Abstract
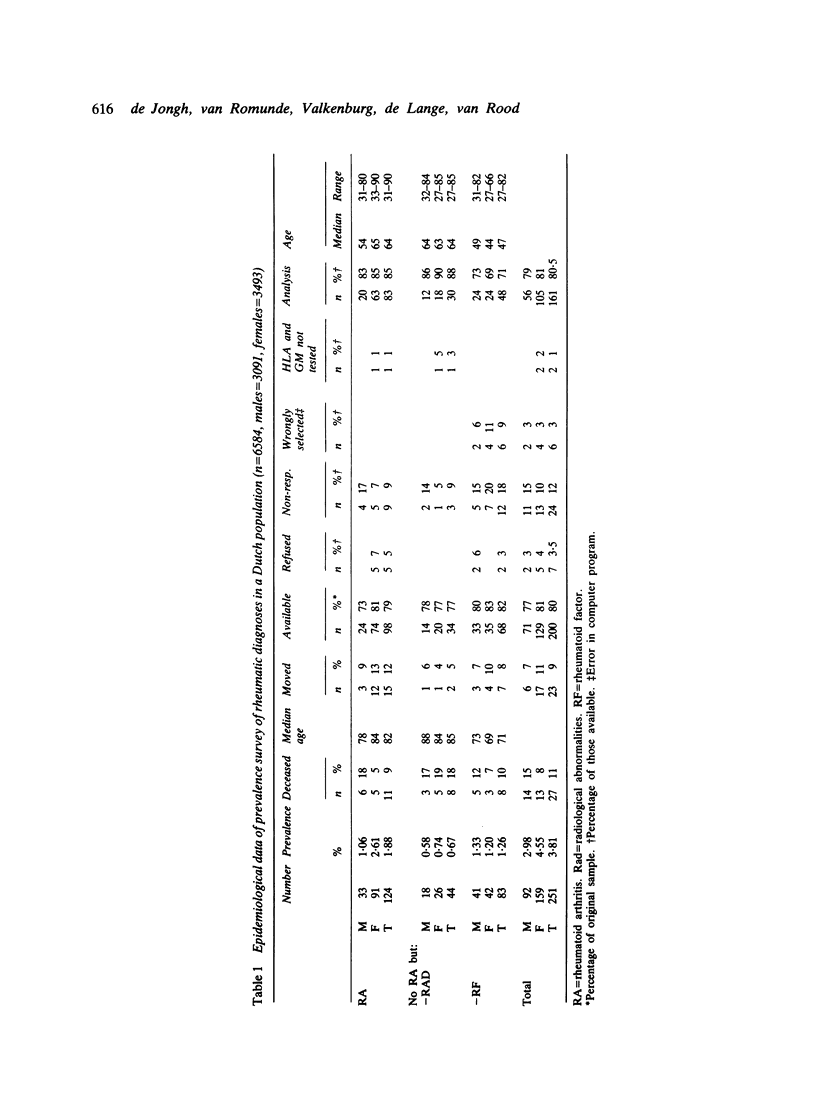
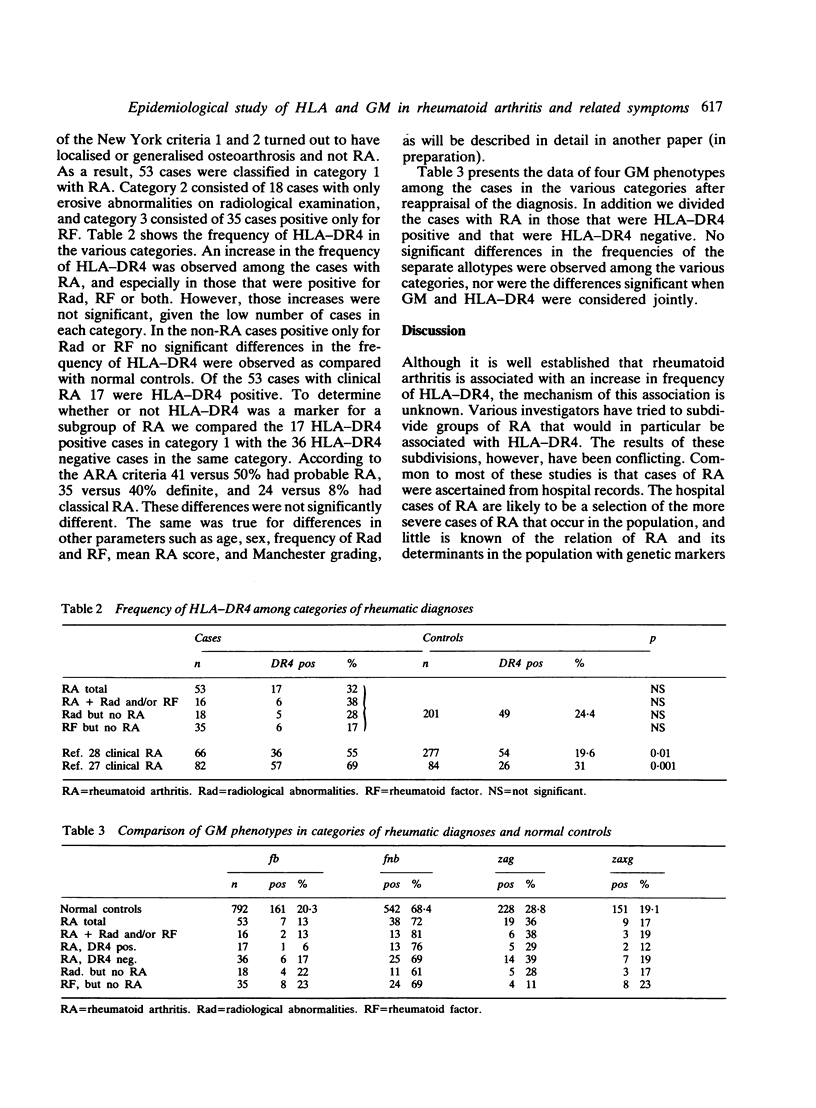
This report deals with the question of whether or not the established association of HLA-DR4 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can also be detected in cases of RA as diagnosed in a population survey. For this purpose 6584 persons older than 19 years living in a single community in The Netherlands were investigated for the presence of rheumatoid arthritis and related abnormalities. After five years 83 patients with RA, 30 with only erosive abnormalities on radiological examination (Rad), and 48 with only rheumatoid factor (RF) were reinvestigated and typed for HLA and allotypes of immunoglobulin G heavy chain (GM). On the classification of the initial survey no significant association of HLA-DR4 or GM could be detected in any of the three categories. When the information of the follow-up investigation was taken into account, a reappraisal of the classification resulted in 53 cases with RA, 18 with Rad only, and 35 with RF only. The frequencies of HLA-DR4 and GM in the three categories were also about the same as those in normal controls. However, an increase in the frequency of HLA-DR4 was observed in cases of RA positive for Rad, RF, or both. We found no evidence for an interaction between HLA-DR4 and GM. Our results suggest that rheumatoid arthritis is a heterogeneous disorder, only a fraction of which is associated with HLA-DR4. At present no single determinant of RA such as Rad or RF can characterise the HLA-DR4-associated, and most probably more severe, type of RA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón G. S., Koopman W. J., Acton R. T., Barger B. O. Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. A distinct immunogenetic disease? Arthritis Rheum. 1982 May;25(5):502–507. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Hazevoet H. M. Significance of positive tests for rheumatoid factor in the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis. A follow-up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):254–260. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinant H. J., Hissink Muller W., van den Berg-Loonen E. M., Nijenhuis L. E., Engelfriet C. P. HLA-DRw4 in Felty's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Nov;23(11):1336–1336. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug J. H., Førre O., Kåss E., Thorsby E. HLA antigens and rheumatoid arthritis. Association between HLA-DRw4 positivity and IgM rheumatoid factor production. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):309–313. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Sponzilli E. E., Batey M. E., Ramcharan S., McDevitt H. O. Mixed lymphocyte reaction in healthy women with rheumatoid factor. Lack of association with HLA-Dw4. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):690–693. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. R., Volkers W. S., Bernini L. F., van Loghem E., Meera Khan P., Nijenhuis L. E. Gene frequencies in a Dutch population. Hum Hered. 1974;24(5-6):435–448. doi: 10.1159/000152680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Gran J. T., Ostensen M., Johannessen A., Thorsby E. HLA-DRw4 and rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1979 Mar 10;1(8115):549–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H., LAWRENCE J. S. Rheumatoid arthritis in a population sample. Ann Rheum Dis. 1956 Mar;15(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/ard.15.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J. B., Cathcart E. S. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis. Follow-up evaluation of the effect of criteria on rates in Sudbury, Massachusetts. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):573–577. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Wooley P. H., Batchelor J. R. HLA-DRw4 and rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1979 Mar 31;1(8118):730–730. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roitt I. M., Corbett M., Festenstein H., Jaraquemada D., Papasteriadis C., Hay F. C., Nineham L. J. HLA-DRW4 and prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):990–990. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherak O., Smolen J. S., Mayr W. R. Rheumatoid arthritis and B lymphocyte alloantigen HLA-DRw4. J Rheumatol. 1980 Jan-Feb;7(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speerstra F., Reekers P., van de Putte L. B., Vandenbroucke J. P., Rasker J. J., de Rooij D. J. HLA-DR antigens and proteinuria induced by aurothioglucose and D-penicillamine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1983 Dec;10(6):948–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Jersild C., Nielsen L. S., Bodmer W. F. HL-A antigens and disease. Statistical and genetical considerations. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(2):95–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1974.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen M., Morling N., Snorrason E., Svejgaard A., Sørensen S. F. HLA--Dw4 and rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Jan;13(1):56–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


