Abstract
Background/objective
Bodyweight exercises performed at home could be a complementary approach to improve health-related fitness in people having little spare time and during stay-at-home periods. This study then investigated body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, and neuromuscular adaptations to a home-based, video-directed, whole-body high-intensity interval training (WB-HIIT).
Methods
Fourteen subjects participated to an 8-week WB-HIIT (6 females, 23 ± 1 years) and fourteen were included in a non-exercise control group (CTL; 6 females, 24 ± 4 years). All took part to pre- and post-intervention assessments of body composition, peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) and first ventilatory threshold (VT1; index of aerobic capacity), dynamic (leg press 3-repetition maximum) and isometric strength (knee extensors maximal isometric contractions with assessment of voluntary activation), and muscle endurance during an isometric submaximal contraction maintained till exhaustion. WB-HIIT consisted in 30-s all-out whole-body exercises interspaced with 30 s of active recovery. Training sessions were performed at home by means of videos with demonstration of exercises. Heart rate was monitored during sessions.
Results
WB-HIIT increased VO2peak (5%), VT1 (20%), leg lean mass (3%), dynamic (13%) and isometric strength (6%), and muscle endurance (28%; p < 0.05), while they did not improve in CTL. VO2peak increase was correlated (r = 0.56; p < 0.05) with the time spent above 80% of maximal heart rate during training sessions. Isometric strength increase was correlated with change in voluntary activation (r = 0.74; p < 0.01).
Conclusion
The home-based WB-HIIT induced concomitant cardiorespiratory fitness and neuromuscular improvements. The predominant effect was observed for aerobic capacity and muscle endurance which could improve exercise tolerance and reduce fatigability.
Keywords: VO2peak, First ventilatory threshold, Muscle strength, Muscle endurance, Voluntary activation
1. Introduction
It is commonly admitted that regular physical activity is beneficial for health.1 The World Health Organization recommends practicing 150–300 min of moderate to vigorous intensity aerobic activity per week, and muscle-strengthening activities on 2 or more days a week.2 Unfortunately, a large part of the population does not meet these recommendations.3 Among barriers to physical activity, lack of time or nearby facilities, cost, and weather conditions are the most mentioned.4 More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions exacerbated sedentary behavior and limited participation in outdoor activities.5, 6, 7 In this context, a call was made to develop exercise interventions easily achievable at home, and building both endurance and strength.7, 8, 9 These type of interventions could be also useful to overcome the above-mentioned barriers to physical activity. Several previous studies proposed home-based interventions, but mostly in a context of telerehabilitation for patients with chronical diseases10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 or elderly subjects.18, 19, 20 In these studies, exercise type and intensity were adapted for the targeted population, and interventions either focused on a single component (e.g., endurance, strength, or balance)10,12,18 or aimed to improve both strength and endurance.11,15,16,20 The latter approach involves several aerobic and strength training sessions per week16 or longer sessions combining both types of training.11,15,20 Protocols and results of these interventions may thus not be transferable to healthy adults having many constraints on their time.
Among interventions that can be proposed at home, whole-body high intensity interval training (WB-HIIT) could be particularly relevant for promoting physical activity in healthy adults. WB-HIIT is a form of high intensity interval training (HIIT) considered as a time-efficient modality to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.21 While traditional HIIT involves running, biking, or rowing exercises, WB-HIIT uses multi-joint exercises performed with the resistance of bodyweight. It has then the potential to target simultaneously the cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular systems.22 Therefore, WB-HIIT could be an attractive option for healthy adults having little spare time. Another advantage of WB-HIIT is that it can be easily provided by means of videos. Videos are more engaging than text-based content and can be easily shared through social media platforms.23,24
Benefits of WB-HIIT on health-related fitness were exposed in a recent meta-analysis highlighting improvements of cardiorespiratory fitness, body composition, and muscle strength and endurance.25 However, only a few studies used home-based interventions.26, 27, 28, 29, 30 In addition, none investigated the neuromuscular function (i.e., maximal strength and associated volitional drive, and endurance time during a submaximal contraction). There is then no evidence that home-based WB-HIIT could simultaneously improve body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, and neuromuscular function.
Accordingly, the aim of this study is to assess the effectiveness of an 8-week home-based WB-HIIT to improve the above-mentioned components, and to better understand the determinants of training-induced adaptations. We hypothesize that the home-based WB-HIIT will simultaneously improve body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, and neuromuscular function.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Participants and study design
This study used a randomized controlled design with 2 groups (WB-HIIT and control) and repeated measures on time (baseline to post-intervention). To be included, subjects had to be aged between 18 and 50 years, and to be below the World Health Organization's recommendations in terms of physical activity participation.2 Exclusion criteria were: (1) being involved in a structured endurance or strength training within the last 6 months, (2) having a condition limiting participation to maximal physical tests and training (e.g., cancer, cardiovascular or lung disease, neuromuscular or musculoskeletal disorder). All volunteers received written information regarding the protocol and had the opportunity to ask questions before signing the written consent. The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Erasmus Hospital in Brussels (reference: B4062019942321).
The study took place during the COVID-19 pandemic period (between February and November 2021). Participants were randomly assigned either to the WB-HIIT or to the control group (CTL). Participants assigned to the WB-HIIT participated to an 8-week intervention performed at home while maintaining their dietary habits. CTL participants were asked to keep their physical and dietary habits as stable as possible.
Participants first completed the global physical activity questionnaire to ensure they met inclusion criteria regarding physical activity participation. Before and after the intervention, evaluation sessions were carried out in our laboratory on 3 different days interspaced by 48 h. During the first session, participants underwent body composition assessment and a maximal cardiopulmonary exercise test to assess cardiorespiratory fitness. Neuromuscular assessment was performed during 2 separate sessions to avoid fatigue accumulation. Firstly, knee extensors maximal isometric torque, voluntary activation, and endurance time during a submaximal isometric contraction were assessed. Then, during the last session, lower limb dynamic strength was assessed by measuring the 3-repetition maximum (3-RM) on a leg press.
Neither participants nor investigators were blinded regarding group allocation during the intervention and assessments. However, each assessment protocol was standardized. Indeed, the investigator followed written instructions indicating the sequence of steps and encouragement during tests. Then, group allocation and timing of evaluation sessions were concealed, and data were independently analyzed by two investigators.
Based on the size effect reported in a recent meta-analysis on the effects of WB-HIIT on health-related fitness,25 sample size calculation was performed using G∗Power (University of Düsseldorf, Germany). The following parameters were used: 2 groups, 2 measurements, effect size of 0.38, two-tailed alpha error of 0.05, power (1-ß error) of 0.90, nonsphericity correction of 1, and correlation between repeated measures of 0.5. The calculation suggested a minimal total sample of 22 participants to identify statistically meaningful effects.
