Abstract
Critically ill children with acute neurologic dysfunction are at risk for a variety of complications that can be detected by noninvasive bedside neuromonitoring. Continuous electroencephalography (cEEG) is the most widely available and utilized form of neuromonitoring in the pediatric intensive care unit. In this article, we review the role of cEEG and the emerging role of quantitative EEG (qEEG) in this patient population. cEEG has long been established as the gold standard for detecting seizures in critically ill children and assessing treatment response, and its role in background assessment and neuroprognostication after brain injury is also discussed. We explore the emerging utility of both cEEG and qEEG as biomarkers of degree of cerebral dysfunction after specific injuries and their ability to detect both neurologic deterioration and improvement.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12028-023-01686-5.
Keywords: Continuous electroencephalography, Quantitative electroencephalography, Critical care neuromonitoring, Seizure, Status epilepticus, Encephalopathy
Introduction
One in six admissions to pediatric intensive care units (ICUs) is attributable to an acute brain disorder [1]. The nervous system is also susceptible to secondary insult related to a primary systemic illness. Neurological dysfunction during pediatric critical illness manifests in several ways, including seizures and encaphalopathy. Underlying etiologies can include ischemia, hemorrhage, cerebral edema, metabolic injury, and infection. Detection of neurologic dysfunction classically relies on the neurologic examination; however, the ICU environment limits clinical detection of neurological dysfunction because sedation, analgesia, and neuromuscular blockade, which are required to ensure patient comfort and facilitate life-sustaining therapies, interfere with neurologic assessment [2, 3].
Electroencephalography (EEG) serves as a noninvasive bedside neuromonitoring tool that provides high spatial and temporal resolution of brain activity. Continuous EEG (cEEG) yields an uninterrupted stream of brain activity data. Running cEEGs on multiple patients per day for several days in an ICU results in large quantities of data, and not all institutions have around-the-clock support for review and interpretation of the EEGs. Analytical and visualization tools termed quantitative EEG (qEEG) transform the raw digital EEG into its waveform components (e.g., amplitude and frequency), allowing for quantification of EEG features and time-condensed displays. The ability to view large amounts of data at one time allow detection of subtle changes that may occur over hours and are not easily noted on second-by-second review of the raw EEG. This makes qEEG particularly appealing for application in critical care and has the potential to increase efficiency and allow for bedside monitoring and interpretation.
This article provides a broad overview of the technical aspects and clinical applications of cEEG and qEEG in the pediatric ICU.
cEEG Monitoring
Technical Aspects of cEEG Monitoring
The EEG recording is obtained by applying electrodes to the scalp and measuring the electrical activity of the underlying brain. The activity measured represents a summation of excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials of predominantly superficial cortical neurons. A cortical area of at least 6 cm2 of synchronous neuronal activity is required to generate an epileptiform discharge detectable on scalp EEG [4, 5].
Electrode disks or cups are typically made of silver chloride or gold and require removal and reapplication for emergent brain imaging with either computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) because of electrode artifact and risk of thermal burns in the case of MRI. Imaging-compatible electrodes are available [6, 7]. cEEG is typically recorded using the International 10-20 System which includes 21 electrodes [8]. Limited electrode arrays or montages can be used in the ICU. The neonatal “double distance” montage uses fewer electrodes to account for smaller neonatal head size [9]. A limited array may also be used when a patient is anticipated to need cEEG monitoring for several days to reduce the number of sites at risk of skin breakdown. Risk factors for electrode-related skin injury include critical illness, longer duration of monitoring, age less than 1 year, fever, lack of headwrap, and need for vasoactive support [10–12]. The skin should be checked daily, and scalp rest should be provided if breakdown is identified. Some centers perform scheduled scalp rest at protocolized intervals regardless of skin findings. Synchronous video recording is recommended for cEEG [13] to allow for the detection of clinical seizures, artifacts caused by movement or electrical components, and observation of the patient’s clinical state.
The minimum recommended written reporting rate of the ICU EEG is once every 24 h and when there is a significant change. Verbal communication of results to the clinical team should occur at least twice a day [14].
Indications for cEEG Monitoring
Indications for ICU cEEG include seizure monitoring [15–23], background pattern assessment, neuroprognostication, and detection of new brain injury [24–29]. cEEG indications are outlined in critical care policy statements and society guidelines [9, 30–37].
Background Assessment
EEG background activity is used to assess the patient’s baseline level of brain activity. It can be used to confirm alterations in consciousness, determine a patient’s ability to cycle between awake and sleep states, assess for reactivity, grade depth of sedation, and detect focal abnormalities [27, 30, 38, 39]. If diffuse background abnormalities are detected, this is often summarized in EEG reports as a graded severity of cerebral dysfunction or consistent with a degree of encephalopathy.
cEEG assessment of background has been studied and validated for numerous conditions resulting in acute brain injury. For perhaps the most widely described patient population—children who remain comatose after cardiac arrest (CA)—a cEEG background category of normal, slow-disorganized, discontinuous, burst suppression, and attenuated-featureless has strong interrater agreement [40] and a specificity as high as 95% for predicting unfavorable neurologic outcome [27]. cEEG has also been used to grade degree of encephalopathy in conjunction with the neurologic examination to detect clinical worsening. In children with acute liver failure who develop hepatic encephalopathy, an initial EEG on admission was predictive of outcomes such as survival and liver transplantation [29, 41]. A similar assessment, applied in children with altered mental status or concerns for seizures who received chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy, demonstrated that EEG background correlated with the clinical examination measured by the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium [42].
A recent study surveyed members of the Critical Care EEG Monitoring Research Consortium (CCEMRC) to determine the common features used by adult and pediatric EEG readers to grade cerebral dysfunction [43]. Common features (used by > 90% of respondents) included posterior dominant rhythm, predominant awake frequencies, and reactivity. Interrater agreement among the respondents grading the background of 40 EEGs was fair. Thus, although recognition of distinct EEG background patterns has good reliability, translation of these features into a graded level of “cerebral dysfunction” has limitations due to variability in interpretation. Standardization through use of a common schema may reduce variability in reporting. Based on the adult grading system, Table 1 proposes a potential framework for categorizing electrographic cerebral dysfunction in children.
Table 1.
Proposed pediatric cerebral dysfunction grading scale
| EEG features | Severity of cerebral dysfunction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Mild | Mild-moderate | Moderate | Moderate-severe | Severe | Lack of cerebral rhythms | |
| Posterior dominant rhythm (PDR) |
Normal for age 2–4 mo, 3–4 Hz By 6 mo, 4–6 Hz By 12 mo, 5–7 Hz By 3 y, 8 Hz By 10 y, > 8.5 Hz |
Detectable PDR but slower than expected | Features of both mild and moderate dysfunction | Absent | Features of Both Moderate and Severe Dysfunction | Absent | No detectible cerebral activitya |
| Predominant frequencies |
Normal admixture Normal organization |
Diffuse slowing Poor organization |
Diffuse slowing Loss of organization |
Monotonous and limited frequenciesb Attenuated featureless |
|||
| Sleep architecture | Presentc | Presentc | Absent | Absent | |||
| State changes | Presentc | Presentc | Present | Absent or SIRPIDs only | |||
| Reactivity | Presentc | Presentc | Present | Absent | |||
| Continuity | Present | Present | Nearly continuous | Burst suppressedd | |||
This is a proposed grading scale for cerebral dysfunction in children aged 2 months to 18 years that has not been validated in this age group. Adapted from The Yale Adult Background EEG Grading Scale [43]
EEG electroencephalogram, Hz Hertz, mo months, PDR posterior dominant rhythm, SIRPIDs stimulus-induced rhythmic, periodic, or ictal-appearing discharges, y years
aThis categorization does not imply the EEG was performed to meet minimum technical requirements for assessment of electrocerebral inactivity when using EEG as an ancillary study for determination of death by neurologic criteria
bFor EEGs that are not burst suppressed
cEEGs that have limited duration may only demonstrate a single state or may not sufficiently assess reactivity
dFor EEGs that are not attenuated or featureless
Seizure Detection
Detection of seizures is the most frequent indication for pediatric ICU cEEG [44, 45], with seizure incidence in the ICU ranging from 10 to 47% [15, 19, 44, 46–53]. Seizures may be defined as “clinical” if there is an observable change during the seizure or as “nonconvulsive” if there is no observed motor activity. The term “subclinical” is often avoided in ICU EEG terminology because the clinical impact of seizures on awareness is often unknown during critical illness [14]. “Electrographic seizures” refers to seizures observed on EEG, and “electrographic-only” refers to seizures visible on EEG without any clinical change. Because of the impact of sedation and neuromuscular blockade on the observable manifestations of seizures, cEEG is required for accurate detection of seizures in the ICU [30]. In a study of 98 children presenting with convulsive status epilepticus, 33% had electrographic seizures and one third of those were electrographic-only with no observable clinical component [54]. When comparing analogous conditions, such as acute ischemic stroke or central nervous system infection, children have a higher seizure rate than adults [30], with neonates carrying the highest risk [30, 55–58]. Table 2 reviews seizure rates for children versus adults for the same acute neurologic conditions [20, 30, 56, 59–86].
Table 2.
Seizure rates in hospitalized or critically ill children versus adults for analogous conditions
| Neurologic condition | Children (%) | Adults (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CNS infection [25] | 16–100 | 10–33 |
| Moderate to severe TBI [19, 25] | 14–70 | 18–33 |
| Postconvulsive status epilepticus [25] | 26–57 | 48 |
| Acute arterial ischemic stroke [15, 54–63] | 16–59 | 3.3–7 |
| Intraparenchymal hemorrhage [20, 53, 60, 64, 65] | 11–100 | 16–23 |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass [66–69] | 8–12 | 2.4–3 |
| Cardiopulmonary arrest [25] | 16–79 | 10–59 |
| Septic encephalopathy [25] | 58 | 32 |
| Extracorporeal life support [70–75] | 17–40 | 0–6 |
| COVID-19 [76–80] | 8–22 | 0.5–9 |
CNS, central nervous system; COVID-19, coronavirus disease of 2019; TBI, traumatic brain injury
Evidence suggests that seizure burden (percentage of an hour occupied by seizure) is independently associated with neurodevelopmental outcome [15, 18, 50, 87]. In a prospective single-center study of 259 children in the ICU undergoing cEEG monitoring, neurologic outcome was worse when maximal seizure burden exceeded 20% [18]. Based in part on these findings, the 2021 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society (ACNS) updated the definition of electrographic status epilepticus (ESE) from > 50% over 1 hour to the lower threshold of ≥ 20% [14]. This change prompted further consideration of the risk versus benefit calculation for the treatment of ESE. The short-term and long-term impact of antiseizure medications used to treat this lower ESE threshold must be considered as they may add additional risk to outcome by impacting likelihood of hypotension, hypoxia, sedation, and need for mechanical ventilation [88–92]. Further prospective studies are needed to better understand the impact of treatment strategies on outcomes for seizures, ranging from short, infrequent seizures to status epilepticus, in critically ill children.
