Abstract
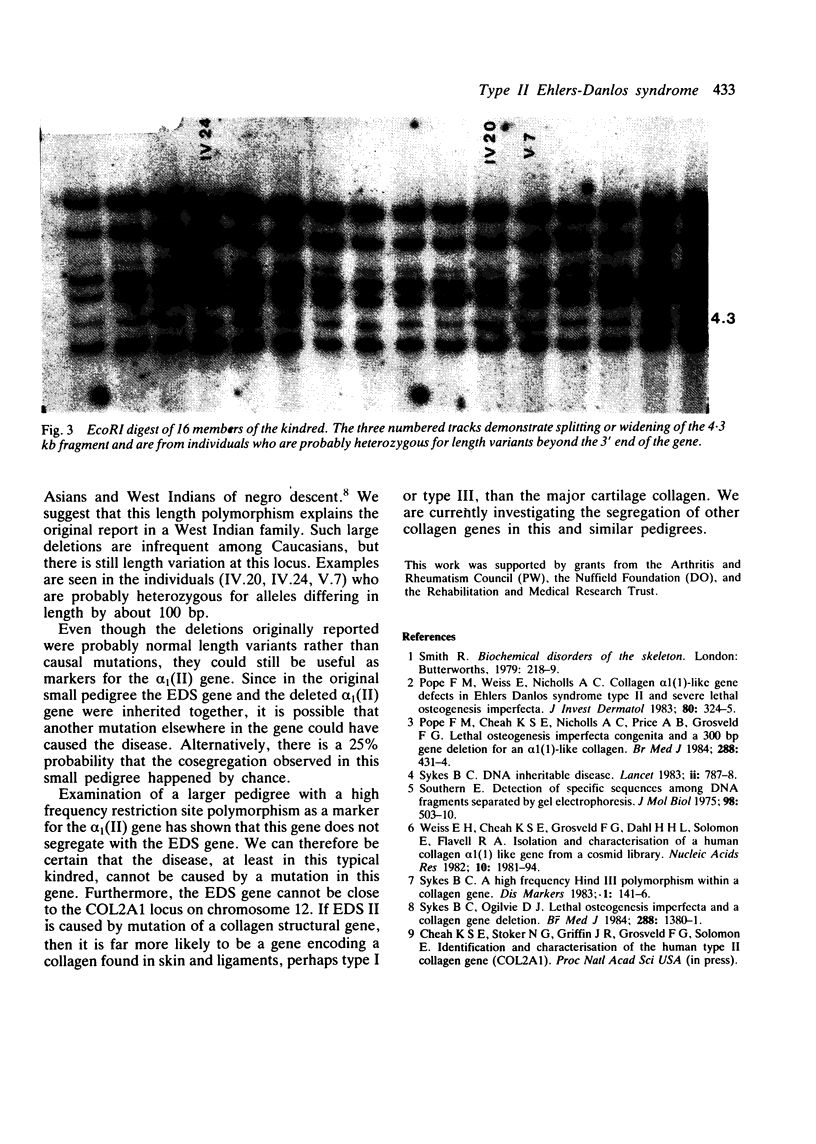
We have used a high frequency site polymorphism within the human pro-alpha 1(II) collagen gene (COL2A1) in order to examine the segregation of this gene within a large pedigree with type II Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). The EDS gene and the collagen gene segregate independently within the pedigree and therefore COL2A1 can be excluded as the mutant locus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pope F. M., Cheah K. S., Nicholls A. C., Price A. B., Grosveld F. G. Lethal osteogenesis imperfecta congenita and a 300 base pair gene deletion for an alpha 1(I)-like collagen. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Feb 11;288(6415):431–434. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6415.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C. DNA in heritable disease. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):787–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Ogilvie D. Lethal osteogenesis imperfecta and a gene deletion. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 5;288(6427):1380–1381. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6427.1380-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Cheah K. S., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Solomon E., Flavell R. A. Isolation and characterization of a human collagen alpha 1(I)-like gene from a cosmid library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1981–1994. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]