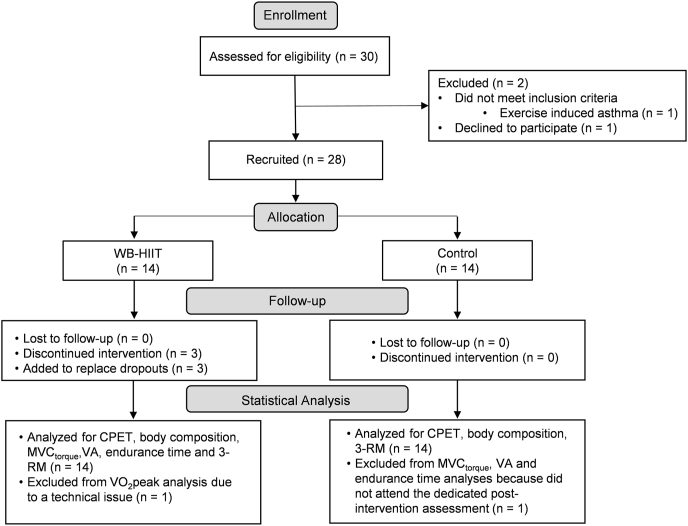
The participant flowchart is presented in Fig. 1. Thirty healthy adults were initially recruited. One of them declined to participate, and one did not meet inclusion criteria. The remaining subjects were assigned to the WB-HIIT group or the CTL group. To balance the number of males and females between both groups, participants were first stratified by sex (two strata: male and female). Within each stratum, block randomization was then applied to assign an equal number of subjects to the WB-HIIT and control group. Three subjects from the WB-HIIT group discontinued the exercise intervention after a few sessions, two due to a health problem, unrelated to the study, and the third one due to a lack of time. To replace these early dropouts, three additional subjects were included. Ultimately, 28 subjects took part to pre-intervention sessions and finished the WB-HIIT (n = 14) or CTL intervention (n = 14). Their anthropometric characteristics and physical activity participation at inclusion are presented in Table 1.
Fig. 1.
Participant flowchart. CPET, cardiopulmonary exercise test; MVC, maximum voluntary contraction; 3-RM, 3-repetition maximum; VA, voluntary activation; WB-HIIT, whole-body high intensity interval training.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics and recreational physical activity of the subjects at inclusion.
| Group | Ratio F/M | Age (years) | Height (cm) | Body mass (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Intense PA (min/wk) | Moderate PA (min/wk) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WB-HIIT | 6/8 | 23.1 ± 1.3 | 170.6 ± 11.5 | 63.8 ± 11.2 | 21.7 ± 3.3 | 8 ± 20 | 19 ± 25 |
| CTL | 6/8 | 24.0 ± 3.9 | 170.8 ± 8.2 | 70.3 ± 18.1 | 23.8 ± 5.3 | 6 ± 17 | 41 ± 43 |
BMI, body mass index. CTL, control group. F, female. M, male. PA, physical activity. WB-HIIT, whole-body high-intensity interval training group. wk, week.
Out of these 28 subjects, MVC torque, voluntary activation, and endurance time of one female subject from the CTL group were excluded from the analysis since she did not take part to the post-intervention session dedicated to these measurements. The VO2peak value of one female subject from the WB-HIIT group was also excluded due to a technical problem with the breath-by-breath analyzer during the post-intervention session.
2.2. Body composition assessment
Total and segmental body composition was assessed after overnight fast using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry31 (DXA; Lunar Prodigy, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, USA), and was analyzed using the enCORE software (version 15.0).
2.3. Cardiorespiratory fitness assessment
Cardiorespiratory fitness was assessed during an incremental cardiopulmonary exercise test performed on a stationary bike (Ergoselect 100, Ergoline GmbH, Germany) following standard recommendations.32 Oxygen uptake (VO2), carbon dioxide production (VCO2) and ventilation (VE) were collected breath-by-breath through a tightly fitted facial mask. Expiratory gas was analyzed using a cardiopulmonary exercise system (Ergocard, Medisoft, Belgium) calibrated with room and standardized gas. The testing protocol started with a 3-min warm up at 20 W for women and 30 W for men. Workload was increased by 15 W/min for women and 20 W/min for men until exhaustion. The test was considered as maximal when at least two of the following criteria were met: (1) an increase in VO2 of less than 100 ml/min with a further increase in workload (plateau of VO2), (2) a respiratory exchange ratio greater than 1.15, (3) inability to maintain a pedaling frequency of 50 rpm, (4) or achievement of age-predicted maximal heart rate (HR). Since a plateau of VO2 was not observable in most of participants, VO2peak measured during the last minute of the test was reported. HR was monitored with a 12-lead EKG. The cardiopulmonary exercise test allowed the determination of VO2peak, maximal HR (HRmax), maximal power output (Wmax), and first ventilatory threshold (VT1) determined using the V-slope and the ventilatory equivalents method.32,33 VT1 is considered as the intensity associated with the onset of anaerobic metabolism during exercise, and is an objective index of aerobic exercise capacity in patients and healthy subjects.34 VO2peak and VO2 at VT1 were reported in absolute values (L/min) and in relative values (per kilogram of total lean mass).35
2.4. Neuromuscular assessments
2.4.1. Maximal isometric torque and muscle endurance
For the recording of neuromuscular parameters, subjects were sitting on an adjustable chair with a back rest. Their hip and knee angles were set at 100°. The right leg was attached to a force transducer, connected to the front of the chair using a velcro strap placed ∼2 cm above the lateral malleolus (detailed description previously published).36 To limit trunk displacement during contractions, the subject was secured to the chair by a harness.
The isometric torque produced by the knee extensor muscles was measured using a force transducer (linear range, 0–2500 N; U2000 load cell, Maywood Instruments Ltd, Basingstoke, UK). Torque was calculated by multiplying the force measured with the transducer by the lever arm (i.e., distance between the center of the transducer and the axis of rotation of the knee joint). Electromyographic activities (EMG) were recorded from the rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and biceps femoris muscles by means of 2 self-adhesive electrodes (3 M, Red Dot™) placed over each muscle belly. The reference electrodes were located over the lateral condyle of the tibia. Before placing the electrodes, skin was shaved when necessary and cleaned with a solution of alcohol, ether, and acetone to reduce electrode-skin impedance. To ensure similar recording conditions during the pre- and post-intervention sessions, location of the EMG electrodes on each muscle was recorded during the first session to place them in the same position during the post-intervention session. EMG signals were amplified (x 1000) and filtered (10 Hz - 1 kHz) by a custom-made differential amplifier.
Torque and EMG signals were acquired on a computer at a sampling rate of 2 kHz with a data-acquisition system (Model MP 150, Biopac Systems, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) and analyzed off-line with associated AcqKnowledge 4.1 software.
To assess voluntary activation and muscle contractile properties, electrical stimulation was delivered to the femoral nerve by a constant current stimulator (pulse duration 200-μs; DS7AH Digitimer, Welwyn Garden City, UK) through self-adhesive electrodes (3 M, Red Dot™). The electrodes were placed over the nerve in the femoral triangle (cathode) and between the greater trochanter and the iliac crest (anode).36 The precise location of the cathode was determined at rest by using weak electrical stimulation. The stimulus intensity was then increased to induce a maximal twitch and EMG response in the vastus medialis. The intensity of the stimulation was set 30% above to ensure a maximal activation of the muscles at rest and during contraction.
The testing took place as follows. At their arrival to the laboratory, EMG and stimulating electrodes were placed and subjects were installed in the experimental chair. After a warm-up (3 × 5 contractions at respectively 25, 50, and 75% of the maximum estimated by the subject), two familiarization 3-s isometric maximal voluntary contractions (MVC) were performed with a 3-min rest interval. The experimental recordings then started with three 3-s MVC interspersed by 3-min rest intervals. Voluntary activation was tested using the interpolated twitch technique with paired supramaximal electrical stimuli delivered at 10-ms interval during the MVC plateau and at rest, immediately after the end of the MVC.36 Finally, after a 10-min rest period, muscle endurance (i.e., the ability to maintain a specific percentage of MVC for a prolonged period of time)37 was assessed during a 30% MVC contraction maintained till exhaustion.38 Visual feedback of the actual and target torque was displayed on a monitor located in front of the subject.
