Abstract
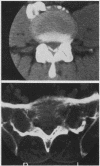
An axial computed tomographic (CT) scan of the lumbosacral regions was performed in 65 patients. The patient population was divided into two groups. The first (control) group included 40 elderly patients without calcification of the ligamenta flava. The second group included 25 patients with ankylosing spondylitis. More than 90% of those in the second group showed calcified lumbosacral ligamenta flava. In two patients these calcifications produced spinal stenosis. The diagnostic and practical importance of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowie E. A., Glasgow G. L. Cauda Equina Lesions Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Br Med J. 1961 Jul 1;2(5243):24–27. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5243.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakura K., Furukawa T., Takasu T., Mannen T., Toyokura Y. [Cervical myelopathy due to ossification of ligamenta flava: report of a case (author's transl)]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1978 Feb;18(2):96–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano N., Yoshida S., Ohwada T., Yada K., Sasaki K., Matsuno T. Cervical radiculomyelopathy caused by deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the ligamenta flava. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1980 Feb;52(2):279–283. doi: 10.3171/jns.1980.52.2.0279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota M., Baba I., Sumida T. Myelopathy due to ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the cervical spine. A report of two cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1981 Nov-Dec;6(6):553–559. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198111000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luken M. G., 3rd, Patel D. V., Ellman M. H. Symptomatic spinal stenosis associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Neurosurgery. 1982 Nov;11(5):703–705. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198211000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. B. The neurological complications of ankylosing spondylitis. J Neurol Sci. 1968 May-Jun;6(3):561–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka K., Kaneda K., Ito T., Takei H., Sugimoto S., Tsuru M. Ossification of spinal ligaments causing thoracic radiculomyelopathy. Radiology. 1982 May;143(2):463–468. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.2.7071348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka K., Kaneda K., Sato S., Iwasaki Y., Abe S., Takei H., Tsuru M., Tashiro K., Abe H., Fujioka Y. Myelopathy due to ossification or calcification of the ligamentum flavum: radiologic and histologic evaluations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1983 May-Jun;4(3):629–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Miyaoka M., Sumie H., Nakazato T., Ishii S. Cervical radiculomyelopathy due to calcification of the ligamenta flava. Surg Neurol. 1984 May;21(5):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(84)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omojola M. F., Cardoso E. R., Fox A. J., Drake C. G., Durward Q. J. Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossified ligamentum flavum. J Neurosurg. 1982 Mar;56(3):448–450. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.56.3.0448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. L., Gordon D. A., Ogryzlo M. A., McPhedran R. S. The cauda equina syndrome of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Apr;78(4):551–554. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-4-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi T., Kato H., Shiozawa Z., Yasuhara T., Kanematsu H. [Neurologic disorders caused by ossification of the ligamenta flava of the thoracic spine; analysis of x-ray picture and diagnostic significance]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1972 Nov;12(11):562–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]