Abstract
The molecular basis of activation and regulation of the phagocyte respiratory burst is discussed with particular reference to the role of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, guanine nucleotide coupling proteins, and activation of protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF
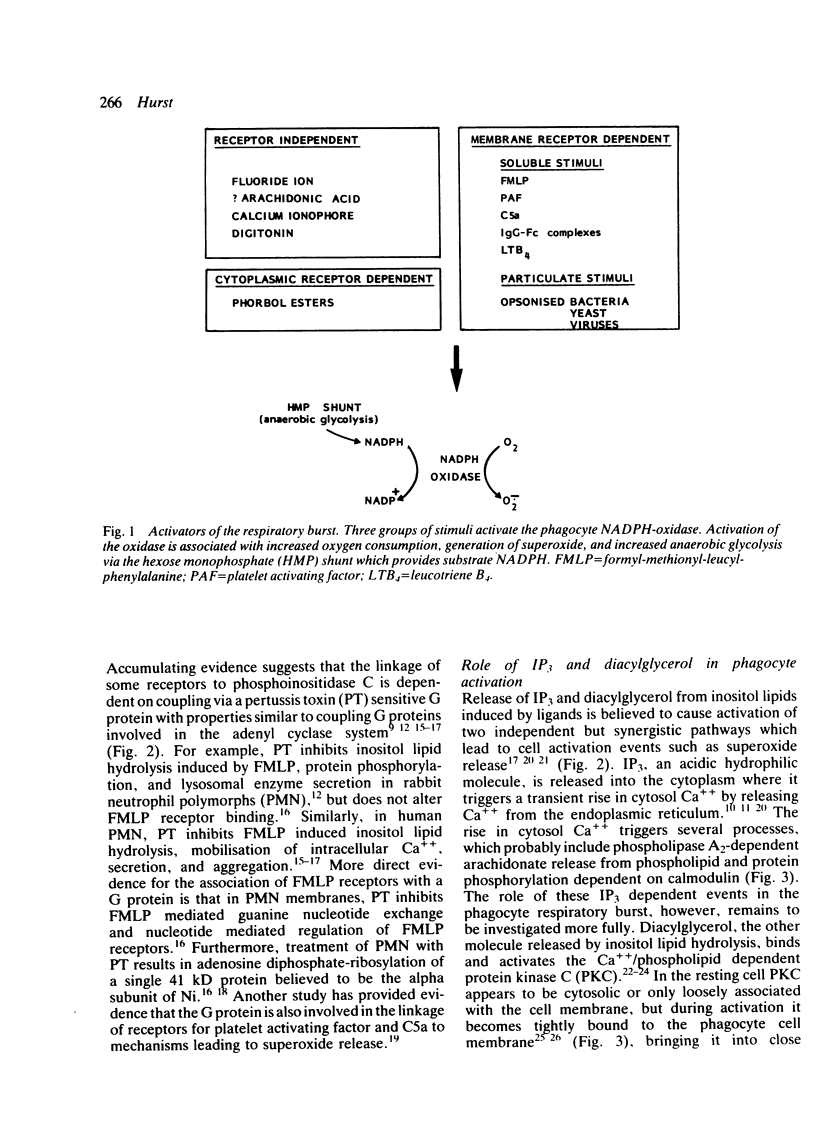
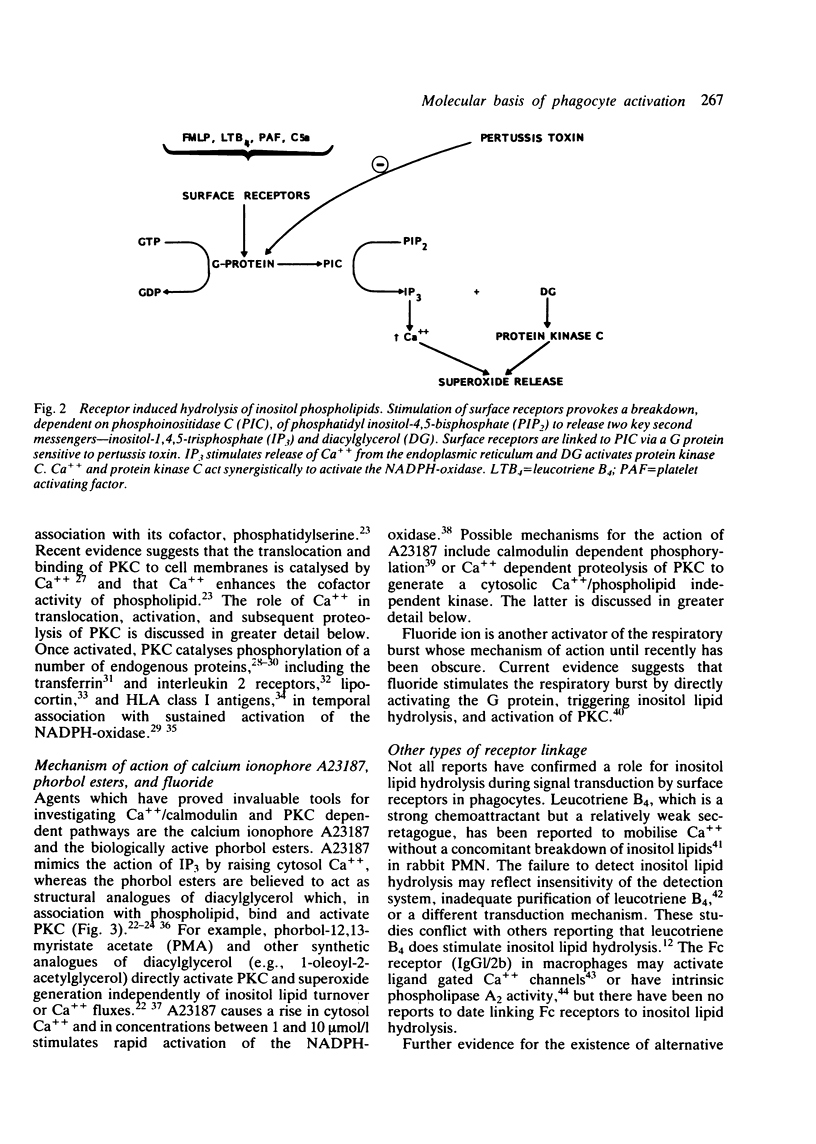
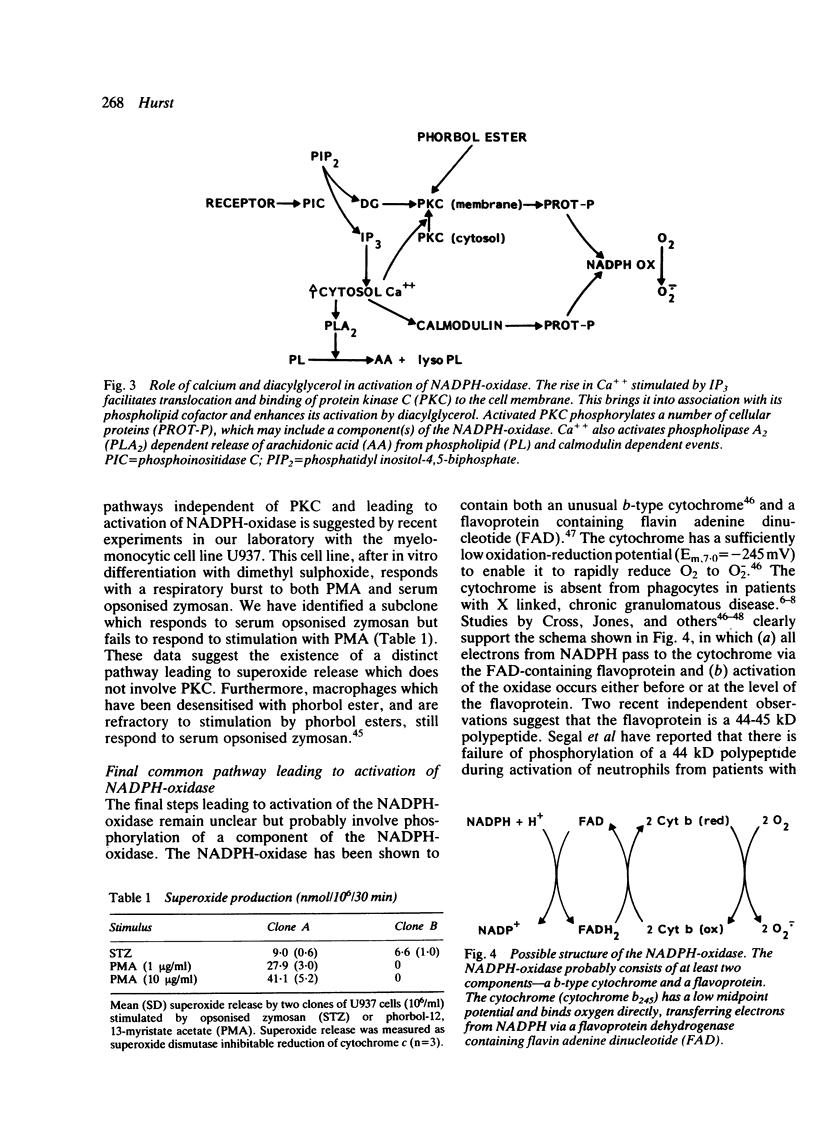




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Birx D. L., Wetzler E. M., O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J., Cross A. S. Calcium requirements for increased complement receptor expression during neutrophil activation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1342–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Gordon S. Desensitization of macrophages to stimuli which induce secretion of superoxide anion. Down-regulation of receptors for phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):620–627. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic factor-induced phospholipase C stimulation and lysosomal enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80801-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate may be a signal for f-Met-Leu-Phe-induced intracellular Ca mobilisation in human leucocytes (HL-60 cells). FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M., Gomperts B. D. Breakdown and synthesis of polyphosphoinositides in fMetLeuPhe-stimulated neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Jeng A. Y., Sharkey N. A., Blumberg P. M., Tauber A. I. Activation of the human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-oxidase by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1932–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI112190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Jones O. T., Harper A. M., Segal A. W. Oxidation-reduction properties of the cytochrome b found in the plasma-membrane fraction of human neutrophils. A possible oxidase in the respiratory burst. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):599–606. doi: 10.1042/bj1940599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Jones O. T. The effect of the inhibitor diphenylene iodonium on the superoxide-generating system of neutrophils. Specific labelling of a component polypeptide of the oxidase. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):111–116. doi: 10.1042/bj2370111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Parkinson J. F., Jones O. T. The superoxide-generating oxidase of leucocytes. NADPH-dependent reduction of flavin and cytochrome b in solubilized preparations. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):337–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2230337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinmark S. J., Lindgren J. A., Claesson H. E., Malmsten C., Samuelsson B. Stimulation of human leukocyte degranulation by leukotriene B4 and its omega-oxidized metabolites. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 21;136(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein N., Monos D. S., Cooper H. L. Phorbol ester effect in platelets, lymphocytes, and leukemic cells (HL-60) is associated with enhanced phosphorylation of class I HLA antigens. Coprecipitation of myosin light chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):206–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro R., Florio C., Romeo D. Activation of protein kinase C in neutrophil cytoplasts. Localization of protein substrates and possible relationship with stimulus-response coupling. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro R., Florio C., Romeo D. Co-activation of protein kinase C and NADPH oxidase in the plasma membrane of neutrophil cytoplasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., McPhail L. C., Marfat A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Bass D. A., McCall C. E. Role of protein kinases in stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte oxidative metabolism by various agonists. Differential effects of a novel protein kinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):61–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI112302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie L. A., McPhail L. C., Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Priming of neutrophils for enhanced release of oxygen metabolites by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Evidence for increased activity of the superoxide-producing enzyme. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1656–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Aksamit R. R. Oxidized N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine: effect on the activation of human monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis and superoxide production. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1471–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Appelbaum B. D., Vogler W. R., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its substrates in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higson F. K., Durbin L., Pavlotsky N., Tauber A. I. Studies of cytochrome b-245 translocation in the PMA stimulation of the human neutrophil NADPH-oxidase. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst N. P., Bell A. L., Nuki G. Studies of the effect of D-penicillamine and sodium aurothiomalate therapy on superoxide anion production by monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for in vivo stimulation of monocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jan;45(1):37–43. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Betts W. H., Cleland L. G. Chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from rheumatoid joints. J Rheumatol. 1983 Apr;10(2):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki C., Bloom B. R. Activation of murine macrophage cell lines. Possible involvement of protein kinases in stimulation of superoxide production. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):923–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B., Andersson T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Chemotactic peptide activation of human neutrophils and HL-60 cells. Pertussis toxin reveals correlation between inositol trisphosphate generation, calcium ion transients, and cellular activation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Di Nitto P. A., Blumberg P. M. Phospholipid and Ca++ dependency of phorbol ester receptors. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(3):255–265. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., DiNitto P. A., Blumberg P. M. Stoichiometric binding of diacylglycerol to the phorbol ester receptor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(1):37–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S. A step sensitive to pertussis toxin and phorbol ester in human neutrophils regulates chemotaxis and capping but not phagocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80517-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S., Scott S. J. A pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the