MVC torque and associated average value of the rectified EMG (aEMG) of the vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, and biceps femoris were measured for a 500-ms period during the plateau of the three MVC. Values measured during the two trials that yielded the largest MVC torque were averaged and used to calculate 30% MVC. The peak torque of the twitch evoked at rest by the paired stimulation was also measured. Voluntary activation level was calculated according to the following equation: (1 – superimposed torque/torque of the twitch induced at rest in response to paired stimulation) x 100.39,40 The superimposed torque was calculated as the difference between the superimposed peak torque and the MVC torque. To quantify muscle endurance, we measured the endurance time from the beginning of the contraction till the moment subjects were 10% below the target torque, for at least 5 s, despite verbal encouragement.
2.4.2. Dynamic lower limb strength
Dynamic lower limb strength was assessed through the 3-RM performed on an inclined leg press (Hammer strength, IL, USA). Evaluation began with a 5-min warm-up on a stationary bike. Subjects were then asked to perform a specific warm-up consisting in 10 repetitions on the unloaded press (53 kg). Position of the feet on the press plate was recorded to reproduce the positioning during the post-intervention test. The load was then progressively increased, and participants were asked to achieve 4 repetitions with each load. A repetition was valid if it was performed over the full range of motion (90° flexion to full extension). A 5-min resting period was given between tries and the 3-RM was considered reached if participants achieved 3 repetitions and failed the 4th.
2.5. WB-HIIT intervention
The 8-week home WB-HIIT content was conceptualized by the investigators and was provided to the subjects by means of 4 videos created by the “French and Fit” company (Brussels, Belgium). In the videos, instructions of each exercise were given by a professional coach, and the exercise was simultaneously demonstrated by a subject. Training sessions started with a 3-min warm-up and ended with a few minutes of stretching. The conditioning phase consisted in sets of 4 × 30-s all-out whole-body exercises (Table 2) interspaced with 30 s of active recovery (jogging on the spot). Participants performed 3 sets during week 1 and 2, and 4 sets during week 3–8. Subjects were instructed to perform as many repetitions as possible during the exercise phase, and the coach gave verbal incentives. For the sake of progression, each exercise presented on the videos was proposed with a basic and harder variant (Table 2). Participants were asked to perform 3 sessions a week, on non-consecutive days, and to use each video for 2 weeks in a row. They were advised to perform the basic variant during the first week and the harder one during the second week. In addition, the technical and muscular difficulty of the exercises increased from video 1 to 4.
Table 2.
Description of the whole-body high intensity intervention exercises.
| Weeks | Sets number | Training program |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic variant | Harder variant | ||
| 1–2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| 3–4 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| 5–6 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| 7–8 | 4 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
HR was recorded during the sessions using a Polar H9 heart rate sensor (Polar, Finland) connected to the “Polar Beat” app on a smartphone or tablet. It was then exported to the Polar Flow app which displays mean and peak HR of each session, and the time spent in different intensity zones, expressed in percentage of the estimated HRmax based on age (220 – age): light (60–70%), moderate (70–80%), high 80–90%, and maximal (>90% HRmax) intensity.
Participants could contact the investigators in case of difficulty with the execution of exercises or with the recording of HR. They were also contacted regularly to ensure that the training is going well. At the end of the study, the WB-HIIT videos were made available to all participants.
2.6. Statistical analysis
Normality of the data was controlled using a Shapiro–Wilk normality test. To test if both groups presented similar characteristics at baseline (i.e., pre-intervention), a between-group comparison was conducted using either an independent t-test or a Mann-Whitney U test depending on the normality of distribution. A two-factor ANOVA (time [baseline vs. post-intervention] × group [WB-HIIT vs. CTL]) with repeated measures on time was used to analyze training induced changes when the distribution was normal. When a significant time × group interaction was found, the Bonferroni's post hoc test was used to compare baseline to post-intervention values in each group. When data did not present normal distribution (i.e., percentage of body fat, trunk fat mass, relative VO2peak, and endurance time), a Wilcoxon test was used to analyze within-group changes.
Since the initial voluntary activation level of our subjects was high (>90% in most of the subjects), and therefore less likely to improve, we correlated the individual initial voluntary activation level with the percentage of change in voluntary activation. To identify the main mechanism contributing to a potential improvement in MVC torque,41 the percentage of change in torque was correlated with the changes in voluntary activation and leg lean mass. As VO2peak changes could be influenced by the cardiorespiratory strain imposed during training sessions,42,43 the correlation between the time spent above 80% HRmax and the percentage of change in VO2peak was assessed. Pearson (rp) or Spearman (rs) correlation coefficients were calculated depending on data distribution.
Statistical analyses were performed using Jamovi software (version 2.2.5). Data are presented as mean ± SD when normally distributed or as median [25th, 75th percentiles] for data not normally distributed. The statistical level of significance was set at 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Intensity of WB-HIIT sessions
Except 2 subjects who missed 2 training sessions, all the participants completed the 24 sessions of the exercise intervention. Maximal and mean HR recorded during the WB-HIIT sessions were respectively 88 ± 5 and 74 ± 5 %HRmax. The time spent within the four intensity zones is presented in Table 3.
Table 3.
Time spent in the different intensity zones.
| Intensity zone | %HRmax | Time spent (min:sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light | 60–70% | 0:57 | [0:06, 1:44] |
| Moderate | 70–80% | 5:45 | [3:25, 7:44] |
| High | 80–90% | 5:58 | [3:56, 8:13] |
| Maximal | >90% | 0:11 | [0:00, 1:06] |
Time spent in each zone is presented as median [25th, 75th percentile]. %HRmax, percentage of maximum heart rate (220 − age).
3.2. Body composition
Data and statistical analysis of body composition at baseline and post-intervention are presented in Table 4. There was no significant difference at baseline between groups for total and segmental fat and lean mass (all baseline p-values >0.05). The statistical analysis did not reveal any significant change in total and segmental fat mass, percentage of body fat, and in total, arm and trunk lean mass (all ANOVA and within group comparisons p-values >0.05). A slight increase was observed for leg lean mass (3%) after WB-HIIT (p = 0.022), while it did not change in the CTL group (p > 0.99).
Table 4.
