Abstract
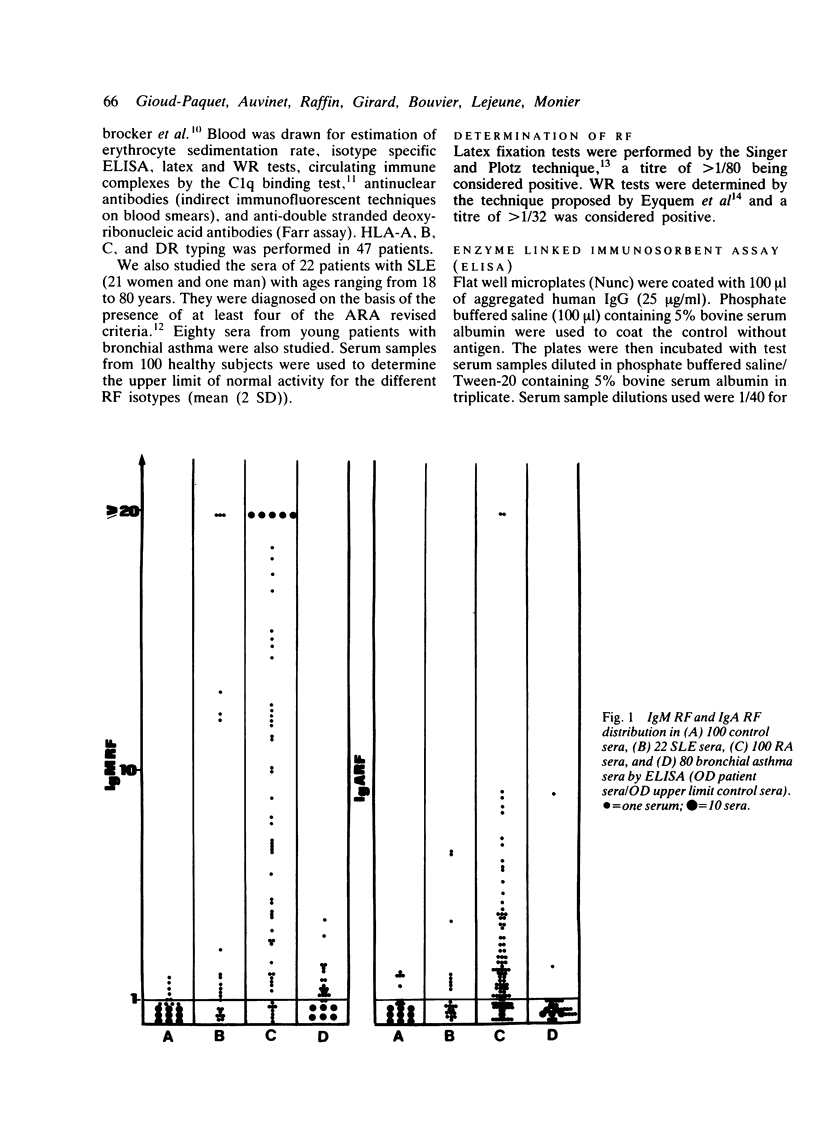
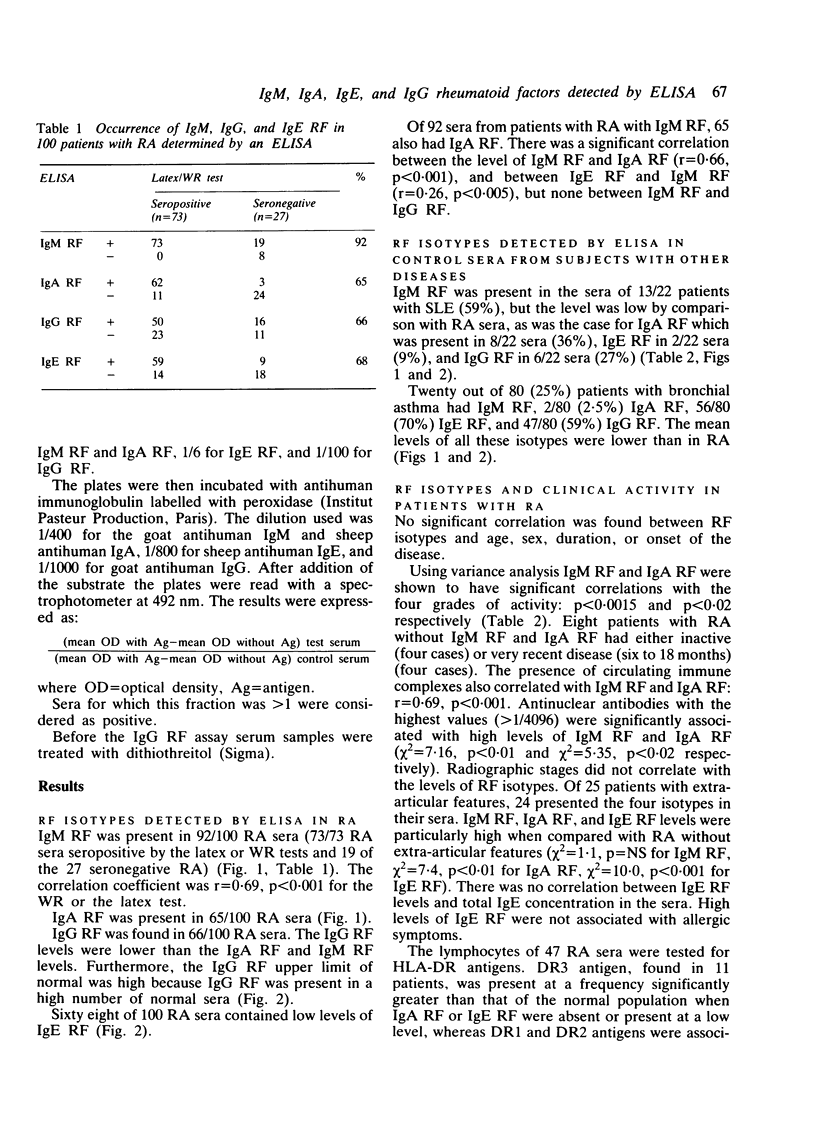
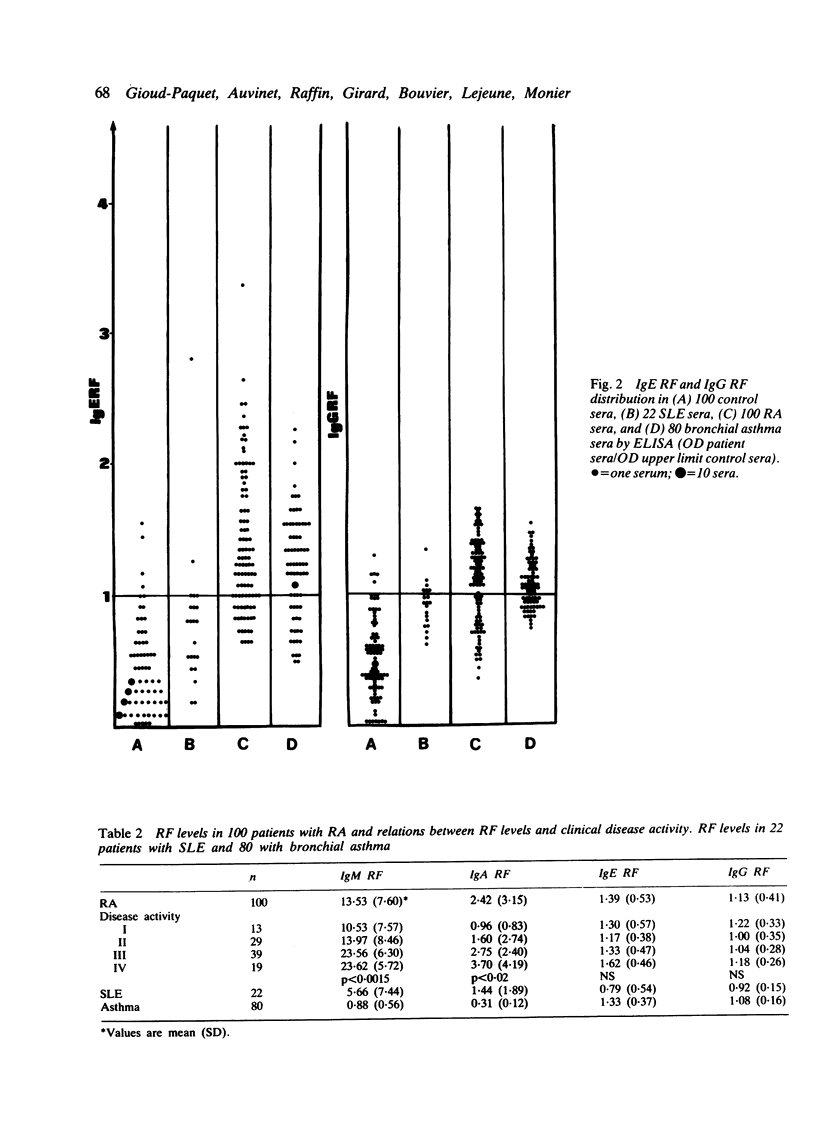
One hundred patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), of whom 73 were seropositive by latex or Waaler-Rose (WR) assays, or both, 100 healthy subjects, and 102 diseased controls (22 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and 80 with bronchial asthma) were evaluated for the presence of IgM rheumatoid factor (RF), IgA RF, IgE RF, and IgG RF by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Ninety two per cent, 65%, 68%, and 66% of the patients with RA were found to be positive for IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgG respectively. A positive correlation existed between the levels of IgM RF and IgA RF on the one hand and disease activity on the other, and the levels of IgM RF and IgA RF correlated with the levels of circulating immune complexes as measured by a C1q binding assay. The presence of extra-articular features also correlated positively with the levels of IgA RF and IgE RF. Five out of six patients with Sjögren's syndrome had very high levels of IgA RF. Of 47 patients typed for HLA-DR, DR1 and DR2 were significantly more frequent in those with the highest levels of IgM RF. Conversely, DR3 was associated with low levels or absence of IgA RF and IgE RF. These results suggest that immune response genes may regulate the level of different RF isotypes. The frequencies of IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgG RF were 59%, 36%, 9%, and 27% respectively in SLE and 25%, 2.5%, 70%, and 59% in bronchial asthma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bampton J. L., Cawston T. E., Kyle M. V., Hazleman B. L. Measurement of rheumatoid factors by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and comparison with other methods. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jan;44(1):13–19. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Gharavi A. E., Patel B. M., Hughes G. R., Frankel A. IgA and IgM rheumatoid factors in serum, saliva and other secretions: relationship to immunoglobulin ratios in systemic sicca syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):75–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faith A., Pontesilli O., Unger A., Panayi G. S., Johns P. ELISA assays for IgM and IgG rheumatoid factors. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg M., Wafin F., Isomäki H., Linder E. A simple enzyme immunoassay for the demonstration of rheumatoid factor. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Karsh J., Anken M. A quantitative enzyme immunoassay for IgM rheumatoid factor using human immunoglobulin G as substrate. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;74(6):776–784. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.6.