Abstract
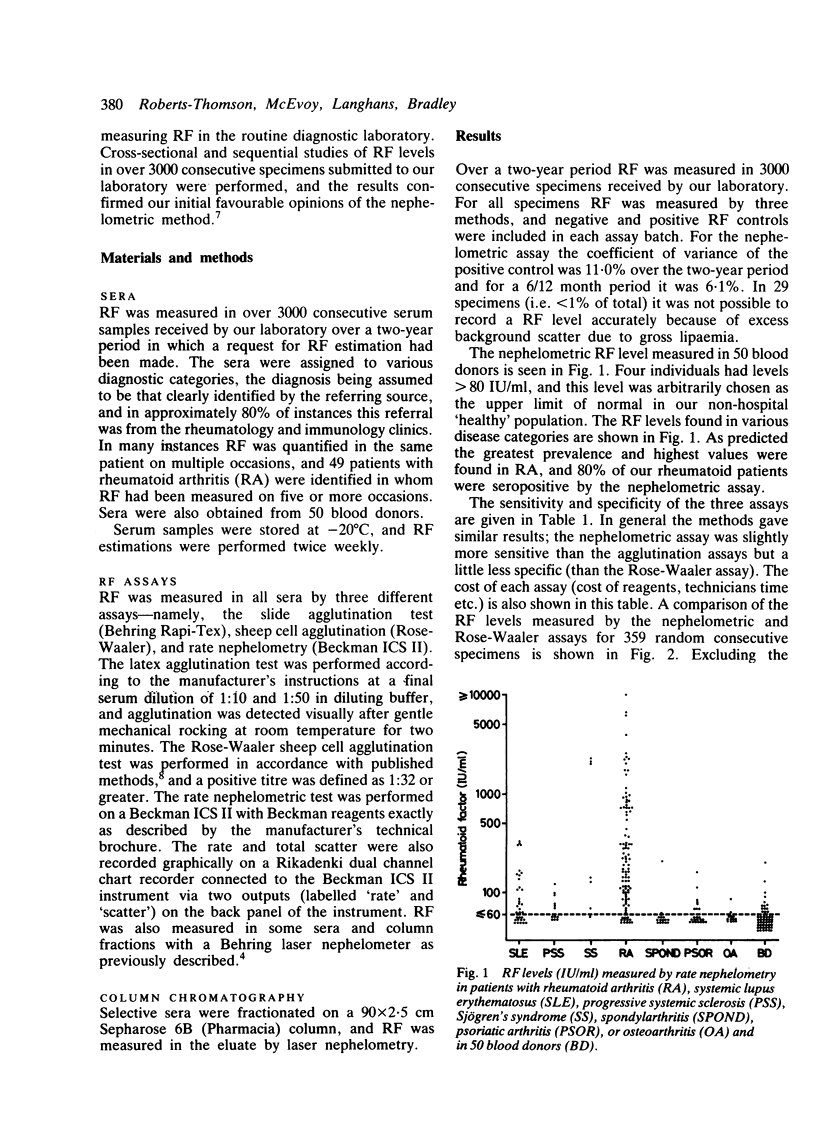
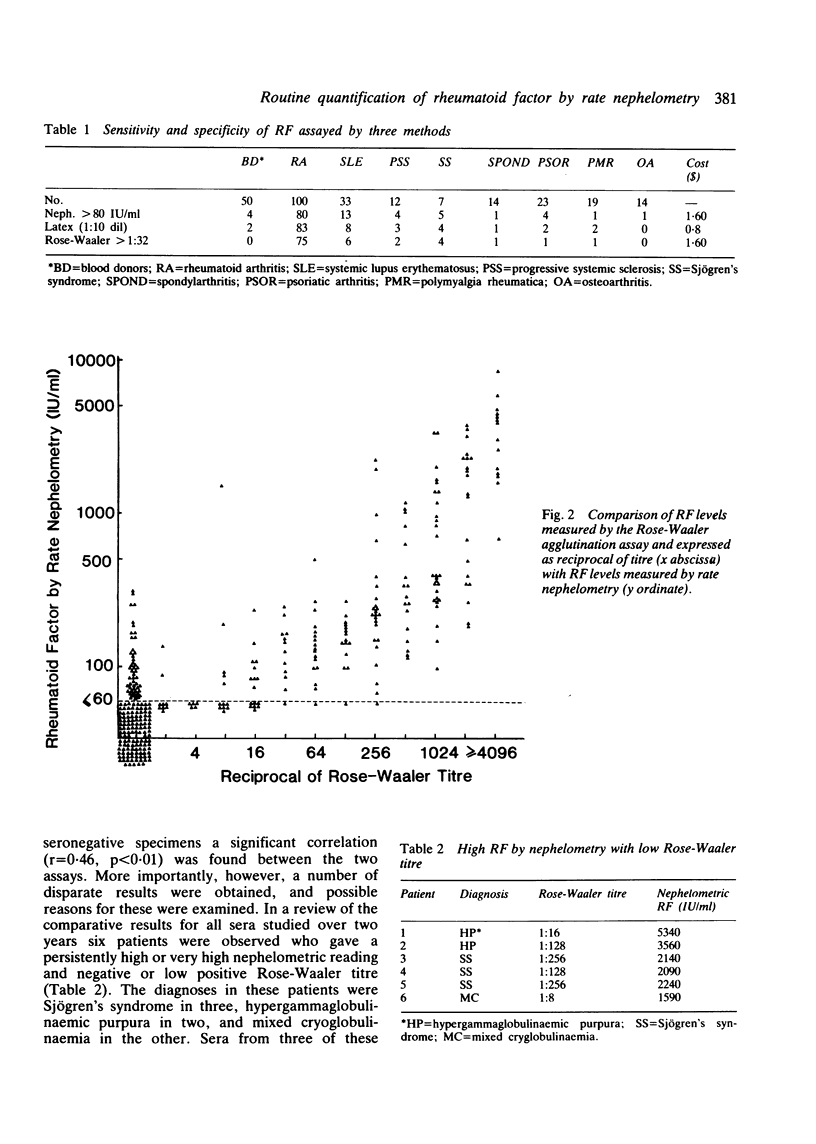
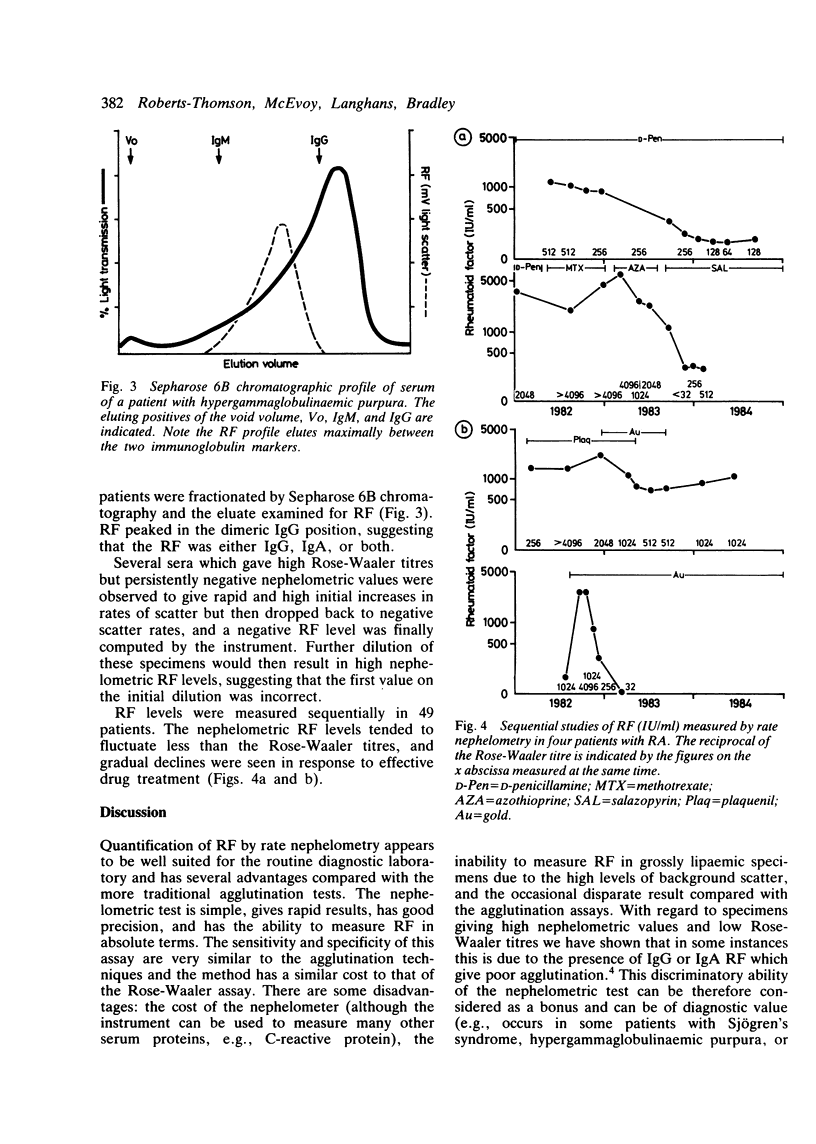
In a cross-sectional study of over 3000 consecutive serum specimens the levels of rheumatoid factor (RF) measured by rate nephelometry (Beckman ICS II) were compared with values obtained by the more traditional methods of sheep cell agglutination (Rose-Waaler) and latex agglutination. Similar values for sensitivity and specificity were found for all three methods for rheumatoid arthritis, with nephelometry giving slightly higher levels of sensitivity for other rheumatic disorders. A significant correlation (r = 0.46, p less than 0.01) was found between the nephelometric and Rose-Waaler method for 147 consecutive seropositive specimens. Of interest, however, several disparate results were observed, and explanations for these were sought. Longitudinal studies of RF were performed in 49 seropositive patients over a two-year period. The nephelometric method was considered superior compared with the other techniques because of its ability to detect changes in absolute levels at earlier stages and its low interassay coefficient of variance (11%). We conclude that the nephelometric technique appears suitable for routine diagnostic use, offers several advantages compared with more traditional methods, and is no more expensive per test specimen than the Rose-Waaler technique.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Finley P. R., Hicks M. J., Williams R. J., Hinlicky J., Lichti D. A. Rate nephelometric measurement of rheumatoid factor in serum. Clin Chem. 1979 Nov;25(11):1909–1914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. K., Pritchard M. H. Nephelometry compared with differential antibody titre in routine rheumatoid factor measurements. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Aug;41(4):426–430. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. H., Jobbins K. Nephelometry v differential agglutination titre in the measurement of rheumatoid factors. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(4):396–399. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.4.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P. J., Wernick R. M., Ziff M. Quantitation of rheumatoid factor by laser nephelometry. Rheumatol Int. 1982;2(1):17–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00541265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virella G., Waller M., Fudenberg H. H. Nephelometric method for determination of rheumatoid factor. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(3-4):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller M. Methods of measurement of rheumatoid factor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):5–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Schur P. H. Rheumatoid factor detection by nephelometry. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):777–779. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


