FIGURE 1.
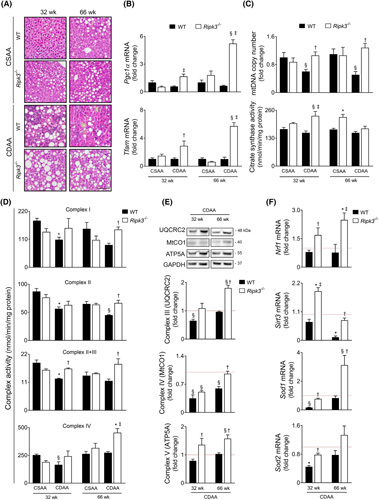
Ripk3 deficiency rescues mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondria respiratory chain (MRC) activity, and reactive oxygen species scavenging systems in choline‐deficient, amino acid‐defined (CDAA) diet–induced experimental NASH. C57BL/6 wild‐type (WT) or Ripk3 −/− mice were fed a CDAA or an isocaloric control choline‐sufficient L‐amino acid‐defined (CSAA) diet for 32 or 66 weeks. (A) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin–stained liver sections. Scale bar = 100 μM. (B) qRT‐PCR analysis of Pgc1α and Tfam in mouse liver. (C) Quantification of relative mitochondrial DNA copy number assessed by qPCR analysis of mitochondria‐encoded gene mt‐Co1. Nuclear Rn18s was used as loading control (top); and citrate synthase activity determined as described in Supplementary Materials and Methods (bottom). (D) MRC activity determined as described in Supplementary Materials and Methods. (E) Immunoblotting and densitometry of oxidative phosphorylation protein complexes in mouse liver, namely UQCRC2 (CIII), mtCO1 (CIV), and ATP5A (CV). Blots were normalized to endogenous GAPDH. F. qRT‐PCR analysis of Nrf1, Sod1, Sod2, and Sirt3 in mouse liver. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM arbitrary units or fold change of 6–7 individual mice. Red dashed line represents the CSAA diet‐fed WT mice levels. § p < 0.05 and *p < 0.01 from CSAA diet‐fed WT mice; † p < 0.05 and ‡ p < 0.01 from CDAA diet‐fed WT mice.