human neutrophil regulates multiple receptors, calcium mobilization, and lectin-induced capping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8643–8647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Smiley P. A. Association of the N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe receptor in human neutrophils with a GTP-binding protein sensitive to pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):869–873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Molski T. F., Volpi M., Pelz C., Kanaho Y., Becker E. L., Feinstein M. B., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Treatment of rabbit neutrophils with phorbol esters results in increased ADP-ribosylation catalyzed by pertussis toxin and inhibition of the GTPase stimulated by fMet-Leu-Phe. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Association of phorbol ester-induced hyperphosphorylation and reversible regulation of transferrin membrane receptors in HL60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jr, Sahyoun N., Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P. Role of intracellular calcium mobilization in the regulation of protein kinase C-mediated membrane processes. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):549–551. doi: 10.1038/317549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Sahyoun N., Jacobs S., Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P. Mechanism of phorbol diester-induced regulation of surface transferrin receptor involves the action of activated protein kinase C and an intact cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9419–9426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by chemoattractants and other soluble stimuli. Evidence that the same oxidase is activated by different transductional mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):192–200. doi: 10.1172/JCI110957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Pontremoli S., Michetti M., Sacco O., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Horecker B. L. Binding of protein kinase C to neutrophil membranes in the presence of Ca2+ and its activation by a Ca2+-requiring proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6435–6439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. A., McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Redistribution of protein kinase C activity in human monocytes: correlation with activation of the respiratory burst. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., White J. R., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol esters inhibit the fMet-Leu-Phe- and leukotriene B4-stimulated calcium mobilization and enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Ravid A., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Hydroxyl radical scavengers inhibit lymphocyte mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1171–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Seligmann B. E., Gallin J. I. Cytochrome b translocation to human neutrophil plasma membranes and superoxide release. Differential effects of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine, phorbol myristate acetate, and A23187. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2409–2414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Sacco O., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Horecker B. L. Biochemical responses in activated human neutrophils mediated by protein kinase C and a Ca2+-requiring proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8309–8313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. Variations on the theme of chronic granulomatous disease. Lancet. 