Abstract
HIV self-testing (HIVST) is an essential tool within the combined HIV prevention package and has been available in Latin America since 2015. However, HIVST use among key populations remains low. This study describes awareness, willingness, and barriers to HIVST among MSM in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru. A cross-sectional web-based survey was advertised in two geosocial networking apps (Grindr and Hornet) and Facebook in 2018. We included cisgender men ≥18 years old who self-reported HIV-negative status. We used multivariable Poisson regression models to calculate adjusted prevalence ratios (aPR) to assess the factors associated with willingness to use HIVST for each country. A total of 18,916 completed the survey, 59% from Brazil, 30% from Mexico, and 11% from Peru. Overall, 20% of MSM had never tested for HIV. Awareness and willingness to use HIVST were higher in Brazil than in Peru and Mexico (p < .001). Across the countries, the patterns of association of willingness with HIVST barriers were similar. Most participants think post-test counseling is essential and that dealing with a positive result would be difficult (aPR 1.13 to 1.37, range of aPRs across the three countries). Having the knowledge to deal with a positive HIVST resulted in increased willingness to use HIVST (aPR range: 1.11 to 1.22), while a lack of trust in HIVST compared to HIV testing in clinics was inversely associated (aPR range: 0.80 to 0.90). In general, willingness to use HIVST was associated with higher income (aPR range: 1.49 to 1.97), higher education (aPR range: 1.13 to 1.42), and willingness to use PrEP (aPR range: 1.19 to 1.72). Efforts to increase HIVST knowledge and resolve perceived barriers are warranted, especially among MSM with lower income and education from Brazil, Mexico, and Peru. Personalized virtual counseling could be crucial among this population. In addition, those willing to use HIVST are also willing to use PrEP. It indicates that HIVST delivery could be incorporated into PrEP programs within the Brazilian Public Health System and eventually in Mexico and Peru.
Introduction
In 2020, around 38 million people were estimated to be living with HIV globally, 16% of whom remain unaware of their HIV-positive status [1]. Since 2010, Latin America has shown an increasing trend in new HIV infections among adults. In 2019, there were an estimated 100,000 (95% CI 66,000–150,000) new HIV infections and 2.1 million (95% CI 1.4–2.8) people living with HIV in Latin America [1]. HIV incidence is very high among men who have sex with men (MSM) in the region, accounting for 46% of the total new HIV infections in 2020 [1–3]. MSM have an HIV prevalence at least 10-fold higher than the general populations in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru [4–6]. Therefore, this group requires specialized and focused policies, especially MSM with social conditions conferring higher vulnerability [7].
There is consensus about the importance of applying new strategies to make HIV testing services more convenient and attractive for those in need. The aim is to reach the United Nations target of 95% of people living with HIV being aware of their HIV status by 2030 (the first of the UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets). However, Latin America is far from reaching this target; wide-ranging estimates show that around 79% of men living with HIV know their status [1]. In this situation, the HIV self-test (HIVST) could increase HIV diagnosis, paving the way to the first 95-95-95 UNAIDS target [8]. A systematic review of seven RCTs involving MSM found that HIVST increased HIV testing uptake by 1.5 times (RR 1.48; 95% CI: 1.21–1.81) [9].
In 2016 the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended that HIVST be offered as an additional approach to traditional HIV testing services, while in 2019, the WHO recommended social network-based HIV testing approach for key populations as part of the services package [8,10]. In Latin-America, the evidence of HIV self-testing across countries is limited; studies in Brazil [11–15], Mexico [16], Argentina [17] and Peru [11,18] have shown that almost all people surveyed in each study reported they would like to use HIVST. Factors associated with decreased willingness to use HIVST include the high cost of the test [18], being in a relationship, and condomless anal sex in the last three months [16], concern about receiving results alone [12], and social stigma [7,11,19]. However, these studies were applied in particular country settings such as urban or rural areas, or as part of a project that included training to use HIVST, and most of them were conducted prior to the WHO recommendation of HIVST in 2016 [8].
As part of the formative research for The ImPrEP Project (www.imprep.org), in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, this study aimed to assess awareness, willingness, and barriers to use HIVST among MSM from these countries using a uniform web-based survey.
Methods
Study design
We conducted a cross-sectional web-based survey targeting MSM living in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru between March-June 2018. Details of the study design are described elsewhere along with the original analysis results on willingness to use PrEP [14]. Eligibility criteria were: consenting, ≥18-year-old, cisgender men, residents of their respective countries, and self-report HIV-negative status. The questionnaire was programmed on Alchemer® (Brazil) and SurveyMonkey® (Mexico and Peru). We advertised the survey on two geosocial networking (GSN) apps (Hornet® and Grindr®) and Facebook®. Hornet users received two inbox messages linked to the survey, and Grindr displayed one pop-up advertisement per week to all users for two months. On Facebook®, advertisements were targeted at gay and bisexual men. To lessen potential discomfort with sensitive questions, e.g., those related to sexual behavior, answers options included "I do not want to answer" or "I do not know". These responses were considered missing for data analysis. Participation was voluntary, and no incentives for participation were provided.
Variables
Outcome
Willingness to use HIVST was defined as the “highest interest” using a five-point Likert scale (strongly disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, and strongly agree) in response to the statement “I would use the HIV self-test even if I had to pay for it”, following prior studies accessing willingness to use HIV prevention technologies in Latin America [13,20–22].
Socio-demographics
We gathered information about age and self-reported race/skin color. For Brazil and Peru, this was classified as white and non-white (Asian, Black, Indigenous, and Mixed-race), while, in Mexico, response options were indigenous and non-indigenous. Socioeconomic data were measured through monthly income and education. We used the minimum wage (MW) for each country as a measurement scale. In Brazil, we inquired about family monthly income (low ≤3 MW; middle 4–10 MW; and high >10 MW; MW in 2018 was 954 BRL = 250 USD). For Peru and Mexico, the question inquired about personal monthly income. In Peru, it was categorized as low (≤3 MW), middle (4–10 MW), and high (≥10 MW); (MW 2018 was 850 PEN = 265 USD). For Mexico, this was classified as low <3; middle 3–4; high ≥5 (MW 2018 was 2686 MXN = 141 USD). Details of income stratification and rationale are described elsewhere [23]. Education level was dichotomized into less than high school versus high school graduate or higher education. Recruitment was dichotomized in GSN apps (Grindr and Hornet) vs. Facebook.
Sexual behavior
Participants were asked about sexual attraction (men only, women only, both men and women) and having a steady partner. In addition, we measured the frequency of using apps for sex and categorized as never, sometimes (once a month, once a week, only on weekends), and daily. HIV perceived risk was measured with the question “In your opinion, what is your risk of getting HIV in the next year?” and dichotomized into “low” and “high” following previous studies [20,24]. The risk of HIV infection was assessed using the HIV Incidence Risk for MSM (HIRI-MSM) scale [25,26], used in previous analyses among MSM in Latin America [13,22,27]. The HIRI-MSM was calculated based on sexual behavior over the last six months (number of partners, condomless receptive anal intercourse, sex with an HIV-positive partner, and use of stimulants). If the participant scored ≥10 points on this scale, they were considered high risk; otherwise, they were deemed low risk. Participants were also asked about sex under the influence of alcohol or drugs (‘Chemsex’) and if they had sex in exchange for money or gifts each during the previous six months.
