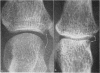
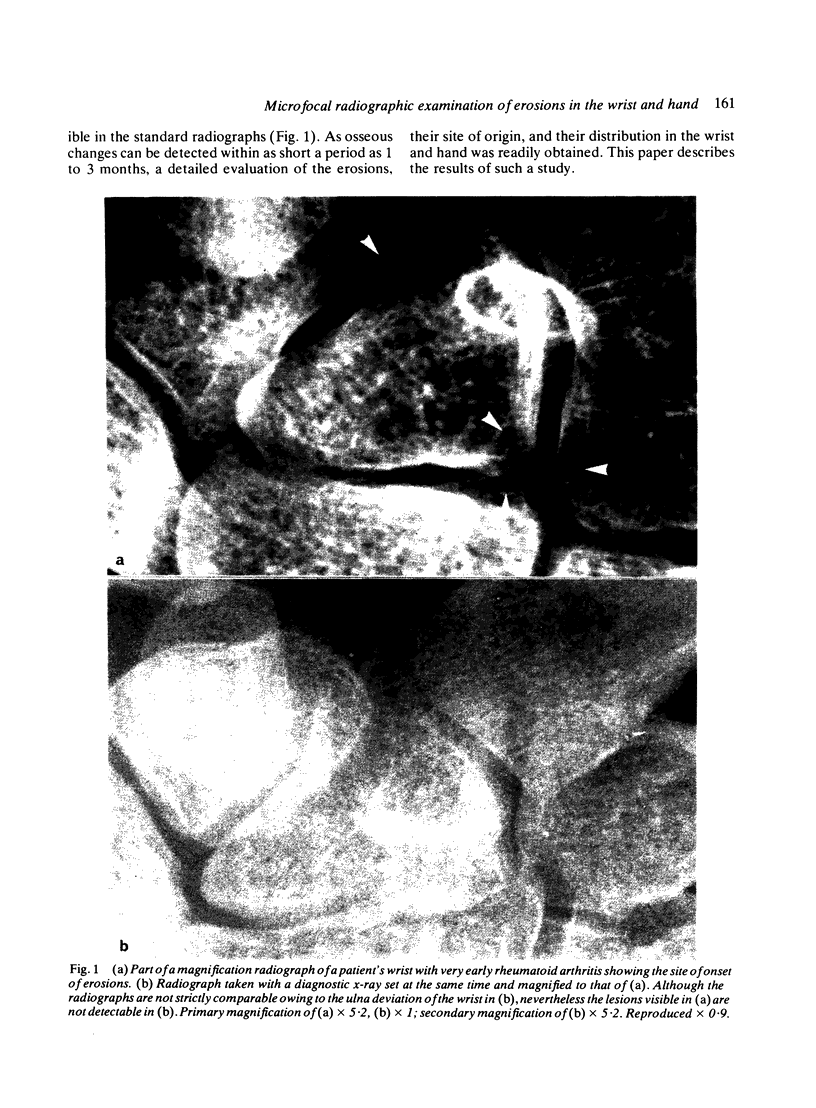
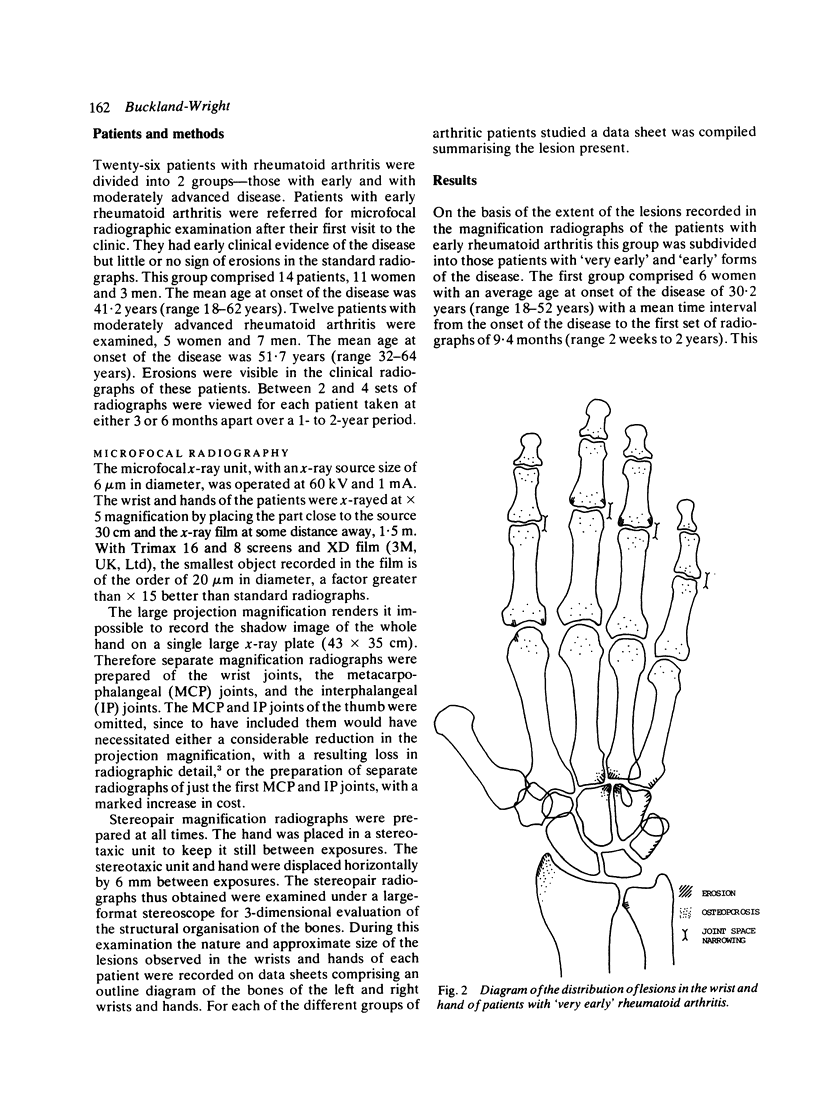
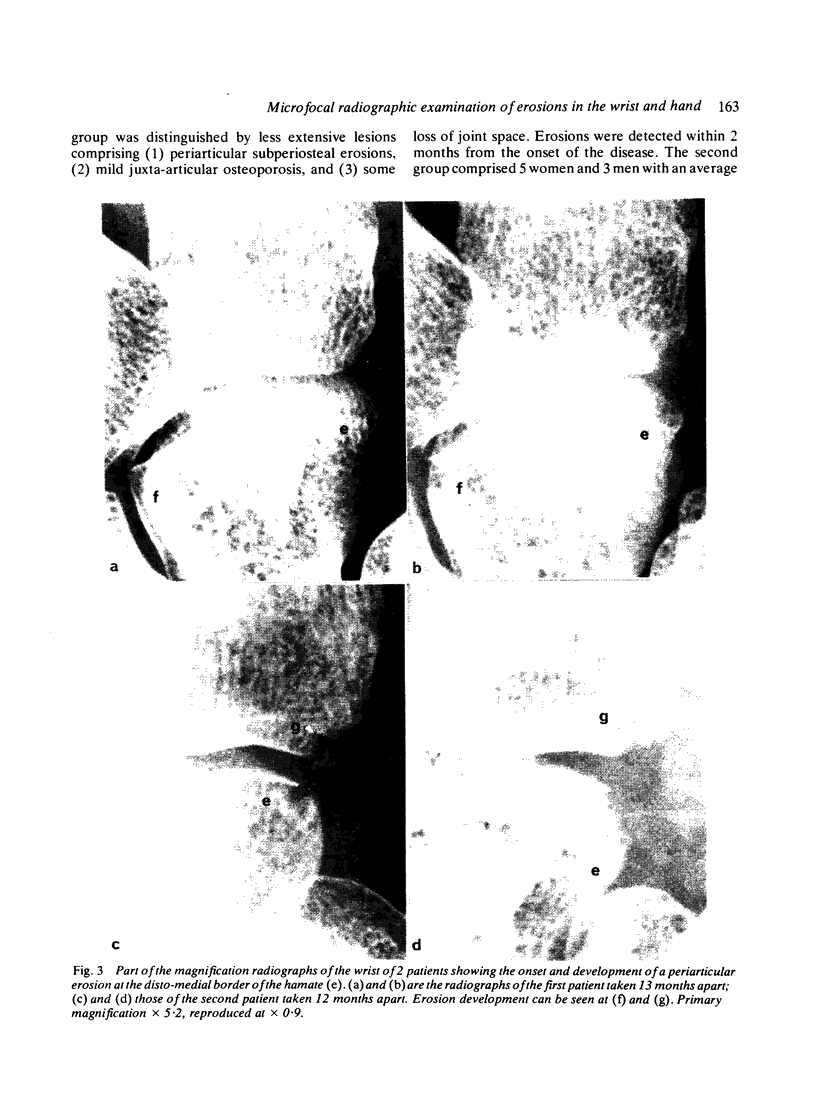
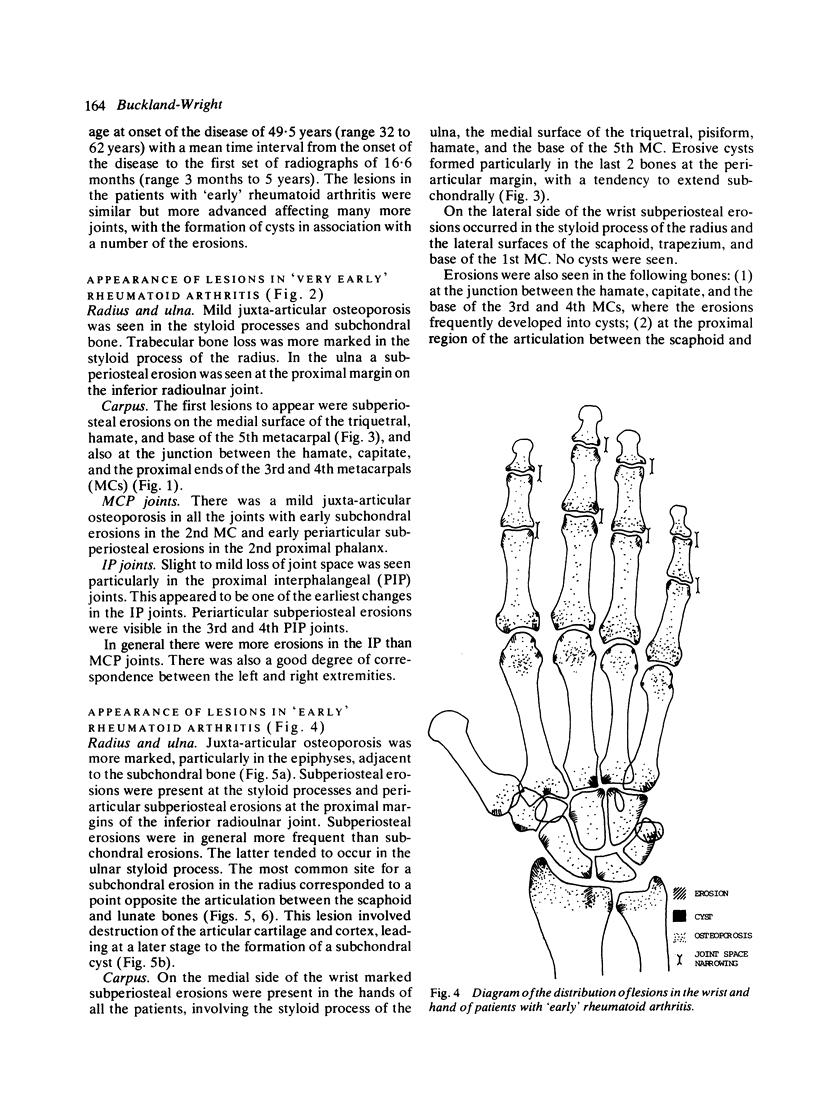
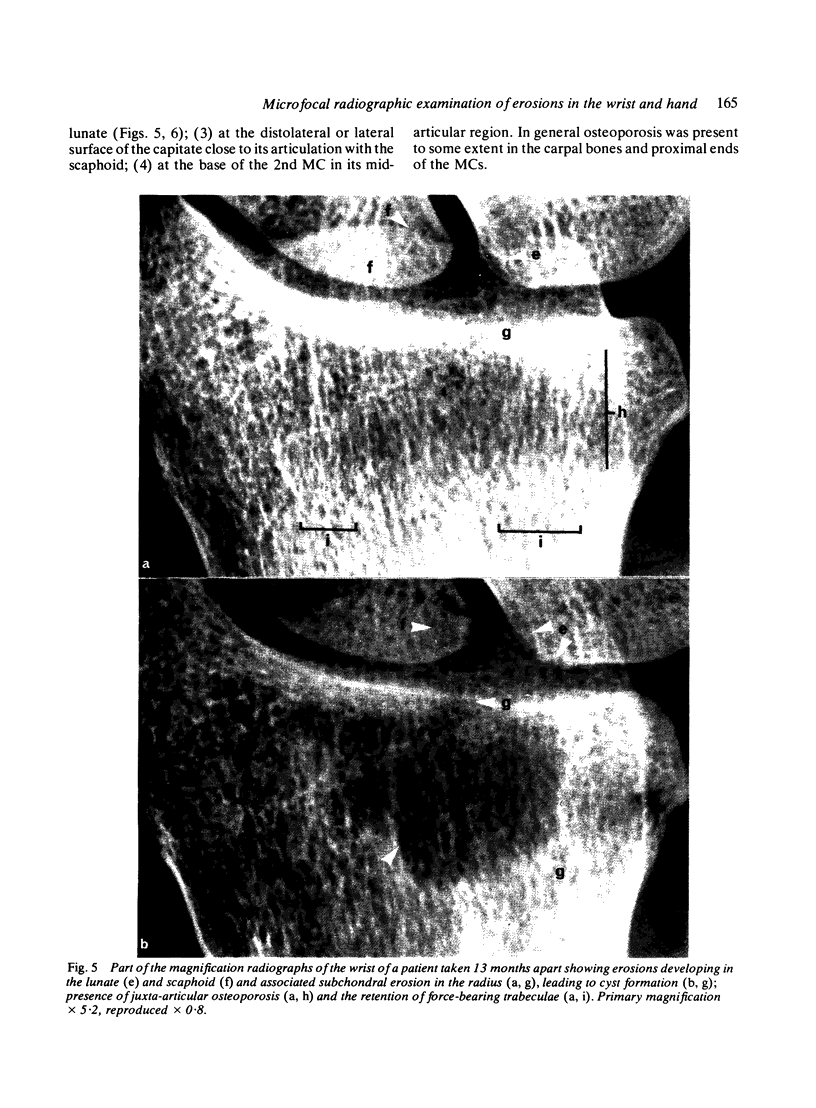
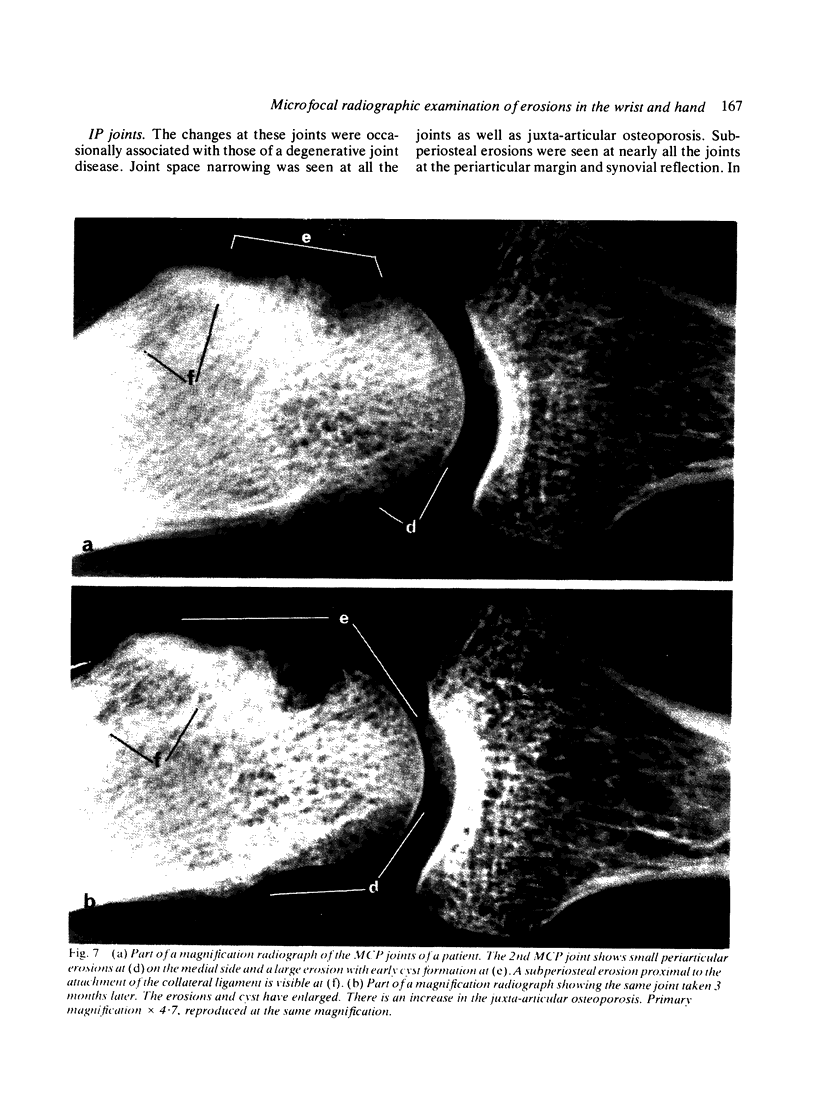
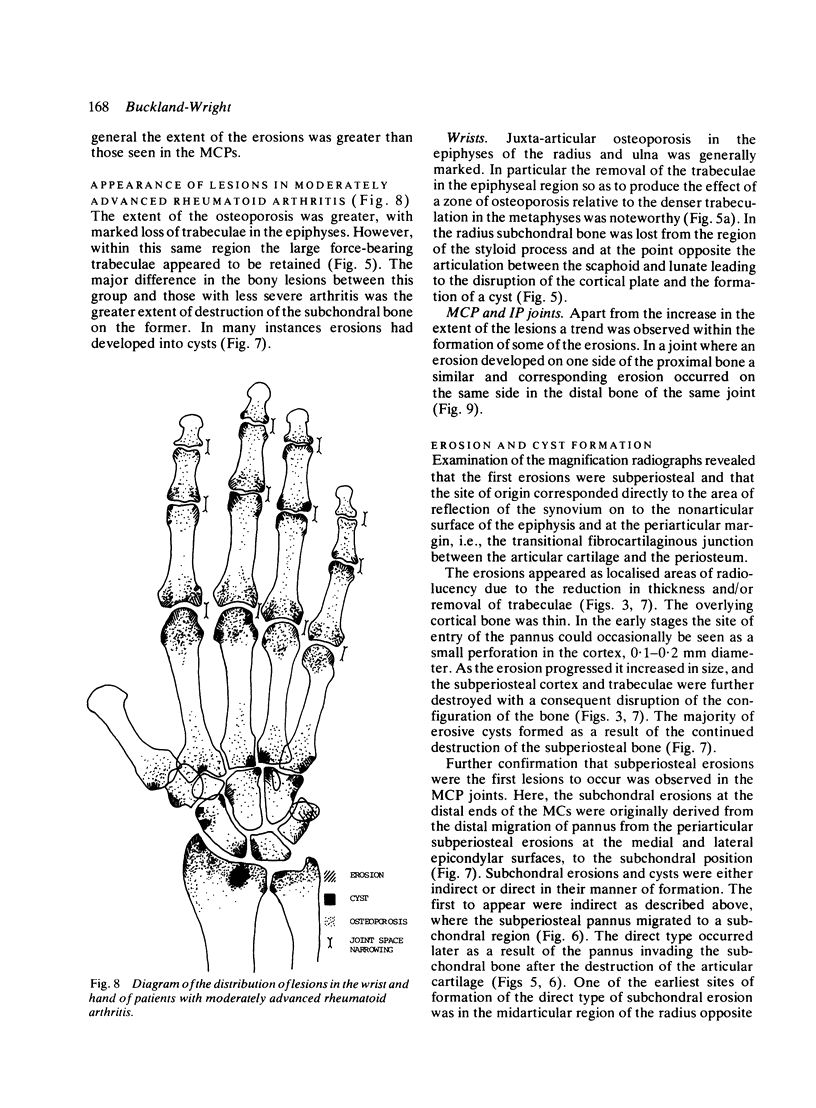
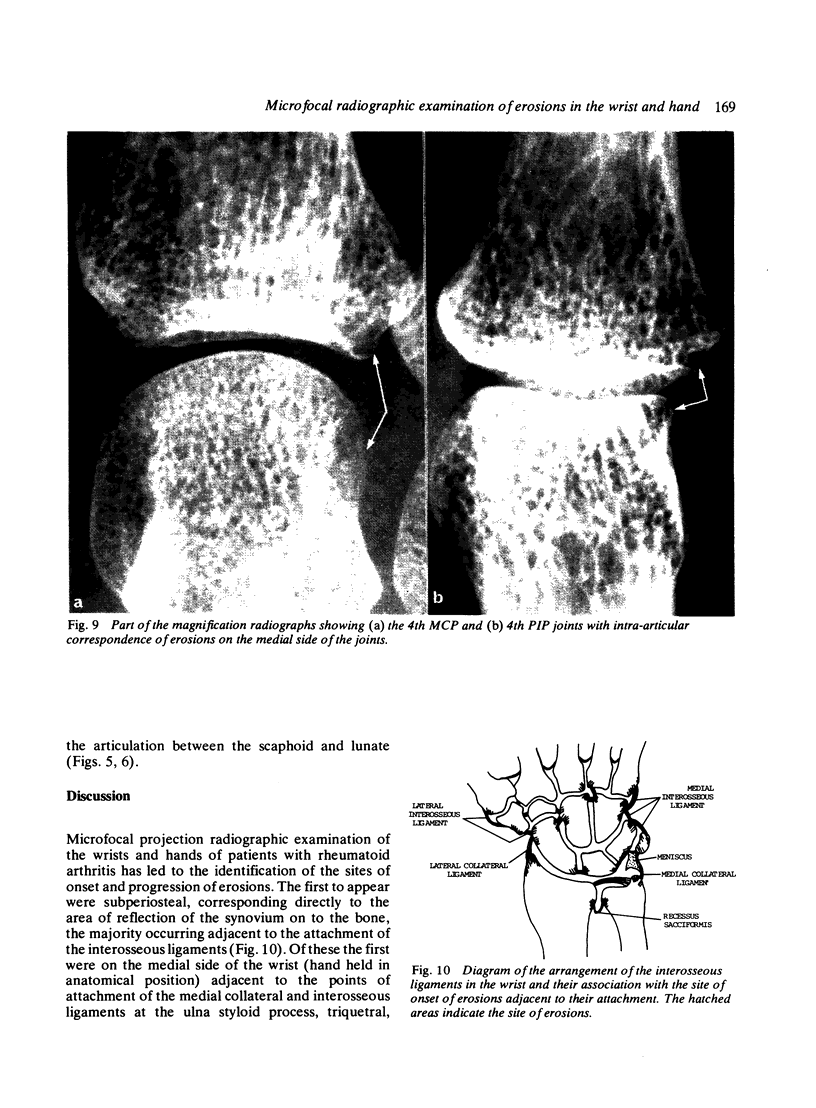
Abstract
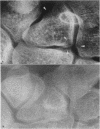
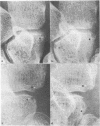
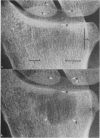
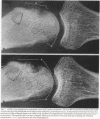
