Abstract
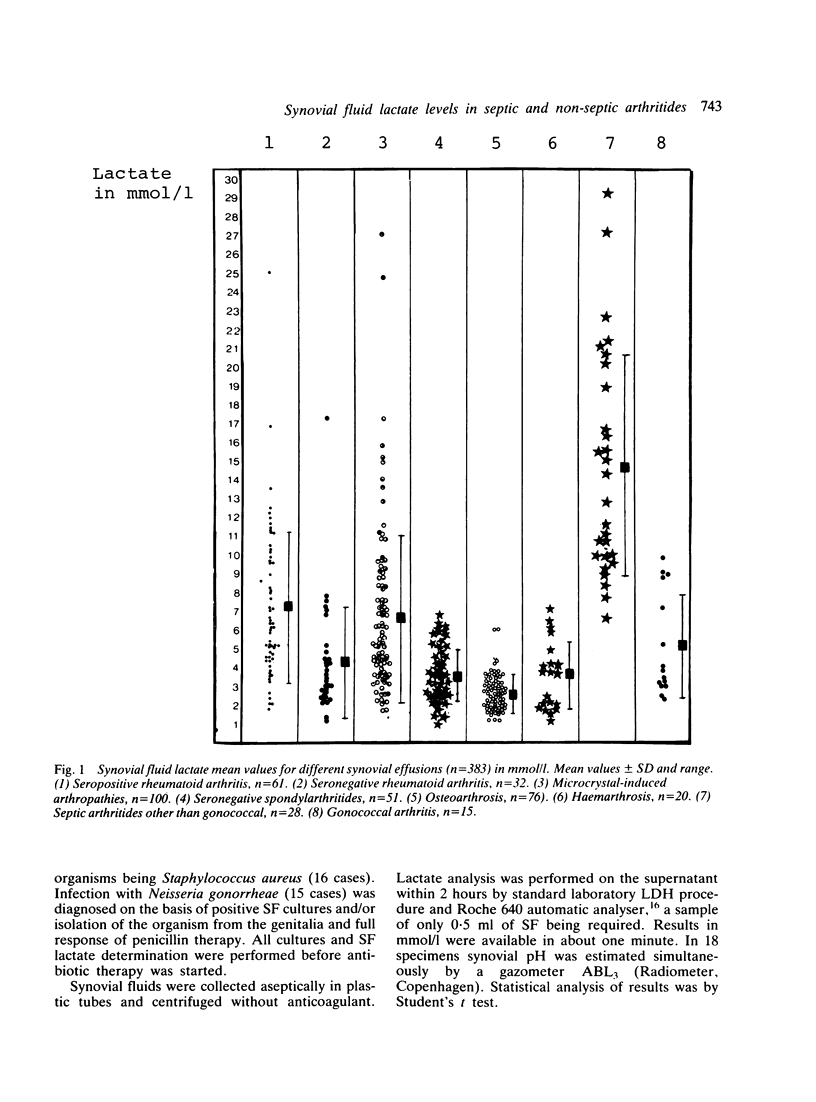
Lactate concentration was studied in 383 synovial fluid specimens from patients with various arthritides. The highest concentrations of lactate occurred in non-gonococcal septic synovial fluids. High values were recorded in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis and crystal-induced arthritides, medium values in synovial fluids from seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides, gonococcal arthritis and haemarthrosis, and the lowest values in aspirates from osteoarthrotic joints. There was a positive correlation between synovial pH and lactic acid concentration. These data suggest that determination of lactate in synovial fluid can be valuable in the rapid exclusion of septic arthritis. Its value for differentiating between other inflammatory arthritides is discussed.
