Abstract
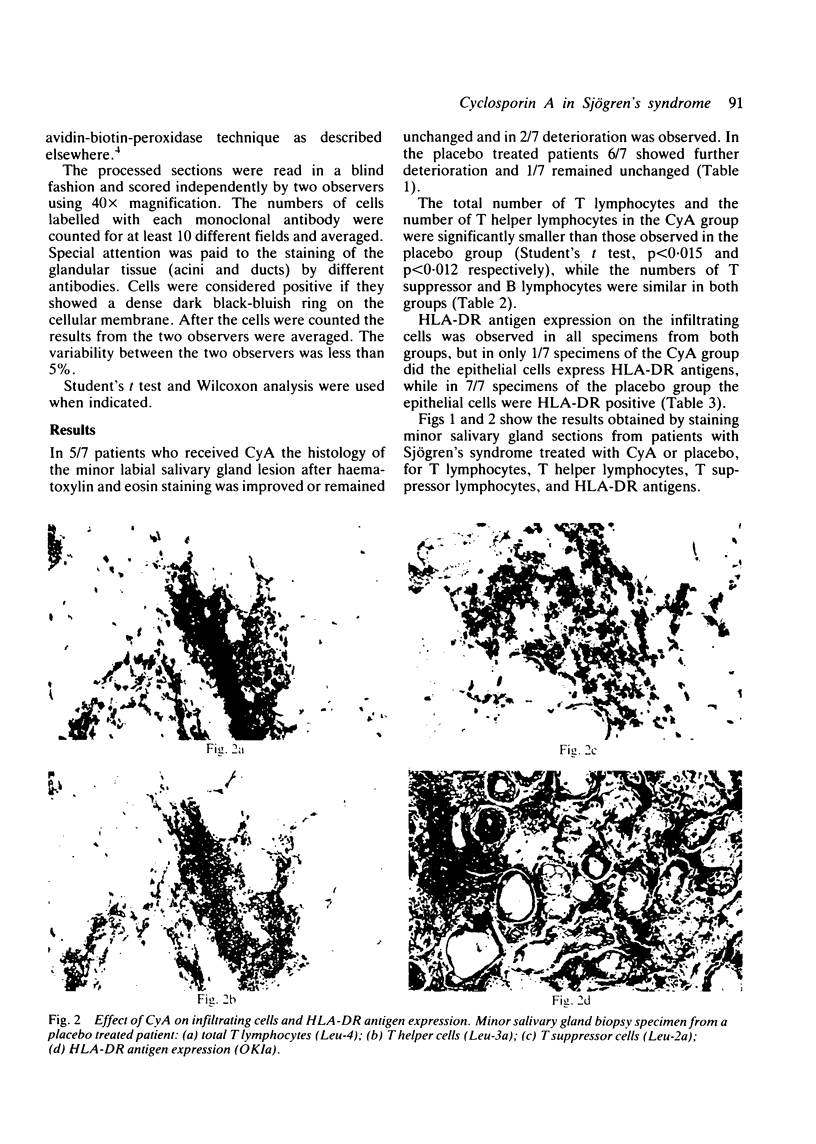
Labial minor salivary gland biopsy specimens from 14 patients with Sjögren's syndrome treated either with cyclosporin A (CyA) or placebo (5 mg/kg body weight day for six months) were studied to determine T lymphocyte subsets and HLA-DR antigen expression using the avidin-biotin-peroxidase technique. In all CyA treated patients we observed a decrease in the number of T lymphocytes and in the number of T helper cells, while the percentage of T suppressor cells and B cells was the same in both treated and untreated groups. It was also shown that the HLA-DR antigen expression on the epithelial cells was eliminated in the CyA treated patients. These findings suggest that the HLA-DR antigen expression on the epithelial cells is the result rather than the triggering factor of this T cell mediated process and is probably related to decreased lymphokine production by activated T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrus L., Lafferty K. J. Inhibition of T-cell activity by cyclosporin A. Scand J Immunol. 1981 May;15(5):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S., Palacios R. Cyclosporin A--usefulness, risks and mechanism of action. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drosos A. A., Skopouli F. N., Costopoulos J. S., Papadimitriou C. S., Moutsopoulos H. M. Cyclosporin A (CyA) in primary Sjögren's syndrome: a double blind study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):732–735. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Carstens S. A., Fong S., Robinson C. A., Howell F., Vaughan J. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies to analyze peripheral blood and salivary gland lymphocyte subsets in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):419–426. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Chang A. E., Robb R. J., Rosenberg S. A. Mechanism of action of Cyclosporin A: inhibition of lymphokine secretion studied with antigen-stimulated T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3107–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutsopoulos H. M., Hooks J. J., Chan C. C., Dalavanga Y. A., Skopouli F. N., Detrick B. HLA-DR expression by labial minor salivary gland tissues in Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Aug;45(8):677–683. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.8.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Palestine A. G., Rook A. H., Scher I., Wacker W. B., Gery I. Treatment of intraocular inflammatory disease with cyclosporin A. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):235–238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Mechanism of T cell activation: role and functional relationship of HLA-DR antigens and interleukins. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:73–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routhier G., Epstein O., Janossy G., Thomas H. C., Sherlock, Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Effects of cyclosporin A on suppressor and inducer T lymphocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1980 Dec 6;2(8206):1223–1226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpley T. M., Jr, Anderson L. G., White C. L. Minor salivary gland involvement in Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974 Jan;37(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(74)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Volkman D. J., Burman K. D., Gerrard T. L., Fauci A. S. The in vitro regulation of human thyrocyte HLA-DR antigen expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Nov;61(5):817–824. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-5-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