Epileptiform Patterns and the Ictal–Interictal Continuum
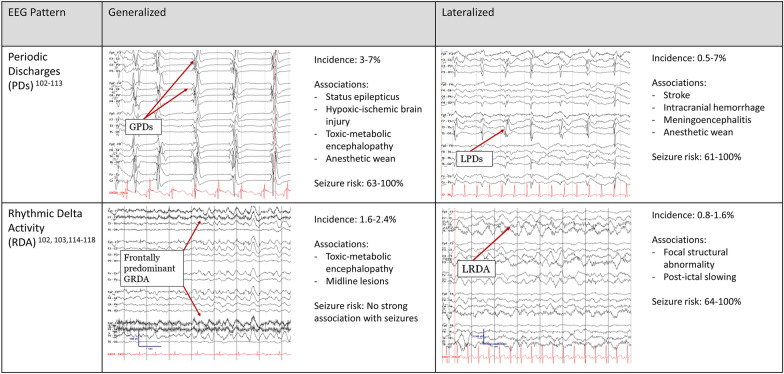
A common challenge of interpreting ICU cEEG is distinguishing which patterns of electrographic discharges and rhythmic activity are “ictal” (seizures) or “interictal” (in between seizures) [93]. It must be recognized that although there are criteria, a spectrum exists. Electrographic patterns with epileptiform features that stand out from the background but lack adequate evolution or clinical correlation consistent with definite seizures represent the ictal–interictal continuum (IIC) [14]. Discharges are considered on the IIC when they last more than 10 seconds and include one of the following: (1) periodic or spike wave discharges occurring at 1–2.5 Hz, (2) periodic or spike wave discharges with additional epileptiform features (e.g., superimposed fast activity) averaging 0.5–1 Hz, or (3) lateralized rhythmic delta activity ≥ 1 Hz with features associated with increased risk of seizures [14]. Periodic discharges (PDs) are repetitive waveforms with no more than 3 phases and interdischarge intervals of regular duration. Rhythmic delta activity (RDA) is defined as consecutive, uniform 0.5- to ≤ 4-Hz activity without an interval in between (Fig. 1) [14]. The ACNS definition of electrographic seizures and ESE is largely based on the Salzburg consensus criteria [94–96]. A seizure is defined as epileptiform discharges > 2.5 Hz for ≥ 10 seconds or any pattern ≤ 2.5 Hz with clear evolution lasting ≥ 10 seconds [14]. If the IIC pattern and there is a clinical improvement in the patient after parenteral antiseizure medication administration, then the pattern is favored to be ictal. ESE occurs when a seizure lasts 10 consecutive minutes or cumulatively ≥ 12 min (20%) of a 60-min epoch [14].
Fig. 1.
Periodic and rhythmic patterns in pediatric critical care EEG. EEG electroencephalography, GPD generalized periodic discharges, GRDA generalized rhythmic delta activity, LPD lateralized periodic discharges, LRDA lateralized rhythmic delta activity
Understanding PDs and RDAs as they relate to the IIC, their potential contribution to ongoing brain injury, and the complex underlying physiology that results in these rhythms is crucial to clinical interpretation of ICU EEG. Reported incidence of rhythms on the IIC (PDs and RDA) ranges from 1.2 to 12% in critically ill children [19, 27, 46, 97]. A study of 1399 critically ill children described periodic and rhythmic patterns and IIC patterns and found that 142 (10%) had periodic and rhythmic patterns, and 93 of those 142 (65%) also met criteria for an IIC patterns [98]. Another study of 719 consecutive children demonstrated that electrographic patterns on the IIC were independently associated with worse outcomes as measured by the Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended Pediatric Version, the Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category score, and mortality [46].
Generalized periodic discharges (GPDs) were present in 21 of 296 (7%) critically ill children in a two-center study [99] and in 43 of 1399 (3%) critically ill children in a single-center study [98]. Common etiologies include encephalitis and hypoxic-ischemic injury. Seizures occurred in 63–100% of children with GPDs [97–99]. GPDs also occur in the setting of anesthetic weans (particularly barbiturates), often resolve with time, and can be stimulus induced [100]. Lateralized periodic discharges (LPDs) are associated with acute structural etiologies, including stroke or encephalitis [101–103], with incidence ranging from 0.5 to 7% [97, 98, 103, 104]. LPDs have a strong association with seizures, which occur in 61–100% of pediatric patients with LPDs [97, 101, 105].
The other pattern associated with the IIC is RDA, further categorized as generalized RDA (GRDA), lateralized RDA (LRDA), continuous or intermittent RDA, and RDA with “plus modifiers,” including fast activity or superimposed sharps or spikes. Incidence of GRDA is 1.6–2.4%, and GRDA is not associated with seizures [97, 98]. A common ICU pattern is bifrontally predominant intermittent GRDA, associated with nonspecific encephalopathies and midline lesions [106–108], although the latter correlation may be more true in adults than in children [109]. LRDA incidence in critically ill children ranges from 0. to 1.6% but may be underreported [97, 98]. It is often associated with a focal cortical lesion [110, 111]. Association of LRDA with seizure is high. A study of 1399 ICU EEGs detected LRDA in 11 patients, and seven (64%) had seizures [98]. Another study noted that 100% of patients with LRDA developed seizures [97]. The association was highest when rhythm frequency was > 1.5 Hz. While numbers are small, these findings suggest the risk of seizures when LRDA is present may be similar to that of LPDs in children.
These patterns have been studied in greater detail in critically ill adults in far greater numbers, including in an investigation into the clinical significance of each type of rhythm, frequency, plus modifiers, and stimulus-induced patterns [112]. Plus modifiers include superimposed fast activity (+ F), which can occur with PDs or RDA; rhythmic activity (+ R), which only applies to PDs; and superimposed sharps and spikes (+ S), which only applies to RDA [14]. A three-center retrospective study from the CCEMRC studied more than 4,500 critically ill patients monitored on EEG and found that LPDs, LRDA, bilateral independent PDs with and without plus features, and GPDs with plus features conferred an increased risk of seizures, whereas GRDA did not [112].
Brief potentially ictal rhythmic discharges are focal or generalized > 4-Hz rhythmic activity lasting 0.5 to < 10 seconds, which may evolve or demonstrate similar morphology and location as interictal epileptiform discharges or seizures already observed in a particular patient [14, 113]. Critically ill children may also exhibit stimulus-induced rhythmic, periodic, or ictal-appearing discharges (SIRPIDs) [114] (Supplemental Fig. 1). The stimulus can be any alerting stimulus, ranging from auditory to tactile to noxious, and the type of stimulus should be documented when reporting this phenomenon [14, 114]. An early descriptive study of SIRPIDS in children found a high association with seizures and status epilepticus.
Key to the discussion of the clinical implications and treatment strategies of the IIC is the degree to which it may contribute to brain injury. Are these patterns a biomarker of acute injury or do they pose an independent risk of causing new brain injury? When the pattern meets the Salzburg and ACNS criteria for nonconvulsive status epilepticus, it is common practice to treat and evaluate the response to treatment to prevent further neurologic injury. But these criteria rely on a frequency cutoff of > 2.5 Hz to define seizure when there is inadequate evolution to otherwise qualify it as ictal. Studies of cerebral metabolic demand during IIC patterns indicate that the threshold for impending new metabolic injury may occur at lower frequencies. In a study of nine patients with concurrent LPDs and positron emission tomography scans, 1-Hz LPDs increased F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake by 100% compared with LPDs occurring at < 1-Hz frequency, and FDG uptake was further increased by > 300% for frequencies > 1 Hz [115]. A study using invasive measures of cerebral blood flow and brain tissue oxygenation demonstrated increasing cerebral blood flow with every 0.5-Hz increase in LPD frequency, and when discharges surpassed 2-Hz frequency, regional hypoxia was detected [116]. Similarly, periodic discharges after traumatic brain injury are associated with a higher lactate/pyruvate ratio and lower glucose levels [59], supporting the potential for LPDs to contribute to regional metabolic demand in brain injury.
Prognostication After Brain Injury
cEEG is used to assist in the prognostication process and in risk stratification when patients present with acute brain injury or when an underlying illness puts them at risk for neurological complications. Post-CA prognosis is one of the areas with the most active research and best evidence base for both children and adults. For children post CA, the background category (normal, slow-disorganized, discontinuous, burst suppression, and attenuated-featureless) was highly predictive of outcomes [25, 27, 117]. Severely abnormal EEG backgrounds were highly specific for poor neurodevelopmental outcomes, and more benign EEG backgrounds had less specificity but were associated with higher proportions of favorable outcomes. Sleep features on 24-h post-CA EEG (sleep spindles) were associated with favorable outcomes, and conversely, the absence of sleep architecture was associated with unfavorable outcomes [118] and was additive to the prognostic ability compared to background EEG features alone [27]. In pediatric extracorporeal life support, the EEG background category within the first 24 h was highly correlated with survival [24]. Future studies to determine optimal and modifiable predictors of outcomes will likely help improve treatment and prognostication in children.
Duration of cEEG Monitoring
cEEG is a resource-intensive and time-intensive form of neuromonitoring [119–121]. Studies have explored parameters and predictors that can determine the optimal length of monitoring required to identify seizures or clinical deterioration [19, 122–127]. When children have seizures on EEG monitoring in the ICU, about 50% occur in the first hour of recording and 90% occur within the first 24 hour [19, 128]. A study of 719 critically ill children, 184 of whom had electrographic seizures (26%), used clinical and electrographic features to identify the minimum duration of monitoring to achieve a < 5% risk of seizure [129]. Features used in this model included age < 1 year, clinical seizure prior to EEG, and interictal or IIC abnormalities. If a child was > 1 year of age and had no prior seizures or epileptiform EEG activity, an EEG duration of 6 hours was sufficient to reach a risk of < 5% for developing seizures, whereas an infant < 1 year with prior clinical seizure required 2.5 days of monitoring based on their model to reach a seizure risk of < 5%. The ACNS recommends a minimum of 24 hours of monitoring in most cases, although shorter or longer duration can be applied depending on the clinical scenario [30]. Risk factors for predicting seizures in pediatric patients include age, clinical seizures prior to EEG, and presence of interictal discharges [19, 129, 130].
Limitations of cEEG
cEEG use can be limited by the amount of resource it requires. This includes in-house technologists to apply the EEG, professionals trained in interpretation reviewing at regular intervals, communication of findings to the clinical team, documentation of the EEG report, and storage of large data files in archives. EEG review is also almost always retrospective, even if reviewed at very frequent intervals, which has its limitations in the acute care setting, where real-time detection of changes in organ function is vital.
Localization of brain dysfunction is limited by the spatial resolution of standard electrode placement. Small abnormalities may not be detectible within the resolution of scalp EEG. EEG findings are not specific to the type of injury that causes abnormalities; for example, LRDA may be present as a postictal rhythm or after an acute stroke. Finally, many necessary treatments in the ICU can impact the EEG signal, including the impact of neuroactive medications and artifacts from ICU equipment, electrical artifact, and movement.
Quantitative EEG
Introduction to qEEG Monitoring
A recent survey of neuromonitoring practices in North America found that 96% of institutions use ICU cEEG [28], with cEEG review by a trained electroencephalographer remaining the gold standard [30]. However, there are practical limitations, such as the time-intensive nature of review and the need for real-time data in the ICU. qEEG allows large amounts of electrographic data to be viewed in a condensed form and can be displayed at the bedside, enabling real-time monitoring of cerebral function. qEEG use in the ICU is growing, increasing from 34% in 2010 to 50% in 2016 [131–133], and two pediatric-specific surveys reported 38–50% qEEG availability [28, 134]. Challenges for the widespread implementation of qEEG in pediatric ICUs include limited age-specific normative value for children, the need for additional software, lack of training in interpretation, and a paucity of data validating appropriate clinical application, making this a tool still under investigation in many scenarios.
Normative Data
Just as other physical parameters, such as blood pressure and heart rate, vary by age, so do the features of the normal EEG. It is essential to have a normative range for comparison with patient data both for clinical care and for research. The frequencies captured with cEEG typically fall into five ranges that are commonly referred to as follows: delta (0.5 to < 4 Hz), theta (4 to < 8 Hz), alpha (8 to < 13 Hz), beta (13 to < 30 Hz), and gamma (> 30 Hz). In a study of qEEG features in pediatric acute liver failure, normative values from 70 pediatric age-grouped normal EEGs were used to create a normative qEEG data set focusing on EEG frequency and relative power. A recent study reported the qEEG features from 1,289 healthy volunteers, including more than 500 pediatric patients (ages 4.5–20 years) [135]. These studies showed high-amplitude, slow-frequency delta power predominated in infants and decreased into childhood, whereas higher frequency power (theta and alpha) increased with age. Children demonstrate frequency admixtures similar to adults beginning in early teenage years [8, 136].