HIV testing, awareness of biomedical HIV prevention, STI testing
Participants were asked about previously testing for HIV with possible answers: “never,” “last three months,” “last 6 months”, “last 12 months”, “more than 12 months,” and “never.” For those who answered never, we inquired about reasons for not testing, including options such as fear of a positive result, self-perception of not being at risk for HIV infection, shame of doing the test and reasons related to reluctance to go to the clinic.
We measured the use of HIV pre-and post-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP and PEP). First, PrEP awareness was assessed by asking if they previously heard of PrEP. Then, a brief description of PrEP was provided before questions about PrEP willingness, assessed using a five-point Likert scale of willingness to take daily PrEP (1 = highly unlikely to 5 = highly likely). Thus, PrEP willingness was defined as anyone answering “highly likely.” Furthermore, we asked about previous sexually transmitted infections (STI) diagnoses -gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis- in the last six months [13,14].
Awareness of and barriers to HIVST
To assess HIVST awareness, participants were asked if they ever heard about HIVST for HIV diagnosis or not. Independent of their awareness, the questionnaire showed a paragraph explaining HIVST, the need for a confirmatory laboratory test in case of an HIVST positive result, and information about the immunological window period for HIVST. After this explanation, the survey inquired about their willingness to use HIV self-testing.
Barriers to HIVST were assessed with a five-point Likert scale (i.e., strongly disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, and strongly agree). The statements were related to fear (e.g., afraid of doing the self-test alone), shame (e.g., if someone knew that participant uses an HIVST), concerns (about potential HIVST positive result), and trust in using an HIVST (compared to clinic HIV test). The questionnaire also inquired about the best way to provide counseling after testing and personal support to the user who receives an HIVST. The response options were a toll-free telephone call, online chat, mobile app, or clinic visit. We also asked what personal information they would be willing to provide if there was a website where they could register to order an HIVST.
Statistical analysis
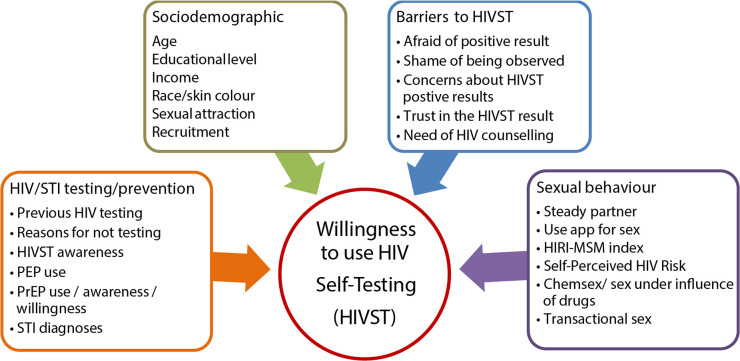
Bivariate and multivariable modeling was performed using generalized linear modeling (GLM) with Poisson regression and robust adjustment. Poisson regression with robust adjustment was used to obtain efficient results closest to the Mantel-Hansel prevalence ratio [28]. Results are presented as prevalence ratios (PR), adjusted prevalence ratios (aPR), and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Bivariate analysis was performed to evaluate the association between willingness to use HIVST and sociodemographic, sexual behavior, HIV/STI testing/prevention, and barriers to HIVST for each country (Fig 1).
Fig 1. Potential factors associated with willingness to use HIVST.
The final multivariable model for each country included variables defined a priori as confounders, irrespective of their statistical significance, such as age, education level, monthly income, and race (only in Brazil). Then, additional variables were assessed for inclusion in models for each country using backward stepwise selection; variables with a bivariate p-value<0.01 were included in the initial model and then eliminated if their multivariate p-value was >0.05. Backward elimination started with the least significant variable and then rerunning the model to repeat the process. The final models only kept variables that remained significant (p<0.05) after the deletion process, but included all a priori defined cofounders. Statistical analysis was performed using R version 4.2.0 (www.r-project.com).
Ethical Issues
The ethics committee approved this study in each country. In Brazil, it was obtained from the IRB of INI Evandro Chagas-FIOCRUZ (#CAAE 82021918.0.0000.5262); in Mexico, the research ethics committee of the National Institute of Psychiatry Ramón de la Fuente Muñiz (#CEI/C/038/2018); in Peru, the Research Ethics Committee of Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia (#101460). All participants provided their online informed consent before answering the survey, which was completed anonymously.
Results
Study population
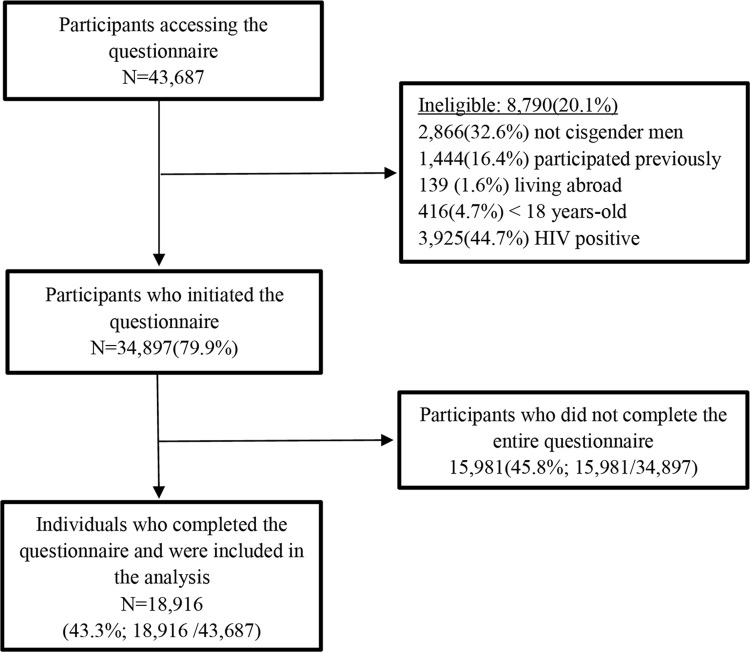
A total of 43,687 respondents provided informed consent, around 80% (n = 34,897) were eligible to participate, and 43.3% (18,916) completed the survey and were included in the study (Fig 2). As shown in Table 1, of the total eligible, 58.8% (11,118) were from Brazil; 30.3% (5,724) from Mexico; and 11.0% (2,074) from Peru. Nearly half of participants (46.2%), were from the principal cities of each country: São Paulo 16.4% (3,198), Mexico City 13.5% (2,618), Rio de Janeiro 8.2% (1,589), and Lima 8.1% (1,576). The median age was 28 years (IQR 24–34). Race/skin color was differently distributed in each country, reflecting its population’s characteristics. In Brazil, 47.2% were non-white, while in Peru 80.5% were non-white. Only 104 (1.8%) of Mexicans self-reported as Indigenous. Of the total participants, 67.9% had a high school or higher education, and nearly half of individuals (43.3%) were classified as middle income. In Mexico and Brazil, the majority were recruited from advertisements in GSN apps, and in Peru from Facebook.
Fig 2. Study flow-chart.
Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, 2018.
