Abstract
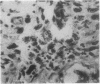
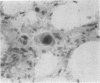
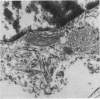
A 45-year-old female with selective deficiency of C4 and systemic lupus erythematosus developed puzzling gastrointestinal and systemic symptoms in the last 6 months of her life. Extensive investigation of the gastrointestinal tract did not yield any diagnosis, and the patient died shortly afterwards. Autopsy revealed evidence of a typical Whipple's disease of the jejunum and lymph nodes. This association has not been previously described. The disease is reviewed with emphasis on its being an opportunistic infection in an immunosuppressed host with a complement deficiency and SLE.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Keren D. F. Whipple's disease: a review emphasizing immunology and microbiology. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1981;14(2):75–108. doi: 10.3109/10408368109106451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksche L. W., Blümcke S., Fritsche D., Küchemann K., Schüler H. W., Grözinger K. H. Whipple's disease: etiopathogenesis, treatment, diagnosis, and clinical course. Case report and review of the world literature. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1974 Aug;21(4):307–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta J. O., Urowitz M. B., Gladman D. D., Irizawa T., Biggar W. D. Selective deficiency of the fourth component of complement in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): immunochemical and biological studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jul;45(1):72–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urowitz M. B., Gladman D. D., Minta J. O. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a patient with C4 deficiency. J Rheumatol. 1981 Sep-Oct;8(5):741–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]