Abstract
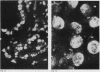
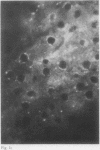
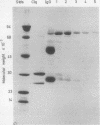
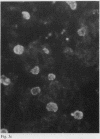
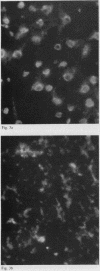
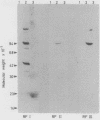
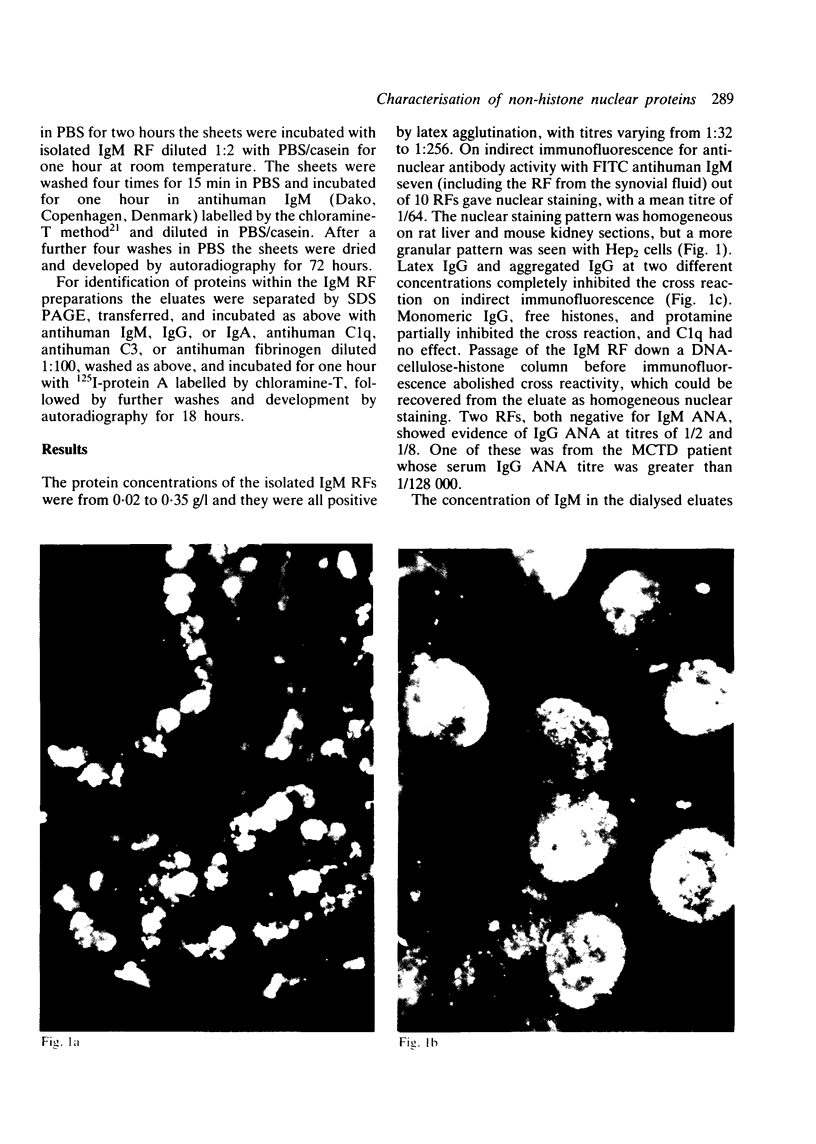
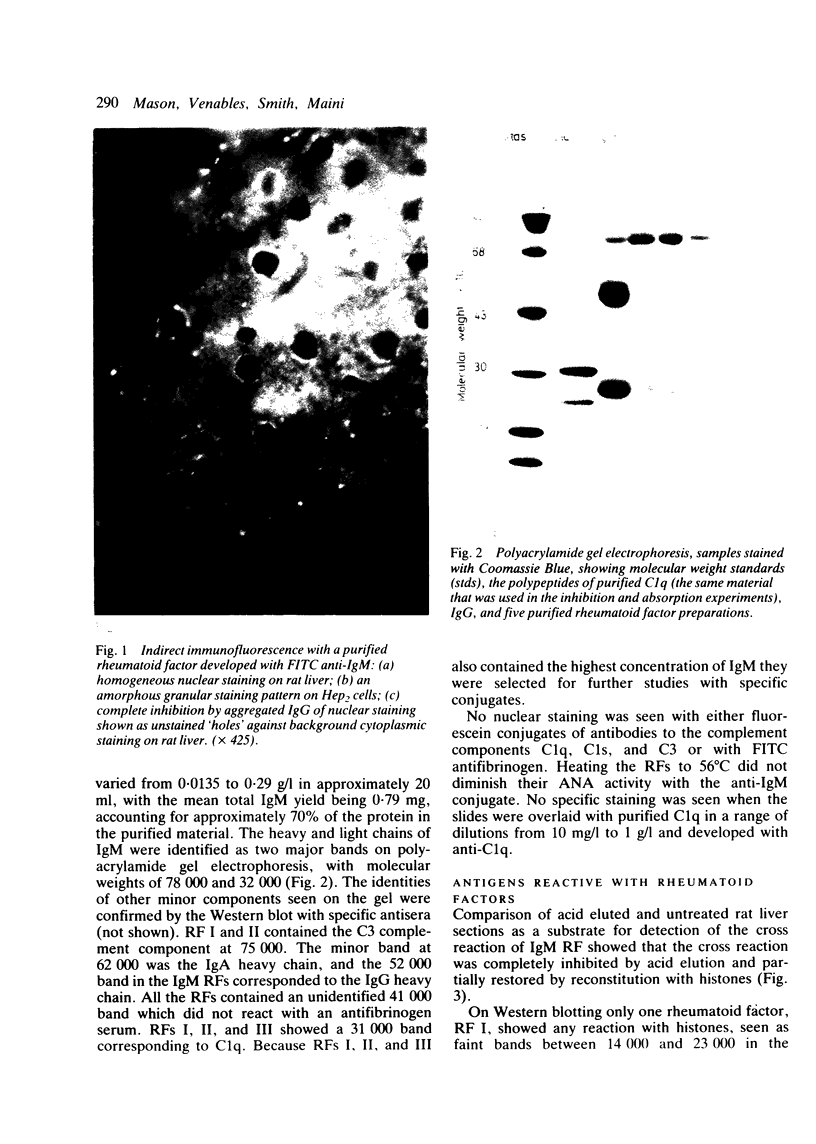
In order to examine the interactions between isolated rheumatoid factors (RFs) and cell nuclear antigens we have prepared 10 RFs by affinity chromatography against IgG coupled to Sepharose. Of these, seven cross reacted with cell nuclei on indirect immunofluorescence. The nuclear antigen appeared to be DNA histones by indirect immunofluorescence on rat liver, though on immunoblotting the rheumatoid factors also reacted with three non-histone polypeptides which were identified in the soluble fraction of nuclear extracts. We were unable to show any relationship between these polypeptides and rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen. These reactions represent a hitherto unrecognised phenomenon, which extends the range of antigens recognised by rheumatoid factors. We suggest that the immunopathogenic significance of RFs may not be restricted to their reactivity with IgG, and that non-histone nuclear proteins merit further investigation.
