Abstract
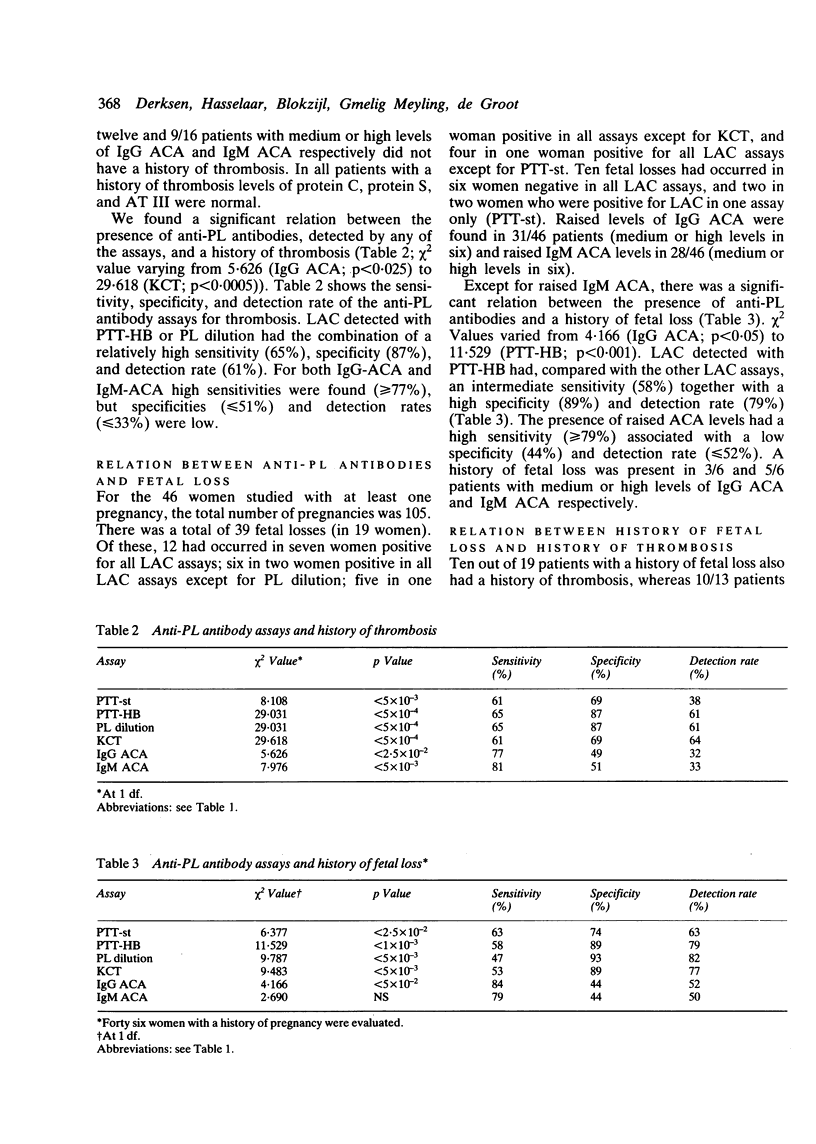
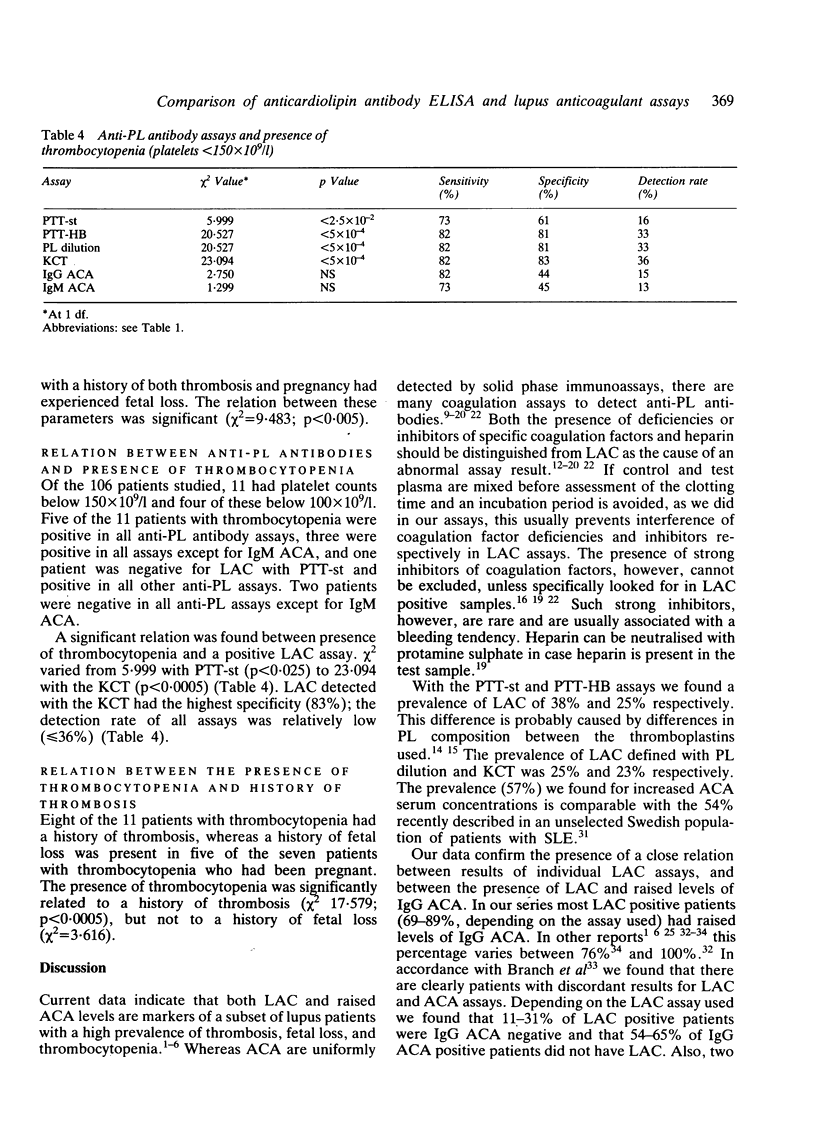
In 111 lupus patients we compared the potential of the IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibody (ACA) enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and four different lupus anticoagulant (LAC) assays (partial thromboplastin time (PTT) of a 1:1 mixture of patient and control plasma with phospholipids from animal (PTT-st) or human brain (PTT-HB); PTT with dilutions of human brain phospholipids (PL dilution); and kaolin clotting time of mixtures of patient and control plasma (KCT] to identify patients with thrombosis (26/111), fetal loss (19/46), and/or thrombocytopenia (11/106). The highest specificity for thrombosis (87%) was found with PTT-HB and PL dilution (sensitivity 65%, detection rate 61%); for fetal loss (93%) with PL dilution (sensitivity 47%; detection rate 82%), and for thrombocytopenia (83%) with KCT (sensitivity 82%; detection rate 36%). Compared with LAC assays, the sensitivity of ACA-ELISA was high (greater than or equal to 77%), but specificity (less than or equal to 51%) and detection rate (less than or equal to 52%) were low. So, a panel of three LAC assays (PTT-HB, PL dilution, and KCT) can identify lupus patients apparently at risk for thrombosis, fetal loss, and/or thrombocytopenia, whereas the ACA-ELISA is insufficiently specific.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving B. M., Baldwin P. E., Richards R. L., Jackson B. J. The dilute phospholipid APTT: a sensitive assay for verification of lupus anticoagulants. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):709–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer M., Ellman L., Carvalho A. The lupus anticoagulant. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1244–1248. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Rote N. S., Dostal D. A., Scott J. R. Association of lupus anticoagulant with antibody against phosphatidylserine. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jan;42(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Rote N. S., Scott J. R. The demonstration of lupus anticoagulant by an enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 May;39(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canoso R. T., Hutton R. A., Deykin D. A chlorpromazine-induced inhibitor of blood coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1977;2(2):183–191. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaço C. B., Male D. K. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in syphilis and a thrombotic subset of SLE: distinct profiles of epitope specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):449–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen R. H., Biesma D., Bouma B. N., Gmelig Meyling F. H., Kater L. Discordant effects of prednisone on anticardiolipin antibodies and the lupus anticoagulant. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Oct;29(10):1295–1296. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen R. H., Bouma B. N., Kater L. The striking association between lupus anticoagulant and fetal loss in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):695–696. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen R. H., Kater L. Lupus anticoagulant: revival of an old phenomenon. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Oct-Dec;3(4):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza L. R., Hartmann R. C. Significance of the lupus anticoagulant. Am J Hematol. 1986 Jul;22(3):331–337. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Rickard K. A., Kronenberg H. A sensitive test demonstrating lupus anticoagulant and its behavioural patterns. Br J Haematol. 1978 Sep;40(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein D. I. Lupus anticoagulant, thrombosis, and fetal loss. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 21;313(21):1348–1350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511213132109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D., Hougie C., Kazmier F. J., Lechner K., Mannucci P. M., Rizza C. R., Sultan Y. Report of the Working Party on Acquired Inhibitors of Coagulation: studies of the "lupus" anticoagulant. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Apr 28;49(2):144–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P., RAPAPORT S. I., OWREN P. A. A simple, specific one-stage prothrombin assay using Russell's viper venom in cephalin suspension. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jul;46(1):89–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Chan J. K., Asherson R. A., Aber V. R., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Predictive value of the anticardiolipin antibody test. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Nov;146(11):2153–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Patel S. P., Hughes G. R. Evaluation of the anti-cardiolipin antibody test: report of an international workshop held 4 April 1986. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):215–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey P. R., Stevenson K. J., Poller L. The diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants by the activated partial thromboplastin time--the central role of phosphatidyl serine. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Oct 31;52(2):172–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Sueishi M., Funaki H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Anti-phospholipid antibodies and biological false positive serological test for syphilis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner K. A new type of coagulation inhibitor. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Jun 15;21(3):482–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner K., Pabinger-Fasching I. Lupus anticoagulants and thrombosis. A study of 25 cases and review of the literature. Haemostasis. 1985;15(4):254–262. doi: 10.1159/000215157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Druzin M. L., Goei S., Qamar T., Magid M. S., Jovanovic L., Ferenc M. Antibody to cardiolipin as a predictor of fetal distress or death in pregnant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):152–156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507183130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Qamar T., Druzin M. L., Goei S. Antibody to cardiolipin, lupus anticoagulant, and fetal death. J Rheumatol. 