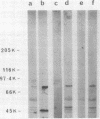
Abstract
The complement activating aggregates in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have been isolated using monoclonal IgM anti-C3d antibodies attached to solid phases, and the content of the material bound has been analysed. High levels of aggregated IgG bearing C3d were found in RA synovial fluids, and IgG was the major immunoglobulin bound from such synovial fluids by anti-C3d Sepharose. A strong correlation was shown between levels of aggregated IgG bearing C3d and complement activation, as judged by C3d levels. Significant (but less strong) relationships were also observed between C3d levels and both complement consuming and C1q binding activity. C3d levels and levels of aggregated IgG bearing C3d were both significantly associated with the numbers of polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNs) found in RA synovial fluids. From these results it is concluded that the aggregated immunoglobulins bearing C3d (particularly IgG) isolated from RA synovial fluids are responsible for activating complement and attracting PMNs into the joint space. Radioimmunoassay showed no correlation, however, between levels of aggregated IgG (or IgM) bearing C3d and rheumatoid factor (RF) activity bound by anti-C3d. In addition, the material bound by anti-C3d Sepharose from most synovial fluid polyethylene glycol precipitates did not contain either IgM or IgG RF. Thus both techniques show that the majority of complexes bearing C3d do not contain RF. As the complement fixing aggregates apparently contain only immunoglobulin and complement components the results raise the problem of how the aggregates are formed. It is suggested that RA IgG may remain aggregated after either antigen or antibody (RF) has dissociated from the complex.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowicz A., Kappelgaard E., Petersen J., Nielsen H., Ingemann-Hansen T., Halkjaer-Kristensen J., Sørensen H. Complement C3c and C3d in plasma and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1983 Dec;91(6):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandslund I., Siersted H. C., Svehag S. E., Teisner B. Double-decker rocket immunoelectrophoresis for direct quantitation of complement C3 split products with C3d specificities in plasma. J Immunol Methods. 1981;44(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. B., Nardella F. A., Mannik M. Human complement activation by self-associated IgG rheumatoid factors. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1101–1107. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Naish P., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolism of radio-labelled C3: effects of in vivo activation in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):445–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., Schouten J., Cats A., Daha M. R. Reduction of the complement activation capacity of soluble IgG aggregates and immune complexes by IgM-rheumatoid factor. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):555–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Carter S. D., Cottrell B. J., Scott D. G., Bacon P. A., Wallington T. B. Complement activating properties of complexes containing rheumatoid factor in synovial fluids and sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):285–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Carter S. D., Scott D. G., Bacon P. A., Lowe J. A new assay for IgG rheumatoid factor activity and its use to analyse rheumatoid factor reactivity with human IgG isotypes. Rheumatol Int. 1985;5(4):175–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00541519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. J., Scott D. G., Blake D. R., Bacon P. A., Holt P. D. Complement-activating rheumatoid-factor-containing complexes in patients with rheumatoid vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Apr;42(2):147–150. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadd K. J., Reid K. B. The binding of complement component C3 to antibody-antigen aggregates after activation of the alternative pathway in human serum. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1950471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace S. A., Elson C. J. Continuous production of anti-host IgG antibodies contained in circulating IgG-anti-IgG complexes. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):289–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Brown D. L. Detection of immune complexes by a new assay, the polyethylene glycol precipitation-complement consumption test (PEG-CC). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):117–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H., Lundh B., Laurell A. B. Studies of the third component of complement in synovial fluid from arthritic patients. II. Conversion and its relation to total complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):707–712. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. D., Donaldson C., Judson P. A., Johnson P., Parsons S. F., Anstee D. J. NBTS/BRIC 8. A monoclonal anti-C3d antibody. Transfusion. 1985 May-Jun;25(3):267–269. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1985.25385219912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C., Mullen B. J. Activation of complement components C3 and factor B in synovial fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Jan;89(1):160–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator-C1s complexes in inflammatory joint disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):521–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. A., Curd J. G., Deheer D. H., Carson D. A., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Vaughan J. H. Metabolism of C4 and factor B in rheumatoid arthritis. Relation to rheumatoid factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):911–920. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Shapleigh C., Goetzl E. J. Lipoxygenation of arachidonic acid as a source of polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotactic factors in synovial fluid and tissue in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1166–1170. doi: 10.1172/JCI109947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Oldroyd R. G., Milstein C., Wright B. W. Three rat monoclonal antibodies to human C3. Immunology. 1980 Nov;41(3):503–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D. K., Roitt I. M. Molecular analysis of complement-fixing rheumatoid synovial fluid immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):521–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Roitt I. M., Hay F. C. Analysis of immune complexes in synovial effusions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Zubler R. H., Gabay R., Joliat G., Karagevrekis C. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating complement breakdown products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation between plasma C3d, circulating immune complexes, and clinical activity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):862–868. doi: 10.1172/JCI108708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEKIN T. J., Jr, ZVAIFLER N. J. HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT IN SYNOVIAL FLUID. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1372–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI105013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh R. B., Dwek R. A., Sutton B. J., Fernandes D. L., Leung A., Stanworth D., Rademacher T. W., Mizuochi T., Taniguchi T., Matsuta K. Association of rheumatoid arthritis and primary osteoarthritis with changes in the glycosylation pattern of total serum IgG. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):452–457. doi: 10.1038/316452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A. B., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Detection and partial characterization of circulating immune complexes with solid-phase anti-C3. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Complement breakdown products in plasma from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and patients with membranoproliferative or other glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):165–176. doi: 10.1172/JCI108065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Nydegger U. E., Zubler R. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Correlation between levels of breakdown products of C3, C4, and properdin factor B in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Mar;20(2):647–652. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes P. A., Maluf J. G., Curd J. G., Vaughan J. H. Association of rheumatoid factor with complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):391–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Medof M. E. Membrane complement receptors specific for bound fragments of C3. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:217–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabharwal U. K., Vaughan J. H., Fong S., Bennett P. H., Carson D. A., Curd J. G. Activation of the classical pathway of complement by rheumatoid factors. Assessment by radioimmunoassay for C4. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Feb;25(2):161–167. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauder D. N., Mounessa N. L., Katz S. I., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Chemotactic cytokines: the role of leukocytic pyrogen and epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor in neutrophil chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Twose T. M., Paterson D. S., Sim E. The covalent-binding reaction of complement component C3. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1930115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Cooper N. R., Johnson J. S., Vaughan J. H. Complement fixation by rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):437–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI107949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Upsahl M. M., Johnson P. M., Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. A study of complement fixation by rheumatoid factor using a haemolytic assay system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):204–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes A. S., Marcus R. L. Complement-fixing activity of rheumatoid synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Sep;31(5):393–401. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.5.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Dinarello C. A., Cohen P. L. Isolation of an interleukin-1-like factor from human joint effusions. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;26(8):975–983. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Breakdown products of C 3 in human synovial fluids. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1532–1542. doi: 10.1172/JCI106119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Breakdown products of C 3 in human synovial fluids. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1532–1542. doi: 10.1172/JCI106119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]