Children in the ICU rarely have completely normal electrographic brain function. Sedating medications commonly contribute to EEG abnormalities [137]. Supplemental Fig. 2 summarizes the impact of commonly used sedatives, anesthetics, and analgesics on the cEEG and qEEG. By altering the electrophysiologic profile of brain activity, these medications may impact how qEEG is interpreted in the setting of acute neurological injuries. Further work to understand normative parameters in the ICU may help distinguish sedated children with and without neurologic injury. Preliminary experience from adult literature provides some reassurance that these agents do not negate the diagnostic utility of the EEG; in a study of 496 adults post CA, propofol administration and discontinuation did not alter the prognostic value of the post-CA EEG [138].
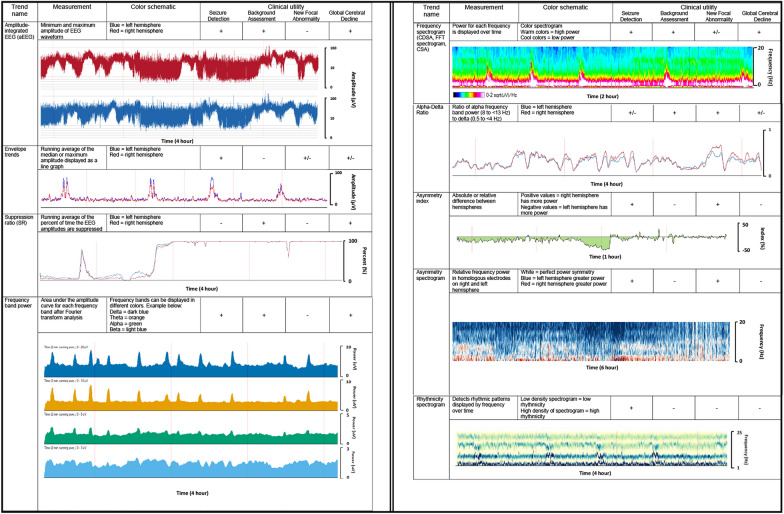
Fig. 2.
Summary of quantitative EEG trends used in the pediatric ICU. *CDSA color density spectral array, CSA compressed spectral array, EEG electroencephalography, FFT Fast Fourier Transform. *Trends, color schematics, axes, and scales may vary by quantitative EEG software
Building qEEG Trends
All qEEG software relies on processing the raw EEG signal through different computational methods and displays this information visually as time-compressed trends. The primary ways of processing cEEG are based on amplitude and/or frequency over time. Figure 2 provides an overview of the different qEEG trends and their common applications. It should be noted that the trends, color schematics, scales, and axes may vary between different qEEG software companies. We will first describe the features of the major amplitude-focused and frequency-focused trends, and then we will provide an overview of how trends are commonly used clinically, providing available supporting data in pediatric populations. It should be noted that such data are limited and qEEG remains a largely investigational tool. Large-scale validation studies are needed to better understand its role in pediatric critical care.
Amplitude-Focused Trends
Amplitude-integrated EEG
The first iterations of amplitude-integrated EEG (aEEG) came into use in clinical practice in the 1960s–1970s and were used as “cerebral function monitors” in adult patients post CA or in perioperative open-heart surgery neuromonitoring [139, 140]. In recent decades, aEEG has been more commonly used in the neonatal ICU for assessment of neonatal EEG background and seizure detection. At least three electrodes are required to build the aEEG; typically, these include homologous electrode pairs in either the parietal or central regions (traditionally P3–P4) and a ground electrode [141]. Software may offer different electrode pair options, and it is important to note which electrodes are being used to build the aEEG, as abnormalities occurring far from the electrodes may not be detected.
The EEG signal is filtered to amplify frequencies between 2 and 20 Hz and emphasize cortically derived rhythms over artifact. The signal is then displayed using semilogarithmic compression, which accounts for the naturally high variation in amplitudes, with the y-axis starting linearly from 0 to 10 μV then logarithmically from 10 to 100 μV [141–143]. aEEG may be displayed as a single graph or separated by the right and left hemispheres.
-
2.
Envelope trends
These trends are made by plotting the running average of either the median amplitude (envelope trend) or the maximum amplitude (peak envelope) of waveforms between 2 and 20 Hz, displaying amplitude variation over time. Like aEEG, envelope trends may be displayed as a single graph or separated between the right and left hemispheres. This trend can be helpful for detecting qEEG changes during a seizure, as amplitudes typically increase during a seizure, or other neuropathology that particularly affects EEG voltage.
-
3.
Suppression ratio
The suppression ratio displays the percentage of time the EEG signal is below a prespecified amplitude consistent with suppression. For example, if during a 10-second epoch of EEG, eight of the seconds had maximum amplitudes < 5 μV, the percentage suppression would be 80%. A running average is calculated with percentage suppression on the y-axis. This qEEG tool is particularly useful for neurologic conditions that result in background suppression, such as severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [144], refractory intracranial hypertension, or pharmacologically induced burst suppression [145–148].
Frequency-Focused Trends
Frequency-based trends rely on a Fast Fourier Analysis/Transform (FFT). This algorithm separates frequency from the time domain into individual oscillatory waveforms. Frequency power is the area under the FFT amplitude curve for each frequency and is displayed as the square of the amplitude (μV2) [149]. This modality breaks down the EEG into the contributions from each frequency over time. qEEG displays can highlight individual wavelengths (frequency band power) or spectrograms of selected or all EEG channels. These are frequently referred to as a color density spectral array (CDSA) and may be displayed at the bottom of a traditional cEEG recording. Other techniques to analyze the EEG using FFT include measures of asymmetry across brain regions, ratios comparing different frequency bands (e.g., alpha/delta ratio [ADR]), and rhythmicity detection.
FFT spectrogram or CDSA
The FFT spectrogram or CDSA displays the power for each frequency over time. Frequencies are displayed on the y-axis, time is displayed on the x-axis, and power is represented by a color spectrogram that can be adjusted to the user specification depending on the software, but traditionally warm colors, such as red, pink, and white, represent high power, whereas dark blue to black represents low power. The color spectrogram trend is commonly used for seizure identification, as described below, as well as for detection of state changes and effect of anesthetics.
-
2.
Alpha/delta ratio
The ADR is a power ratio of faster alpha frequencies over slower delta frequencies. The ratio is averaged over time and displayed as a line graph, with the y-axis as the numerical value for the ratio, the left hemisphere classically displayed as a blue line, and the right hemisphere in red. This trend is often applied to detect focal cerebral ischemia based on the principle that as cerebral blood flow decreases, the first electrographic change is a decrease in alpha frequencies, followed by an increase in slower theta then delta frequencies [150]. Because relative alpha and delta frequencies vary inversely in the setting of decreased cerebral perfusion, this ratio amplifies these changes. This contrasts with extracerebral pathology (subdural fluid collection), which would blunt alpha and delta amplitudes similarly, often without a noticeable change in the ratio.
-
3.
Asymmetry index and spectrogram
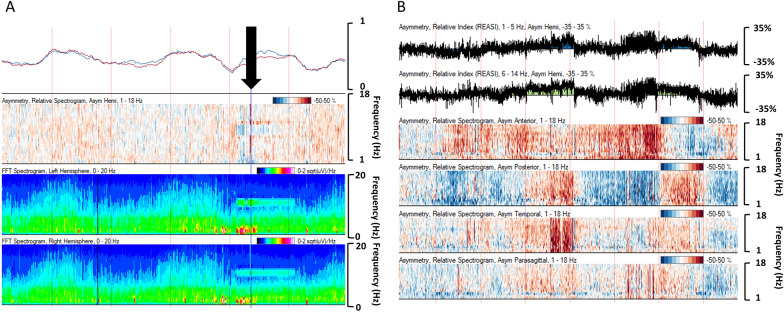
Asymmetry trends display absolute or relative asymmetries between electrodes in different brain regions, typically between hemispheres. The absolute asymmetry index graphs the absolute difference (0–100%) between the hemispheres as a running average. The relative asymmetry index displays a line graph of the relative asymmetry between regions over time, with index values (− 100 to 100%) on the y-axis: negative values when the left hemisphere has more power and positive values when the right hemisphere predominates.
The asymmetry spectrogram relies on FFT to display the comparison of relative power for each frequency as it relates to homologous regions in the contralateral hemisphere. The y-axis is power frequency (typically 0–20 Hz), and the color spectrogram displays right hemisphere dominance for a specific frequency as red and left hemisphere dominance for a specific frequency as blue. The darker the color, the greater the hemispheric asymmetry. It can be displayed as a holohemispheric comparison or by region (anterior, posterior, temporal, parasagittal). This trend is particularly helpful at displaying focal abnormalities in the brain, such as seizure or stroke.
-
4.
Rhythmicity spectrogram
The rhythmicity spectrogram (Persyst Development Corporation, Solana Beach, CA) uses a density spectral array that displays greater rhythmicity as denser blue, calculated across sequential groupings of the 1- to 25-Hz frequency bands over time. When used along with automated seizure detection, it can be useful clinically to identify ictal events [151, 152]. However, this trend is susceptible to highlighting nonictal rhythmic patterns, including sleep spindles, or the posterior dominant rhythm and repetitive artifacts (respiratory treatments or patting). Discussion of similar trends to detect rhythmicity offered by specific software is outside the scope of this review.
-
5.
Coherence, entropy, and connectivity
The extent to which two waveforms correlate at a given frequency is coherence [153, 154]. Entropy, on the other hand, describes the inherent disorder or randomness of the waveforms [155]. Measurements of coherence and entropy have been used to measure connectivity between brain regions and quantify brain reactivity. Connectivity between brain regions can rely on amplitude or frequency-focused tools [156]. These methods have been applied in investigations of disorders of consciousness [155, 157–159] and in seizure prediction modelling [160, 161]. Very few data exist for application of these qEEG measures in children.
Clinical Application of qEEG in the Pediatric ICU
Seizure Detection
Seizure detection is one of the most common indications for cEEG monitoring in the pediatric ICU, and seizures occur frequently in critically ill children [15, 19, 44, 46–53]. qEEG has the potential to improve timely recognition and treatment of seizures in this vulnerable population. Multiple qEEG trends can detect seizures, depending on the type of seizure (focal versus generalized), location, and duration. CDSA is commonly used. A seizure will appear as a “solid flame” pattern [162, 163]. Power abruptly increases, peaks, and then attenuates during a seizure typically for both fast and slow frequencies, resulting in a flame-like appearance on the color spectrogram (Fig. 3). On an aEEG, if the seizure involves the electrodes used in the aEEG algorithm, the seizure appears as a sudden upward arched pattern because amplitude of the EEG waveform typically increases during the seizure. The envelope trend will also peak during a seizure, as another amplitude-focused trend. In the case of a focal seizure, the asymmetry index and spectrogram can be useful in highlighting laterality of ictal and postictal patterns.
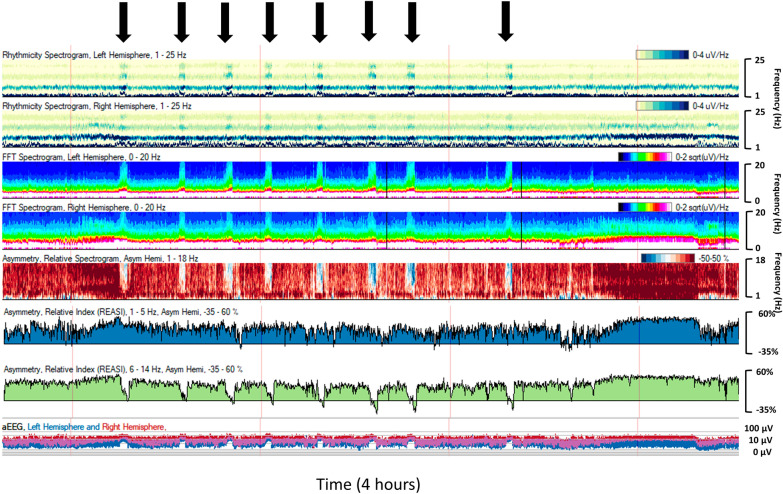
Fig. 3.