Table 1. Sociodemographic and Sexual Behavior of MSM from Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, 2018.
| Total N = 18916 (100%) |
Brazil N = 11118 (58.8%) |
Mexico N = 5724 (30.3%) |
Peru N = 2074 (11.0%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic | ||||
| Age (years) (n = 18915) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 28 (24–34) | 29 (24–35) | 28 (24–34) | 26 (22–31) |
| 18–24 | 5698 (30.1) | 3146 (28.3) | 1702 (29.7) | 850 (41.0) |
| 25–35 | 9085 (48) | 5272 (47.4) | 2880 (50.3) | 933 (45.0) |
| ≥ 25 | 4132 (21.8) | 2699 (24.3) | 1142 (20.0) | 291 (14.0) |
| Race/Skin color (n = 13118) | ||||
| White | 6263 (47.7) | 5873 (52.8) | NA | 390 (19.5) |
| Non-white a | 6855 (52.3) | 5245 (47.2) | NA | 1610 (80.5) |
| Monthly income b (n = 18148) | ||||
| Low | 7155 (39.4) | 4990 (44.9) | 1484 (28.7) | 681 (36.7) |
| Middle | 7855 (43.3) | 4627 (41.6) | 2316 (44.7) | 912 (49.2) |
| High | 3138 (17.3) | 1501 (13.5) | 1376 (26.6) | 261 (14.1) |
| Education level (years) (n = 18788) | ||||
| < High school | 6033 (32.1) | 4259 (38.6) | 1332 (23.3) | 442 (21.6) |
| ≥ High school | 12755 (67.9) | 6761 (61.4) | 4392 (76.7) | 1602 (78.4) |
| Recruitment (n = 18916) | ||||
| Apps | 15,998 (84.6) | 9,895 (89.0) | 5,184 (90.5) | 919 (44.3) |
| 2,918 (15.4) | 1,223(11.0) | 540 (9.5) | 1155 (55.7) | |
| Sexual Behavior | ||||
| Sexual attraction (n = 18862) | ||||
| Only men | 16837 (89.3) | 10163 (91.6) | 5032 (88.2) | 1642 (79.7) |
| Men and women | 2025 (10.7) | 934 (8.4) | 673 (11.8) | 418 (20.3) |
| Steady partner(n = 18759) | ||||
| No | 13804 (73.6) | 8191 (74.2) | 4165 (73.3) | 1448 (71.1) |
| Yes | 4955 (26.4) | 2853 (25.8) | 1514 (26.7) | 588 (28.9) |
| Use of apps to find sexual partners (n = 18913) | ||||
| Never | 1611 (8.5) | 812 (7.3) | 412 (7.2) | 387 (18.7) |
| Sometimes | 8499 (44.9) | 4286 (38.6) | 3214 (56.1) | 999 (48.2) |
| Daily | 8803 (46.5) | 6017 (54.1) | 2098 (36.7) | 688 (33.2) |
| HIV Perceived riskc (n = 18436) | ||||
| Low | 11953 (64.8) | 7,570 (70.1) | 3218 (57.3) | 1165 (57.4) |
| High | 6483 (35.2) | 3223 (29.9) | 2396 (42.7) | 864 (42.6) |
| HIRI-MSM d (n = 18916) | ||||
| <10 points; low risk | 8989 (47.5) | 5269 (47.4) | 2774 (48.5) | 946 (45.6) |
| ≥10 points; high risk | 9927 (52.5) | 5849 (52.6) | 2950 (51.5) | 1128 (54.4) |
| Sex under the influence of alcohol (n = 18875) | ||||
| No | 11994 (63.5) | 6978 (63.0) | 3695 (64.6) | 1321 (63.8) |
| Yes | 6881 (36.5) | 4105 (37.0) | 2027 (35.4) | 749 (36.2) |
| Chemsexe (n = 18861) | ||||
| No | 15748 (83.5) | 9122 (82.4) | 4792 (83.8) | 1834 (88.6) |
| Yes | 3113 (16.5) | 1954 (17.6) | 923 (16.2) | 236 (11.4) |
| Transactional sexe (n = 18915) | ||||
| No | 17901 (94.6) | 10515 (94.6) | 5461 (95.4) | 1925 (92.8) |
| Yes | 1014 (5.4) | 602 (5.4) | 263 (4.6) | 149 (7.2) |
Note:
a Asian, Black, Indigenous, and Mix-race
b For Brazil, we considered the number of minimum wages (MW) in the family monthly income: Low < 3 MW; middle 4–10 MW; high > 10 MW (MW in 2018 was 954 BRL = 250 USD, currency from June 2018). For Peru and Mexico, we considered individual monthly income: Low < 3 MW; middle 4–10 MW; high > 10 MW (MW in June 2018 was 850PEN = 265USD [Peru] and 5302MXL = 261USD [Mexico])
c In the coming year
d The HIV Incidence Risk Index for MSM (HIRI-MSM) scale was calculated based on sexual behavior in the previous six months (number of partners, condomless receptive anal intercourse, sex with HIV+ partner and use of stimulants; if ≥10 points, PrEP is recommended); “Unknown” answers scored 0 points in the HIV Incidence Risk for MSM scale.
e During the previous 6 months.
Most participants, 89.3%, reported sexual attraction for men only and 26.4% had a steady partner. The frequency of daily use of apps for sex was higher in Brazil (54.1%), while in Mexico and Peru lower (36.7% and 33.2%, respectively). Sex under the influence of alcohol was proportionally similar among the three countries (overall, 36.5%), but the chemsex was lower in Peru (11.4%), compared to Brazil (17.6%) and Mexico (16.2%). Transactional sex was somewhat higher in Peru (7.2%) compared to Brazil (5.4%) and Mexico (4.6%). During the previous six months, the self-reported prevalence of STI diagnosis was 13.3% in Brazil, 9.6% in Peru, and 6.6% in Mexico. In Brazil, high HIV risk perception reached 29.9%, whereas in Mexico and Peru was similar (~42.6%). However, according to the HIRI-MSM, all participants had similar scores; overall, 52.5% reached the cut-off score (≥10 points) for high HIV risk (Table 1).
Overall, 19.8% never tested for HIV with the highest proportion in Peru (24.2%), while Brazil had the highest proportion of participants who reported an HIV test within the past three months (31.1%). The main reasons for not getting an HIV test were “I feel afraid of a positive result” (28.4%), “I am not at risk of getting infected” (22.2%), “I feel ashamed to get tested” (21.3%). The proportion of MSM aware of HIVST was 35.0%, and the lowest proportion was in Peru (24.8%), followed by Mexico (27.9%) and Brazil (41.0%). Willingness to use HIVST showed similar proportions and order: Brazil, 43.7%; Mexico, 36.3%; Peru, 32.1% (Table 2).
Table 2. HIV/STI testing and prevention, including HIVST among MSM from Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, 2018.
