Abstract
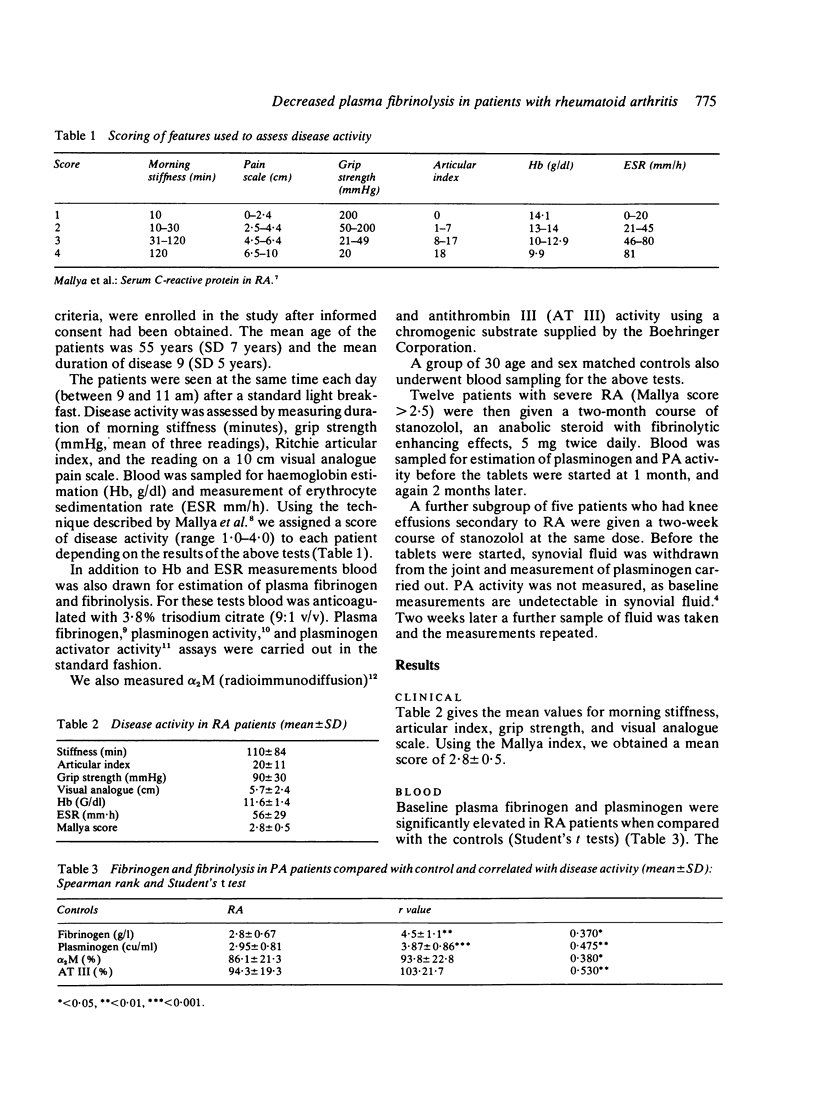
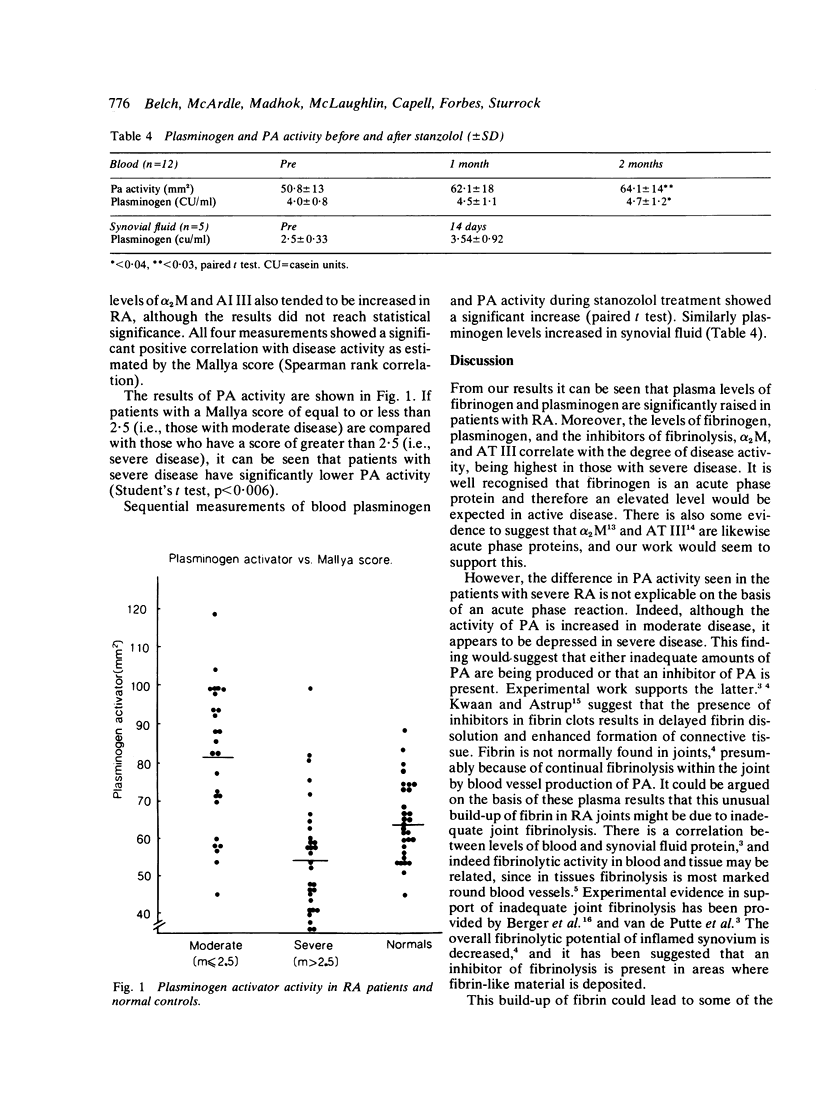
We have investigated the fibrinolytic status of 56 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Plasma fibrinogen and plasminogen were significantly elevated. Levels of these two substrates, along with alpha 2 macroglobulin and antithrombin III correlated with disease activity. Plasminogen activator (PA) activity was decreased in patients with severe disease. Twelve patients were given stanozolol, a fibrinolytic enhancing agent, for two months as a test for endothelial production of plasminogen activator. This caused a significant increase in blood plasminogen and PA activity. Five patients received a two-week course of stanozolol with joint aspiration before and after. Joint plasminogen levels were increased. We suggest that inadequate fibrinolysis occurs in RA, and that this may contribute to some of the pathological features of the disease. It is possible to stimulate both blood and joint fibrinolysis by stanozolol. A more prolonged increase in plasminogen activator activity might decrease joint fibrin deposition, and stanozolol should be investigated as a therapeutic agent in RA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. B., Gormsen J. Fibrinolytic and fibrin stabilizing activity of synovial membranes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):287–293. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Jr Secretion of plasminogen activator by rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid synovial cells in culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1198–1205. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn D. L., McDuffie F. C., Kazmier F. J., Schroeter A. L., Sun N. C. Coagulation abnormalities in rheumatoid disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1237–1243. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearnley G. R., Chakrabarti R. Fibrinolytic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with phenformin plus ethyloestrenol. Lancet. 1966 Oct 8;2(7467):757–761. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory E. D., Clarris B. J., Muirden K. D. Deposits of alpha 2M in the rheumatoid synovial membrane. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):520–526. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C., Astrup T. Tissue repair in presence of locally applied inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Aug;11(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., de Beer F. C., Berry H., Hamilton E. D., Mace B. E., Pepys M. B. Correlation of clinical parameters of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with serum concentration of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. J Rheumatol. 1982 Mar-Apr;9(2):224–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the metabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):624–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Putte L. B., Hegt V. N., Overbeek T. E. Activators and inhibitors of fibrinolysis in rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid synovial membranes. A histochemical study. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Mar;20(2):671–678. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


