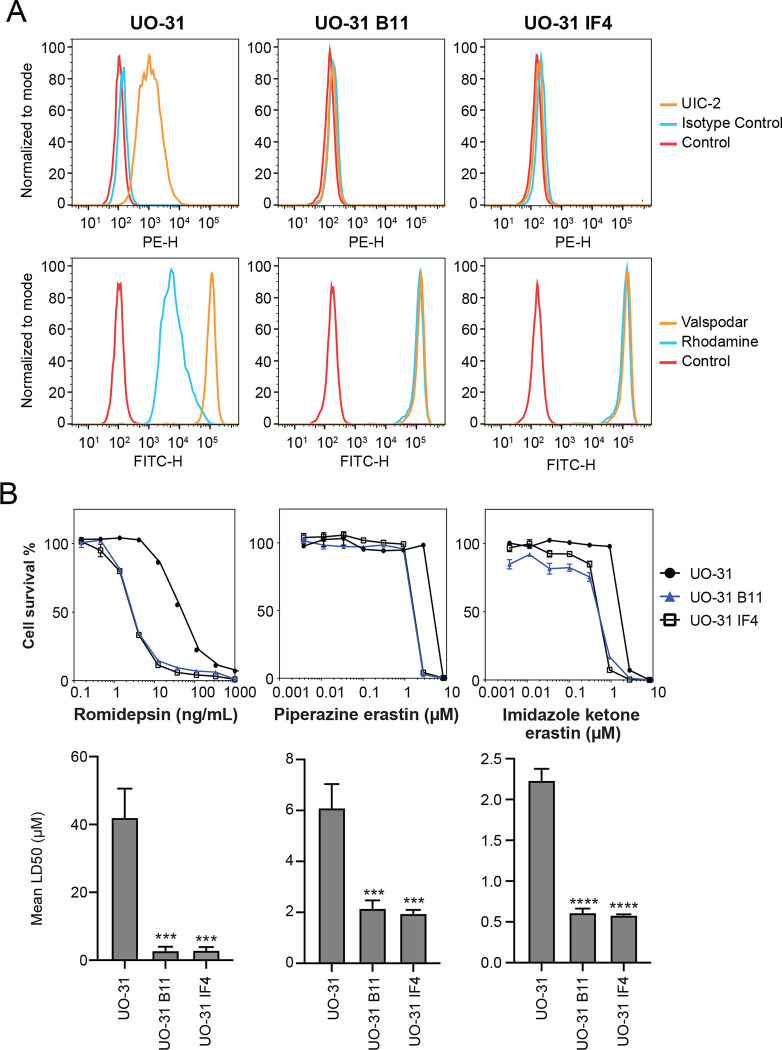
Fig. 3.
CRISPR-mediated deletion of ABCB1 sensitizes UO-31 cells to FINs. (A) Top row: UO-31 cells or the ABCB1 knockout clones (B11, 1F4) were trypsinized and incubated with 2% bovine serum albumin/PBS containing phycoerythrin-labeled UIC-2 antibody or isotype control antibody for 20 min after which cells were washed in PBS and read on a flow cytometer. Control cells (no antibody) are denoted by red curves, isotype control staining is denoted by blue curves and staining with UIC-2 is denoted by orange curves. Bottom row: Cells were incubated with rhodamine 123 (0.5 μg/ml) with or without 10 μM valspodar for 30 min after which media was removed and replaced with substrate-free medium continuing with or without inhibitor for an additional 1 h. Cell autofluorescence (control) is denoted by red histograms, rhodamine efflux by blue histograms and cells with rhodamine and inhibitor are denoted by orange histograms. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (B) Three-day cytotoxicity assays were performed on UO-31 cells or the ABCB1 knockout clones with rhodamine, imidazole ketone erastin or piperazine erastin. Results from one of 3 independent experiments are shown. GI50 values from 3 independent experiments are shown under the representative graphs. Significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA with a test for multiple comparisons. Asterisks denote significant difference from the parental UO-31 cell line, where p<0.001(***), or p<0.0001(****).