| Total N = 18916 (100%) |
Brazil N = 11118 (58.8%) |
Mexico N = 5724 (30.2%) |
Peru N = 2074 (11.0%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV/STI testing and prevention | ||||
| HIV testing (n = 18780) | ||||
| Last 3 months | 5333 (28.4) | 3436 (31.1) | 1368 (24.1) | 529 (25.7) |
| Last 6 months | 3248 (17.3) | 1942 (17.6) | 994 (17.6) | 312 (15.2) |
| Last 12 months | 2878 (15.3) | 1790 (16.2) | 818 (14.4) | 270 (13.1) |
| More than 12 months | 3606 (19.2) | 1945 (17.6) | 1211 (21.4) | 450 (21.9) |
| Never | 3715 (19.8) | 1940 (17.6) | 1277 (22.5) | 498 (24.2) |
| Reasons for not testinga (n = 3469) | ||||
| “I feel afraid of a positive result” | 1037 (28.4) | 448 (23.1) | 431 (35.5) | 158 (32.3) |
| “I’m not at risk of getting infected” | 809 (22.2) | 411 (21.2) | 295 (24.3) | 103 (21.1) |
| “I feel ashamed to get tested” | 775 (21.3) | 423 (21.7) | 233 (19.2) | 119 (24.3) |
| “I think it is not practical going to the clinic” or “I feel lazy” | 633 (17.4) | 400 (20.6) | 152 (12.5) | 81 (16.6) |
| “Other” | 393 (10.8) | 261 (13.4) | 104 (8.6) | 28 (5.7) |
| PEP use, last 12 months (yes; n = 18855) | 1605(8.5) | 1266 (11.4) | 267 (4.7) | 72 (3.5) |
| PrEP | ||||
| Awareness (yes; n = 18857) | 12304 (65.2) | 7641 (69.0) | 3688 (64.6) | 975 (47.2) |
| Willingness to use (yes; 18916) | 12187 (64.4) | 6961 (62.6) | 4027 (70.4) | 1199 (57.8) |
| Ever used PrEP (yes; n = 18894) | 383 (2.0) | 258 (2.3) | 84 (1.5) | 41 (2.0) |
| STI diagnosis, last 6 months (yes; n = 18349) | 1996 (10.9) | 1447 (13.3) | 362 (6.6) | 187 (9.6) |
| HIVST | ||||
| Awareness (yes; n = 18678) | 6578 (35.2) | 4488 (41.0) | 1582 (27.9) | 508 (24.8) |
| Willingness to use (yes; n = 18916) | 7609 (40.2) | 4864 (43.7) | 2080 (36.3) | 665 (32.1) |
| Best way to provide counseling/support after HIVST (n = 17891) | ||||
| Toll-free telephone number | 5693 (31.8) | 3417 (32.5) | 1627 (30.3) | 649 (32.7) |
| Online chat | 1492 (8.3) | 769 (7.3) | 521 (9.7) | 202 (10.2) |
| App | 4322 (24.2) | 2479 (23.6) | 1289 (24.0) | 554 (27.9) |
| Clinic visit | 6384 (35.7) | 3863 (36.7) | 1940 (36.1) | 581 (29.3) |
| Which personal data would you provide to order an HIVST? (yes, n = 18573) | ||||
| Name | 12173 (65.5) | 7810 (70.8) | 3414 (61.8) | 949 (47.1) |
| National Identification Number | 7839 (42.2) | 5555 (50.3) | 1518 (27.5) | 766 (38.0) |
| 13492 (72.6) | 8780 (79.6) | 3662 (66.3) | 1050 (52.1) | |
| Mobile number | 13515 (72.8) | 8222 (74.5) | 3891 (70.5) | 1402 (69.5) |
| Facebook profile | 2438 (13.1) | 1443 (13.1) | 721 (13.1) | 274 (13.6) |
| Landline number | 2516 (13.5) | 1758 (15.9) | 645 (11.7) | 113 (5.6) |
| I would provide no data | 1353 (7.3) | 811 (7.4) | 363 (6.6) | 179 (8.9) |
| Other | 342 (1.8) | 257 (2.3) | 56 (1.0) | 29 (1.4) |
aOnly those who reported never tested for HIV.
Participants preferred post-HIVST counseling via toll-free calls by support (31.8%) or by clinic visits (35.7%). The personal data that participants would provide to get an HIVST via website showed different concerns about privacy information. Brazil had the highest percentage of participants willing to give their names (70.8%), while in Mexico was 61.8%, and in Peru 47.1%. Furthermore, Mexico had the lowest proportion of participants who would give their national identification number (27.5%), whereas in Brazil this result reached 50.3%, and Peru 38.0%. On the other hand, similar proportions of participants from the three countries agreed on providing a cell phone number (72.8%). Similarly, a small percentage said that they would not provide any information (7.3%).
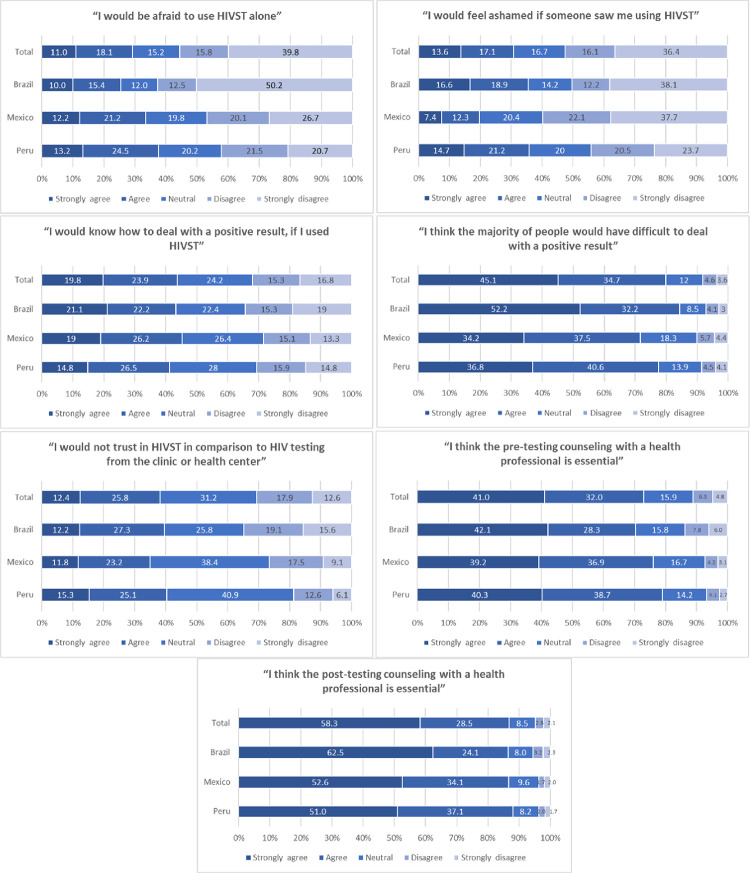
Barriers related to use HIVST according to each country are depicted in Fig 3. The most reported barrier was the post-HIVST counselling from a health professional. Additionally, most of the participants strongly agreed or agreed with the need for pre and post-HIVST counselling (73.0% and 86.8%, respectively). Another critical barrier was the difficulty of dealing with an HIVST positive result according to 80.1% of participants who strongly agreed or agreed. In contrast, less than half (43.8%) strongly agreed or agreed on the statement, “I would know how to deal with a positive result if I used HIVST.” Other reported barriers that participants strongly agreed or agreed were the shame if someone saw they use HIVST (30.6%), and the fear of using HIVST alone (29.0%). Lastly, 38.2% strongly agreed or agree regarding the statement related to trust in HIVST: “I would not trust an HIVST in comparison to HIV testing from the clinic or health center”.
Fig 3. Barriers to use HIVST among MSM in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, 2018.
Factors associated with willingness to use HIVST
In the adjusted multivariate models (Table 3), reporting high monthly income (aPR: 1.49 to 1.97, range of aPRs across the three countries) and high educational level (aPR range: 1.13 to 1.42) were associated with willingness to use HIVST for the three countries, and recruitment through GSN apps only for Brazil (aPR: 1.11, 95%CI 1.00–1.23). Regarding sexual behavior, in Brazil high score in HIRI-MSM scale (aPR: 1.06, 95%CI 1.00–1.14), the use of apps for sex in Peru (aPR 1.43, 95%CI 1.17–1.75), and sex under the influence of alcohol in Mexico (aPR 1.13, 95%CI 1.01–1.27) were associated with willingness to use HIVST. Likewise, willingness to use PrEP showed a positive association with willingness to use HIVST in all three countries (aPR range: 1.19 to 1.72). In contrast, transactional sex in Brazil (aPR 0.85, 95%CI 0.73–0.99) and HIVST awareness in Mexico (aPR 0.80, 95%CI 0.70–0.91) were inversely associated with willingness to use HIVST.
