Abstract
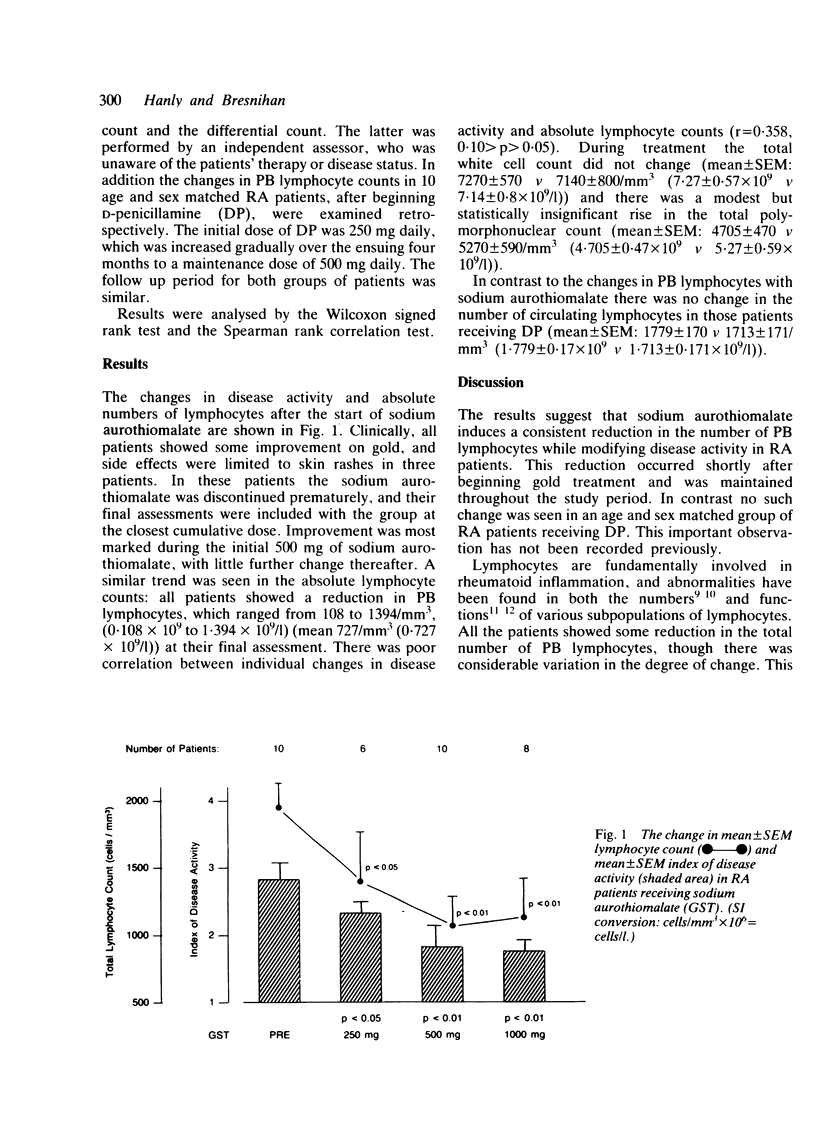
Peripheral blood lymphocytes were monitored prospectively in 10 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving up to 1 g of sodium aurothiomalate. There was a significant fall in the absolute lymphocyte count from a mean +/- SEM of 1956 +/- 190/mm3 (1.956 +/- 0.19 X 10(9)/l) to 1232 +/- 210/mm3 (1.232 +/- 0.21 X 10(9)/l) (p less than 0.01). The number of of circulating lymphocytes fell in all patients by an amount which ranged between 108/mm3 (0.108 X 10(9)/l) and 1394/mm3 (1.394 X 10(9)/l), with a mean fall of 727/mm3 (0.727 X 10(9)/l). No significant change was noted in the total white cell count or total polymorphonuclear cell count over the same period. In contrast there was no change in the total lymphocyte count in an age and sex matched group of RA patients treated with penicillamine. This previously unreported observation may give new insight into the mechanism of action of gold salts in RA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W., Tidman N. Analysis of T cell subsets in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by means of monoclonal antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):357–361. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsh J., Klippel J. H., Plotz P. H., Decker J. L., Wright D. G., Flye M. W. Lymphapheresis in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jul;24(7):867–873. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Cardin C., Paulus H. E. Inhibition by gold of human lymphocyte stimulation. An in vitro study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):216–218. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Ziff M. Inhibition of antigen- and mitogen-induced human lymphocyte proliferation by gold compounds. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):455–466. doi: 10.1172/JCI108660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., Mace B. E. The assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis using a multivariate analysis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1981 Feb 1;20(1):14–17. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/20.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel V., Panayi G. S. Enhanced T helper cell function for the spontaneous production of IgM rheumatoid factor in vitro in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):584–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus H. E., Machleder H. I., Levine S., Yu D. T., MacDonald N. S. Lymphocyte involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Studies during thoracic duct drainage. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1249–1262. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veys E. M., Hermanns P., Schindler J., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Symoens J., Van Wauwe J. Evaluation of T cell subsets with monoclonal antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


