Abstract
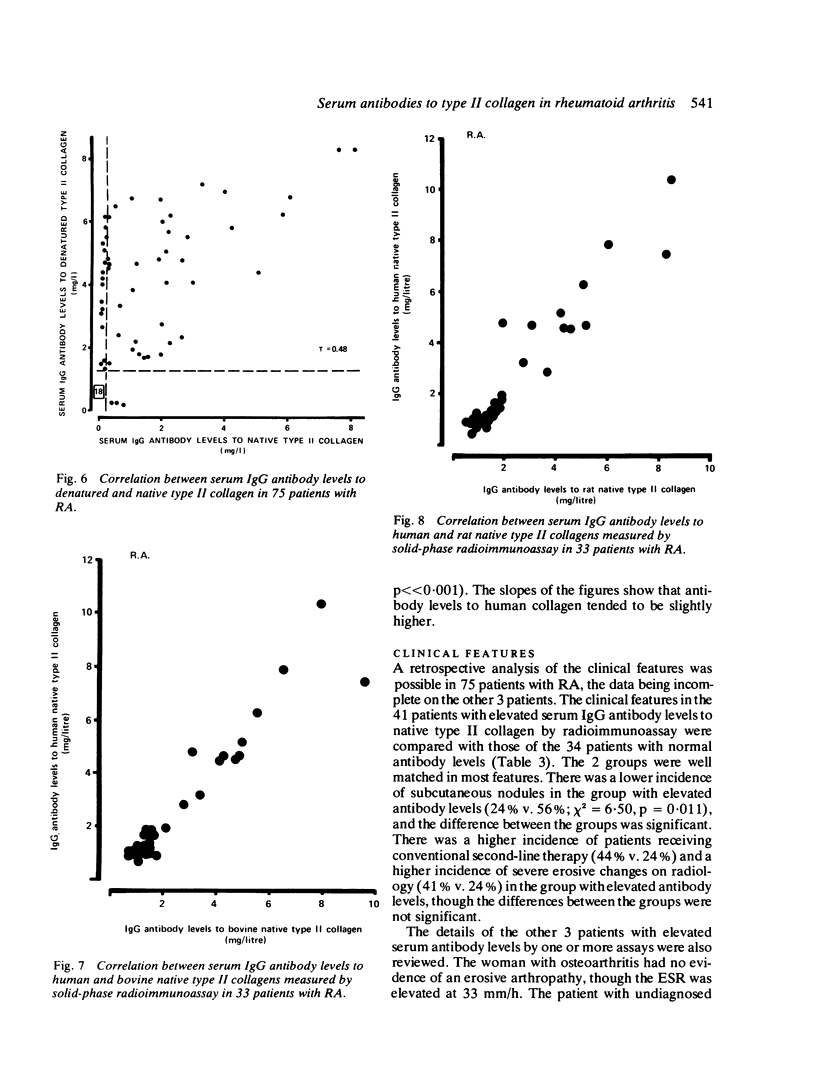
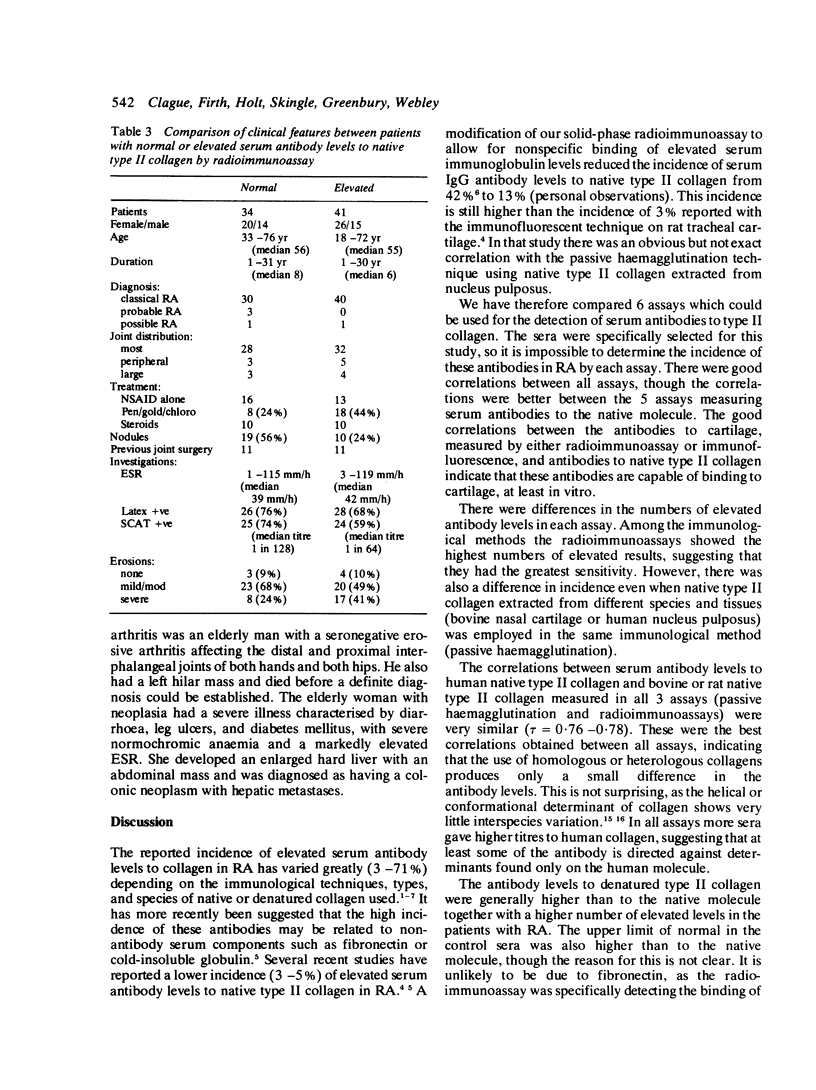
A collaborative study of 75 selected patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) employing 6 different methods for the detection of antibodies to type II collagen showed highly significant correlations between all the assays. The radioimmunoassays showed a greater sensitivity than either the passive haemagglutination or immunofluorescent techniques, and when the native collagen molecule was heat-denatured a higher number of patients showed increased antibody levels. In 33 patients the measurement of serum antibody levels to human, bovine, and rat native type II collagen showed a lack of species specificity, indicating that heterologous collagens can be employed in these assays. A retrospective analysis of the clinical, laboratory, and radiological features in the 41 patients with raised antibody levels and the 34 patients with normal antibody levels showed very few differences, but there was a significantly lower incidence of subcutaneous nodules (24% versus 56%) in patients with raised antibody levels. This study emphasizes the need to standardize assays for the measurement of serum antibody levels to native type II collagen. More extensive studies will be required before the clinical significance of these antibodies can be fully established.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriopoulos N. A., Mestecky J., Miller E. J., Bradley E. L. Antibodies to native and denatured collagens in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19(3):613–617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard H. K., Lea D. J., Ryvar R. Anomalous reactions in the haemagglutination assay for anti-collagen antibodies: studies on patients with rheumatoid arthritis or chronic low back pain. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W., Timpl R., Furthmayr H. Conformation dependence of antigenic determinants on the collagen molecule. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):13–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague R. B., Brown R. A., Weiss J. B., Holt P. J. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of antibodies to collagen. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Holt P. J. Incidence and correlation between serum IgG and IgM antibodies to native type II collagen in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Feb;40(1):6–10. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Holt P. J. Incidence of serum antibodies to native type I and type II collagens in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Jun;39(3):201–206. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay J. S., Dallman M. J., Dayan A. D., Martin A., Mosedale B. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):666–668. doi: 10.1038/283666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Gay R. E., Miller E. F. The collagens of the joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):937–941. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbury C. L., Skingle J. Anti-cartilage antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):826–831. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A. Evaluation of the simultaneous estimation of anti-dsDNA and anti-ssDNA antibodies for clinical purposes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Mar;31(3):472–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli D., Fudenberg H. H. The incidence and antigenic specificity of antibodies against denatured human collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Jan;2(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Lunde L. G. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(II) chain of bovine and human cartilage collagen. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3153–3159. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Firth S. A., Twose T. M., Holt P. J. Native type II collagen--induced arthritis in the rat: the effect of complement depletion by cobra venom factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1356–1362. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Holt P. J. Native type II collagen-induced arthritis in the rat. I. Incidence and humoral response to collagen. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Jun;39(3):285–290. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFFEN C., TIMPL R. Antigenicity of collagen and its application in the serological investigation of rheumatoid arthritis sera. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;22:333–349. doi: 10.1159/000229376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Martin G. R., Miller E. J., Dorfman A., Swarm R. Nature of the collagen synthesized by a transplanted chondrosarcoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cremer M. A., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Passive transfer with serum and evidence that IgG anticollagen antibodies can cause arthritis. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]