Abstract
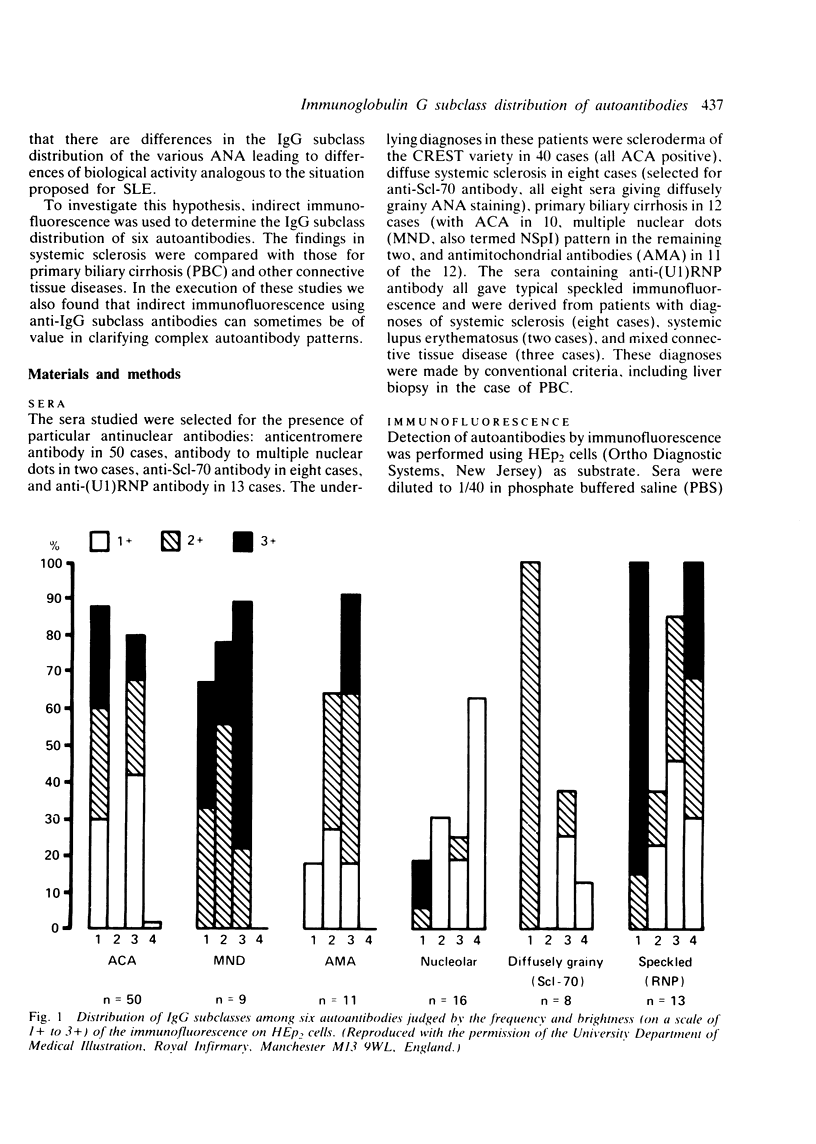
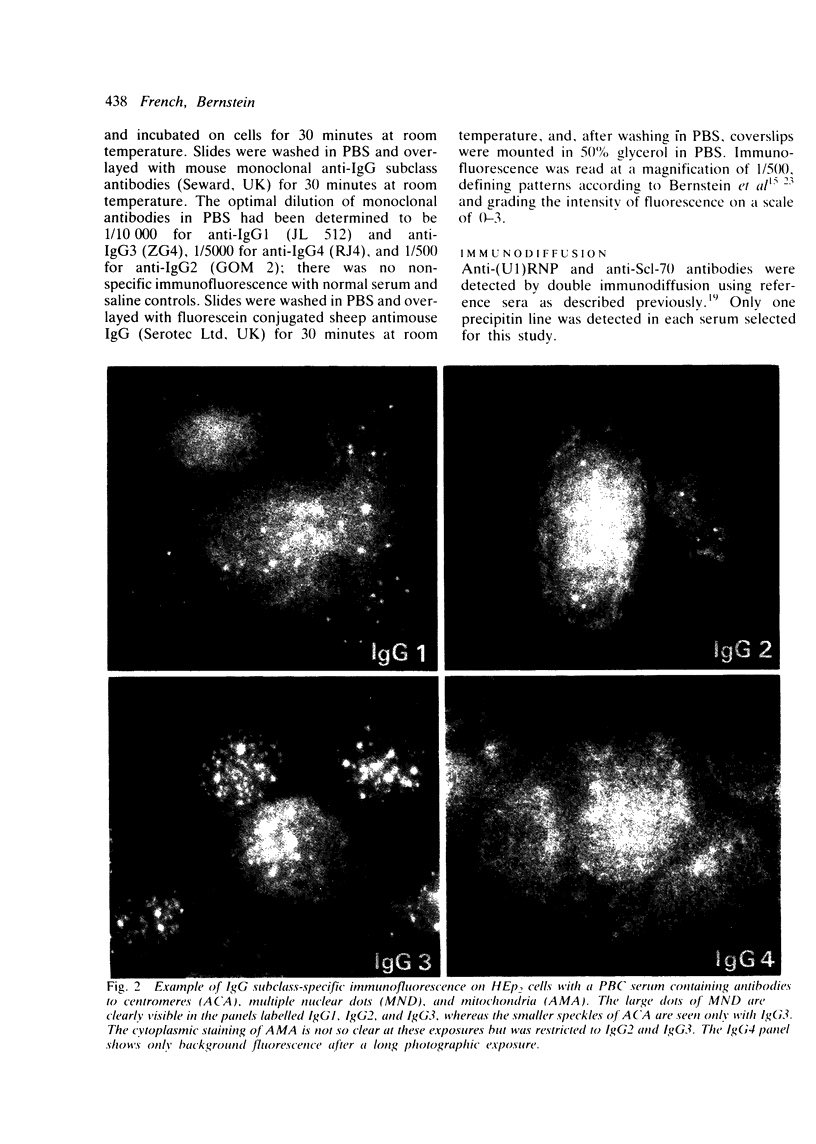
The IgG subclass reactivities of six anticellular antibodies were measured by indirect immunofluorescence on HEp2 cells using murine monoclonal antibodies to the four human IgG subclasses. Patients with scleroderma, primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), systemic lupus erythematosus, and mixed connective tissue disease were studied. Anticentromere antibody (ACA) was virtually all IgG1 and 3; antibody to multiple nuclear dots (NSpI) was IgG1, 2, and 3; antimitochondrial antibody was mainly IgG2 and 3; nucleolar staining was varied in subclass reactivity but most often IgG4; the diffusely grainy staining associated with Scl-70 antibody was chiefly IgG1; and the speckled pattern associated with anti-RNP antibody was always IgG1 and 4, with IgG2 and 3 in some cases. These data fail to support the hypothesis that the various patterns of autoimmune disease reflect differences in the biological properties of the associated antibodies. The prominence of IgG2 in antibodies associated with PBC suggests the possibility of an immune response independent of T cells in that condition. Differential subclass staining showed an unexpectedly high frequency of antibody to multiple nuclear dots in ACA positive sera, and such patients (all with CREST syndrome) could be at increased risk of developing PBC later.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg P. A., Baum H. Serology of primary biliary cirrhosis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 Dec;3(3):355–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02054110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Bunn C. C., Hughes G. R., Francoeur A. M., Mathews M. B. Cellular protein and RNA antigens in autoimmune disease. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Apr;2(2):105–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Callender M. E., Neuberger J. M., Hughes G. R., Williams R. Anticentromere antibody in primary biliary cirrhosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Dec;41(6):612–614. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.6.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Hobbs R. N., Lea D. J., Ward D. J., Hughes G. R. Patterns of antihistone antibody specificity in systemic rheumatic disease. I Systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease, primary sicca syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Mar;28(3):285–293. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Steigerwald J. C., Tan E. M. Association of antinuclear and antinucleolar antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., Virella G., Tung H. E., Ainsworth S. K., Silver R. M., Wang A. C., LaVia M. F., Maricq H. R., Dobson R. L. Immune complexes and antinuclear, antinucleolar, and anticentromere antibodies in scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 Sep;11(3):461–467. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)70191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. A., Harrison G., Penning C. A., Cunningham J., Hughes P., Rowell N. R. Serum immune complexes in systemic sclerosis: relationship with precipitating nuclear antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Feb;44(2):89–92. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacaki J. N., Callerame M. L., Blomgren S. E., Vaughan J. H. Immunoglobulin G subclasses of antinuclear antibodies and renal deposits. Comparison of systemic lupus erythematosus, drug-induced lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):276–282. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M. Myositis autoantibody inhibits histidyl-tRNA synthetase: a model for autoimmunity. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):177–179. doi: 10.1038/304177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puritz E. M., Yount W. J., Newell M., Utsinger P. D. Immunoglobulin classes and IgG subclasses of human antinuclear antibodies. A correlation of complement fixation and the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Nov;2(1):98–113. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggione O., Stokes R. P., Thompson R. A. Predominance of IgG3 subclass in primary cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 26;286(6370):1015–1016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6370.1015-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M., Rothfield N. The gammaG subclass of antinuclear and antinucleic acid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):174–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Bordwell B., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. High titers of autoantibodies to topoisomerase I (Scl-70) in sera from scleroderma patients. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.3003910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. DNA antibody class, subclass, and complement fixation in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Aug;10(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppo A. M., Kurki P., Helve T., Wegelius O. DNA antibodies with and without complement-binding ability. Rheumatol Int. 1984;4(4):173–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00541210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Carter R., Stokes R. P., Geddes A. M., Goodall J. A. Serum immunoglobulins, complement component levels and autoantibodies in liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jul;14(3):335–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Analysis of autoimmunity through experimental models of thyroiditis and allergic encephalomyelitis. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:159–273. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Jefferis R., Eyquem A. IgG subclass distribution of autoantibodies to DNA and to nuclear ribonucleoproteins in autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):595–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]