Table 3. Factors associated with willingness to use HIVST among MSM from Brazil, Mexico, and Peru, 2018.
| Brazil | Mexico | Peru | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Crude PR (95% CI) |
Adjusted aPR (95% CI)a |
Crude PR (95% CI) |
Adjusted aPR (95% CI)a |
Crude PR (95% CI) |
Adjusted aPR (95% CI)a |
|
| Sociodemographic | |||||||
| Age (years) | |||||||
| 18–24 | 0.80 | 0.94 (0.86–1.02) | 0.89 | 1.11 (0.97–1.27) | 0.80 | 1.22 (0.97–1.54) | |
| ≥ 25 years | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Race/skin color | |||||||
| White | Ref. | Ref. | NA | NA | Ref. | b | |
| Non-white c | 0.91 | 1.00 (0.93–1.06) | NA | NA | 1.03 | B | |
| Monthly incomed | |||||||
| Low | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Middle | 1.34 | 1.33 (1.23–1.43) | 1.17 | 1.15 (1.00–1.33) | 1.20 | 1.10 (0.86–1.39) | |
| High | 1.66 | 1.79 (1.62–1.99) | 1.41 | 1.49 (1.26–1.76) | 1.72 | 1.97 (1.41–2.75) | |
| Educational level | |||||||
| < High school | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | |
| ≥ High school | 1.34 | 1.24 (1.15–1.33) | 1.19 | 1.13 (1.00–1.31) | 1.43 | 1.42 (1.07–1.88) | |
| Recruitment | |||||||
| GSN App | 1.08 | 1.11 (1.00–1.23) | 0.96 | b | 1.08 | b | |
| Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | ||
| Sexual behavior | |||||||
| Sexual attraction | |||||||
| Men | 1.03 | b | 1.10 | b | 1.07 | b | |
| Men and women | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| Steady partner (yes vs. no) | |||||||
| Yes | 1.06 | b | 1.01 | b | 1.00 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| Use apps for sex | |||||||
| Never/sometimes | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Daily | 1.03 | b | 1.11 | b | 1.29 | 1.43 (1.17–1.75) | |
| HIV Perceived riske | |||||||
| Low | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| High | 1.02 | b | 1.06 | b | 1.06 | b | |
| HIRI-MSM scale f | |||||||
| Low | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| High | 1.05 | 1.06 (1.00–1.14) | 1.07 | b | 1.00 | b | |
| Sex under the influence of alcohol g | |||||||
| Yes | 1.04 | b | 1.12 | 1.13 (1.01–1.27) | 1.10 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | |
| Chemsex g | |||||||
| Yes | 1.00 | b | 1.09 | b | 1.01 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| Transactional sex g | |||||||
| Yes | 0.80 | 0.85 (0.73–0.99) | 1.13 | b | 1.14 | b | |
| No | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| STI diagnoses | |||||||
| Yes | 0.99 | b | 1.06 | b | 1.00 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| HIV/STI testing and prevention | |||||||
| HIV testing | |||||||
| At least once lifetime | 1.11 | b | 0.98 | b | 1.17 | b | |
| Never | Ref. | b | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | |
| HIVST awareness | |||||||
| Yes | 1.05 | b | 0.93 | 0.80 (0.70–0.91) | 0.90 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | |
| PEP use | |||||||
| Yes | 0.99 | b | 1.06 | b | 1.18 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| PrEP awareness | |||||||
| Yes | 1.10 | b | 1.08 | b | 1.27 | b | |
| No | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| Willingness to use PrEP | |||||||
| Yes | 1.21 | 1.19 (1.12–1.28) | 1.45 | 1.44 (1.27–1.63) | 1.68 | 1.72 (1.40–2.11) | |
| No | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Ever used PrEP | |||||||
| Yes | 0.86 | 1.19 | b | 1.15 | b | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | b | Ref. | b | |
| Barriers to HIVST | |||||||
| “I would not trust in HIVST in comparison to HIV testing from the clinic or health center” | 0.91 | 0.90 (0.88–0.93) | 0.87 | 0.80 (0.76–0.84) | 0.87 | 0.82 (0.74–0.90) | |
| “I would be afraid to use HIVST alone” | 0.90 | 0.91 (0.88–0.93) | 0.92 | b | 0.89 | 0.92 (0.85–0.99) | |
| “I would feel ashamed if someone knew I am using an HIVST” | 0.99 | b | 0.90 | 0.96 (0.92–0.99) | 0.93 | b | |
| “I would know how to deal with a positive result, if I used HIVST” | 1.10 | 1.11 (1.08–1.14) | 1.18 | 1.21 (1.15–1.27) | 1.20 | 1.22 (1.12–1.33) | |
| “I think the majority of people would have difficult to deal with a positive result” | 1.03 | 1.09 (1.05–1.14) | 1.06 | 1.08 (1.02–1.14) | 1.07 | 1.14 (1.03–1.27) | |
| “I think the pre-test counseling with a health professional is essential” | 0.94 | 0.95 (0.91–0.98) | 1.06 | b | 1.02 | b | |
| “I think the post-test counseling with a health professional is essential” | 1.02 | 1.13 (1.08–1.18) | 1.29 | 1.37 (1.29–1.48) | 1.18 | 1.33 (1.16–1.52) | |
Barriers to HIVST were also associated with willingness to use HIVST in the final multivariate models. Among the three countries, knowing how to deal with an HIV positive result was associated with willingness to use HIVST (aPR range: 1.11 to 1.20), while not trusting in HIVST in comparison to HIV testing from clinic or health center was associated with lower willingness to use HIVST (aPR range: 0.80 to 0.90). In Brazil and Mexico, being afraid to use HIVST alone was associated with lower willingness to use HIVST (aPR range: 0.89 to 0.91); in Mexico, feeling ashamed if someone knew you were using HIVST showed a similar effect (aPR: 0.96, 95%CI 0.92–099). Lastly, thinking that post-test counseling with a health professional is essential was associated with higher willingness to use HIVST in all countries (aPR range: 1.13 to 1.37). In contrast, indicating an importance of pre-test counseling was associated with lower willingness to use HIVST only in Brazil (aPR 0.95, 95%CI 0.91–0.98).
Discussion
This study provides information on awareness, willingness to use, and barriers related to HIVST among a large sample of MSM from Brazil, Mexico, and Peru. Our results suggest that approximately 35% of participants in Peru and Mexico and 40% in Brazil were aware and willing to use HIVST. Across the countries, willingness to use HIVST was associated with higher income, higher education, and willingness to use PrEP. Existing pre- and pos-test counseling with a health professional and difficulties of dealing with an HIVST positive result were the main endorsed HIVST barriers in the three countries.
Our regression models suggest some factors associated with willingness to use HIVST that are common in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru and other factors that are only significant for one or two countries. Socioeconomic indicators, such as higher income and education level [11,29–32], were directly related to willingness to use HIVST, statistically significant for all three countries. These relationships could reflect that more years of education could lead to a higher knowledge of new self-diagnostic methods [33,34]. Likewise, purchasing power would be a precondition related to willingness to get an HIV self-test kit [35,36] in countries where HIVST is not available free of charge through the Public Health System, as in Brazil. Although we did not evaluate it here, other studies have shown that the HIVST kit’s price plays a critical role in its use [18]. Also, our findings suggest that sexual health education approach including HIVST might be crucial among key populations [37–39], since poverty, lack of schooling along with existing social inequities are barriers to HIV services that could have been increased during and after the COVID-19 pandemic [1].