Baseline to post-intervention comparison of body composition.
| Parameter | Baseline | Post | Baseline WB-HIIT vs. CTL |
ANOVA Time × group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | p-value | |||
| Body fat percentage | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 31.6 [23.3, 34.7] | 31.5 [21.8, 34.3] | 0.541 | N/A |
| CTL | 31.3 [28.2, 37.4] | 31.4 [29.0, 36.9] | ||
| Total fat mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 18.4 ± 5.8 | 18.4 ± 5.9 | 0.195 | 0.556 |
| CTL | 22.0 ± 8.3 | 22.3 ± 8.5 | ||
| Total lean mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 42.4 ± 7.8 | 43.0 ± 7.7 | 0.420 | 0.261 |
| CTL | 45.5 ± 11.5 | 45.5 ± 11.8 | ||
| Leg fat mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 8.1 ± 2.3 | 8.0 ± 2.3 | 0.341 | 0.329 |
| CTL | 9.0 ± 2.9 | 9.2 ± 3.1 | ||
| Leg lean mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 16.6 ± 2.7 | 17.1 ± 2.6∗ | 0.290 | 0.014 |
| CTL | 18.0 ± 4.1 | 18.0 ± 4.0 | ||
| Arm fat mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 0.233 | 0.272 |
| CTL | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | ||
| Arm lean mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 4.5 ± 1.4 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | 0.361 | 0.922 |
| CTL | 5.1 ± 2.0 | 5.1 ± 2.1 | ||
| Trunk fat mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 7.7 [5.0, 9.4] | 7.4 [4.8, 9.4] | 0.401 | N/A |
| CTL | 9.2 [5.1, 11.3] | 8.9 [5.6, 11.7] | ||
| Trunk lean mass (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 18.4 ± 3.5 | 18.4 ± 3.5 | 0.594 | 0.943 |
| CTL | 19.3 ± 5.3 | 19.3 ± 5.5 | ||
Data presented as mean ± standard deviation or median [25th, 75th percentile]. ∗Significantly different from baseline value within this group (p < 0.05). CTL, control group. N/A, not applicable. WB-HIIT, whole-body high intensity interval training group.
3.3. Cardiorespiratory fitness adaptations
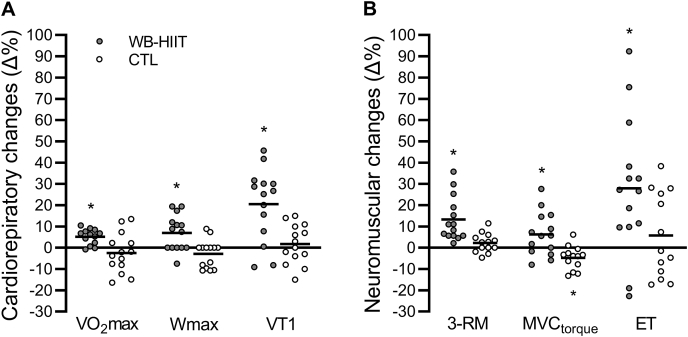
Data and statistical analysis of cardiorespiratory fitness at baseline and post-intervention are presented in Table 5. No statistical difference between groups was observed at baseline (all baseline p-values >0.05). The statistical analysis revealed a significant increase for the absolute and relative VO2peak (p = 0.031 and 0.027, respectively), VT1 (p = 0.002), and Wmax (p = 0.008) after WB-HIIT. No change was found in the CTL group (all within group comparisons p-values >0.05). The individual and mean percentages of change in VO2peak, Wmax, and VT1 after WB-HITT and in the CTL group are illustrated in Fig. 2A.
Table 5.
Baseline to post-intervention comparison of the cardiopulmonary exercise test parameters.
| Parameter | Baseline | Post | Baseline WB-HIIT vs. CTL |
ANOVA Time × group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | p-value | |||
| VO2peak (L/min) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 2.35 ± 0.51 | 2.46 ± 0.50∗ | 0.694 | 0.012 |
| CTL | 2.25 ± 0.69 | 2.20 ± 0.71 | ||
| Relative VO2peak (ml/kgLM/min) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 50.3 [49.3, 59.3] | 56.2 [50.9, 62.7]∗ | 0.155 | N/A |
| CTL | 47.8 [41.4, 57.7] | 48.3 [42.5, 53.6] | ||
| Wmax (Watts) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 193 ± 43 | 204 ± 40∗ | 0.743 | 0.004 |
| CTL | 186 ± 54 | 182 ± 57 | ||
| HRmax (bpm) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 193 ± 8 | 191 ± 8 | 0.131 | 0.835 |
| CTL | 187 ± 11 | 186 ± 9 | ||
| VO2at VT1 (L/min) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 1.31 ± 0.33 | 1.56 ± 0.36∗ | 0.922 | 0.012 |
| CTL | 1.30 ± 0.56 | 1.29 ± 0.46 | ||
| Relative VO2at VT1 (ml/kgLM/min) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 30.9 ± 4.5 | 36.3 ± 5.3∗ | 0.362 | 0.006 |
| CTL | 28.5 ± 8.5 | 28.4 ± 6.9 | ||
Data presented as mean ± standard deviation or median [25th, 75th percentile]. ∗Significantly different from baseline value within this group (p < 0.05). HRmax, maximal heart rate. LM, total lean mass. N/A, not applicable. Relative VO2peak, peak oxygen uptake per kilogram of total lean mass. Relative VO2at VT1, oxygen uptake at VT1 per kilogram of lean mass. VO2peak, peak oxygen uptake measured during the last minute of the test. VT1, first ventilatory threshold. Wmax, maximal power output.
Fig. 2.
Individual and mean changes in cardiorespiratory fitness (A) and neuromuscular function (B) expressed in percentage of baseline values. The horizontal lines represent the mean changes. ∗Significant change from baseline value within this group (p < 0.05). CTL, control group. ET, endurance time during submaximal contraction. MVC, maximum voluntary contraction. 3-RM, 3-repetition maximum. VO2peak, peak oxygen uptake. VT1, first ventilatory threshold. WB-HIIT, whole-body high-intensity interval training. Wmax, maximal power output.
There was a significant correlation between the time spent above 80% HRmax and the percentage of change in absolute (rs = 0.56; p = 0.049) and relative VO2peak (rs = 0.56; p = 0.048).
3.4. Neuromuscular adaptations
Data and statistical analysis of neuromuscular parameters at baseline and post-intervention are presented in Table 6. There was no significant difference between groups at baseline for any of the parameters (all baseline p-values >0.05). The 3-RM and MVC torque increased after WB-HIIT (p < 0.001 and 0.033, respectively), while MVC torque decreased in the CTL group (p = 0.033). Voluntary activation, aEMG during the MVC, and twitch torque at rest did not change significantly in any of the groups (all ANOVA and within group comparisons p-values >0.05). Endurance time measured during the 30% MVC contraction increased after WB-HIIT (p = 0.026) but did not change in the CTL group (p = 0.553). The individual and mean percentages of change in 3-RM, MVC torque, and endurance time after WB-HITT and in the CTL group are illustrated in Fig. 2B.
Table 6.
Baseline to post-intervention comparison of neuromuscular parameters.
| Parameter | Baseline | Post | Baseline WB-HIIT vs. CTL |
ANOVA Time × group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | p-value | |||
| 3-RM (kg) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 247 ± 62 | 278 ± 71∗ | 0.102 | 0.009 |
| CTL | 312 ± 127 | 321 ± 135 | ||
| MVC torque (N.m) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 159 ± 50 | 168 ± 54∗ | 0.451 | 0.001 |
| CTL | 177 ± 70 | 167 ± 65∗ | ||
| Voluntary activation (%) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 93 ± 6 | 95 ± 4 | 0.343 | 0.264 |
| CTL | 91 ± 8 | 91 ± 7 | ||
| Twitch torque (N.m) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 60 ± 16 | 62 ± 14 | 0.125 | 0.127 |
| CTL | 71 ± 22 | 71 ± 20 | ||
| VL aEMG (μV) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 324 ± 131 | 333 ± 145 | 0.291 | 0.342 |
| CTL | 381 ± 146 | 362 ± 155 | ||
| VM aEMG (μV) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 626 ± 330 | 618 ± 228 | 0.219 | 0.608 |
| CTL | 499 ± 153 | 467 ± 190 | ||
| RF aEMG (μV) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 376 ± 203 | 388 ± 160 | 0.295 | 0.558 |
| CTL | 301 ± 154 | 292 ± 158 | ||
| BF aEMG (μV) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 122 ± 71 | 130 ± 68 | 0.161 | 0.089 |
| CTL | 91 ± 29 | 79 ± 21 | ||
| Endurance time (s) | ||||
| WB-HIIT | 133 [114, 181] | 187 [131, 252]∗ | 0.730 | N/A |
| CTL | 151 [114, 244] | 166 [108, 229] | ||
Data presented as mean ± standard deviation, or median [25th, 75th percentile], ∗Significantly different from baseline value within this group (p < 0.05). aEMG, average value of the rectified electromyographic activities. BF, biceps femoris. MVC, maximal voluntary contraction. N/A, not applicable. RF, rectus femoris. 3-RM, 3- repetition maximum. VL, vastus lateralis. VM, vastus medialis.
