Abstract
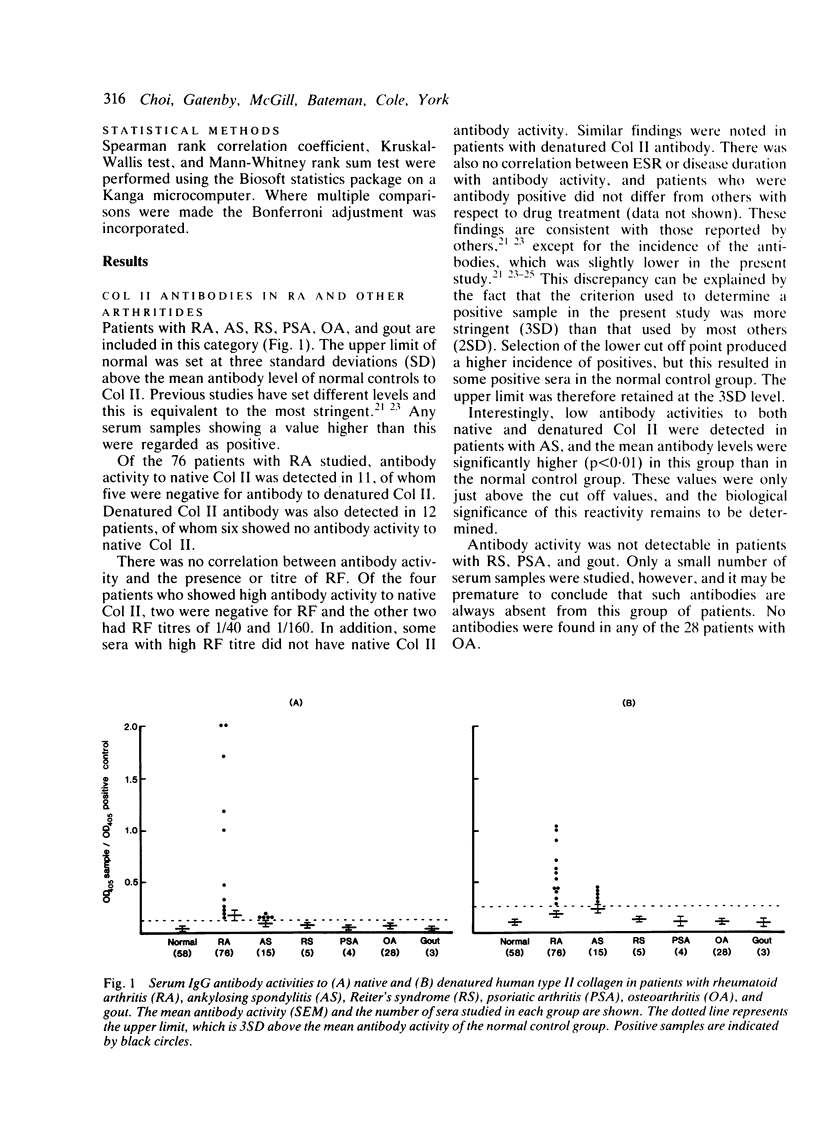
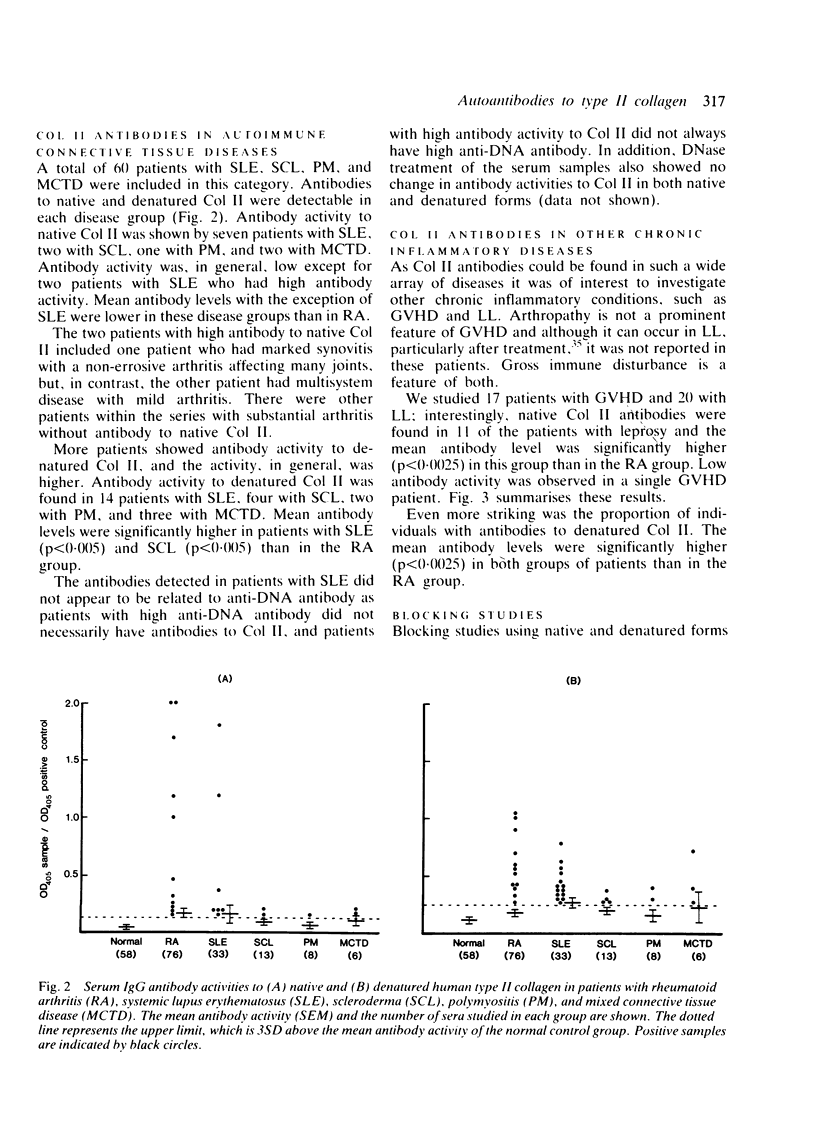
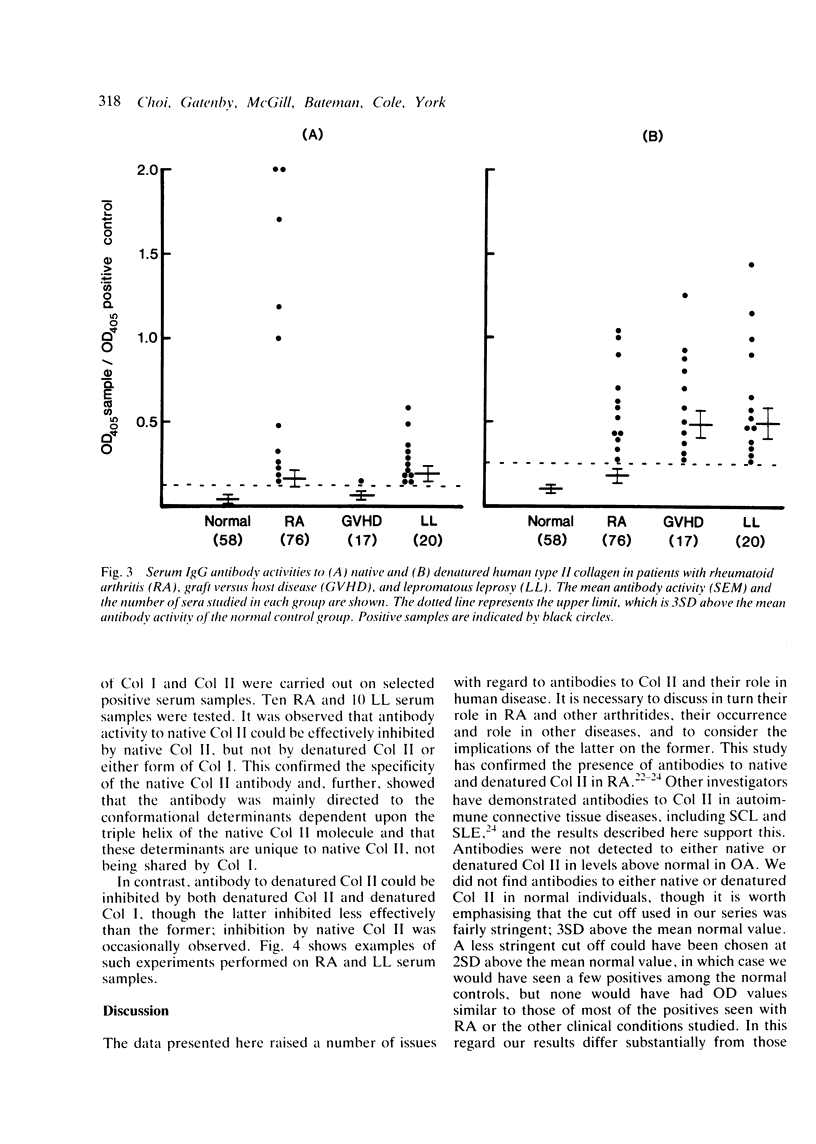
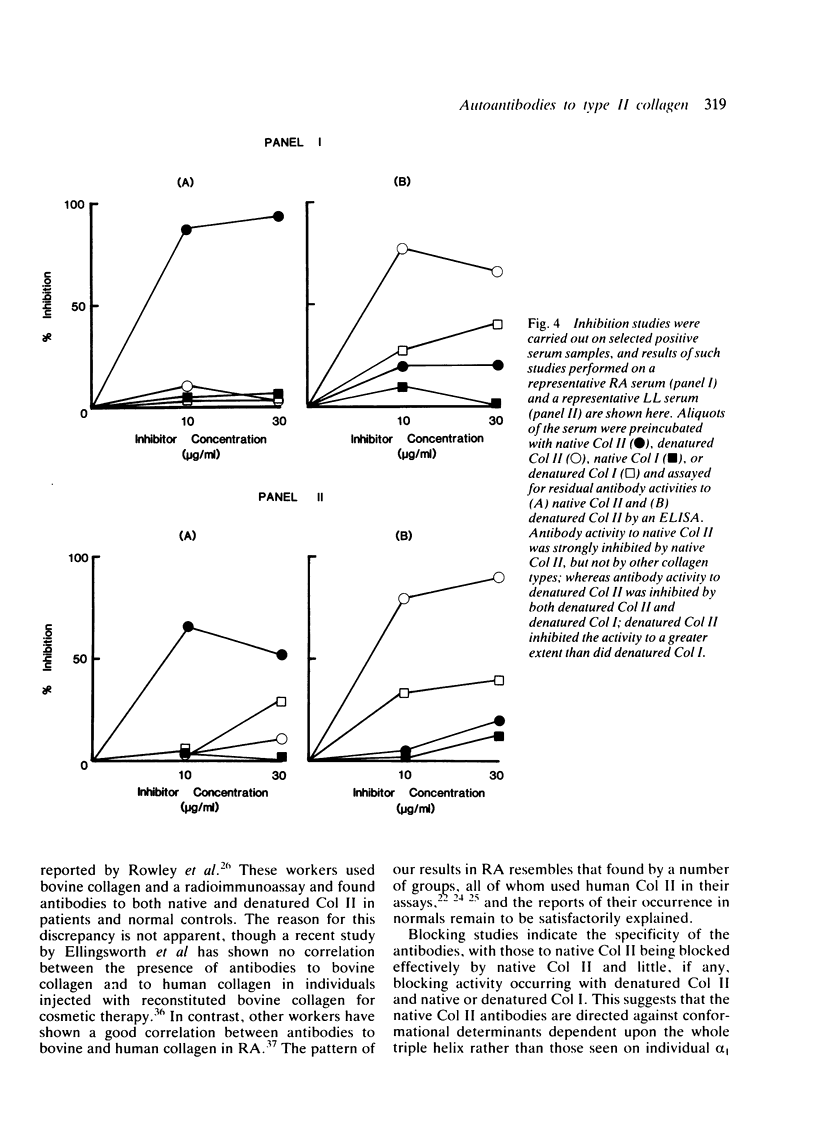
Serum IgG antibodies to native and denatured human type II collagen (Col II) were measured using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). One hundred and thirty one patients with various forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriatic arthritis (PSA). Reiter's Syndrome (RS), osteoarthritis (OA), and gout, 60 with autoimmune connective tissue disease, and 37 with the chronic inflammatory conditions--graft versus host disease and leprosy--were studied. With the exception of RS, PSA, OA, and gout, significant levels of Col II antibodies were detected in each disease group. Blocking studies with types I and II collagen on selected serum samples confirmed the specificity to native Col II, though some cross reactivity was apparent with denatured collagen. The patients with RA who were Col II antibody positive tended to fall into stage III of disease progression. There was, however, no correlation with rheumatoid factor, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or disease duration and this, together with the finding that Col II antibodies are present in a wide array of diseases, makes their role in the pathogenesis of RA questionable. They may arise as a secondary disease perpetuating mechanism in some patients, or in turn may be an epiphenomenon secondary to generalised disturbed immunoregulation or B cell hyperreactivity, or both, that characterises these clinical conditions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgeson R. E., Hollister D. W. Collagen heterogeneity in human cartilage: identification of several new collagen chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1124–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbury C. L., Skingle J. Anti-cartilage antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):826–831. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., DeWitt C. W. Genetic control of collagen-induced arthritis in rats: the immune response to type II collagen among susceptible and resistant strains and evidence for multiple gene control. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Stuart J. M., Tovey J., Chiller J. M. Murine T cells reactive to type II collagen. II. Functional characterization. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):776–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. The structure of fibril-forming collagens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Firth S. A., Twose T. M., Holt P. J. Native type II collagen--induced arthritis in the rat: the effect of complement depletion by cobra venom factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1356–1362. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Tomoda K., Yoo T. J., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis. II. Identification and localization of autoantibody to type II collagen in donor and recipient rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1237–1244. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


