Abstract
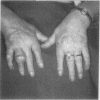
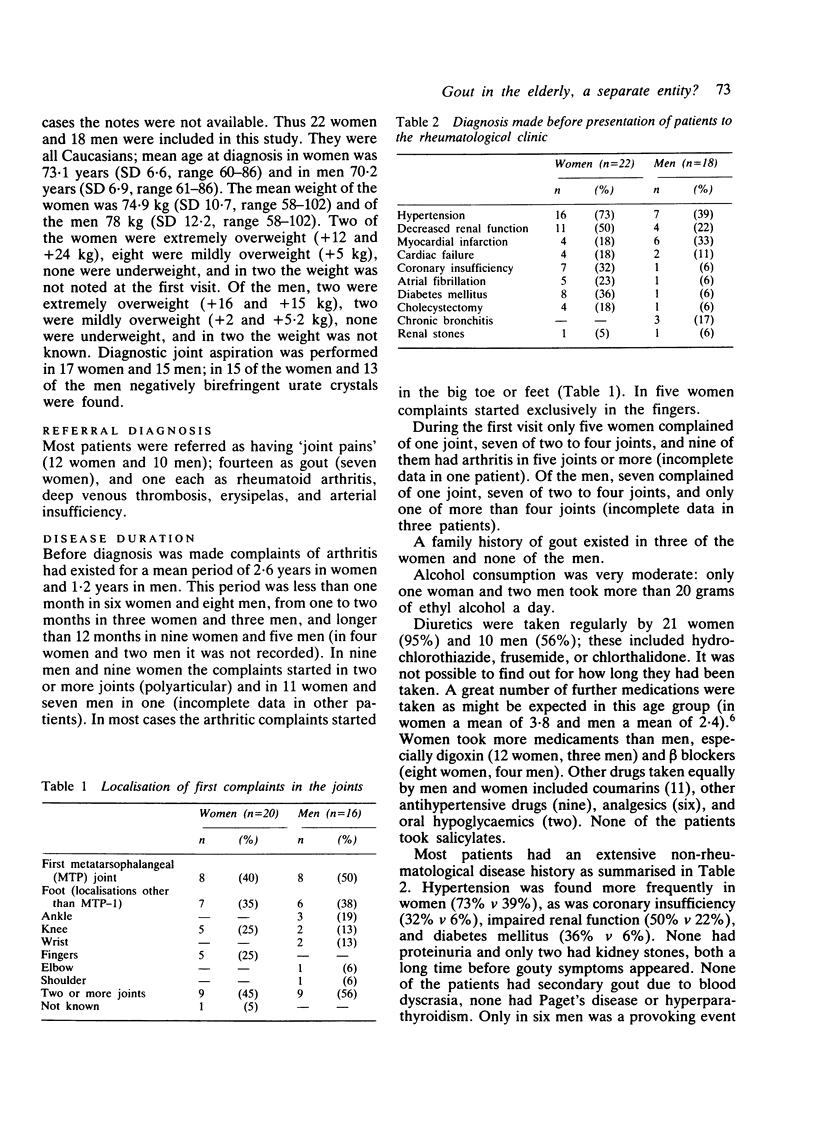
To evaluate whether the clinical pattern of gout differed between elderly women and men a retrospective study was performed in all women (22) and men (18) in our rheumatological clinics who developed gout after the age of 60. The diagnosis was made after a mean of 2.6 years of joint complaints in women and after 1.2 years in men. In about half the patients complaints started in more than one joint, often including the big toe. In five women, but none of the men, complaints started in the fingers. No correlation was found between gout and the presence of tophi or Heberden's nodes in the finger joints. The mean uric acid level was higher in women (0.61 mmol/l) than in men (0.53 mmol/l), and almost all the women (95%) used diuretics and only 56% of the men did so.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dorhout Mees D. J. Urinezuurstofwisseling, in het bijzonder de invloed van diuretica daarop. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1979 Aug 25;123(34):1468–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck W. A., Bress N. M., Singer F. R., Krane S. M. Rheumatic manifestations of Paget's disease of bone. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):592–603. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90629-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn R. J., Campion E. W., Silbert J. E. Trends in serum uric acid levels 1961--1980. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):87–93. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R., Scott J. T. Clinical survey of 354 patients with gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Sep;29(5):461–468. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.5.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler N. M., Franck W. A., Bress N. M., Robinson D. R. Acute polyarticular gout. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):715–719. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90639-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. P., Barry P. E., Dawber T. R., McNamara P. M. Epidemiology of gout and hyperuricemia. A long-term population study. Am J Med. 1967 Jan;42(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama N. A direct colorimetric determination of uric acid in serum and urine with uricase-catalase system. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Feb;31(2):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin R. J. Rapid enzymatic determination of free and esterified cholesterol content of serum and tissues. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Aug 16;71(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieselbach R. E., Steele T. H. Influence of the kidney upon urate homeostasis in health and disease. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):665–675. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90633-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. T. Factors inhibiting the excretion of uric acid. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Apr;59(4):310–313. doi: 10.1177/003591576605900405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkin P. A., Campbell P. M., Larson E. B. Gout in Heberden's nodes. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):94–97. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkin P. A. Management of gout. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):812–816. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. L., Robinson H., Masi A. T., Decker J. L., McCarty D. J., Yü T. F. Selected data on primary gout. Bull Rheum Dis. 1978;29(7):992–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. Prescribing problems in the elderly. Practitioner. 1978 May;220(1319):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]