Although there was no significant change in the mean voluntary activation after the WB-HIIT, our results indicated a negative correlation (rp = −0.80; p < 0.001) between the subjects’ initial voluntary activation level and the percentage of change in voluntary activation, and a positive correlation (rp = 0.55; p = 0.040) between the percentage of change in voluntary activation and in MVC torque. In contrast, the correlation between the percentage of change in leg lean mass and MVC torque was not significant (p = 0.418).
4. Discussion
The present study assessed the adaptations of body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness, and neuromuscular function induced by a WB-HIIT performed at home. Our results show that the home-based WB-HIIT improved cardiorespiratory fitness (VO2peak and VT1), muscle strength and endurance, and slightly increased leg lean mass. The predominant effect was observed for aerobic capacity (VT1) and muscle endurance. A dose-response relationship was observed between the time spent at high intensity during training sessions and VO2peak change. Changes in voluntary activation and MVC torque were correlated, suggesting that strength improvement after WB-HIIT was mainly related to an increased volitional drive.
4.1. Body composition
The absence of change in fat mass is consistent with most of previous studies that proposed both supervised44, 45, 46, 47 and home-based WB-HIIT in normoweight subjects.27,29 In contrast, fat loss was reported after supervised and home-based WB-HIIT in overweight participants.26,48,49 Total lean mass was not significantly changed after WB-HIIT. This result is in agreement with previous studies showing mitigated effects of supervised44,46,48, 49, 50 and home-based26,27,30 WB-HIIT on total lean mass.
To our best knowledge, no other study assessed segmental body composition changes after supervised or home-based WB-HIIT. The small improvement observed in leg lean mass, but not in trunk and arm lean mass, could be explained by the type of exercises. Indeed, our training protocol was composed of bodyweight exercises mostly involving lower limbs. Muscle hypertrophy is considered to be initiated by high mechanical loading of the muscle.51,52 However, recent literature suggested that hypertrophy may also be triggered by rapid and repeated transitions from eccentric to concentric portion of the movement (i.e., stretch-shortening cycles),53,54 and accumulation of fatigue related metabolites (i.e., metabolic stress).51,52,54, 55, 56 Although the training load is moderate (i.e., bodyweight), WB-HIIT involves fast concentric and eccentric contractions of the lower limbs. This, combined to the previously reported high blood lactate concentration attained during WB-HIIT,56 could have triggered the slight increase in leg lean mass.56,57
4.2. Cardiorespiratory fitness adaptations
The VO2peak improvement after WB-HIIT is consistent with previous studies using either supervised44,45,48, 49, 50,58, 59, 60 or home-based WB-HIIT.26,28,30 The slight increase observed for VO2peak (5%) could be due to the short time spent at high intensity (see Table 3). This is in line with a recent study showing that oxygen consumption is lower during WB-HIIT compared to a running HIIT with a similar exercise to rest ratio.56 This hypothesis is also supported by the dose-response relationship between the time spent at high intensity and VO2peak improvements shown by present and previous studies.61 WB-HIIT is indeed characterized by a greater complexity and muscle strain, due to the use of bodyweight multi-joint exercises, which may limit execution pace and HR increase as compared to unimodal HIIT.56
The large improvement of VT1 (20%) indicates a stronger effect of WB-HIIT on the submaximal aerobic exercise capacity than on VO2peak. VT1 corresponds to an intensity at which ventilation starts to increase faster than VO262 to compensate the metabolic acidosis by the bicarbonate buffering system.32,63 A low VT1 is associated with a premature onset of exercise-related hyperventilation, a higher perceived exertion during exercise,64 and an earlier exercise cessation.65 VT1 is therefore considered as a better indicator of aerobic endurance capacity (i.e., maximal time spent at a submaximal intensity) than VO2peak.34,65,66 To our knowledge, only two studies assessed VT1 change after home-based WB-HIIT, and reported a significant increase.28,30 Given the low impact of WB-HIIT on VO2peak, VT1 enhancement is most probably due to an improvement in muscle aerobic capacity, rather than a greater ability of the cardiorespiratory system to deliver oxygen to the muscles.66
While the exact muscular mechanisms induced by WB-HIIT still need to be investigated, they could be partly common to those reported after HIIT: increased muscle mitochondrial content and function,67 reduced glycogen utilization, and greater muscle buffering capacity.68,69 This would delay lactate production and accumulation, and slow down the development of peripheral fatigue.70 This is supported by a recent study showing that home-based WB-HIIT induces similar improvements in muscle capillarization and mitochondrial density than home-based moderate intensity continuous training or supervised HIIT.26
4.3. Neuromuscular adaptations
4.3.1. Muscle strength and voluntary activation
The strength increase observed after the home-based WB-HIIT is in line with previous studies that investigated effect of WB-HIIT on dynamic muscle strength (i.e., 1-repetition maximum).49,59,71 However, to our best knowledge, our study is the first to investigate changes in MVC torque and voluntary activation of the knee extensors after WB-HIIT. This approach allows a further discussion of the mechanisms involved in strength improvement.
The MVC torque increased after WB-HIIT, whereas it was reduced in the CTL group. The decrease in the CTL group is most probably due to a slightly lower involvement in physical activity and/or active displacements during the COVID-19 pandemic,72 despite the instruction to keep physical activity habits stable. The associated EMG activities of the agonist (vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and rectus femoris) and antagonist (biceps femoris) muscles were not modified in any group. This is in line with the absence of change in the mean voluntary activation. However, the initial level of voluntary activation was already high in our subjects (93 and 91% in the WB-HIIT and CTL group, respectively). This may have reduced the extent of possible improvement and the sensitivity of the interpolated twitch technique to detect changes.39,40 For this reason, we correlated the individual initial activation level with the change in voluntary activation after WB-HIIT, and observed a negative relation. This observation suggests that WB-HIIT has a greater potential to improve voluntary activation in subjects with a lower initial activation level. Also, as MVC torque increase was positively correlated with voluntary activation change, but not with leg lean mass change, neural mechanisms should have mainly contributed to the strength improvement. This is also supported by the absence of change in twitch torque which is an indicator of muscle contractile properties.73
Resistance training, using high loads, is considered as the best strategy to improve muscle strength.55 However, improvements in MVC torque have also been reported following biking or running HIIT,38,74, 75, 76 although not systematically.77, 78, 79 The strength increase observed after HIIT is thought to be related to the high intensity of the working phases and short recovery times favoring type 2 fibers recruitment.80,81 WB-HIIT involves repeated multi-joint explosive exercises performed with bodyweight as resistance. Performance of this type of exercises requires an intense volitional drive that could result in an even larger type 2 fibers recruitment and strengthening effect. The greater improvements of the 3-RM, proportionally to MVC torque (see Fig. 2B), is most probably linked to the specific motor skills and segmental coordination trained during whole-body exercises. It would then further improve performance at multi-joint dynamic strength tests than at monoarticular isometric tests.
