill in the treatment of male idiopathic oligoasthenospermia. Xin Zhong Yi 2021; 53: 88-92. [Google Scholar]
- 67. Yang D, Xian H, Teng WD, Cheng QJ. Clinical efficacy and safety of Wuzi Yanzong pill and Qilin pill in the treatment of male idiopathic oligoasthenospermia. Zhong Guo Xing Ke Xue 2019; 28: 77-80. [Google Scholar]
- 68. Li YC, Pan ES, Chen CP. Effect of Shengjing Zhongyu decoction on oligospermia and asthenospermia infertility and its influence on caspase 3 and caspase 8 in semen. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2019; 14: 2359-62+6. [Google Scholar]
- 69. Tan WJ, Han WW, Yan L. Clinical observation of Shugan Yiyang capsule in the treatment of abnormal semen liquefaction. Zhong Cheng Yao 2018; 40: 1227-30. [Google Scholar]
- 70. Zhang LJ, Luan HT. Modified Wuzi Yanzong pills in the treatment of 86 cases of adolescent dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Hebei Zhong Yi 2012; 34: 56-7. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Sun QF. Clinical study on Wuzi Yanzong pills in the treatment of ovulation dysfunction infertility. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2012; 32: 1243-4. [Google Scholar]
- 72. Wang K, Wang J, Liu XJ, Ma AW. The effect of Wuzi Yanzong pills on the endocrine and metabolism of infertility patients caused by luteal insufficiency due to kidney deficiency and essence deficiency. Zhong Yao Cai 2021; 44: 720-3. [Google Scholar]
- 73. Zhang LM, Liao BN, Zhou HG, Niu CQ. Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pills in the treatment of female infertility caused by luteal insufficiency due to kidney deficiency and essence deficiency. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2017; 23: 197-202. [Google Scholar]
- 74. Li LR, Zhang XF, Pan SJ. Observation on the efficacy of Wuzi Yanzong pills combined with western medicine in the treatment of anovulatory infertility. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2014; 6: 4-5. [Google Scholar]
- 75. HHe JQ, Liu FP, Huang YL, Deng LJ, Huang LH. Pregnancy promoting effect of Wuziyanzong pill combined with Western Medicine on patients with ovulatory infertility. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 16: 1463-7. [Google Scholar]
- 76. Li WW, Wang LL, Fu H, Liu GX, Wang XM. Research status of neuroprotective mechanism of Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong formula. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2105; 21: 219-23. [Google Scholar]
- 77. Pan M, Li YJ, Wang HY. Wuzi Yanzong pills for the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2011; 24: 632-3. [Google Scholar]
- 78. Li L, Sun YX, Ma JY, Ning SS, Li Y. Clinical observation of compound Wuzi oral liquid in the treatment of female urethral syndrome. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2018; 52: 62-4+ 8. [Google Scholar]
- 79. Wang XD. Clinical observation of Huangkui capsule combined with Wuziyanzong pill in the treatment of IgA nephropathy proteinuria damp heat syndrome. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2017; 33: 618-9. [Google Scholar]
- 80. Li G. Clinical observation on Wuzi Yanzong pill combined with moxibustion in the treatment of enuresis in children with deficiency cold syndrome of lower Yuan Dynasty. Shenzhen Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2020; 30: 38-40. [Google Scholar]
- 81. Guo L. Clinical observation of Wuzi Yanzong pill combined with Western Medicine in the treatment of lung kidney Qi (Yang) deficiency in stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2016; 35: 78-80. [Google Scholar]
- 82. Cao S, Li YP, Wu P, Tong L. Clinical research progress of Wuzi Yanzong pill. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Yi Yao 2017; 13: 55-6. [Google Scholar]
- 83. Ji LN, Zhang XY, Liang ZY, Shi BZ. Study on the effect of Jiawei Wuzi Yanzong pills on the outcome of assisted pregnancy in patients with low ovarian response. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2021; 27: 106-10. [Google Scholar]
- 84. Liu GN. Clinical efficacy analysis of Wuziyanzong pill in the treatment of liver injury after chemotherapy. Haerbin: Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018: 16-23. [Google Scholar]
- 85. Wang XL, Fan HJ, Chai Z, et al. Research progress in the mechanism of common monomers in Wuzi Yanzong pills on central nervous system diseases. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2021; 39, 166-70. [Google Scholar]
- 86. Li GL. The mitigation effect of quercetin on the damage of diethylstilbestrol-induced spermatogenesis in hamsters. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2010: 15-22. [Google Scholar]
- 87. Zhang YW, Shao DY, Shi JL, Zhu J, Huang QS, Yang H. Research progress in the biological function of kaempferol. Sheng Ming Ke Xue 2017; 29: 400-5. [Google Scholar]
- 88. Wang HJ, Guo HJ, Zhang XY. The effect of kaempferol on HepG2 cell apoptosis. Wei Chang Bing Xue He Gan Bing Xue Za Zhi 2018; 27: 617-22. [Google Scholar]
- 89. Zhang YH, Li CM. Estrogen-like functions of phytosterols and their effects on animal reproduction and development. Xu Mu Yu Shou Yi 2011; 43: 103-7. [Google Scholar]
- 90. Hao HX, Xie XM, He JB. The effect of plant sterols on the growth and reproductive hormones of KM female mice. Xian Dai Xu Mu Shou Yi 2014; 305: 19-22. [Google Scholar]