1987 Apr;14(2):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Canciani M. T., Mari D., Meucci P. The varied sensitivity of partial thromboplastin and prothrombin time reagents in the demonstration of the lupus-like anticoagulant. Scand J Haematol. 1979 May;22(5):423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueh J. R., Herbst K. D., Rapaport S. I. Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):156–159. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri M., Rheinschmidt M., Whiting-O'Keefe Q., Hellmann D., Corash L. The frequency of lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus. A study of sixty consecutive patients by activated partial thromboplastin time, Russell viper venom time, and anticardiolipin antibody level. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):524–531. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner E., Pauzner R., Lusky A., Modan M., Many A. Detection and quantitative evaluation of lupus circulating anticoagulant activity. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Apr 7;57(2):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosove M. H., Ismail M., Koziol B. J., Runge A., Kasper C. K. Lupus anticoagulants: improved diagnosis with a kaolin clotting time using rabbit brain phospholipid in standard and high concentrations. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):472–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleider M. A., Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A., Coleman M. A clinical study of the lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1976 Oct;48(4):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Thiagarajan P. Lupus anticoagulants. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1982;6:263–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturfelt G., Nived O., Norberg R., Thorstensson R., Krook K. Anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Apr;30(4):382–388. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiagarajan P., Pengo V., Shapiro S. S. The use of the dilute Russell viper venom time for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):869–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A., Brandt J. T., Kaczor D., Schaeffer J. Laboratory diagnosis of lupus inhibitors: a comparison of the tissue thromboplastin inhibition procedure with a new platelet neutralization procedure. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;79(6):678–682. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.6.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A., Brandt J. T., Maas R. L. The laboratory heterogeneity of lupus anticoagulants. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Oct;109(10):946–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Gaston L. W. Purification and kinetic studies on a circulating anticoagulant in a suspected case of lupus erythematosus. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Sep 1;14(1-2):88–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