A 9-year-old boy with a left frontotemporal tumor and new onset left hemispheric onset seizures (black arrows). Trend description from top to bottom: rhythmicity spectrogram for left then right hemisphere demonstrates increased rhythmicity over the left hemisphere during seizures. Fast Fourier Transform spectrogram left over right hemisphere shows solid flames best formed over the left during seizures. Asymmetry spectrogram shows greater power over the left hemisphere during seizures (blue color change). Asymmetry indices for slower frequencies (1–5 Hz) over faster frequencies (6–14 Hz) show discrete graph trend toward less positive values during seizures, indicating greater relative power of the left hemisphere. Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography (EEG) shows classic arched pattern during seizures (Color figure online)
Several studies have reported success in training bedside ICU providers to recognize qEEG seizures after a brief training session, with sensitivity for seizure detection ranging from 73 to 100% [151, 164–170]. In a prospective study of qEEG program initiation, pediatric ICU providers identified 100% (12 of 12) of patients with electrographic seizures recorded using qEEG, with most (67%) of the seizures recognized when a neurophysiologist was not available for interpretation [170]. Eleven patients had false positive identification of seizures, and 64% (7 of 11) received antiseizure medication. A recent 2-year qEEG education and implementation program providing instruction to pediatric ICU nurses found a much lower seizure detection rate at only 10% (1 of 10) with prospective monitoring; however, the frequency of monitoring was not standardized [171].
Another option for rapid seizure recognition in the ICU is the application of commercially available seizure detection algorithms. Several different proprietary algorithms were compared to the gold standard of expert neurophysiologist review [172]. The algorithm from Stellate Harmonie Version 7 (Natus Medical, Middleton, WI, USA) had the highest sensitivity for seizure detection at 92% but a daily false positive rate of 126.3 incorrectly detected events/day, whereas Persyst Version 11 had a balance of sensitivity and the false positive rate: 76% and 5.1 events/day, respectively. False positive rates, unnecessary medication administration, and alarm fatigue are important considerations when implementing bedside use of qEEG for seizure identification, and ideally, a neurophysiologist should be available to confirm findings on raw cEEG.
qEEG may also aid in efficient seizure burden estimation after super refractory status epilepticus (SRSE) [173]. A recent study used a novel seizure detection education approach, allowing review of ten different trends and use of spike detection frequency above or below 3-Hz frequency to help distinguish seizures from the IIC. Novice qEEG readers overestimated seizure burden, identifying about double the number of minutes of confirmed seizures. qEEG experts, on the other hand, were very accurate in their estimate of seizure burden (3126 minutes by qEEG estimate vs. 3257 minutes by expert raw EEG review). Although this study did not include children, it provided exciting results, suggesting that qEEG can reasonably estimate seizure burden after SRSE.
Assessing Response to Antiseizure Medication and Infusion Titration
qEEG trend panels can aid the ICU provider in assessing patient response to antiseizure medications [174]. For patients with recurrent seizures who are treated with multiple antiseizure medications in a short period of time, review of the qEEG trends can help distinguish which medications were the most effective and thus guide drug selection individualized to the patient response (Fig. 4). The suppression ratio can be used to assess the degree of burst suppression and titrate anesthetic infusions to a specific target for SRSE and refractory intracranial hypertension management.
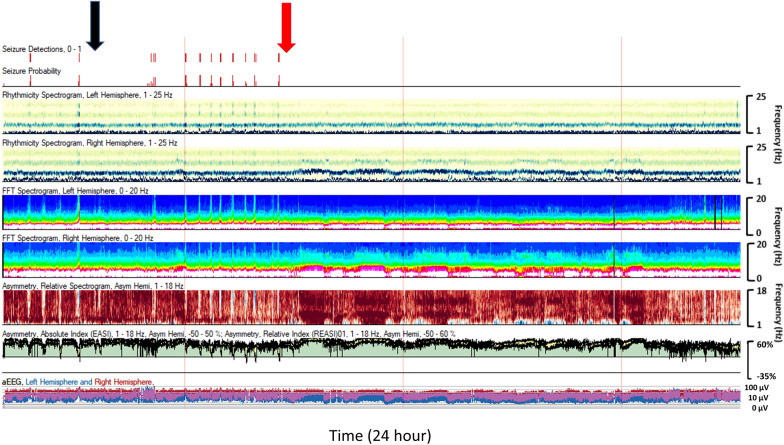
Fig. 4.
A 9-year-old with a left hemispheric-onset seizures. Levetiracetam 40 mg/kg (black arrow) slowed seizures but did not resolve them. Lacosamide 5 mg/kg (red arrow) provided definitive seizure suppression (Color figure online)
Background Assessment
The FFT spectrogram or CDSA is used in clinical practice to assess state change and variability. Quantifiable differences in band power on FFT spectrogram are associated with recovery of children post CA [175]. In a study of 69 pediatric post-CA patients with early (< 17 hour after return of circulation) and late (> 18 hour) EEG, higher power in the gamma, beta, and delta frequencies early in EEG monitoring was predictive of favorable outcomes, and delta and alpha powers were more important predictive features in late EEG. Gamma frequencies are faster than what are traditionally identified as cortically derived frequencies on scalp EEG and often represent myogenic artifact, suggesting that the ability to generate such artifact post CA may be associated with a more favorable outcome. Similarly, the presence of early sleep spindles post CA is associated with favorable outcome [118], which may account for the influence of beta power in the prediction modeling.
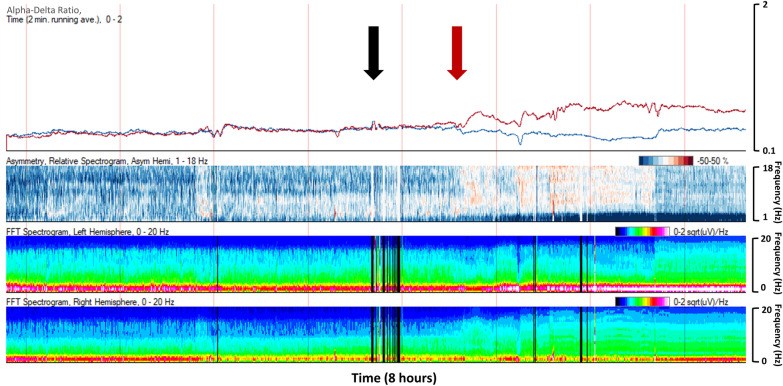
The ability to use qEEG to create an objective, linear, real-time measure of encephalopathy compared to subjective intermittent examinations may have substantial advantage in the ICU, as these measures may serve as a live neuromonitoring “vital sign,” viewable at bedside. For example, in the setting of pediatric acute liver failure, the assessment and diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy has treatment implications and influences transplant priority. Hepatic encephalopathy grade and qEEG spectrogram features were compared in 33 children with acute liver failure [41]. qEEG features were both associated with the degree of encephalopathy and outcomes (liver transplant or death). Infants generally had a loss of total power in response to encephalopathy, whereas older children tended to have decreased theta/delta ratios. Figure 5 illustrates the qEEG progression from stage II to stage III hepatic encephalopathy grade, demonstrating how qEEG can be a dynamic measure of brain function.
Fig. 5.
A 13-year-old with acute liver failure and progression from stage II to stage III hepatic encephalopathy. Dashed blue arrow notes gradual decline in the alpha/delta ratio, which is confirmed to be due to both loss of alpha power and increase in delta power as demonstrated by the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) spectrogram trends for the left and right hemispheres. This change in quantitative electroencephalography (EEG) trends corresponded to the patient no longer following commands and progressing to extensor posturing of arms and legs, sustained clonus at the ankles, hyperreflexia, and positive Babinski sign bilaterally (Color figure online)
Although studies are lacking in children, qEEG is being used to better understand and perhaps find a measurable therapeutic target in disorders of consciousness. Having a bedside tool to detect covert consciousness in patients who appear otherwise unresponsive could significantly improve our ability to neuroprognosticate and advise families in the initial days after acute brain injury. One such assessment tool is the “ABCD model,” which has been applied in adult patients with disorders of consciousness after CA. The model is predicated on the central thalamus being a hub of networks involved in consciousness and grades four spectral patterns of the EEG on a scale of corticothalamic activity [176]. Patterns range from type A, representing complete electrographic corticothalamic deafferentation, to type D with normal corticothalamic function. Spectral typing correlated with bedside behavioral assessment using the Coma Recovery Scale—Revised and outcome as measured by the Cerebral Performance Category. Another study of 104 adults who had no clinically apparent response to standard examination found that 16 (15%) demonstrated cognitive-motor dissociation, defined as specific regional and frequency band changes in response to two spoken commands [177]. Eight of those patients were following verbal commands by a median of 6 days. Detection of language comprehension in patients with disorders of consciousness has also been demonstrated by identifying patients with time-locked EEG oscillations that correspond to word, phrase, and sentence frequencies, which have been shown to only be present in patients who can comprehend speech [178]. In this study, electrographic evidence of tracking higher-level linguistic structure correlated with better outcome at 3 and 6 months.
Detection of Acute Neurologic Decline
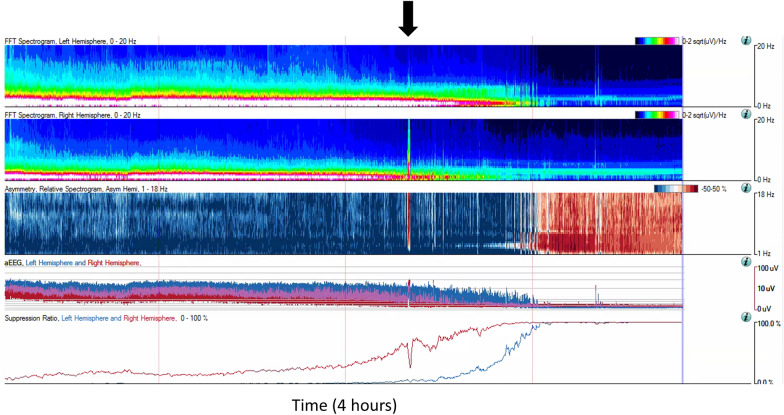
qEEG is also used to detect life-threatening neurologic decompensation before becoming irreversible (e.g., cerebral herniation). Two recent publications evaluated qEEG trends for identifying intracranial emergencies prior to clinical deterioration in children [145, 146]. One study used qualitative review of the qEEG by neurophysiologists and the Persyst Z-score trend to create alerts for 10 patients. The Z-score measures deviations from a user-defined and patient-specific baseline. The user can then set an alarm for specified cutoffs beyond this Z-score. Identification of neurologic deterioration using expert qEEG review occurred a median of 5.2 hours before raw EEG changes were detected and a median of 5.5 hours before a clinical change was noted. The Z-score qEEG alert detected the change before expert review in 50% (5 of 10) of the patients. The second study comprised 13 patients with increased intracranial pressure and found that a detectable rise in the suppression ratio occurred a median of 3.1 hours prior to the first clinically detectable change [146].