Willingness to use PrEP was directly associated with willingness to use HIVST, and it was statistically significant in the final model for all three countries. This positive relationship could be explained since PrEP and HIVST have a common target population and interest in both may represent individuals open to innovation in HIV prevention. This finding suggests that HIVST and PrEP could be offered together and delivered through the same platform. Previous studies have made both services available through a mobile app [40,41], while other pilot studies have jointly offered PrEP and HIVST [42,43], with an increasing in testing. Telemedicine procedures and HIVST distribution were implemented in Brazilian PrEP services since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic [44], and the acceptability of both strategies was very high [45]. Future research in Latin America could explore the interaction of PrEP and HIVST to improve PrEP adherence and testing frequency, likewise a better understanding of the demand for these services.
The relationship of sexual behavior characteristics with willingness to use HIVST differed by country. MSM at higher risk for HIV (measured by HIRI-MSM scale) and sex under the influence of alcohol was associated with higher willingness to use HIVST in Mexico and Brazil, respectively. Both results are promising and indicate that MSM with a high vulnerability for HIV may be more interested in HIVST. Conversely, individuals reporting transactional sex, who maybe have higher vulnerability to HIV, had reduced willingness to use HIVST in Brazil. In our study, the proportion of Brazilian MSM who strongly agreed or agreed with the statement “I would be afraid to use HIVST alone” was higher among those reporting transactional sex vs. not reporting (29.4% vs. 25.1%; p = 0.019), which could partially explain our findings. Daily use of apps for sex was only associated with willingness to use HIVST in Peru. Thus, in Peru, these apps could be segmented to a population group more adapted to the use of new technologies such as HIVST. However, the use of apps for sex is lower in Peru than in the remaining countries: 18.7% of Peruvians had never used an app for sex, whereas in Brazil and Mexico, that answer was only 7%. Likewise, in Peru, participants were principally recruited from Facebook 55.7%, while in Brazil and Mexico, almost 90% were reached through GSN apps (Grindr and Hornet). The latter result could make it more difficult to find differences in the adjusted model for willingness to use HIVST among those who use and do not use these apps in Brazil and Mexico.
Surprisingly, HIVST awareness was associated with lower willingness to use HIVST in the adjusted model for Mexico. This could be a sign that a communication campaign to clarify doubts and fears about HIVST would be crucial, especially highlighting the utility of HIVST and its use as a preliminary test that would then require confirmation, but can help identify individuals in need of further testing. The lack of adequate information is a barrier identified and translated into two questions. First, only 27.9% of Mexican MSM from our sample had heard of HIVST before. Second, participants who disagreed with the statement "I would not trust in HIVST compared to HIV testing from the clinic or health center" had significantly higher willingness to use HIVST willingness in all three countries. Both results suggest an excellent opportunity for information campaigns, distribution of HIVST through web channels, pharmacies, and for HIV partner notification services.
Indicating the need for post-test counseling had a positive relationship with willingness to use HIVST in all three countries, but the statement about the need for pre-test counseling had an inverse relationship, only in Brazil. The positive association with post-test counseling reveals that there would be tension between preferences for privacy and support [35]. It would be interesting to know if virtual counseling would be an acceptable replacement [46,47]. A real-time conversation with a professional while knowing that the health professional is not observing the participants could be a relief for some participants. It is a possible mechanism since 72.8% of participants agreed to provide their cell phone number to access an HIVST through a website that requires this type of information. Conversely, pre-test counseling may be perceived by Brazilian MSM as an obstacle to obtaining the HIVST kit, or it may be seen as an intrusion to privacy if pre-counseling implies knowing the identity of the person who will use the test.
Regarding barriers, statements related to knowledge about dealing with an HIVST positive result was associated with higher willingness to use HIVST in all three countries. In contrast, fear of using HIVST alone was associated with lower willingness in Brazil and Peru but not in Mexico. Both results confirm the importance of counseling, usually accompanying home-based testing studies [48]. Different non-personal counseling mechanisms have been piloted in urban and rural settings and high-income and low-income countries [49,50]. Virtual counseling represents an excellent opportunity to become a valuable tool to empower people for self-care, reducing the problems associated with HIV/AIDS-related stigmas [7,11,19]. Approximately 20% had never taken an HIV test in our whole sample, and another 20% had not been tested in the last 12 months, which is worrisome considering UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets to end HIV epidemic [1]. The possibility of implementing virtual or telephone counseling would increase the use of HIVST [10,51] and consequently increase HIV testing and diagnoses. It could be helpful since most previously focused MSM services in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru are centered in urban areas and cannot cover all the territory. However, HIVST could be an approach to expanding health services related to HIV and other STIs, as well as increase HIV testing uptake, frequency, and yield without social harms as previously observed in other settings [9,52]. Previous pilot studies conducted in Brazil [53], China [54], Uganda [55], Nigeria [56] and South Africa [57] have shown that HIVST is highly acceptable and feasible to implement among MSM and other populations.
Among limitations, first, the cross-sectional design did not permit causal inference; we only assessed factors associated with willingness to use HIVST. Second, since it is a web-based survey, the sample was not probabilistic, and it is only representative of an MSM population with access to smartphones or computers. Third, the high attrition (45.8%) may preclude the generalizability of our findings, as the characteristics of MSM who do not complete the survey may differ from those who complete it, as seen in previous studies [13,58]. In this study, the MSM sample who did not complete the survey vs. those who completed was mainly composed by Brazilians (64.9% vs. 58.8%; p < .001), aged 18–24 years (38.1% vs. 30.1%; p < .001), non-white (55.0 vs. 51.6%; p < .001), lower income (50.4% vs. 39.4%; p < .001), and lower education (44.1% vs. 32.1%; p < .001). Forth, self-reporting in a web-based survey could introduce a social desirability bias. Finally, the questionnaire’s length was designed to be answered online, which limited the number of questions.
Conversely, the study’s strength lies in the analysis of three Latin American countries with a questionnaire adapted for each setting. This study would be the first joint research among countries in the region to assess willingness to use HIVST. The MSM population was adequately targeted, via Facebook or apps such as Grindr and Hornet, resulting in a worthwhile sample. Furthermore, the privacy of participants to answer the questionnaire could be an advantage over face-to-face surveys.
Finally, it is essential to mention the promising future of HIVST. As a consequence of COVID-19, especially in low- and middle-income countries, the current crisis of public health services lays bare the need for innovative approaches to continue offering HIV testing services while maintaining a physical distance. HIVST could become a valuable tool to keep HIV testing advances achieved in the last years, focused on the UNAIDS target of 95-95-95 to 2030 [51]. Future research in this area needs to understand what factors and strategies could be crucial to delivering HIV-related health services successfully.
Conclusions
Overall, we identified factors associated with HIVST that were relevant in all three countries. Sociodemographic variables such as income and education level; other prevention variables such as the willingness to use PrEP; and potential barriers that could be a challenge to HIVST expansion, such as the importance of pre- and post-test counseling for HIVST and doubts about how to deal with a positive HIVST result. These findings should promote future research about HIVST, considering the cultural reception, demand characteristics, and other barriers or incentives that could play a crucial role among potential users.
