Abstract
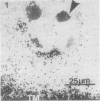
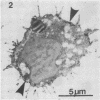
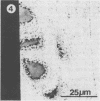
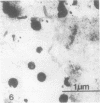
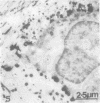
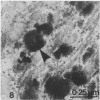
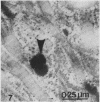
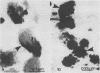
The distribution of alkaline phosphatase activity in human articular cartilage from normal and osteoarthritic joints has been examined by an electron microscope technique, probably for the first time. In osteoarthritic cartilage chondrocytes and matrix vesicles close to the tidemark were positive for alkaline phosphatase activity. Large numbers of matrix vesicles were found within the extracellular matrix of osteoarthritic cartilage, and there is a specific relation between phosphatase activity, matrix vesicles, and initial mineral formation in the tidemark region of articular cartilage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. Y. Apatite-type crystal deposition in arthritic cartilage. Scan Electron Microsc. 1985;(Pt 4):1555–1566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y., Evans L. Enzymic degradation of cartilage in osteoarthritis. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1494–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y., Griffiths S. Formation of calcium phosphate crystals in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42 (Suppl 1):45–48. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.suppl_1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y. New knowledge of osteoarthrosis. J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol) 1978;12:191–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y., Sajdera S. W., Anderson H. C. Isolation and characterization of calcifying matrix vesicles from epiphyseal cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1513–1520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. C., Sajdera S. W. The fine structure of bovine nasal cartilage. Extraction as a technique to study proteoglycans and collagen in cartilage matrix. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):650–663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieppe P. A., Crocker P., Huskisson E. C., Willoughby D. A. Apatite deposition disease. A new arthropathy. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):266–269. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty S. B., Schofield B. H. Enzyme histochemistry of bone and cartilage cells. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1976;8(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6336(76)80010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSH I., CATCHPOLE H. R. The nature of ground substance of connective tissue. Perspect Biol Med. 1960;3:282–319. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1960.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomori G. Calcification and Phosphatase. Am J Pathol. 1943 Mar;19(2):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthlin G., Ericsson J. L. Fine structural localization of alkaline phosphomonoesterase in the fracture callus of the rat. Isr J Med Sci. 1971 Mar;7(3):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewinson D., Toister Z., Silbermann M. Quantitative and distributional changes in the activity of alkaline phosphatase during the maturation of cartilage. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Mar;30(3):261–269. doi: 10.1177/30.3.7061826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikle M. C. The mineralization of condylar cartilage in the rat mandible: an electron microscopic enzyme histochemical study. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(76)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orams H. J., Snibson K. J. Ultrastructural localization and gradient of activity of alkaline phosphatase activity during rodent odontogenesis. Calcif Tissue Int. 1982 May;34(3):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF02411250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin E. L., Swann D. A., Paul I. L., McGrath P. J. Factors influencing articular cartilage wear in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Aug;25(8):974–980. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R. The Possible Significance of Hexosephosphoric Esters in Ossification. Biochem J. 1923;17(2):286–293. doi: 10.1042/bj0170286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOKOLOFF L. ELASTICITY OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE: EFFECT OF IONS AND VISCOUS SOLUTIONS. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1055–1057. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon C. D. A fine structural study on the extracellular activity of alkaline phosphatase and its role in calcification. Calcif Tissue Res. 1974;15(3):201–212. doi: 10.1007/BF02059057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Toda Y. Electron microscopic study of the intercellular activity of alkaline phosphatase in rat epiphyseal cartilage. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1979;28(2):117–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Friberg U. Electron microscopic enzyme histochemical studies on the cellular genesis of matrix vesicles in the epiphyseal plate. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Oct;41(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpin G., Rees J. A., Ali S. Y., Bentley G. Distribution of alkaline phosphatase activity in experimentally produced callus in rats. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986 Aug;68(4):629–634. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.68B4.3733843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells K. D. William Charles Wells and the races of man. Isis. 1973 Jun;64(222):215–225. doi: 10.1086/351082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]