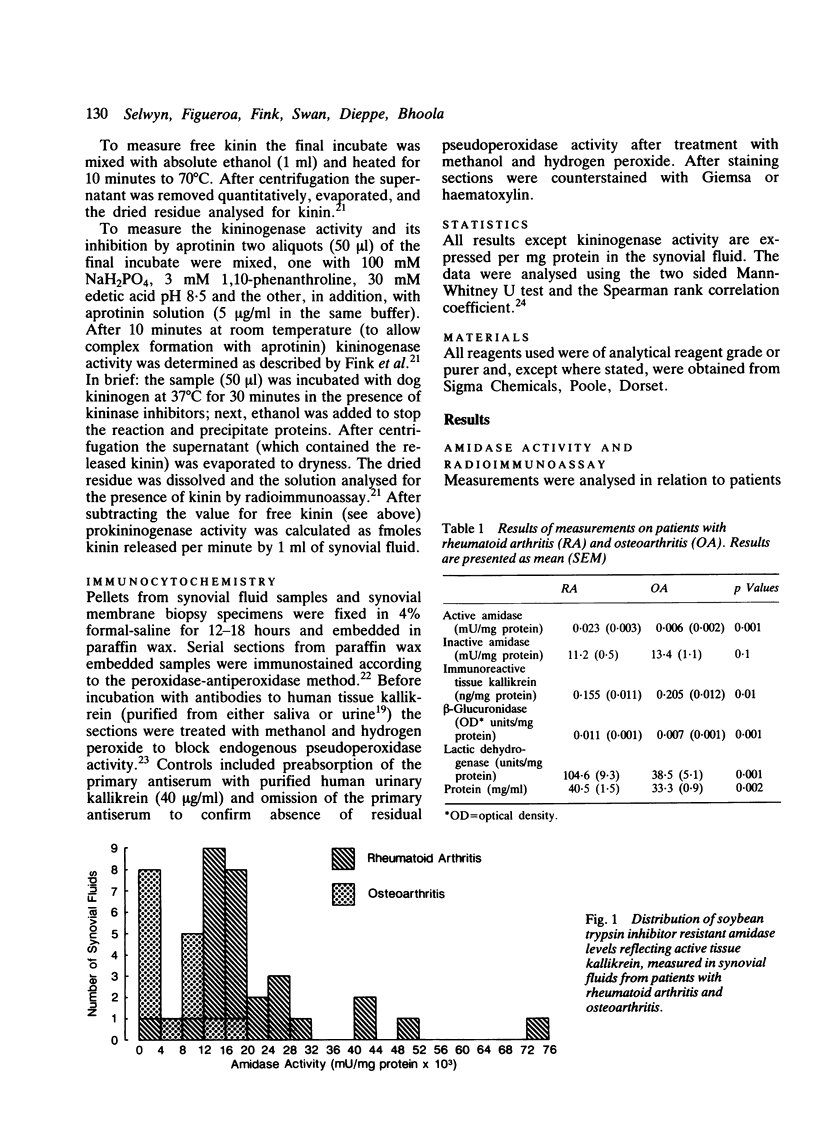
Abstract
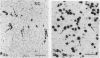
Tissue kallikrein is an enzyme that forms the vasoactive peptide kallidin from an endogenous substrate L-kininogen. Tissue kallikrein has been identified in joint fluids and in inflammatory infiltrates within synovial membranes. It is suggested that tissue kallikrein and kinins have an important role in synovitis and joint damage. Immunoreactive tissue kallikrein and amidase activity were both measured in the synovial fluid of 24 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 12 with osteoarthritis (OA). Active enzyme concentrations were higher in RA than in OA and correlated well with the lysosomal enzymes beta-glucuronidase and lactate dehydrogenase. Both total immunoreactive tissue kallikrein and the proenzyme values were similar in RA and OA. Tissue kallikrein was localised by immunocytochemistry to the polymorphonuclear leucocytes present in the synovial fluid and membranes of patients with RA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 1958 REVISION of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1959 Feb;2(1):16–20. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(195902)2:1<16::aid-art1780020104>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG D., JEPSON J. B., KEELE C. A., STEWART J. W. Pain-producing substance in human inflammatory exudates and plasma. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):350–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw A. F., Bhoola K. D., Lemon M. J., Whicher J. T. Development and characterization of a radioimmunoassay to measure human tissue kallikrein in biological fluids. J Endocrinol. 1984 May;101(2):173–179. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1010173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Hagmann J., Kueppers F. Proteinase inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Jun;34(3):225–230. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Plasma kinins in synovial exudates. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):322–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Urates and kinin formation in synovial fluid. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Apr;59(4):302–307. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink E., Schill W. B., Fiedler F., Krassnigg F., Geiger R., Shimamoto K. Tissue kallikrein of human seminal plasma is secreted by the prostate gland. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Sep;366(9):917–924. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller P. J., Funder J. W. The cellular physiology of glandular kallikrein. Kidney Int. 1986 May;29(5):953–964. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson G. T., Ljunggren O., Boonekamp P., Lerner U. Stimulation of bone resorption in cultured mouse calvaria by Lys-bradykinin (kallidin), a potential mediator of bone resorption linking anaphylaxis processes to rarefying osteitis. Bone Miner. 1986 Sep;1(4):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Isobe M., Moriya H. Kallikrein inhibitors in rat plasma. J Biochem. 1977 Jan;81(1):37–46. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasani M. K., Katori M., Lewis G. P. Intracellular enzymes and kinin enzymes in synovial fluid in joint diseases. Origin and relation to disease category. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Sep;28(5):497–512. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.5.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLERMEYER R. W., BRECKENRIDGE R. T. THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS IN ACUTE GOUTY ARTHRITIS. I. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SODIUM URATE CRYSTALS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner U. H., Jones I. L., Gustafson G. T. Bradykinin, a new potential mediator of inflammation-induced bone resorption. Studies of the effects on mouse calvarial bones and articular cartilage in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):530–540. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lâuar N., Bhoola K. Release of tissue kallikrein from the isolated perfused kidney. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;198(Pt A):347–354. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5143-6_47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Webster M. E., Goldfinger S. E., Seegmiller J. E. The presence of a kinin in inflammatory synovial effusion from arthritides of varying etiologies. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. D., Boyden K. N., Hendrickson S. M., Muirden K. D. Antitrypsin activity and enzyme inhibitors in the rheumatoid joint. J Rheumatol. 1981 Jul-Aug;8(4):547–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPECTOR W. G., WILLOUGHBY D. A. VASOACTIVE AMINES IN ACUTE INFLAMMATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:839–846. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M. Kallikreins (kininogenases)--a group of serine proteases with bioregulatory actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Mar;31(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streefkerk J. G. Inhibition of erythrocyte pseudoperoxidase activity by treatment with hydrogen peroxide following methanol. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Oct;20(10):829–831. doi: 10.1177/20.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Ito A., Mori Y., Hayashi Y., Matsuta K. Kallikrein in synovial fluid with rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1987 Apr;37(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(87)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Irie A., Katayama Y., Ito K., Miyake Y. Activation mechanism of human urinary prokallikrein using trypsin as a model activator. Biochem Int. 1987 Mar;14(3):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]