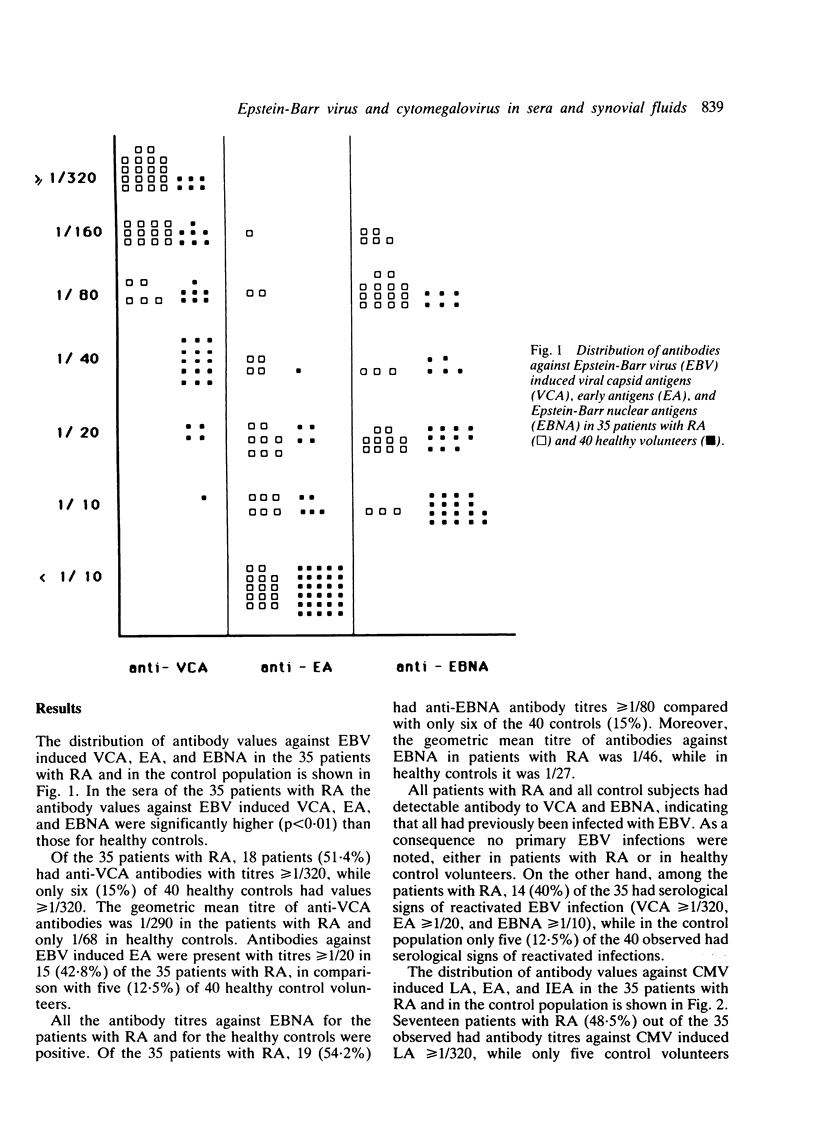
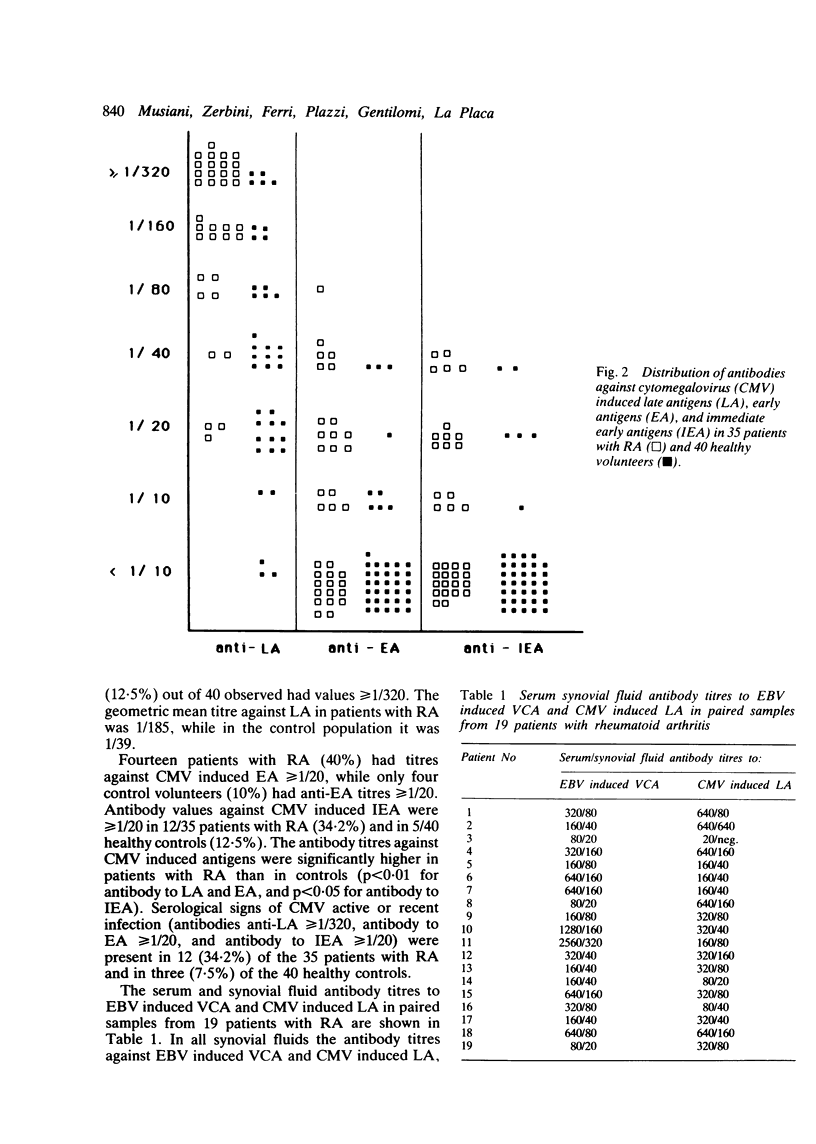
Abstract
The immune response against two herpesviruses has been determined in sera and matched synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and compared with that of a healthy control population. The increased level of antibody to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induced antigens in patients with RA resembles the antibody pattern observed against cytomegalovirus (CMV) induced antigens, which suggests the presence of a pathological condition in patients with RA that can reactivate latent viral infections. The antibody response against EBV and CMV observed in synovial fluids excludes the local production of specific antibodies against EBV and CMV antigens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alspaugh M. A., Henle G., Lennette E. T., Henle W. Elevated levels of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus antigens in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1134–1140. doi: 10.1172/JCI110127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslpaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Serum antibody in rheumatoid arthritis reactive with a cell-associated antigen. Demonstration by precipitation and immunofluorescence. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jul-Aug;19(4):711–719. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197607/08)19:4<711::aid-art1780190409>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Niederman J. C., Feorino P., Vaughan J. H. Antibody to the rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen. Its relationship to in vivo Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1238–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa S., Barrasso R., Terzano P., Zerbini M., Carpi C., Musiani M. Detection of active Epstein-Barr infection in pregnant women. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):335–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02013663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Edwards J. M., Sweny P., Hoffbrand A. V., Janossy G. Studies on long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-BArr virus in immunosuppressed renal allograft recipients. Int J Cancer. 1981 Dec;28(6):705–709. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAGNOSTIC criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 1958 revision by a committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Mar;18(1):49–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J. Impaired regulation of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphocyte proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis is due to a T cell defect. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1899–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell P. B., Aitcheson C. T., Pearson G. R., Tan E. M. Seroepidemiological study of relationships between Epstein-Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):681–687. doi: 10.1172/JCI110083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Chilton T., Rhodes G., Vaughan J. H. Lack of reactivity of rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane DNA with cloned Epstein Barr virus DNA probes. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):498–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R., Sportsman R., Rhodes G., Luka J., Pearson G., Vaughan J. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane contains a 62,000-molecular-weight protein that shares an antigenic epitope with the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded associated nuclear antigen. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1539–1547. doi: 10.1172/JCI112469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus-specific serology in immunologically compromised individuals. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4222–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Young A., Pilkington C., Sutherland S., Roitt I. M. Antibodies to EB virus- and cytomegalovirus-induced antigens in early rheumatoid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):341–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musiani M., Zerbini M., Gentilomi G., La Placa M. Indirect alkaline phosphatase immunoenzymatic staining for the detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-induced virus capsid antigens and early antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):302–304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.302-304.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musiani M., Zerbini M., La Placa M. Rapid diagnosis of viral infections by an alkaline phosphatase immunocytochemical method. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 17;88(2):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Carson D. A., Valbracht J., Houghten R., Vaughan J. H. Human immune responses to synthetic peptides from the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto K., Aiba M., Katayama I., Sullivan J. L., Humphreys R. E., Purtilo D. T. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-specific antigens in patients with hairy-cell leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1981;27(4):453–458. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. W., McGinty L., Simon L., Smith C. A., Godzeski C. W., Boyd R. J. Association of parvoviruses with rheumatoid arthritis of humans. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1425–1428. doi: 10.1126/science.6701529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumaya C. V., Myers L. W., Ellison G. W. Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1980 Feb;37(2):94–96. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500510052009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Andersen H. K., Spencer E. S., Klein G. Antibodies against cytomegalovirus-induced early antigens (CMV-EA) in immunosuppressed renal-allograft recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):502–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Steinberg A. D., Yarchoan R., Heilman C. A., Pike S. E., De Seau V., Blaese R. M. Abnormally elevated frequency of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in the blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1789–1795. doi: 10.1172/JCI111388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltri R. W., Wainwright W. H., Sprinkle P. M. Immunologic identification of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen in a P3HR-1 cell extract. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Aug;57(2):245–253. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbini M., Musiani M., Gentilomi G., La Placa M. Detection of specific immunoglobulin M antibodies to cytomegalovirus by using monoclonal antibody to immunoglobulin M in an indirect immunofluorescence assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):166–168. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.166-168.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