1985 Jun 15;1(8442):1378–1383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91796-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Trowbridge I. S. Induction of expression and phosphorylation of the human interleukin 2 receptor by a phorbol diester. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11706–11712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad C. F., Parente J. E., Wong K. Use of fluoride ion as a probe for the guanine nucleotide-binding protein involved in the phosphoinositide-dependent neutrophil transduction pathway. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Saito-Taki T., Sadasivan R., Nitta T. Biochemical signal transmitted by Fc gamma receptors: phospholipase A2 activity of Fc gamma 2b receptor of murine macrophage cell line P388D1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):591–595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Ishitoya J., Homma Y., Kato M., Nagai Y. Role of enhanced inositol phospholipid metabolism in neutrophil activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 1;34(11):1931–1935. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P. M., Murray A. W. Modulation of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in platelets treated with a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P. M., Murray A. W. Platelet Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase: evidence for proteolytic activation of the enzyme in cells treated with phospholipase C1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touqui L., Rothhut B., Shaw A. M., Fradin A., Vargaftig B. B., Russo-Marie F. Platelet activation--a role for a 40K anti-phospholipase A2 protein indistinguishable from lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):177–180. doi: 10.1038/321177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Yassin R., Tao W., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Leukotriene B4 mobilizes calcium without the breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and the production of phosphatidic acid in rabbit neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5966–5969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Ampel N. M., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) enhances the capacity of murine macrophages to secrete oxygen reduction products. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2052–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson M., McPhail L. C., Nasrallah V. N., Snyderman R. Phorbol myristate acetate mediates redistribution of protein kinase C in human neutrophils: potential role in the activation of the respiratory burst enzyme. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2057–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Hoffman M. D. The protein kinase C inhibitors H-7 and H-9 fail to inhibit human neutrophil activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):749–755. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90992-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Young T. M., Mauro A., Cohn Z. A. Role for mouse macrophage IgG Fc receptor as ligand-dependent ion channel. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):186–189. doi: 10.1038/306186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Halenda S. P., Sha'afi R. I., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits thrombin-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3859–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