Supporting information
(CSV)
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This project was made possible thanks to funding and support from Unitaid. Unitaid accelerates access to innovative health products and lays the foundations for their scale-up by countries and partners. Unitaid is a hosted partnership of the WHO. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.UNAIDS. 2021 UNAIDS Global AIDS Update—Confronting inequalities—Lessons for pandemic responses from 40 years of AIDS. 2021 [cited 18 Jul 2021]. Available: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2021/2021-global-aids-update.
- 2.Luz PM, Veloso VG, Grinsztejn B. The HIV epidemic in Latin America: accomplishments and challenges on treatment and prevention. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2019;14: 366–373. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Coelho LE, Torres TS, Veloso VG, Grinsztejn B, Jalil EM, Wilson EC, et al. The prevalence of HIV among men who have sex with men (MSM) and young MSM in Latin America and the Caribbean: A systematic review. AIDS Behav. 2021; 1–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.UNAIDS. UNAIDS epidemiological estimates. 2020 [cited 19 Jul 2020]. Available: https://aidsinfo.unaids.org/.
- 5.Baral S, Sifakis F, Cleghorn F, Beyrer C. Elevated risk for HIV infection among men who have sex with men in low-and middle-income countries 2000–2006: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007;4. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.De Boni R, Veloso VG, Grinsztejn B. Epidemiology of HIV in Latin America and the Caribbean. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014;9: 192–8. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cáceres CF, Aggleton P, Galea JT. Sexual diversity, social inclusion and HIV/AIDS. AIDS Lond Engl. 2008;22: S45–S55. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000327436.36161.80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.WHO. WHO recommends HIV self-testing. World Health Organization; 2016. [cited 6 May 2020]. Available: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/vct/who-recommends-hiv-self-testing/en/. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Witzel TC, Eshun-Wilson I, Jamil MS, Tilouche N, Figueroa C, Johnson CC, et al. Comparing the effects of HIV self-testing to standard HIV testing for key populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2020;18: 1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.WHO. WHO recommends HIV self-testing–evidence update and considerations for success. 2019 [cited 6 May 2020]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/who-recommends-hiv-self-testing-evidence-update.
- 11.Volk JE, Lippman SA, Grinsztejn B, Lama JR, Fernandes NM, Gonzales P, et al. Acceptability and feasibility of HIV self-testing among men who have sex with men in Peru and Brazil. Int J STD AIDS. 2016;27: 531–536. doi: 10.1177/0956462415586676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lippman SA, Périssé ARS, Veloso VG, Sullivan PS, Buchbinder S, Sineath RC, et al. Acceptability of self-conducted home-based HIV testing among men who have sex with men in Brazil: data from an on-line survey. Cad Saúde Pública. 2014;30: 724–734. doi: 10.1590/0102-311x00008913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Torres TS, De Boni RB, de Vasconcellos MT, Luz PM, Hoagland B, Moreira RI, et al. Awareness of Prevention Strategies and Willingness to Use Preexposure Prophylaxis in Brazilian Men Who Have Sex With Men Using Apps for Sexual Encounters: Online Cross-Sectional Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2018;4: e11. doi: 10.2196/publichealth.8997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Torres TS, Konda KA, Vega-Ramirez EH, Elorreaga OA, Diaz-Sosa D, Hoagland B, et al. Factors associated with willingness to use pre-exposure prophylaxis in Brazil, Mexico, and Peru: Web-based survey among men who have sex with men. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2019;5: e13771. doi: 10.2196/13771 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Magno L, Leal AF, Knauth D, Dourado I, Guimarães MDC, Santana EP, et al. Acceptability of HIV self-testing is low among men who have sex with men who have not tested for HIV: a study with respondent-driven sampling in Brazil. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20: 865. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05589-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oldenburg CE, Nunn AS, Montgomery M, Almonte A, Mena L, Patel RR, et al. Behavioral Changes Following Uptake of HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Among Men Who Have Sex with Men in a Clinical Setting. AIDS Behav. 2018;22: 1075–1079. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1701-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pando MA, Dolezal C, Marone RO, Barreda V, Carballo-Diéguez A, Avila MM, et al. High acceptability of rapid HIV self-testing among a diverse sample of MSM from Buenos Aires, Argentina. PloS One. 2017;12: e0180361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bustamante MJ, Konda KA, Joseph Davey D, León SR, Calvo GM, Salvatierra J, et al. HIV self-testing in Peru: questionable availability, high acceptability but potential low linkage to care among men who have sex with men and transgender women. Int J STD AIDS. 2017;28: 133–137. doi: 10.1177/0956462416630674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Doherty T, Tabana H, Jackson D, Naik R, Zembe W, Lombard C, et al. Effect of home based HIV counselling and testing intervention in rural South Africa: cluster randomised trial. BMJ. 2013;346. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f3481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hoagland B, De Boni RB, Moreira RI, Madruga JV, Kallas EG, Goulart SP, et al. Awareness and Willingness to Use Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Among Men Who Have Sex with Men and Transgender Women in Brazil. AIDS Behav. 2017;21: 1278–1287. doi: 10.1007/s10461-016-1516-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Torres TS, Hoagland B, Bezerra DR, Garner A, Jalil EM, Coelho LE, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on sexual minority populations in Brazil: an analysis of social/racial disparities in maintaining social distancing and a description of sexual behavior. AIDS Behav. 2021;25: 73–84. doi: 10.1007/s10461-020-02984-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Torres TS, Marins LMS, Veloso VG, Grinsztejn B, Luz PM. How heterogeneous are MSM from Brazilian cities? An analysis of sexual behavior and perceived risk and a description of trends in awareness and willingness to use pre-exposure prophylaxis. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19: 1067. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4704-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Torres Thiago S., Coelho Lara E., Konda Kelika A., Vega-Ramirez E Hamid Elorreaga Oliver A., Diaz-Sosa Dulce, et al. Low Socioeconomic status is associated with self-reported HIV positive status among young MSM in Brazil and Peru. BMC Inf Dis. 2021. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06455-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Luz PM, Torres TS, Almeida-Brasil CC, Marins LMS, Veloso VG, Grinsztejn B, et al. High-Risk Sexual Behavior, Binge Drinking and Use of Stimulants are Key Experiences on the Pathway to High Perceived HIV Risk Among Men Who Have Sex with Men in Brazil. AIDS Behav. 2021;25: 748–757. doi: 10.1007/s10461-020-03035-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.CDC. US Public Health Service preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States–2014 clinical practice guideline. Atlanta GA USA CDC. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Smith DK, Pals SL, Herbst JH, Shinde S, Carey JW. Development of a clinical screening index predictive of incident HIV infection among men who have sex with men in the United States. JAIDS J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;60: 421–427. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318256b2f6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Torres TS, Bastos LS, Kamel L, Bezerra DRB, Fernandes NM, Moreira RI, et al. Do men who have sex with men who report alcohol and illicit drug use before/during sex (chemsex) present moderate/high risk for substance use disorders? Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020;209: 107908. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.107908 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bastos LS, Oliveira R de VC de, Velasque L de S. Obtaining adjusted prevalence ratios from logistic regression models in cross-sectional studies. Cad Saude Publica. 2015;31: 487–495. doi: 10.1590/0102-311x00175413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Flowers P, Riddell J, Park C, Ahmed B, Young I, Frankis J, et al. Preparedness for use of the rapid result HIV self-test by gay men and other men who have sex with men (MSM): a mixed methods exploratory study among MSM and those involved in HIV prevention and care. HIV Med. 2017;18: 245–255. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Oldenburg CE, Biello KB, Perez-Brumer AG, Rosenberger J, Novak DS, Mayer KH, et al. HIV testing practices and the potential role of HIV self-testing among men who have sex with men in Mexico. Int J STD AIDS. 2017;28: 242–249. doi: 10.1177/0956462416641556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ren XL, Wu ZY, Mi GD, Mcgoogan J, Rou KM, Zhao Y. Uptake of HIV Self-testing among Men Who have Sex with Men in Beijing, China: a Cross-sectional Study. Biomed Environ Sci. 2017;30: 407–417. doi: 10.3967/bes2017.054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Devez P-E, Epaulard O. Perceptions of and intentions to use a recently introduced blood-based HIV self-test in France. AIDS Care. 2018;30: 1223–1227. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2018.1485837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee VJ, Tan SC, Earnest A, Seong PS, Tan HH, Leo YS. User Acceptability and Feasibility of Self-Testing With HIV Rapid Tests. JAIDS J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;45: 449–453. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318095a3f3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stevens DR, Vrana CJ, Dlin RE, Korte JE. A Global Review of HIV Self-testing: Themes and Implications. AIDS Behav. 2018;22: 497–512. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1707-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lippman SA, Moran L, Sevelius J, Castillo LS, Ventura A, Treves-Kagan S, et al. Acceptability and Feasibility of HIV Self-Testing Among Transgender Women in San Francisco: A Mixed Methods Pilot Study. AIDS Behav. 2016;20: 928–938. doi: 10.1007/s10461-015-1236-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Estem KS, Catania J, Klausner JD. HIV Self-Testing: a Review of Current Implementation and Fidelity. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016;13: 107–115. doi: 10.1007/s11904-016-0307-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kinney S, Lea CS, Kearney G, Kinsey A, Amaya C. Predictors for Using a HIV Self-Test Among Migrant and Seasonal Farmworkers in North Carolina. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015;12: 8348–8358. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120708348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wei C, Herrick A, Raymond HF, Anglemyer A, Gerbase A, Noar SM. Social marketing interventions to increase HIV/STI testing uptake among men who have sex with men and male-to-female transgender women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; CD009337. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yang X, Fang T, Mobarak SA, Wang J, Wang C, Huang S, et al. Social network strategy as a promising intervention to better reach key populations for promoting HIV prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Infect. 2020;96: 485–491. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2019-054349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Biello KB, Marrow E, Mimiaga MJ, Sullivan P, Hightow-Weidman L, Mayer KH. A Mobile-Based App (MyChoices) to Increase Uptake of HIV Testing and Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis by Young Men Who Have Sex With Men: Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res Protoc. 2019;8: e10694. doi: 10.2196/10694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sullivan PS, Driggers R, Stekler JD, Siegler A, Goldenberg T, McDougal SJ, et al. Usability and Acceptability of a Mobile Comprehensive HIV Prevention App for Men Who Have Sex With Men: A Pilot Study. JMIR MHealth UHealth. 2017;5: e26. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.7199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ngure K, Heffron R, Mugo N, Thomson KA, Irungu E, Njuguna N, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of HIV self-testing among pre-exposure prophylaxis users in Kenya. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017;20: 21234. doi: 10.7448/IAS.20.1.21234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ortblad KF, Chanda MM, Musoke DK, Ngabirano T, Mwale M, Nakitende A, et al. Acceptability of HIV self-testing to support pre-exposure prophylaxis among female sex workers in Uganda and Zambia: results from two randomized controlled trials. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18: 503. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3415-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hoagland B, Torres TS, Bezerra DR, Geraldo K, Pimenta C, Veloso VG, et al. Telemedicine as a tool for PrEP delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic in a large HIV prevention service in Rio de Janeiro-Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2020;24: 360–364. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2020.05.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hoagland B, Torres TS, Bezerra DR, Benedetti M, Pimenta C, Veloso VG, et al. High acceptability of PrEP teleconsultation and HIV self-testing among PrEP users during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2021;25. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2020.11.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang Z, Lau JTF, Ip M, Ho SPY, Mo PKH, Latkin C, et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Efficacy of Promoting a Home-Based HIV Self-Testing with Online Counseling on Increasing HIV Testing Among Men Who Have Sex with Men. AIDS Behav. 2018;22: 190–201. doi: 10.1007/s10461-017-1887-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Horvath KJ, Walker T, Mireles L, Bauermeister JA, Hightow-Weidman L, Stephenson R. A Systematic Review of Technology-Assisted HIV Testing Interventions. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2020; 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sabapathy K, Bergh RV den, Fidler S, Hayes R, Ford N. Uptake of Home-Based Voluntary HIV Testing in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS Med. 2012;9: e1001351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rosengren AL, Huang E, Daniels J, Young SD, Marlin RW, Klausner JD. Feasibility of using GrindrTM to distribute HIV self-test kits to men who have sex with men in Los Angeles, California. Sex Health. 2016;13: 389–392. doi: 10.1071/SH15236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Indravudh PP, Fielding K, Kumwenda MK, Nzawa R, Chilongosi R, Desmond N, et al. Community-led delivery of HIV self-testing to improve HIV testing, ART initiation and broader social outcomes in rural Malawi: study protocol for a cluster-randomised trial. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19: 814. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4430-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.UNAIDS. SEIZING THE MOMENT: Tackling entrenched inequalities to end epidemics. GLOBAL AIDS UPDATE | 2020; 2020. Available: https://aids2020.unaids.org/report/. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang C, Li X, Brecht M-L, Koniak-Griffin D. Can self-testing increase HIV testing among men who have sex with men: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. 2017;12: e0188890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Boni RBD, Veloso VG, Fernandes NM, Lessa F, Corrêa RG, Lima RDS, et al. An Internet-Based HIV Self-Testing Program to Increase HIV Testing Uptake Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in Brazil: Descriptive Cross-Sectional Analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21: e14145. doi: 10.2196/14145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yan H, Yang H, Raymond HF, Li J, Shi L, Huan X, et al. Experiences and correlates of HIV self-testing among men who have sex with men in Jiangsu province, China. AIDS Behav. 2015;19: 485–491. doi: 10.1007/s10461-014-0968-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Choko AT, Nanfuka M, Birungi J, Taasi G, Kisembo P, Helleringer S. A pilot trial of the peer-based distribution of HIV self-test kits among fishermen in Bulisa, Uganda. PLOS ONE. 2018;13: e0208191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tun W, Vu L, Dirisu O, Sekoni A, Shoyemi E, Njab J, et al. Uptake of HIV self-testing and linkage to treatment among men who have sex with men (MSM) in Nigeria: A pilot programme using key opinion leaders to reach MSM. J Int AIDS Soc. 2018;21: e25124. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lippman SA, Lane T, Rabede O, Gilmore H, Chen Y-H, Mlotshwa N, et al. High Acceptability and Increased HIV-Testing Frequency After Introduction of HIV Self-Testing and Network Distribution Among South African MSM. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1999. 2018;77: 279–287. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Torres TS, Luz PM, De Boni RB, de Vasconcellos MTL, Hoagland B, Garner A, et al. Factors associated with PrEP awareness according to age and willingness to use HIV prevention technologies: the 2017 online survey among MSM in Brazil. AIDS Care. 2019;31: 1193–1202. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2019.1619665 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(CSV)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.