When cerebral perfusion gradually decreases because of progressive cerebral edema, the qEEG changes may be most apparent in the FFT spectrogram, with initial loss of fast frequencies and gain of slower frequencies, followed by loss of slower frequencies as the ischemic threshold is crossed [150] (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
A 10-year-old with metastatic brain tumor in the right hemisphere who developed progressive cerebral herniation and loss of cortical activity. There was a right hemispheric onset seizure prior to herniation (black arrow)
Focal Cerebral Dysfunction Detection
Critically ill children may be at risk for focal neurologic dysfunction and injury, depending on their underlying disease. For example, children requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation are at risk for both focal ischemia and hemorrhage [179–181]. New EEG abnormalities, such as focal slowing or new interictal or ictal activity, can be the first indicator of injury in critically ill children who may otherwise have a limited neurologic examination. The roles of both cEEG and qEEG specifically for detection of ischemia and hemorrhage are reviewed elsewhere in this issue in the article titled “Neuromonitoring in Children With Neurovascular Disorders.” A single-center study of children with acute unilateral anterior circulation ischemic stroke (n = 5) and hemorrhagic stroke (n = 6) compared qEEG features between the injured and uninjured hemispheres [182]. Patients with ischemic stroke demonstrated decreased alpha and beta power and lower spectral edge frequency in the injured hemisphere, whereas patients with hemorrhage consistently had a negative correlation between total power and mean arterial blood pressure. The loss of faster frequencies in the ischemia group has been well described; the negative correlation between total power and blood pressure was postulated to reflect a significant increase in the delta power in the area of the bleed. This may also reflect loss of autoregulation in the affected hemisphere.
Asymmetry spectrograms are particularly helpful for rapidly identifying differences between hemispheres. Persistent changes in asymmetry spectrograms have been associated with unfavorable outcome (morbidity and mortality) in a small pediatric study aimed at predicting neurologic deterioration [145]. Differences in the asymmetry spectrogram appear related to cerebral perfusion, either increased (seizure) or decreased (stroke, post-ictal state), or extracerebral pathology (subdural hemorrhage or superficial scalp swelling). The relative asymmetry between brain regions has long been appreciated to be useful in ischemia detection and stroke recovery in adult patients [183–186], and this trend has been used to monitor cerebral perfusion in pediatric patients undergoing revascularization surgery for moyamoya [187]. Of note, these displays are relative to the contralateral hemisphere or region in question and are susceptible to overemphasis of noncerebral pathology (scalp edema).
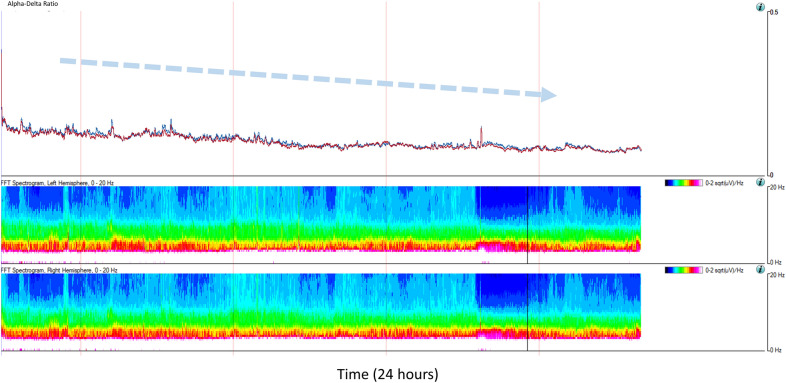
The ADR is also used for assessing perfusion and ischemia (Fig. 7). The most common use is screening adult patients for delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage [188, 189]. Studies have also investigated the utility during carotid endarterectomy [190], mechanical thrombectomy [191], pediatric and adult revascularization for moyamoya [187, 192], and stroke and rehabilitation in adults [185]. Clinical and research applications for individual trends in the pediatric ICU remain open, as well as novel combinations of these trends to for tracking disease trajectory or recovery [193].
Fig. 7.
A 10-year-old boy with at-home cardiac arrest requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Hypotension and arrhythmias resulted in hypoperfusion injury around the time of ECMO cannulation (black arrow). The right hemisphere lost delta power, increasing the alpha/delta ratio (ADR), whereas the left hemisphere lost fast frequencies and gained slow frequencies, resulting in a decrease in ADR (red arrow). Asymmetry spectrogram reflects the increase in delta power over the left hemisphere after cannulation (Color figure online)
Pediatric Macroperiodic Oscillations
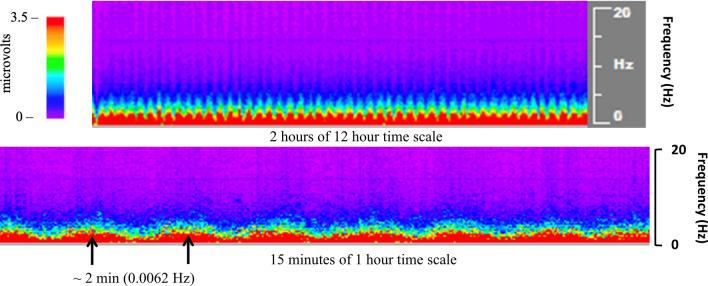
More recently, a new periodic pattern on the power spectrogram has been identified in pediatric patients [194]. This pattern oscillated regularly over minutes and has been termed macroperiodic oscillations (MOs) (Fig. 8). In the first description, this pattern was associated with younger patients and oscillated over 2–7 minutes, with the timing consistent within patients. There was a strong association with refractory seizures in patients with acute injury and without preexisting neurologic conditions. A further computational study to measure the strength and spatial distribution of oscillations found MOs in patients not readily identified on clinical review of the qEEG and in patients without seizures. Importantly, the strength and spatial distribution of the MO pattern was associated with clinical outcomes at hospital discharge [195, 196].
Fig. 8.
Macroperiodic oscillations (MOs) observed in a 6-month-old with traumatic brain injury are visualized on segments of 12-hour and 1-hour time scales on color density spectral array (CDSA). This MOs pattern oscillated over 2 minutes from peak to peak (black arrows). There was a modest change in voltage observed on raw electroencephalography (EEG) during this time, but the periodic invariant quality was only appreciated on the CDSA (Color figure online)
A similar oscillatory pattern in neonates with severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy has been described; this pattern was not clearly associated with seizures but was seen in neonates with more severe background abnormalities and worse neurodevelopmental outcomes [197]. This pattern was termed “pseudo-sawtooth” and described an aEEG cyclical pattern with a cycle duration of 3.3–4.6 minutes consisting of periods of increased amplitude of delta and theta frequencies alternating with profound suppression. This pattern emerged and peaked at a time that closely paralleled the known timing of the secondary phase of brain injury experienced by neonates after hypoxic-ischemic injury, between 6.5 and 28 hours after birth. The authors posited that this may be a biomarker of more severe brain injury and that the rhythmic oscillations may be intrinsic to subcortical structures, emerging when cortical activity is more severely impaired.
Common qEEG Artifacts in the Pediatric ICU
EEG studies in the ICU are prone to artifacts. Most qEEG software offers artifact reduction algorithms, which perform well in removal of artifact from electrical artifact (60 Hz in the United States, 50 Hz in Europe) and myogenic artifact. Less likely to be filtered by artifact reduction are rhythmic patterns such as patting and respiratory therapy artifact, and both can be mistaken for seizures if the raw EEG and video are not reviewed (Fig. 9a). Scalp edema can cause shift asymmetries, depending on head position (Fig. 9b).
Fig. 9.
a Artifact in the 13- to 14-Hz frequency range from a high-frequency chest wall oscillation vest (black arrow) in a 13-year-old. b Quantitative electroencephalography (EEG) in a 3-month-old with congenital heart disease status post surgical repair. Asymmetry indices and spectrograms demonstrate shifting impact of scalp edema on the EEG signal, with changing asymmetric power at regular intervals, reflecting timed repositioning of the patient by the bedside nurses
Limitations of qEEG
An advantage of qEEG in critical care is that it summarizes large amounts of data that can then be trended over time. However, several minutes of EEG need to be collected to display the initial trends, and several hours may be required to make assessments of features such as state cycling, seizure burden, response to medication, and global improvements or decline. qEEG is not yet ready to be used as an independent tool in pediatric neurocritical care; as such, findings should always be verified with review of the raw EEG.
qEEG software does not currently offer easy integration of patient-related events with the EEG, such as medication administration. Some packages do offer integration of qEEG with continuous variables, such as vital signs, intracranial pressure, end-tidal CO2.
Regarding seizure detection, qEEG may miss seizures if the ictal amplitude change is too small, if the seizure is of short duration, or if the seizure is limited to a small area and only detected by a few electrodes [172, 198–200].
Additional limitations include the lack of normative data in critically ill children and the impact of neuroactive medications on qEEG. There are no guidelines for standardized reviewing and reporting of qEEG, many of the patterns have not been studied extensively or validated in children, and formal training in qEEG interpretation is not widely available.
Future Directions
Use of qEEG in clinical practice in the pediatric ICU for brain monitoring is increasing. Continued efforts are ongoing to validate the optimal parameters to detect patterns that are predictive, specific, and clinically actionable. The development of EEG monitoring tools that can be confidently associated with a specific neurologic state, including increased intracranial pressure, hypoperfusion, new ischemia, and status epilepticus, will enable movement of these tools to the bedside for prospective monitoring and interventions that may improve outcomes through early detection, timely intervention, or improved accuracy of prognosis. Multimodal monitoring coupling EEG with other neuromonitoring tools discussed in this article will further advance clinical care in the pediatric ICU.
Conclusions
cEEG offers high-resolution noninvasive neuromonitoring of critically ill children at risk for neurologic complications. cEEG remains the gold standard for seizure detection and background assessment, and qEEG offers real-time display of time-compressed data, holding promise for detecting neurologic compromise more rapidly than traditional EEG review.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to drafting and editing of the manuscript, and the final manuscript was approved by all authors.