The microfocal x-ray unit, a new type of x-ray machine characterised by an extremely small x-ray source, enables great detail to be recorded in the projection radiographs owing to the high object magnification and resolution obtained with this system. Microfocal radiographic examinations were carried out on the wrists and hands of 26 patients with early or moderately advanced rheumatoid arthritis. The macroradiographs confirmed the presence or absence of erosions in patients with early disease activity who otherwise had no detectable lesions visible in standard radiographs. The site of onset, development, and distribution of erosions are described. Their approximate order of appearance is listed. The first to appear occurred in the medial carpal bones, second and third metacarpophalangeal joints and third and fourth proximal interphalangeal joints. In origin they were subperiosteal either immediately adjacent to the insertion of an interosseous ligament or at the transitional zone of the articular cartilage. Erosions in the subchondral bone appeared subsequently and were either indirect (subperiosteal) or direct (subchondral) in origin. Cyst formation was frequently associated with the enlargement of an erosion which it often replaced.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Wright J. C. Microfocal radiography in the quantitative assessment of experimentally induced inflammatory arthritis in guinea-pigs. J Pathol. 1981 Oct;135(2):127–145. doi: 10.1002/path.1711350204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Wright J. C. X-ray assessment of activity in rheumatoid disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1983 Feb;22(1):3–10. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/22.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashin C. H., Doherty N. S., Jeffries B. L., Buckland-Wright J. C. An investigation of the effect of anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatoid drugs in cell-mediated immune arthritis in guinea-pigs by microfocal radiography. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Jun;61(3):296–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick E. N. Influence of mechanical factors on the rheumatoid wrist. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Jun;59(6):555–558. doi: 10.1177/003591576605900627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTEL W., HAYES J. T., DUFF I. F. THE PATTERN OF BONE EROSION IN THE HAND AND WRIST IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Radiology. 1965 Feb;84:204–214. doi: 10.1148/84.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly P. C., Matheson J. A., Dickson R. A. The distribution of radiological joint damage in the rheumatoid hand. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1979 Aug;18(3):142–147. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/18.3.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]