Abstract
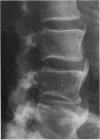
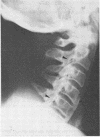
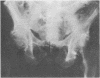
This report describes a patient presenting with a spastic quadriplegia who was found to have both diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) in the cervical spine. There was a dramatic worsening of his symptoms during a myelogram examination of the neck. It is suggested that computed tomographic imaging of the neck is the preferred investigative procedure if OPLL is suspected as a cause of cervical myelopathy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Onji Y., Akiyama H., Shimomura Y., Ono K., Hukuda S., Mizuno S. Posterior paravertebral ossification causing cervical myelopathy. A report of eighteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967 Oct;49(7):1314–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Guerra J., Jr, Robinson C. A., Vint V. C. Association of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and calcification and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978 Dec;131(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.2214/ajr.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]