Abstract
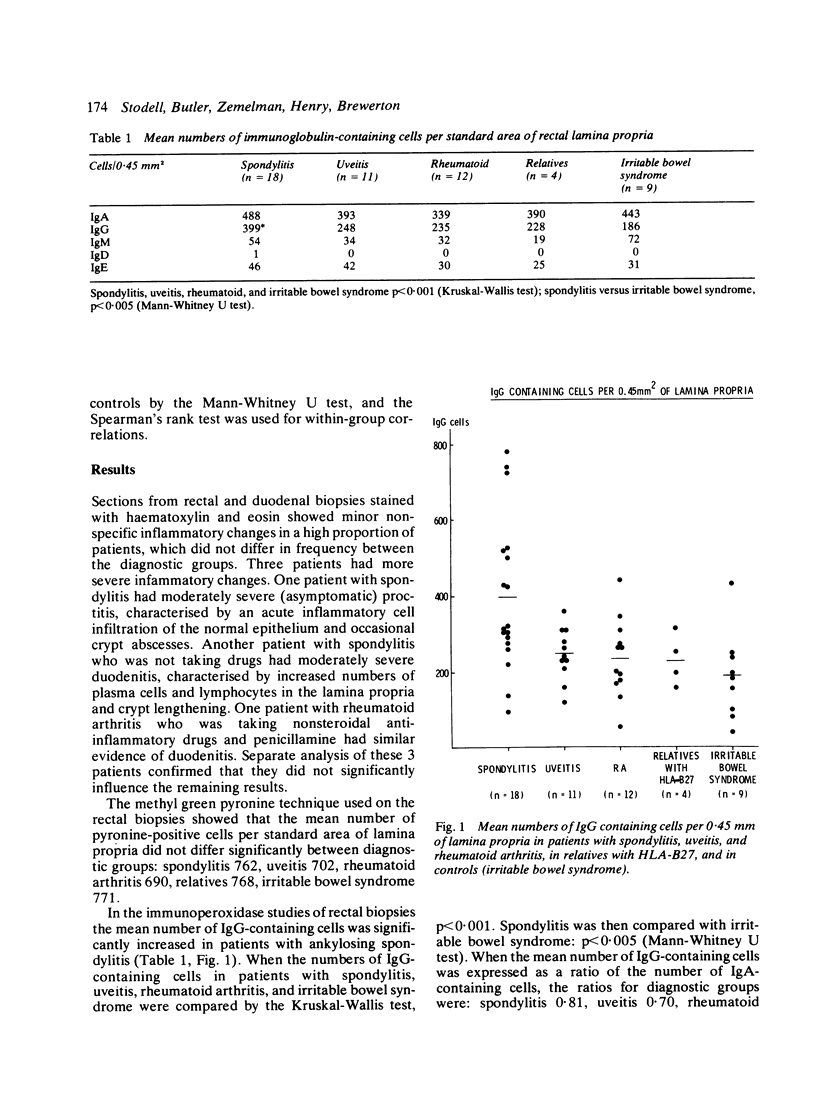
Using an indirect immunoperoxidase technique we found the numbers of IgG-containing cells in the rectal lamina propria to be increased in patients with ankylosing spondylitis compared with controls, but not in patients with acute anterior uveitis or rheumatoid arthritis, or in the first-degree relatives of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. No differences between diagnostic groups were detected in the numbers of cells containing IgA, IgM, IgD, or IgE. The total numbers of plasma cells in the rectal lamina propria were not significantly increased. Similar increases of IgG-containing cells were not found in the duodenal lamina propria of patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K., Fausa O., Hoel P. S. Immunohistochemical characterization of local immunoglobulin formation in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1123–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. Background staining and sensitivity of the unlabelled antibody-enzyme (PAP) method. Comparison with the peroxidase labelled antibody sandwich method using formalin fixed paraffin embedded material. Histochemistry. 1975 Jun 5;43(3):291–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00499711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello P. B., Alea J. A., Kennedy A. C., McCluskey R. T., Green F. A. Prevalence of occult inflammatory bowel disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Oct;39(5):453–456. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.5.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I., Bouchier I. A. Ulcerative colitis with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 May;27(3):219–224. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I., Salmon P. R., Harrison W. J. Inflammatory bowel disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Gut. 1970 Jun;11(6):506–511. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.6.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen S. G., Dekker-Saeys B. J., Agenant D., Tytgat G. N. Ankylosing spondylitis and inflammatory bowel disease. I. Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in patients suffering from ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Feb;37(1):30–32. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosekrans P. C., Meijer C. J., van der Wal A. M., Cornelisse C. J., Lindeman J. Immunoglobulin containing cells in inflammatory bowel disease of the colon: a morphometric and immunohistochemical study. Gut. 1980 Nov;21(11):941–947. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.11.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Spreeuwel J. P., Lindeman J., Van der Wal A., Weterman I., Kreuning J., Meijer C. Morphological and immunohistochemical findings in upper gastrointestinal biopsies of patients with Crohn's disease of the ileum and colon. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):934–940. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.9.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