4.3.2. Muscle endurance
In present study, WB-HIIT induced a larger improvement in muscle endurance than strength. Previous studies have reported that WB-HIIT increases muscle endurance, quantified by plank endurance time or by the number of repetitions performed during a certain time or till exhaustion.27,44,46,47,50,58,59,82,83 However, the similarity of the tests with the exercises performed during training makes it difficult to distinguish improvement due to acquisition of specific motor skills from real gain in muscle endurance. The novel finding of an increased endurance time during a submaximal isometric contraction, untrained during the exercise intervention, supports WB-HIIT effectiveness to enhance muscle endurance.
Intramuscular mechanisms regulating aerobic capacity (evoked above to explain VT1 improvement), but also a greater resistance to inhibitory actions of III/IV muscle afferents84 and tolerance to muscular disconfort,85,86 could contribute to increase muscle endurance after WB-HIIT.
4.4. Limitations and perspectives
There are some limitations to this study. First, our sample was composed of mostly inactive but healthy young adults. Therefore, present results are not transferable to inactive populations with limitations (e.g., subjects with physical limitations/risk factors due to their age, overweight, or medical condition). Enlarge the investigated populations will provide additional information on the feasibility and efficacy of WB-HIIT in various populations with a low participation in physical activities. Further studies should also compare different types of protocols (e.g., different session duration, type of exercises, work/rest ratio, etc.) to optimize WB-HIIT programming.
Second, although the intensity of sessions was monitored through recording of HR, the “all-out” execution of exercises could not be controlled during sessions. This aspect is however intrinsically linked to the training modality and the home-based design of the intervention. To our knowledge, only one study monitored intensity through HR during WB-HIIT sessions.44 Due to the impact of intensity on the induced adaptations, further studies should systematically monitor and report training intensity. This will facilitate results interpretation and between study comparisons.
Finally, the very slight increase in leg lean mass (3%) should be interpreted with caution since it is just above the precision of the Lunar Prodigy DXA (1–2%).31 But if confirmed, it could represent an interesting complementary approach for subjects with limited time or access to fitness facilities.
4.5. Functional implications
Although a significant effect was observed for VO2peak, muscle strength and leg lean mass, WB-HIIT had a greater effect on submaximal performance (i.e., VT1 and muscle endurance). VT1 and muscle endurance were assessed during different types of effort (i.e., dynamic aerobic exercise vs. submaximal isometric contraction) and therefore depend on partly different mechanisms which need further investigations. However, the concomitant enhancement of these parameters should improve exercise tolerance and facilitate performance of daily life activities. Indeed, most of daily tasks involve repeated submaximal aerobic efforts and sustained muscle contractions.87,88
In addition, an advantage of WB-HIIT is the possibility to adapt the type of exercises and execution depending on the primary goal and targeted population. Compared to moderate intensity aerobic training, a recent study also showed greater enjoyment during WB-HIIT sessions89 and higher motivation to exercise after the intervention.71
5. Conclusion
The home-based WB-HIIT is feasible and induces concomitant cardiorespiratory fitness and neuromuscular improvements. A dose-response relationship was observed between the magnitude of VO2peak change and the time spent at high intensity (above 80% of HRmax). Strength improvement was due to a greater volitional drive rather than an increased muscle mass. The predominant effect on submaximal aerobic capacity and muscle endurance should contribute to improve exercise tolerance and reduce fatigue during daily activities.
Author statement
C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, V.Faoro, and M.Klass conceived the study design. C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, and M.Klass conceived the exercise intervention. C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, and M.Klass collected the data. C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, V.Faoro, and M.Klass analyzed the data. C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, and M.Klass performed the statistical analysis. C.Scoubeau, J.Carpentier, V.Faoro, S.Baudry, and M.Klass drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors gave their consent for the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Brussels Region - Innoviris (BRIDGE project, grant DiaType).
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Warburton D.E.R., Bredin S.S.D. Health benefits of physical activity: a systematic review of current systematic reviews. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2017;32(5):541–556. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2020. WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK566045/ [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hallal P.C., Andersen L.B., Bull F.C., et al. Global physical activity levels: surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet Lond Engl. 2012;380(9838):247–257. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60646-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Spiteri K., Broom D., Bekhet A.H., Caro JX de, Laventure B., Grafton K. Barriers and motivators of physical activity participation in middle-aged and older adults—a systematic review. J Aging Phys Activ. 2019;27(6):929–944. doi: 10.1123/japa.2018-0343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martínez-de-Quel Ó., Suárez-Iglesias D., López-Flores M., Pérez C.A. Physical activity, dietary habits and sleep quality before and during COVID-19 lockdown: a longitudinal study. Appetite. 2021;158 doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2020.105019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Meyer J., McDowell C., Lansing J., et al. Changes in physical activity and sedentary behavior in response to COVID-19 and their associations with mental health in 3052 US adults. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2020;17(18):6469. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kirsch M., Vitiello D. The COVID-19 pandemic lowers active behavior of patients with cardiovascular diseases, healthy peoples and athletes. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2022;19(3):1108. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Denay K.L., Breslow R.G., Turner M.N., Nieman D.C., Roberts W.O., Best T.M. ACSM call to action statement: COVID-19 considerations for sports and physical activity. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2020;19(8):326. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ricci F., Izzicupo P., Moscucci F., et al. Recommendations for physical inactivity and sedentary behavior during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Front Public Health. 2020;8:199. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gorzelitz J.S., Stoller S., Costanzo E., et al. Improvements in strength and agility measures of functional fitness following a telehealth-delivered home-based exercise intervention in endometrial cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer Off J Multinatl Assoc Support Care Cancer. 2022;30(1):447–455. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06415-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li J., Liu B., Wang Z., et al. Efficacy of a 6-week home-based online supervised exercise program conducted during COVID-19 in patients with post percutaneous coronary intervention: a single-blind randomized controlled trial. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9 doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.853376. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2022.853376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ali O.I., Abdelraouf O.R., El-Gendy A.M., et al. Efficacy of telehealth core exercises during COVID-19 after bariatric surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022 doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.22.07457-3. Published online July 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Power S., Rowley N., Flynn D., Duncan M., Broom D. Home-based exercise for adults with overweight or obesity: a rapid review. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2022;16(2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2022.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Michaelchuk W., Oliveira A., Marzolini S., et al. Design and delivery of home-based telehealth pulmonary rehabilitation programs in COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Med Inf. 2022;162 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fanget M., Bayle M., Labeix P., Roche F., Hupin D. Effects of cardiac telerehabilitation during COVID-19 on cardiorespiratory capacities in patients with coronary artery disease. Front Physiol. 2022;13 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.837482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Uchiyama K., Adachi K., Muraoka K., et al. Home-based aerobic exercise and resistance training for severe chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(6):1789–1802. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ghahfarrokhi M.M., Banitalebi E., Negaresh R., Motl R.W. Home-based exercise training in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review with implications for future research. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021;55 doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mahjur M., Norasteh A.A. Effects of home-based specific and comprehensive balance-training programs on balance and functional status in healthy older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2022;159 doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.111701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chaabene H., Prieske O., Herz M., et al. Home-based exercise programmes improve physical fitness of healthy older adults: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis with relevance for COVID-19. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;67 doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang S.H., Chiang C.C., Chien N.H. Efficacy of a multicomponent exercise training program intervention in community-dwelling older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Geriatr Nurs N Y N. 2022;49:148–156. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2022.11.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sultana R.N., Sabag A., Keating S.E., Johnson N.A. The effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med Auckl NZ. 2019;49(11):1687–1721. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01167-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Machado A.F., Baker J.S., Figueira Junior A.J., Bocalini D.S. High-intensity interval training using whole-body exercises: training recommendations and methodological overview. Clin Physiol Funct Imag. 2019;39(6):378–383. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McDonough D.J., Helgeson M.A., Liu W., Gao Z. Effects of a remote, YouTube-delivered exercise intervention on young adults' physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep during the COVID-19 pandemic: randomized controlled trial. J Sport Health Sci. 2022;11(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2021.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Soetens K.C.M., Vandelanotte C., de Vries H., Mummery K.W. Using online computer tailoring to promote physical activity: a randomized trial of text, video, and combined intervention delivery modes. J Health Commun. 2014;19(12):1377–1392. doi: 10.1080/10810730.2014.894597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Scoubeau C., Bonnechère B., Cnop M., Faoro V., Klass M. Effectiveness of whole-body high-intensity interval training on health-related fitness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2022;19(15):9559. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Scott S.N., Shepherd S.O., Hopkins N., et al. Home-HIT improves muscle capillarisation and eNOS/NAD(P)Hoxidase protein ratio in obese individuals with elevated cardiovascular disease risk. J Physiol. 2019;597(16):4203–4225. doi: 10.1113/JP278062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sperlich B., Hahn L.S., Edel A., et al. A 4-week intervention involving mobile-based daily 6-minute micro-sessions of functional high-intensity circuit training improves strength and quality of life, but not cardio-respiratory fitness of young untrained adults. Front Physiol. 2018;9 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00423. MAY. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Blackwell J., Atherton P.J., Smith K., et al. The efficacy of unsupervised home-based exercise regimens in comparison to supervised laboratory-based exercise training upon cardio-respiratory health facets. Phys Rep. 2017;5(17) doi: 10.14814/phy2.13390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Connolly L.J., Scott S., Morencos C.M., et al. Impact of a novel home-based exercise intervention on health indicators in inactive premenopausal women: a 12-week randomised controlled trial. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(4):771–782. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sian T.S., Inns T.B., Gates A., et al. Equipment-free, unsupervised high intensity interval training elicits significant improvements in the physiological resilience of older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):529. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03208-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Toombs R.J., Ducher G., Shepherd J.A., De Souza M.J. The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obes Silver Spring Md. 2012;20(1):30–39. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wasserman K., Whipp B.J., Koyl S.N., Beaver W.L. Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973;35(2):236–243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reinhard U., Müller P.H., Schmülling R.M. Determination of anaerobic threshold by the ventilation equivalent in normal individuals. Respir Int Rev Thorac Dis. 1979;38(1):36–42. doi: 10.1159/000194056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Matsumura N., Nishijima H., Kojima S., Hashimoto F., Minami M., Yasuda H. Determination of anaerobic threshold for assessment of functional state in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1983;68(2):360–367. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Krachler B., Savonen K., Komulainen P., Hassinen M., Lakka T.A., Rauramaa R. Cardiopulmonary fitness is a function of lean mass, not total body weight: the DR's EXTRA study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015;22(9):1171–1179. doi: 10.1177/2047487314557962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Klass M., Duchateau J., Rabec S., Meeusen R., Roelands B. Noradrenaline reuptake inhibition impairs cortical output and limits endurance time. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(6):1014–1023. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pescatello L.S., American College of Sports Medicine . ninth ed. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health; Philadelphia: 2014. ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Martinez-Valdes E., Falla D., Negro F., Mayer F., Farina D. Differential motor unit changes after endurance or high-intensity interval training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(6):1126–1136. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Todd G., Taylor J.L., Gandevia S.C. Measurement of voluntary activation of fresh and fatigued human muscles using transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Physiol. 2003;551(Pt 2):661–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.044099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shield A., Zhou S. Assessing voluntary muscle activation with the twitch interpolation technique. Sports Med Auckl NZ. 2004;34(4):253–267. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200434040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moritani T., deVries H.A. Neural factors versus hypertrophy in the time course of muscle strength gain. Am J Phys Med. 1979;58(3):115–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Buchheit M., Laursen P.B. High-intensity interval training, solutions to the programming puzzle: Part I: cardiopulmonary emphasis. Sports Med Auckl NZ. 2013;43(5):313–338. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.MacInnis M.J., Gibala M.J. Physiological adaptations to interval training and the role of exercise intensity. J Physiol. 2017;595(9):2915–2930. doi: 10.1113/JP273196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Menz V., Marterer N., Amin S.B., Faulhaber M., Hansen A.B., Lawley J.S. Functional vs. Running low-volume high-intensity interval training: effects on VO2max and muscular endurance. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(3):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Micielska K., Gmiat A., Zychowska M., et al. The beneficial effects of 15 units of high-intensity circuit training in women is modified by age, baseline insulin resistance and physical capacity. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;152:156–165. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Evangelista A.L., La Scala Teixeira C., Machado A.F., Pereira P.E., Rica R.L., Bocalini D.S. Effects of a short-term of whole-body, high-intensity, intermittent training program on morphofunctional parameters. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019;23(3):456–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schmidt D., Anderson K., Graff M., Strutz V. The effect of high-intensity circuit training on physical fitness. J Sports Med Phys Fit. 2016;56(5):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Murawska-Cialowicz E., Wolanski P., Zuwala-Jagiello J., et al. Effect of HIIT with Tabata protocol on serum irisin, physical performance, and body composition in men. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2020;17(10) doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Batrakoulis A., Jamurtas A.Z., Georgakouli K., et al. High intensity, circuit-type integrated neuromuscular training alters energy balance and reduces body mass and fat in obese women: a 10-month training-detraining randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2018;13(8) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lu Y., Wiltshire H.D., Baker J.S., Wang Q. The effects of running compared with functional high-intensity interval training on body composition and aerobic fitness in female university students. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2021;18(21) doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Duchateau J., Stragier S., Baudry S., Carpentier A. Strength training: in search of optimal strategies to maximize neuromuscular performance. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2021;49(1):2–14. doi: 10.1249/JES.0000000000000234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wackerhage H., Schoenfeld B.J., Hamilton D.L., Lehti M., Hulmi J.J. Stimuli and sensors that initiate skeletal muscle hypertrophy following resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol Bethesda Md. 2019;126(1):30–43. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00685.2018. 1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Arntz F., Mkaouer B., Markov A., et al. Effect of plyometric jump training on skeletal muscle hypertrophy in healthy individuals: a systematic review with multilevel meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2022;13 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.888464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Claflin D.R., Larkin L.M., Cederna P.S., et al. Effects of high- and low-velocity resistance training on the contractile properties of skeletal muscle fibers from young and older humans. J Appl Physiol Bethesda Md. 2011;111(4):1021–1030. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01119.2010. 1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Carvalho L., Moriggi R., Barreira J., Schoenfeld B., Orazem J., Barroso R. Muscle hypertrophy and strength gains after resistance training with different volume-matched loads: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Appl Physiol Nutr Metabol. 