Abstract
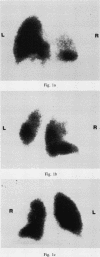
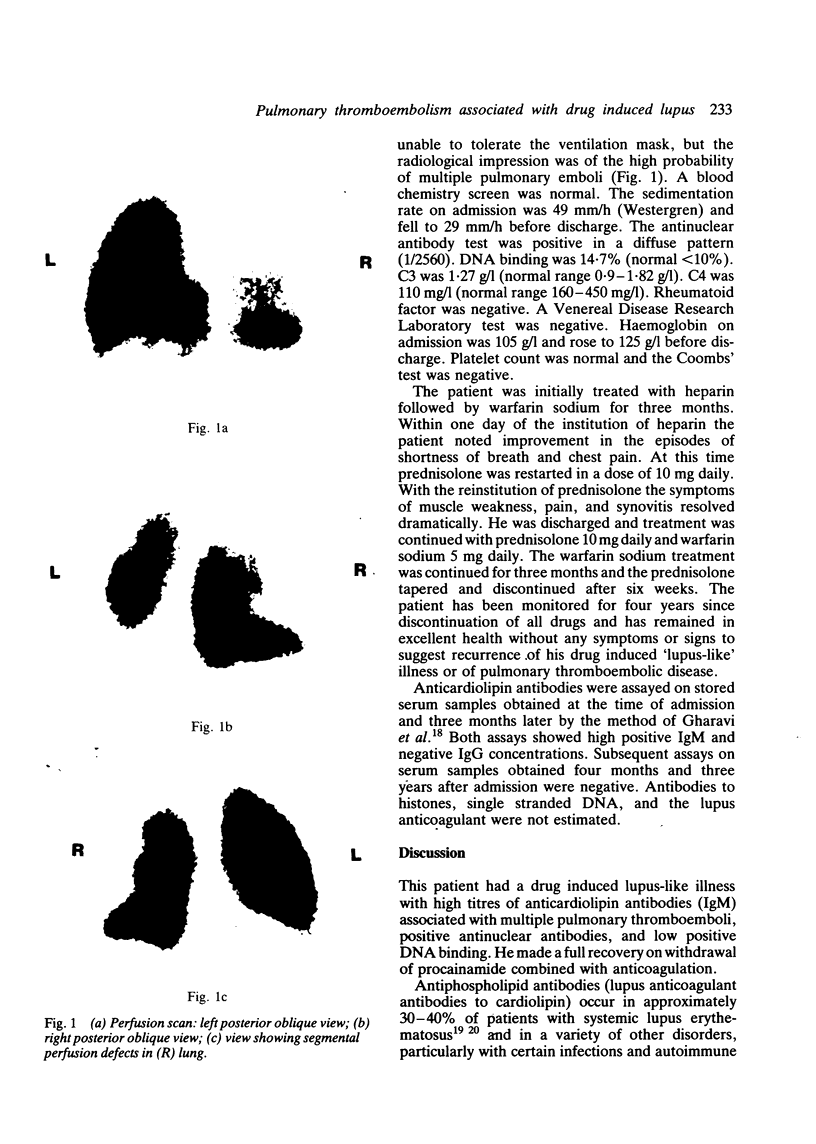
Procainamide is the commonest cause of a drug induced lupus syndrome. Long term administration of this compound may induce a variety of immunological abnormalities, including antinuclear antibodies. Uncommonly, 'lupus anticoagulants' have been demonstrated in the absence of other evidence of drug induced lupus. Details of a 67 year old man who developed not only drug induced lupus but also antiphospholipid antibodies which were associated with multiple pulmonary thromboemboli after the administration of procainamide are recorded.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson R. A., Benbow A. G., Speirs C. J., Jackson N., Hughes G. R. Pulmonary hypertension in hydralazine induced systemic lupus erythematosus: association with C4 null allele. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):771–773. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson R. A., Harris E. N. Anticardiolipin antibodies--clinical associations. Postgrad Med J. 1986 Dec;62(734):1081–1087. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.62.734.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor J. R., Welsh K. I., Tinoco R. M., Dollery C. T., Hughes G. R., Bernstein R., Ryan P., Naish P. F., Aber G. M., Bing R. F. Hydralazine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: influence of HLA-DR and sex on susceptibility. Lancet. 1980 May 24;1(8178):1107–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M., Klajman A., Moalem T., Yaretzky A., Ben-Efraim S. Circulating immune complexes in sera from patients receiving procainamide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Feb;12(2):220–227. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. R., Boss G. R., Wolfson J. S. Circulating anticoagulant in the procainamide-induced lupus syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Oct;137(10):1471–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren S. E., Condemi J. J., Bignall M. C., Vaughan J. H. Antinuclear antibody induced by procainamide. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 10;281(2):64–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907102810203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Christiansen A. H., Ullman S., Asboe-Hansen G. Hydralazine-induced Lupoid syndrome. Biochemical and immunological studies. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Jun;195(6):443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canoso R. T., Sise H. S. Chlorpromazine-induced lupus anticoagulant and associated immunologic abnormalities. Am J Hematol. 1982 Sep;13(2):121–129. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar A. J., Robinson J., Barr L. Antibody deposition in the pleura: a finding in drug-induced lupus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1978 Jun;61(6):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(78)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokron R., Robert A., Rozensztajn L., Abuaf N., Dumoulin P., Valty J. Lupus induit par la procaïnamide avec anticoagulant circulant. Nouv Presse Med. 1982 Sep 4;11(34):2568–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Furie B. C., Griffin J. H., Furie B., Willey R. Circulating inhibitors of blood coagulation associated with procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(4):401–407. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Rick M. E., Wakem C. J. Studies on a circulating anticoagulant in procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Nov;141(12):1688–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson M. F., Martin V. M., Markham R. L. Antinative DNA antibodies as a reaction to pyrazole drugs. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Aug;34(4):373–375. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irias J. J. Hydralazine-induced lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jul;129(7):862–864. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120440078018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C., Phillips P. E. Procainamide-induced lupus with vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1986 Jul-Sep;4(3):290–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. I., Zakher F., Sabin S. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus with in vivo lupus erythematosus cells in pleural fluid. Chest. 1978 Jun;73(6):875–876. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.6.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klajman A., Farkas R., Gold E., Ben-Efraim S. Procainamide-induced antibodies to nucleoprotein, denatured and native DNA in human subjects. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Mar;3(4):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADD A. T. Procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 27;267:1357–1358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212272672608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., CHase P. H. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Aug;5(1):83–103. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(75)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Greenberg C. S., Currie M. S. Procainamide-induced lupus anticoagulants and thrombosis. South Med J. 1988 Feb;81(2):262–264. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198802000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLain D. A., Hahn B. H. Cryoglobulins in the procainamide-induced lupus syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):305–307. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueh J. R., Herbst K. D., Rapaport S. I. Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):156–159. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nick J., Combrisson A., Reignier A., Verdy E., Gally A. M., Bakouche P., Dudognon P., Dray C. Lupus iatrogène à la procaïnamide avec anticoagulant circulant. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1978 Apr;129(4):259–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Agnello V. D., Tan E. M. Reactivity of anti-histone antibodies induced by procainamide and hydralazine. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Oct;25(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Ziff M. Natural antibodies to procaine amide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Nov;3(9):901–909. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahenk Z., Mendell J. R., Rossio J. L., Hurtubise P. Polyradiculoneuropathy accompanying procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus: evidence for drug-induced enhanced sensitization to peripheral nerve myelin. Ann Neurol. 1977 Apr;1(4):378–384. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleider M. A., Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A., Coleman M. A clinical study of the lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1976 Oct;48(4):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsinger P. D., Zvaifler N. J., Bluestein H. G. Hypocomplementemia in procainamide-associated systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Mar;84(3):293–293. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle T. S., Jr, Ainsworth S. K. Procainamide-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Renal involvement with deposition of immune complexes. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Sep;100(9):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Davis J. S., 4th Anti-DNA antibody in procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus. Determinations using DNA fractionated by methylated albumin-Kieselguhr chromatography. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):97–110. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarrabi M. H., Zucker S., Miller F., Derman R. M., Romano G. S., Hartnett J. A., Varma A. O. Immunologic and coagulation disorders in chlorpromazine-treated patients. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):194–199. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zech P., Colon S., Labeeuw M., Bernheim J., Blanc-Brunat N. Nephrotic syndrome in procainamide induced lupus nephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1979 Apr;11(4):218–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]