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallerup H. E., Egeskjold E. M., Graudal H. IgG-, IgM- and IgA-rheumatoid factors in healthy adults and rheumatoid patients determined by an indirect immunofluorescence method. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsh J., Halbert S. P., Klima E., Steinberg A. D. Quantitative determination of rheumatoid factor by an enzyme-labeled immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(2):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Schrohenloher R. E., Solomon A. A quantitative assay for IgA rheumatoid factor. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard J., Nunnery E., Cecere F., McDuffy S., Pope R. M. Relationship between the articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis and circulating immune complexes detected by three methods and specific classes of rheumatoid factors. J Rheumatol. 1983 Jun;10(3):411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiolini R., Ferrua B., Quaranta J. F., Pinoteau A., Euller L., Ziegler G., Massaeyeff R. A sandwich method of enzyme-immunoassay. II. Quantification of rheumatoid factor. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:25–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Hubbard M., McDuffie F. C., Strobel P. L., Smith S. J., Bass N., Goldman J. A., Hartman S., Myerson G., Miller S. Comparison of five assays for immune complexes in the rheumatic diseases. An assessment of their validity for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Oct;25(10):1156–1166. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer O. Les facteurs rhumatoïdes. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1984 Apr;51(4):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima Y., Shoji Y., Hoshi K., Kiyokawa S. Detection and clinical significance of IgE rheumatoid factor. J Rheumatol. 1984 Feb;11(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimaki T., Watanabe S., Yoshida H., Kasukawa R. Immunoglobulin class of rheumatoid factors detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Rheumatol. 1983 Jun;2(2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF02032171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palosuo T., Milgrom F. IgG rheumatoid factor. Detection by enzyme immunoassay in rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Wooley P., Batchelor J. R. Genetic basis of rheumatoid disease: HLA antigens, disease manifestations, and toxic reactions to drugs. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 11;2(6148):1326–1328. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6148.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., McDuffy S. J. IgG rheumatoid factor. Relationship to seropositive rheumatoid arthritis and absence in seronegative disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Sep;22(9):988–998. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Yoshinoya S., McDuffy S. J. Detection of immune complexes and their relationship to rheumatoid factor in a variety of autoimmune disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Nov;46(2):259–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quismorio F. P., Beardmore T., Kaufman R. L., Mongan E. S. IgG rheumatoid factors and anti-nuclear antibodies in rheumatoid vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 May;52(2):333–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherak O., Smolen J. S., Mayr W. R. Rheumatoid arthritis and B lymphocyte alloantigen HLA-DRw4. J Rheumatol. 1980 Jan-Feb;7(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Nilsson L. A. Isotype-specific measurement of rheumatoid factor with reference to clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Nov;12(3):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitsson I., Withrington R. H., Seifert M. H., Valdimarsson H. Prospective study of early rheumatoid arthritis. I. Prognostic value of IgA rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):673–678. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejtorp M., Høier-Madsen M., Halberg P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determination of IgM rheumatoid factor. Scand J Rheumatol. 1979;8(2):65–70. doi: 10.3109/03009747909105338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernick R., Merryman P., Jaffe I., Ziff M. IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors in rheumatoid arthritis. Quantitative response to penicillamine therapy and relationship to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 May;26(5):593–598. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems F. T., Klaasen de Kort C. C. ELISA for rheumatoid factor. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):994–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withrington R. H., Teitsson I., Valdimarsson H., Seifert M. H. Prospective study of early rheumatoid arthritis. II. Association of rheumatoid factor isotypes with fluctuations in disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):679–685. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youinou P., Le Goff P., Miossec P., L'Hostis D. Les polyarthrites rhumatoïdes avec facteurs rhumatoïdes de type IgE. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1982 May;49(6):453–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuraw B. L., O'Hair C. H., Vaughan J. H., Mathison D. A., Curd J. G., Katz D. H. Immunoglobulin E-rheumatoid factor in the serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and other diseases. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1610–1613. doi: 10.1172/JCI110418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