Full text
PDF

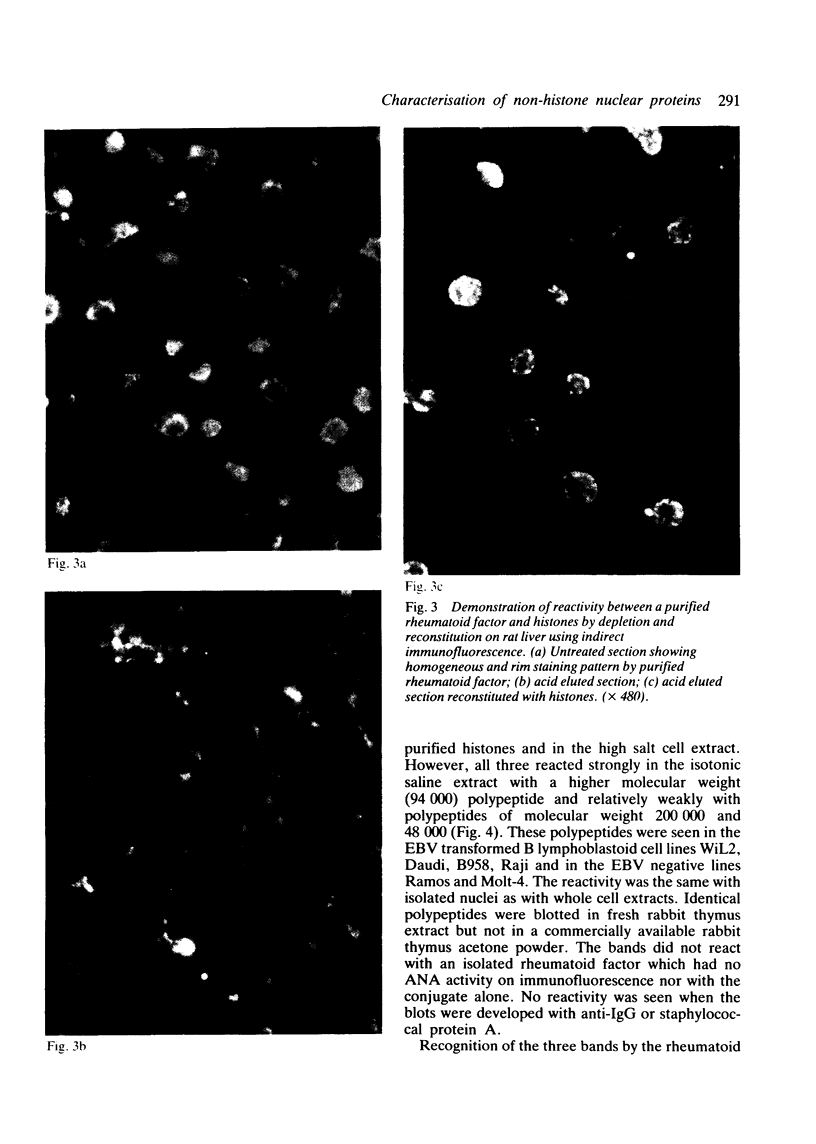


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Arbetter A., Ibanez de Kasep G., Powell R., Tan E. M., Joslin F. Evidence for a subset of rheumatoid factors that cross-react with DNA-histone and have a distinct cross-idiotype. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1514–1527. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitcheson C. T., Peebles C., Joslin F., Tan E. M. Characteristics of antinuclear antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Reactivity of rheumatoid factor with a histone-dependent nuclear antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):528–538. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. R., Charles P. J., Venables P. J., Thompson P. J., Haslam P. L., Maini R. N., Turner Warwick M. E. Definition and clinical relevance of antibodies to nuclear ribonucleoprotein and other nuclear antigens in patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):439–443. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K. Certain rheumatoid factors react with both IgG and an antigen associated with cell nuclei. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(2):127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K., Johannessen A. Polyclonal human antibodies to IgG (rheumatoid factors) which cross-react with cell nuclei. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(5):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K., Stollar B. D. Certain rheumatoid factors react with nucleosomes. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):671–673. doi: 10.1038/275671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Phua K. K., Johnson P. M. Binding of isolated rheumatoid factors to histone proteins and basic polycations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):435–438. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M. IgM-rheumatoid factors cross-reactive with IgG and a cell nuclear antigen: apparent 'masking' in original serum. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(5):461–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb03068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M. IgM-rheumatoid factors cross-reactive with IgG and a cell nuclear antigen: immunopathological implications? Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Dec;39(6):586–588. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.6.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltier A. P., Cyna L., Dryll A. 'In vitro' study of a reaction between the complement system and cellular DNA. Immunology. 1978 Nov;35(5):779–784. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen and Epstein-Barr virus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):476–478. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Balderas R. S., Tan E. M., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Multiple autoantigen binding capabilities of mouse monoclonal antibodies selected for rheumatoid factor activity. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1429–1440. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Robinson J., Robitaille P. Studies on antibodies to histones by immunofluorescence. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):811–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J., Roffe L. M., Erhardt C. C., Maini R. N., Edwards J. M., Porter A. D. Titers of antibodies to RANA in rheumatoid arthritis and normal sera. Relationship to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1459–1468. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J., Smith P. R., Maini R. N. Purification and characterization of the Sjögren's syndrome A and B antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):731–738. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]