2022;47(4) doi: 10.1139/apnm-2021-0515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bellissimo G.F., Ducharme J., Mang Z., et al. The acute physiological and perceptual responses between bodyweight and treadmill running high-intensity interval exercises. Front Physiol. 2022;13 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.824154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lawson D., Vann C., Schoenfeld B.J., Haun C. Beyond mechanical tension: a review of resistance exercise-induced lactate responses & muscle hypertrophy. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2022;7(4):81. doi: 10.3390/jfmk7040081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ballesta-García I., Martínez-González-Moro I., Ramos-Campo D.J., Carrasco-Poyatos M. High-intensity interval circuit training versus moderate-intensity continuous training on cardiorespiratory fitness in middle-aged and older women: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2020;17(5) doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Evangelista A.L., Brigatto F.A., DE Camargo J.B., et al. Effect of a short-term whole-body high-intensity interval training on fitness, morphological, and functional parameters in untrained individuals. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. Published online June. 2021;22 doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.21.12342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schaun G.Z., Pinto S.S., Silva M.R., Dolinski D.B., Alberton C.L. Whole-body high-intensity interval training induce similar cardiorespiratory adaptations compared with traditional high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training in healthy men. J Strength Condit Res. 2018;32(10):2730–2742. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Midgley A.W., Mc Naughton L.R. Time at or near VO2max during continuous and intermittent running. A review with special reference to considerations for the optimisation of training protocols to elicit the longest time at or near VO2max. J Sports Med Phys Fit. 2006;46(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Walsh M.L., Banister E.W. Possible mechanisms of the anaerobic threshold. A review. Sports Med Auckl NZ. 1988;5(5):269–302. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198805050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cerezuela-Espejo V., Courel-Ibáñez J., Morán-Navarro R., Martínez-Cava A., Pallarés J.G. The relationship between lactate and ventilatory thresholds in runners: validity and reliability of exercise test performance parameters. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1320. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Scherr J., Wolfarth B., Christle J.W., Pressler A., Wagenpfeil S., Halle M. Associations between Borg's rating of perceived exertion and physiological measures of exercise intensity. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(1):147–155. doi: 10.1007/s00421-012-2421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vago P., Mercier J., Ramonatxo M., Prefaut C. Is ventilatory anaerobic threshold a good index of endurance capacity? Int J Sports Med. 1987;8(3):190–195. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ghosh A.K. Anaerobic threshold: its concept and role in endurance sport. Malays J Med Sci MJMS. 2004;11(1):24–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jacobs R.A., Flück D., Bonne T.C., et al. Improvements in exercise performance with high-intensity interval training coincide with an increase in skeletal muscle mitochondrial content and function. J Appl Physiol Bethesda Md. 2013;115(6):785–793. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00445.2013. 1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gibala M.J., Little J.P., van Essen M., et al. Short-term sprint interval versus traditional endurance training: similar initial adaptations in human skeletal muscle and exercise performance. J Physiol. 2006;575(Pt 3):901–911. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.112094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.McGinley C., Bishop D.J. Rest interval duration does not influence adaptations in acid/base transport proteins following 10 wk of sprint-interval training in active women. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017;312(5):R702–R717. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00459.2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Allen D.G., Lamb G.D., Westerblad H. Skeletal muscle fatigue: cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(1):287–332. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wilke J., Kaiser S., Niederer D., et al. Effects of high-intensity functional circuit training on motor function and sport motivation in healthy, inactive adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(1):144–153. doi: 10.1111/sms.13313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Mujika I., Padilla S. Muscular characteristics of detraining in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(8):1297–1303. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200108000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Alway S.E., MacDougall J.D., Sale D.G. Contractile adaptations in the human triceps surae after isometric exercise. J Appl Physiol Bethesda Md. 1989;66(6):2725–2732. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.6.2725. 1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bontemps B., Gruet M., Louis J., et al. The time course of different neuromuscular adaptations to short-term downhill running training and their specific relationships with strength gains. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022;122(4):1071–1084. doi: 10.1007/s00421-022-04898-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Jenkins N.D.M., Rogers E.M., Banks N.F., Muddle T.W.D., Colquhoun R.J. Increases in motor unit action potential amplitudes are related to muscle hypertrophy following eight weeks of high-intensity exercise training in females. Eur J Sport Sci. 2021;21(10):1403–1413. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2020.1836262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kinnunen J.V., Piitulainen H., Piirainen J.M. Neuromuscular adaptations to short-term high-intensity interval training in female ice-hockey players. J Strength Condit Res. 2019;33(2):479–485. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bruseghini P., Capelli C., Calabria E., Rossi A.P., Tam E. Effects of high-intensity interval training and isoinertial training on leg extensors muscle function, structure, and intermuscular adipose tissue in older adults. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1260. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Vila-Chã C., Falla D., Correia M.V., Farina D. Changes in H reflex and V wave following short-term endurance and strength training. J Appl Physiol Bethesda Md. 2012;112(1):54–63. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00802.2011. 1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Vera-Ibañez A., Colomer-Poveda D., Romero-Arenas S., Viñuela-García M., Márquez G. Neural adaptations after short-term wingate-based high-intensity interval training. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017;17(4):275–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Callahan M.J., Parr E.B., Hawley J.A., Camera D.M. Can high-intensity interval training promote skeletal muscle anabolism? Sports Med Auckl NZ. 2021;51(3):405–421. doi: 10.1007/s40279-020-01397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Krustrup P., Söderlund K., Mohr M., González-Alonso J., Bangsbo J. Recruitment of fibre types and quadriceps muscle portions during repeated, intense knee-extensor exercise in humans. Pflügers Archiv. 2004;449(1):56–65. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Engel F.A., Rappelt L., Held S., Donath L. Can high-intensity functional suspension training over eight weeks improve resting blood pressure and quality of life in young adults? A randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Publ Health. 2019;16(24):E5062. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Islam H., Siemens T.L., Matusiak J.B.L., et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness and muscular endurance responses immediately and 2 months after a whole-body Tabata or vigorous-intensity continuous training intervention. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab Physiol Appl Nutr Metab. 2019;45(6):650–658. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zghal F., Cottin F., Kenoun I., et al. Improved tolerance of peripheral fatigue by the central nervous system after endurance training. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015;115(7):1401–1415. doi: 10.1007/s00421-015-3123-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.O'Leary T.J., Collett J., Howells K., Morris M.G. High but not moderate-intensity endurance training increases pain tolerance: a randomised trial. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(11):2201–2210. doi: 10.1007/s00421-017-3708-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.O'Leary T.J., Collett J., Howells K., Morris M.G. Endurance capacity and neuromuscular fatigue following high- vs moderate-intensity endurance training: a randomized trial. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017;27(12):1648–1661. doi: 10.1111/sms.12854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hunter S.K. Performance fatigability: mechanisms and task specificity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(7):a029728. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Warburton D.E., Glendhill N., Quinney A. The effects of changes in musculoskeletal fitness on health. Can J Appl Physiol Rev Can Physiol Appl. 2001;26(2):161–216. doi: 10.1139/h01-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Schaun G.Z., Alberton C.L. Using bodyweight as resistance can Be a promising avenue to promote interval training: enjoyment comparisons to treadmill-based protocols. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2022;93(1):162–170. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2020.1817293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]