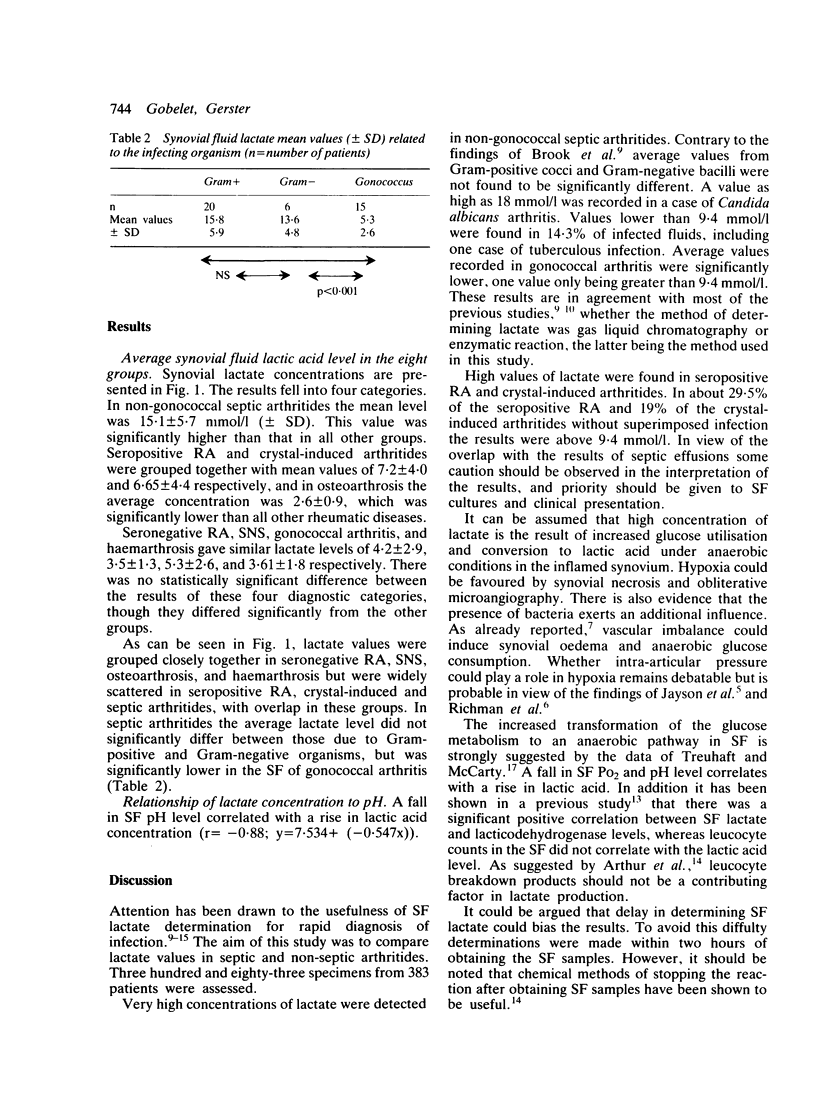
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur R. E., Stern M., Galeazzi M., Baldassare A. R., Weiss T. D., Rogers J. R., Zuckner J. Synovial fluid lactic acid in septic and nonseptic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1499–1505. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein D. G., Gibbs C. A., Jacobs R. P. Gas-liquid chromatographic analysis of synovial fluid. Succinic acid and lactic acid as markers for septic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Aug;25(8):947–953. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Controni G. Rapid diagnosis of septic arthritis by quantitative analysis of joint fluid lactic acid with a monotest lactate kit. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):676–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.676-679.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Reza M. J., Bricknell K. S., Bluestone R., Finegold S. M. Synovial fluid lactic acid. A diagnostic aid in septic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Sep-Oct;21(7):774–779. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza L. R., Vasey F. B., Espinoza C. G., Bocanegra T. S., Germain B. F. Vascular changes in psoriatic synovium. A light and electron microscopic study. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jun;25(6):677–684. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. H., Goetzl E. J., Kulka J. P. Respiratory gases of synovial fluids. An approach to synovial tissue circulatory-metabolic imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1970 Aug;49(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I., St Dixon A. J. Intra-articular pressure in rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. I. Pressure changes during passive joint distension. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):261–265. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J. Selected aspects of synovial membrane physiology. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):289–296. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. R., Miller L. M., Pinals R. S. Pyarthrosis complicating rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1969 Oct 4;2(7623):714–716. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90427-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Lewis D., Ziff M. Light and electron microscopic observations on the synovitis of Reiter's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Dec;9(6):747–757. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman A. I., Su E. Y., Ho G., Jr Reciprocal relationship of synovial fluid volume and oxygen tension. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 May;24(5):701–705. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft P. S., MCCarty D. J. Synovial fluid pH, lactate, oxygen and carbon dioxide partial pressure in various joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(4):475–484. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