Source of Support
There was no funding for this article.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval/Informed Consent
Ethical approvals were not sought given that this is an invited review.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Fink EL, Kochanek PM, Tasker RC, et al. International Survey of Critically Ill children with acute neurologic insults: the prevalence of acute critical neurological disease in children: a global epidemiological assessment study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(4):330–342. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000001093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nasr VG, DiNardo JA. Sedation and analgesia in pediatric cardiac critical care. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016;17(8 Suppl 1):S225–S231. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000000756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Patel AK, Trujillo-Rivera E, Faruqe F, et al. Sedation, analgesia, and neuromuscular blockade: an assessment of practices from 2009 to 2016 in a national sample of 66,443 pediatric patients cared for in the ICU. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(9):e599–e609. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000002351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cooper R, Winter AL, Crow HJ, Walter WG. Comparison of subcortical, cortical and scalp activity using chronically indwelling electrodes in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965;18:217–228. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tao JX, Ray A, Hawes-Ebersole S, Ebersole JS. Intracranial EEG substrates of scalp EEG interictal spikes. Epilepsia. 2005;46(5):669–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.11404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abend NS, Dlugos DJ, Zhu X, Schwartz ES. Utility of CT-compatible EEG electrodes in critically ill children. Pediatr Radiol. 2015;45(5):714–718. doi: 10.1007/s00247-014-3208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mirsattari SM, Lee DH, Jones D, Bihari F, Ives JR. MRI compatible EEG electrode system for routine use in the epilepsy monitoring unit and intensive care unit. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(9):2175–2180. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2004.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ebersole JS, Husain AM, Nordli DR. Current practice of clinical electroencephalography. Berlin: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW); 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shellhaas RA, Chang T, Tsuchida T, et al. The American clinical neurophysiology society's guideline on continuous electroencephalography monitoring in neonates. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;28(6):611–617. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e31823e96d7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moura LM, Carneiro TS, Kwasnik D, et al. cEEG electrode-related pressure ulcers in acutely hospitalized patients. Neurol Clin Pract. 2017;7(1):15–25. doi: 10.1212/cpj.0000000000000312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mietzsch U, Cooper KL, Harris ML. Successful reduction in electrode-related pressure ulcers during EEG monitoring in critically Ill neonates. Adv Neonatal Care. 2019;19(4):262–274. doi: 10.1097/anc.0000000000000641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schindler CA, Barrette R, Sandock A, Kuhn E. Medical device-related pressure injuries associated with electroencephalogram leads in a Tertiary Care Children's Hospital: a retrospective chart review. Wound Manag Prev. 2021;67(9):25–32. doi: 10.25270/wmp.2021.9.2532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Herman ST, Abend NS, Bleck TP, et al. Consensus statement on continuous EEG in critically ill adults and children, part II: personnel, technical specifications, and clinical practice. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(2):96–108. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hirsch LJ, Fong MWK, Leitinger M, et al. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society's standardized critical care EEG terminology: 2021 version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;38(1):1–29. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abend NS, Arndt DH, Carpenter JL, et al. Electrographic seizures in pediatric ICU patients: cohort study of risk factors and mortality. Neurology. 2013;81(4):383–391. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829c5cfe. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Greiner HM, Holland K, Leach JL, Horn PS, Hershey AD, Rose DF. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus: the encephalopathic pediatric patient. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e748–e755. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jette N, Claassen J, Emerson RG, Hirsch LJ. Frequency and predictors of nonconvulsive seizures during continuous electroencephalographic monitoring in critically ill children. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(12):1750–1755. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.12.1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Payne ET, Zhao XY, Frndova H, et al. Seizure burden is independently associated with short term outcome in critically ill children. Brain. 2014;137(Pt 5):1429–1438. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sansevere AJ, Duncan ED, Libenson MH, Loddenkemper T, Pearl PL, Tasker RC. Continuous EEG in pediatric critical care: yield and efficiency of seizure detection. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;34(5):421–426. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tay S, Hirsch LJ, Leary L, Jette N, Wittman J, Akman CI. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in children: clinical and EEG characteristics. Epilepsia. 2006;47(9):1504–1509. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Massey SL, Glass HC, Shellhaas RA, et al. Characteristics of neonates with cardiopulmonary disease who experience seizures: a multicenter study. J Pediatr. 2022;242:63–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.10.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Keene JC, Morgan LA, Abend NS, et al. Treatment of neonatal seizures: comparison of treatment pathways from 11 neonatal intensive care units. Pediatr Neurol. 2022;128:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2021.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wusthoff CJ, Sundaram V, Abend NS, et al. Seizure control in neonates undergoing screening vs confirmatory EEG monitoring. Neurology. 2021;97(6):e587–e596. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sansevere AJ, DiBacco ML, Akhondi-Asl A, et al. EEG features of brain injury during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children. Neurology. 2020;95(10):e1372–e1380. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Topjian AA, Zhang B, Xiao R, et al. Multimodal monitoring including early EEG improves stratification of brain injury severity after pediatric cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2021;167:282–288. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tsuchida TN. EEG background patterns and prognostication of neonatal encephalopathy in the era of hypothermia. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;30(2):122. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3182872ac2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fung FW, Topjian AA, Xiao R, Abend NS. Early EEG features for outcome prediction after cardiac arrest in children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;36(5):349–357. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kirschen MP, LaRovere K, Balakrishnan B, et al. A survey of neuromonitoring practices in North American pediatric intensive care units. Pediatr Neurol. 2022;126:125–130. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2021.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hussain E, Grimason M, Goldstein J, et al. EEG abnormalities are associated with increased risk of transplant or poor outcome in children with acute liver failure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;58(4):449–456. doi: 10.1097/mpg.0000000000000271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Herman ST, Abend NS, Bleck TP, et al. Consensus statement on continuous EEG in critically ill adults and children, part I: indications. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(2):87–95. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kochanek PM, Tasker RC, Carney N, et al. Guidelines for the management of pediatric severe traumatic brain injury, third edition: update of the brain trauma foundation guidelines. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2019;20(3S Suppl 1):S1–s82. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000001735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brophy GM, Bell R, Claassen J, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2012;17(1):3–23. doi: 10.1007/s12028-012-9695-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hutchinson P, O'Phelan K. International multidisciplinary consensus conference on multimodality monitoring: cerebral metabolism. Neurocrit Care. 2014;21(Suppl 2):S148–S158. doi: 10.1007/s12028-014-0035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Riviello JJ, Jr, Ashwal S, Hirtz D, et al. Practice parameter: diagnostic assessment of the child with status epilepticus (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology. 2006;67(9):1542–1550. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000243197.05519.3d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Topjian AA, Raymond TT, Atkins D, et al. Part 4: pediatric basic and advanced life support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2020;142(16_suppl_2):S469–s523. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wyckoff MH, Singletary EM, Soar J, et al. 2021 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science with treatment recommendations: summary from the basic life support; advanced life support; neonatal life support; education, implementation, and teams; first aid task forces; and the COVID-19 Working Group. Resuscitation. 2021;169:229–311. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.10.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Glauser T, Shinnar S, Gloss D, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children and adults: report of the guideline committee of the American Epilepsy Society. Epilepsy Curr. 2016;16(1):48–61. doi: 10.5698/1535-7597-16.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Briatore E, Ferrari F, Pomero G, et al. EEG findings in cooled asphyxiated newborns and correlation with site and severity of brain damage. Brain Dev. 2013;35(5):420–426. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mariani E, Scelsa B, Pogliani L, Introvini P, Lista G. Prognostic value of electroencephalograms in asphyxiated newborns treated with hypothermia. Pediatr Neurol. 2008;39(5):317–324. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abend NS, Massey SL, Fitzgerald M, et al. Interrater agreement of EEG interpretation after pediatric cardiac arrest using standardized critical care EEG terminology. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;34(6):534–541. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Press CA, Morgan L, Mills M, et al. Spectral electroencephalogram analysis for the evaluation of encephalopathy grade in children with acute liver failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(1):64–72. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000001016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gust J, Annesley CE, Gardner RA, Bozarth X. EEG correlates of delirium in children and young adults with CD19-directed CAR T cell treatment-related neurotoxicity. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;38(2):135–142. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dhakar MB, Sheikh ZB, Desai M, et al. Developing a standardized approach to grading the level of brain dysfunction on EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022 doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Benedetti GM, Silverstein FS, Rau SM, Lester SG, Benedetti MH, Shellhaas RA. Sedation and analgesia influence electroencephalography monitoring in pediatric neurocritical care. Pediatr Neurol. 2018;87:57–64. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.LaRovere KL, Graham RJ, Tasker RC. Pediatric neurocritical care: a neurology consultation model and implication for education and training. Pediatr Neurol. 2013;48(3):206–211. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2012.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fung FW, Wang Z, Parikh DS, et al. Electrographic seizures and outcome in critically Ill children. Neurology. 2021;96(22):e2749–e2760. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000012032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shahwan A, Bailey C, Shekerdemian L, Harvey AS. The prevalence of seizures in comatose children in the pediatric intensive care unit: a prospective video-EEG study. Epilepsia. 2010;51(7):1198–1204. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Abend NS, Topjian A, Ichord R, et al. Electroencephalographic monitoring during hypothermia after pediatric cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2009;72(22):1931–1940. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a82687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Williams K, Jarrar R, Buchhalter J. Continuous video-EEG monitoring in pediatric intensive care units. Epilepsia. 2011;52(6):1130–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kirkham FJ, Wade AM, McElduff F, et al. Seizures in 204 comatose children: incidence and outcome. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(5):853–862. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2529-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Piantino JA, Wainwright MS, Grimason M, et al. Nonconvulsive seizures are common in children treated with extracorporeal cardiac life support. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14(6):601–609. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e318291755a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Arndt DH, Lerner JT, Matsumoto JH, et al. Subclinical early posttraumatic seizures detected by continuous EEG monitoring in a consecutive pediatric cohort. Epilepsia. 2013;54(10):1780–1788. doi: 10.1111/epi.12369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.O'Neill BR, Handler MH, Tong S, Chapman KE. Incidence of seizures on continuous EEG monitoring following traumatic brain injury in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015;16(2):167–176. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.Peds14263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sánchez Fernández I, Abend NS, Arndt DH, et al. Electrographic seizures after convulsive status epilepticus in children and young adults: a retrospective multicenter study. J Pediatr. 2014;164(2):339–46.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.09.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tuckuviene R, Christensen AL, Helgestad J, Johnsen SP, Kristensen SR. Paediatric arterial ischaemic stroke and cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in Denmark 1994–2006: a nationwide population-based study. Acta Paediatr. 2011;100(4):543–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2010.02100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Billinghurst LL, Beslow LA, Abend NS, et al. Incidence and predictors of epilepsy after pediatric arterial ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2017;88(7):630–637. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000003603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bruno CJ, Beslow LA, Witmer CM, et al. Haemorrhagic stroke in term and late preterm neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99(1):F48–53. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Beslow LA, Abend NS, Gindville MC, et al. Pediatric intracerebral hemorrhage: acute symptomatic seizures and epilepsy. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(4):448–454. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vespa P, Tubi M, Claassen J, et al. Metabolic crisis occurs with seizures and periodic discharges after brain trauma. Ann Neurol. 2016;79(4):579–590. doi: 10.1002/ana.24606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Abend NS, Beslow LA, Smith SE, et al. Seizures as a presenting symptom of acute arterial ischemic stroke in childhood. J Pediatr. 2011;159(3):479–483. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yock-Corrales A, Mackay MT, Mosley I, Maixner W, Babl FE. Acute childhood arterial ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;58(2):156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2010.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fox CK, Mackay MT, Dowling MM, Pergami P, Titomanlio L, Deveber G. Prolonged or recurrent acute seizures after pediatric arterial ischemic stroke are associated with increasing epilepsy risk. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017;59(1):38–44. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.13198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chadehumbe MA, Khatri P, Khoury JC, et al. Seizures are common in the acute setting of childhood stroke: a population-based study. J Child Neurol. 2009;24(1):9–12. doi: 10.1177/0883073808320756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kurtz P, Gaspard N, Wahl AS, et al. Continuous electroencephalography in a surgical intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(2):228–234. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-3149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Chung B, Wong V. Pediatric stroke among Hong Kong Chinese subjects. Pediatrics. 2004;114(2):e206–e212. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zou S, Wu X, Zhu B, Yu J, Yang B, Shi J. The pooled incidence of post-stroke seizure in 102 008 patients. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2015;22(6):460–467. doi: 10.1179/1074935715z.00000000062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ferreira-Atuesta C, Döhler N, Erdélyi-Canavese B, et al. Seizures after ischemic stroke: a matched multicenter study. Ann Neurol. 2021;90(5):808–820. doi: 10.1002/ana.26212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wang JZ, Vyas MV, Saposnik G, Burneo JG. Incidence and management of seizures after ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology. 2017;89(12):1220–1228. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000004407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lo WD, Lee J, Rusin J, Perkins E, Roach ES. Intracranial hemorrhage in children: an evolving spectrum. Arch Neurol. 2008;65(12):1629–1633. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2008.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kumar R, Shukla D, Mahapatra AK. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage in children. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2009;45(1):37–45. doi: 10.1159/000202622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Williams V, Jayashree M, Bansal A, et al. Spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage in children-intensive care needs and predictors of in-hospital mortality: a 10-year single-centre experience. Childs Nerv Syst. 2019;35(8):1371–1379. doi: 10.1007/s00381-019-04209-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Naim MY, Gaynor JW, Chen J, et al. Subclinical seizures identified by postoperative electroencephalographic monitoring are common after neonatal cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2015.03.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Clancy RR, Sharif U, Ichord R, et al. Electrographic neonatal seizures after infant heart surgery. Epilepsia. 2005;46(1):84–90. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.22504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chen C, Liu J, Du L. Tranexamic acid after cardiopulmonary bypass does not increase risk of postoperative seizures: a retrospective study. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022;70(4):337–346. doi: 10.1007/s11748-021-01709-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gofton TE, Chu MW, Norton L, et al. A prospective observational study of seizures after cardiac surgery using continuous EEG monitoring. Neurocrit Care. 2014;21(2):220–227. doi: 10.1007/s12028-014-9967-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bauer Huang SL, Said AS, Smyser CD, Lin JC, Guilliams KP, Guerriero RM. Seizures are associated with brain injury in infants undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Child Neurol. 2021;36(3):230–236. doi: 10.1177/0883073820966917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mateen FJ, Muralidharan R, Shinohara RT, Parisi JE, Schears GJ, Wijdicks EF. Neurological injury in adults treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Arch Neurol. 2011;68(12):1543–1549. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lorusso R, Gelsomino S, Parise O, et al. Neurologic injury in adults supported with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure: findings from the extracorporeal life support organization database. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(8):1389–1397. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000002502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cook RJ, Rau SM, Lester-Pelham SG, et al. Electrographic seizures and brain injury in children requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;108:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Yuliati A, Federman M, Rao LM, Chen L, Sim MS, Matsumoto JH. Prevalence of seizures and risk factors for mortality in a continuous cohort of pediatric extracorporeal membrane oxygenation patients. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(11):949–958. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000002468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hahn JS, Vaucher Y, Bejar R, Coen RW. Electroencephalographic and neuroimaging findings in neonates undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Neuropediatrics. 1993;24(1):19–24. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lin JE, Asfour A, Sewell TB, et al. Neurological issues in children with COVID-19. Neurosci Lett. 2021;743:135567. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Divani AA, Andalib S, Biller J, et al. Central nervous system manifestations associated with COVID-19. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2020;20(12):60. doi: 10.1007/s11910-020-01079-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Emami A, Fadakar N, Akbari A, et al. Seizure in patients with COVID-19. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(11):3057–3061. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04731-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.LaRovere KL, Riggs BJ, Poussaint TY, et al. Neurologic involvement in children and adolescents hospitalized in the United States for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78(5):536–547. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Fink EL, Robertson CL, Wainwright MS, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of neurologic manifestations in hospitalized children diagnosed with acute SARS-CoV-2 or MIS-C. Pediatr Neurol. 2022;128:33–44. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2021.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lalgudi Ganesan S, Hahn CD. Electrographic seizure burden and outcomes following pediatric status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2019;101(Pt B):106409. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Su Y, Huang H, Jiang M, et al. Phenobarbital versus valproate for generalized convulsive status epilepticus in adults (2): a multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial in China (China 2-P vs. V) Epilepsy Res. 2021;177:106755. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chamberlain JM, Kapur J, Shinnar S, et al. Efficacy of levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate for established status epilepticus by age group (ESETT): a double-blind, responsive-adaptive, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395(10231):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30611-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kapur J, Elm J, Chamberlain JM, et al. Randomized trial of three anticonvulsant medications for status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(22):2103–2113. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chamberlain JM, Okada P, Holsti M, et al. Lorazepam vs diazepam for pediatric status epilepticus: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;311(16):1652–1660. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.2625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.McIntyre J, Robertson S, Norris E, et al. Safety and efficacy of buccal midazolam versus rectal diazepam for emergency treatment of seizures in children: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9481):205–210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)66909-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gelisse P, Crespel A, Genton P, Jallon P, Kaplan PW. Lateralized periodic discharges: Which patterns are interictal, ictal, or peri-ictal? Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;132(7):1593–1603. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2021.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Beniczky S, Hirsch LJ, Kaplan PW, et al. Unified EEG terminology and criteria for nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2013;54(Suppl 6):28–29. doi: 10.1111/epi.12270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Leitinger M, Beniczky S, Rohracher A, et al. Salzburg consensus criteria for non-convulsive status epilepticus—approach to clinical application. Epilepsy Behav. 2015;49:158–163. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Leitinger M, Trinka E, Gardella E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the Salzburg EEG criteria for non-convulsive status epilepticus: a retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(10):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(16)30137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Sansevere AJ, DiBacco ML, Zhang B, et al. Sporadic and periodic interictal discharges in critically Ill children: seizure associations and time to seizure identification. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fung FW, Parikh DS, Massey SL, et al. Periodic and rhythmic patterns in critically ill children: incidence, interrater agreement, and seizures. Epilepsia. 2021;62(12):2955–2967. doi: 10.1111/epi.17068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Akman CI, Abou Khaled KJ, Segal E, Micic V, Riviello JJ. Generalized periodic epileptiform discharges in critically ill children: clinical features, and outcome. Epilepsy Res. 2013;106(3):378–385. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Husari KS, Ritzl EK. Anesthesia-associated periodic discharges. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(4):289–294. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yoshikawa H, Abe T. Periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges in children. J Child Neurol. 2003;18(11):803–805. doi: 10.1177/08830738030180111401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lewis DW, Johnson EL. Prognosis of periodic and rhythmic patterns in adult and pediatric populations. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;35(4):303–308. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Scher MS, Beggarly M. Clinical significance of focal periodic discharges in neonates. J Child Neurol. 1989;4(3):175–185. doi: 10.1177/088307388900400303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chen KS, Kuo MF, Wang HS, Huang SC. Periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges of pediatric patients in Taiwan. Pediatr Neurol. 2003;28(2):100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(02)00493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Raroque HG, Jr, Wagner W, Gonzales PC, et al. Reassessment of the clinical significance of periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges in pediatric patients. Epilepsia. 1993;34(2):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1993.tb02410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Watemberg N, Alehan F, Dabby R, Lerman-Sagie T, Pavot P, Towne A. Clinical and radiologic correlates of frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2002;19(6):535–539. doi: 10.1097/00004691-200212000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Dericioglu N, Khasiyev F, Arsava EM, Topcuoglu MA. Frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity (FIRDA) in the neurological intensive care: prevalence, determinants, and clinical significance. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2018;49(4):272–277. doi: 10.1177/1550059416688108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kim KT, Roh YN, Cho NH, Jeon JC. Clinical correlates of frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity without structural brain lesion. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2021;52(1):69–73. doi: 10.1177/1550059420922741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Menascu S, Mohamed I, Tshechmer SM, Shroff M, Cortez MA. The significance of frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity in children. Can J Neurol Sci. 2010;37(5):656–661. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100010854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Cerrahoğlu Şirin T, Bekdik Şirinocak P, Arkalı BN, Akıncı T, Yeni SN. Electroencephalographic features associated with intermittent rhythmic delta activity. Neurophysiol Clin. 2019;49(3):227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2019.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Appavu B, Riviello JJ. Electroencephalographic patterns in neurocritical care: pathologic contributors or epiphenomena? Neurocrit Care. 2018;29(1):9–19. doi: 10.1007/s12028-017-0424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Rodriguez Ruiz A, Vlachy J, Lee JW, et al. Association of periodic and rhythmic electroencephalographic patterns with seizures in critically Ill patients. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74(2):181–188. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.4990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Yoo JY, Marcuse LV, Fields MC, et al. Brief potentially ictal rhythmic discharges [B(I)RDs] in noncritically Ill adults. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;34(3):222–229. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hirsch LJ, Claassen J, Mayer SA, Emerson RG. Stimulus-induced rhythmic, periodic, or ictal discharges (SIRPIDs): a common EEG phenomenon in the critically ill. Epilepsia. 2004;45(2):109–123. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.38103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Subramaniam T, Jain A, Hall LT, et al. Lateralized periodic discharges frequency correlates with glucose metabolism. Neurology. 2019;92(7):e670–e674. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000006903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Witsch J, Frey HP, Schmidt JM, et al. Electroencephalographic periodic discharges and frequency-dependent brain tissue hypoxia in acute brain injury. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74(3):301–309. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ostendorf AP, Hartman ME, Friess SH. Early electroencephalographic findings correlate with neurologic outcome in children following cardiac arrest. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016;17(7):667. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ducharme-Crevier L, Press CA, Kurz JE, Mills MG, Goldstein JL, Wainwright MS. Early presence of sleep spindles on electroencephalography is associated with good outcome after pediatric cardiac arrest. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(5):452–460. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000001137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Abend NS, Topjian AA, Williams S. How much does it cost to identify a critically ill child experiencing electrographic seizures? J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(3):257–264. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Herman ST, Abend NS. Author Response: Concerns about utility and cost-effectiveness of continuous critical-care EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(5):442–443. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Grillo E. Concerns about utility and cost-effectiveness of continuous critical-care EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(5):442. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Mahfooz N, Weinstock A, Afzal B, et al. Optimal duration of continuous video-electroencephalography in term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and therapeutic hypothermia. J Child Neurol. 2017;32(6):522–527. doi: 10.1177/0883073816689325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Benedetti GM, Vartanian RJ, McCaffery H, Shellhaas RA. Early electroencephalogram background could guide tailored duration of monitoring for neonatal encephalopathy treated with therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr. 2020;221:81–87.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Walker SA, Armour EA, Crants S, Carson RP, Reddy SB. Electroencephalogram background and head ultrasound together stratify seizure risk in neonates undergoing hypothermia. Epilepsy Behav. 2022;133:108784. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.108784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Cornet MC, Pasupuleti A, Fang A, et al. Predictive value of early EEG for seizures in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. Pediatr Res. 2018;84(3):399–402. doi: 10.1038/s41390-018-0040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Fung FW, Jacobwitz M, Parikh DS, et al. Development of a model to predict electroencephalographic seizures in critically ill children. Epilepsia. 2020;61(3):498–508. doi: 10.1111/epi.16448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Fung FW, Parikh DS, Jacobwitz M, et al. Validation of a model to predict electroencephalographic seizures in critically ill children. Epilepsia. 2020;61(12):2754–2762. doi: 10.1111/epi.16724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Abend NS, Dlugos DJ, Clancy RR. A review of long-term EEG monitoring in critically ill children with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, congenital heart disease, ECMO, and stroke. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;30(2):134–142. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3182872af9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Fung FW, Fan J, Vala L, et al. EEG monitoring duration to identify electroencephalographic seizures in critically ill children. Neurology. 2020;95(11):e1599–e1608. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000010421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Hu J, Fung FW, Jacobwitz M, et al. Machine learning models to predict electroencephalographic seizures in critically ill children. Seizure. 2021;87:61–68. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2021.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Abend NS, Dlugos DJ, Hahn CD, Hirsch LJ, Herman ST. Use of EEG monitoring and management of non-convulsive seizures in critically ill patients: a survey of neurologists. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12(3):382–389. doi: 10.1007/s12028-010-9337-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Gavvala J, Abend N, LaRoche S, et al. Continuous EEG monitoring: a survey of neurophysiologists and neurointensivists. Epilepsia. 2014;55(11):1864–1871. doi: 10.1111/epi.12809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Swisher CB, Sinha SR. Utilization of quantitative EEG trends for critical care continuous EEG monitoring: a survey of neurophysiologists. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;33(6):538–544. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Farias-Moeller R, Jayakar A, Guerriero RM, Carpenter JL, Wainwright MS, Harrar DB. Pediatric critical care neurologists in the United States and Canada: a survey of clinical practice experience. J Child Neurol. 2022 doi: 10.1177/08830738211070099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ko J, Park U, Kim D, Kang SW. Quantitative electroencephalogram standardization: a sex- and age-differentiated normative database. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:766781. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.766781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Britton JW, Frey LC, Hopp JL, et al. In: St. Louis EK, Frey LC, eds. Electroencephalography (EEG): An Introductory Text and Atlas of Normal and Abnormal Findings in Adults, Children, and Infants. Chicago: American Epilepsy Society Copyright ©2016 by American Epilepsy Society.; 2016. [PubMed]
- 137.Purdon PL, Sampson A, Pavone KJ, Brown EN. Clinical electroencephalography for anesthesiologists: part I: background and basic signatures. Anesthesiology. 2015;123(4):937–960. doi: 10.1097/aln.0000000000000841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Ruijter BJ, van Putten M, van den Bergh WM, Tromp SC, Hofmeijer J. Propofol does not affect the reliability of early EEG for outcome prediction of comatose patients after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(8):1263–1270. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.04.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Maynard D, Prior PF, Scott DF. Device for continuous monitoring of cerebral activity in resuscitated patients. Br Med J. 1969;4(5682):545–546. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5682.545-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Prior PF, Maynard DE, Sheaff PC, et al. Monitoring cerebral function: clinical experience with new device for continuous recording of electrical activity of brain. Br Med J. 1971;2(5764):736–738. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5764.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Shah NA, Wusthoff CJ. How to use: amplitude-integrated EEG (aEEG) Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2015;100(2):75–81. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-305676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.DeLaGarza-Pineda O, Chang T. Amplitude-integrated EEG in the neonatal intensive care unit. In: Sansevere AJ, Harrar DB, eds. New York: Springer, pp 289–318.
- 143.Tomko SR, Hahn C, Guerriero RM. Quantitative EEG in the pediatric intensive care unit. In: Sansevere AJ, Harrar DB, eds. New York: Springer, pp 319–371.
- 144.Feng G, Jiang G, Li Z, Wang X. Prognostic value of electroencephalography (EEG) for brain injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Neurol Sci. 2016;37(6):843–849. doi: 10.1007/s10072-016-2475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Munjal NK, Bergman I, Scheuer ML, Genovese CR, Simon DW, Patterson CM. Quantitative electroencephalography (EEG) predicting acute neurologic deterioration in the pediatric intensive care unit: a case series. J Child Neurol. 2022;37(1):73–79. doi: 10.1177/08830738211053908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Sansevere AJ, DiBacco ML, Pearl PL, Rotenberg A. Quantitative electroencephalography for early detection of elevated intracranial pressure in critically ill children: case series and proposed protocol. J Child Neurol. 2022;37(1):5–11. doi: 10.1177/08830738211015012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Frohlich J, Johnson MA, McArthur DL, et al. Sedation-induced burst suppression predicts positive outcome following traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol. 2021;12:750667. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.750667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Brandon Westover M, Shafi MM, Ching S, et al. Real-time segmentation of burst suppression patterns in critical care EEG monitoring. J Neurosci Methods. 2013;219(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Ng MC, Jing J, Westover MB. A primer on EEG spectrograms. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(3):177–183. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Foreman B, Claassen J. Quantitative EEG for the detection of brain ischemia. Crit Care. 2012;16(2):216. doi: 10.1186/cc11230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Swarnalingam ES, RamachandranNair R, Choong KLM, Jones KC. Non-neurophysiologist physicians and nurses can detect subclinical seizures in children using a panel of quantitative EEG trends and a seizure detection algorithm. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2020 doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Goenka A, Boro A, Yozawitz E. Comparative sensitivity of quantitative EEG (QEEG) spectrograms for detecting seizure subtypes. Seizure. 2018;55:70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Gudmundsson S, Runarsson TP, Sigurdsson S, Eiriksdottir G, Johnsen K. Reliability of quantitative EEG features. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(10):2162–2171. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Akeju O, Westover MB, Pavone KJ, et al. Effects of sevoflurane and propofol on frontal electroencephalogram power and coherence. Anesthesiology. 2014;121(5):990–998. doi: 10.1097/aln.0000000000000436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Bauerschmidt A, Eliseyev A, Doyle KW, et al. Predicting early recovery of consciousness after cardiac arrest supported by quantitative electroencephalography. Resuscitation. 2021;165:130–137. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Bastos AM, Schoffelen JM. A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015;9:175. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Thul A, Lechinger J, Donis J, et al. EEG entropy measures indicate decrease of cortical information processing in Disorders of Consciousness. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127(2):1419–1427. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Gosseries O, Schnakers C, Ledoux D, et al. Automated EEG entropy measurements in coma, vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome and minimally conscious state. Funct Neurol. 2011;26(1):25–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Chen W, Liu G, Su Y, et al. EEG signal varies with different outcomes in comatose patients: a quantitative method of electroencephalography reactivity. J Neurosci Methods. 2020;342:108812. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Ferlazzo E, Mammone N, Cianci V, et al. Permutation entropy of scalp EEG: a tool to investigate epilepsies: suggestions from absence epilepsies. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Li X, Ouyang G, Richards DA. Predictability analysis of absence seizures with permutation entropy. Epilepsy Res. 2007;77(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Lalgudi Ganesan S, Hahn CD. Spectrograms for seizure detection in critically ill children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(3):195–206. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Zafar SF, Amorim E, Williamsom CA, et al. A standardized nomenclature for spectrogram EEG patterns: Inter-rater agreement and correspondence with common intensive care unit EEG patterns. Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(9):2298–2306. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2020.05.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Topjian AA, Fry M, Jawad AF, et al. Detection of electrographic seizures by critical care providers using color density spectral array after cardiac arrest is feasible. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2015;16(5):461–467. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000000352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Stewart CP, Otsubo H, Ochi A, Sharma R, Hutchison JS, Hahn CD. Seizure identification in the ICU using quantitative EEG displays. Neurology. 2010;75(17):1501–1508. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f9619e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Lalgudi Ganesan S, Stewart CP, Atenafu EG, et al. Seizure identification by critical care providers using quantitative electroencephalography. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(12):e1105–e1111. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000003385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Pensirikul AD, Beslow LA, Kessler SK, et al. Density spectral array for seizure identification in critically ill children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;30(4):371–375. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e31829de01c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Akman CI, Micic V, Thompson A, Riviello JJ., Jr Seizure detection using digital trend analysis: factors affecting utility. Epilepsy Res. 2011;93(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2010.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Du Pont-Thibodeau G, Sanchez SM, Jawad AF, et al. Seizure detection by critical care providers using amplitude-integrated electroencephalography and color density spectral array in pediatric cardiac arrest patients. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(4):363–369. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000001099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Rowberry T, Kanthimathinathan HK, George F, et al. Implementation and early evaluation of a quantitative electroencephalography program for seizure detection in the PICU. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(6):543–549. doi: 10.1097/pcc.0000000000002278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Prendergast E, Mills MG, Kurz J, Goldstein J, Pardo AC. Implementing quantitative electroencephalogram monitoring by nurses in a pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Nurse. 2022;42(2):32–40. doi: 10.4037/ccn2022680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Din F, Lalgudi Ganesan S, Akiyama T, et al. Seizure detection algorithms in critically ill children: a comparative evaluation. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(4):545–552. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000004180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Alkhachroum A, Ganesan SL, Koren JP, et al. Quantitative EEG-based seizure estimation in super-refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2022;36(3):897–904. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01395-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Sansevere AJ, Hahn CD, Abend NS. Conventional and quantitative EEG in status epilepticus. Seizure. 2019;68:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2018.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Lee S, Zhao X, Davis KA, Topjian AA, Litt B, Abend NS. Quantitative EEG predicts outcomes in children after cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2019;92(20):e2329–e2338. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Forgacs PB, Frey HP, Velazquez A, et al. Dynamic regimes of neocortical activity linked to corticothalamic integrity correlate with outcomes in acute anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2017;4(2):119–129. doi: 10.1002/acn3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Claassen J, Doyle K, Matory A, et al. Detection of brain activation in unresponsive patients with acute brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(26):2497–2505. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Sokoliuk R, Degano G, Banellis L, et al. Covert speech comprehension predicts recovery from acute unresponsive states. Ann Neurol. 2021;89(4):646–656. doi: 10.1002/ana.25995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Bembea MM, Felling RJ, Caprarola SD, et al. Neurologic outcomes in a two-center cohort of neonatal and pediatric patients supported on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Asaio J. 2020;66(1):79–88. doi: 10.1097/mat.0000000000000933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Cengiz P, Seidel K, Rycus PT, Brogan TV, Roberts JS. Central nervous system complications during pediatric extracorporeal life support: incidence and risk factors. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(12):2817–2824. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000189940.70617.c3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Xie A, Lo P, Yan TD, Forrest P. Neurologic complications of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a review. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017;31(5):1836–1846. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2017.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Appavu BL, Temkit MH, Foldes ST, et al. Quantitative electroencephalography after pediatric anterior circulation stroke. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(7):610–615. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Nuwer MR, Jordan SE, Ahn SS. Evaluation of stroke using EEG frequency analysis and topographic mapping. Neurology. 1987;37(7):1153–1159. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Ahn SS, Jordan SE, Nuwer MR, Marcus DR, Moore WS. Computed electroencephalographic topographic brain mapping. A new and accurate monitor of cerebral circulation and function for patients having carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 1988;8(3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0741-5214(88)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Brito R, Baltar A, Berenguer-Rocha M, et al. Intrahemispheric EEG: a new perspective for quantitative EEG assessment in poststroke individuals. Neural Plast. 2021;2021:5664647. doi: 10.1155/2021/5664647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Finnigan S, van Putten MJ. EEG in ischaemic stroke: quantitative EEG can uniquely inform (sub-)acute prognoses and clinical management. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013;124(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2012.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Huguenard AL, Guerriero RM, Tomko SR, et al. Immediate postoperative electroencephalography monitoring in pediatric moyamoya disease and syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2021;118:40–45. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2021.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Rosenthal ES, Biswal S, Zafar SF, et al. Continuous electroencephalography predicts delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective study of diagnostic accuracy. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(5):958–969. doi: 10.1002/ana.25232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Baang HY, Chen HY, Herman AL, et al. The utility of quantitative EEG in detecting delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(3):207–215. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Kamitaki BK, Tu B, Wong S, Mendiratta A, Choi H. Quantitative EEG changes correlate with post-clamp ischemia during carotid endarterectomy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;38(3):213–220. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Dickey AS, Mitsias PD, Olango WM, et al. The prognostic value of quantitative EEG in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(4):276–282. doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Zhang X, Su J, Yu J, et al. Application of intraoperative electrocorticography in bypass surgery for adult moyamoya disease: a preliminary study. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2022;27(1):26. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2701026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Nagaraj SB, Tjepkema-Cloostermans MC, Ruijter BJ, Hofmeijer J, van Putten M. The revised Cerebral Recovery Index improves predictions of neurological outcome after cardiac arrest. Clin Neurophysiol. 2018;129(12):2557–2566. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Guerriero RM, Morrissey MJ, Loe M, et al. Macroperiodic oscillations are associated with seizures following acquired brain injury in young children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 doi: 10.1097/wnp.0000000000000828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Loe ME, Khanmohammadi S, Morrissey MJ, et al. Resolving and characterizing the incidence of millihertz EEG modulation in critically ill children. Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;137:84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2022.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Loe ME, Morrissey MJ, Tomko SR, Guerriero RM, Ching S. Detecting slow narrowband modulation in EEG signals. J Neurosci Methods. 2022;378:109660. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Tanaka M, Kidokoro H, Kubota T, et al. Pseudo-sawtooth pattern on amplitude-integrated electroencephalography in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res. 2020;87(3):529–535. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0567-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Falsaperla R, Scalia B, Giaccone F, et al. aEEG vs cEEG's sensivity for seizure detection in the setting of neonatal intensive care units: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2022;111(5):916–926. doi: 10.1111/apa.16251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Rakshasbhuvankar A, Paul S, Nagarajan L, Ghosh S, Rao S. Amplitude-integrated EEG for detection of neonatal seizures: a systematic review. Seizure. 2015;33:90–98. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2015.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Ulate-Campos A, Coughlin F, Gaínza-Lein M, Fernández IS, Pearl PL, Loddenkemper T. Automated seizure detection systems and their effectiveness for each type of seizure. Seizure. 2016;40:88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2016.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.