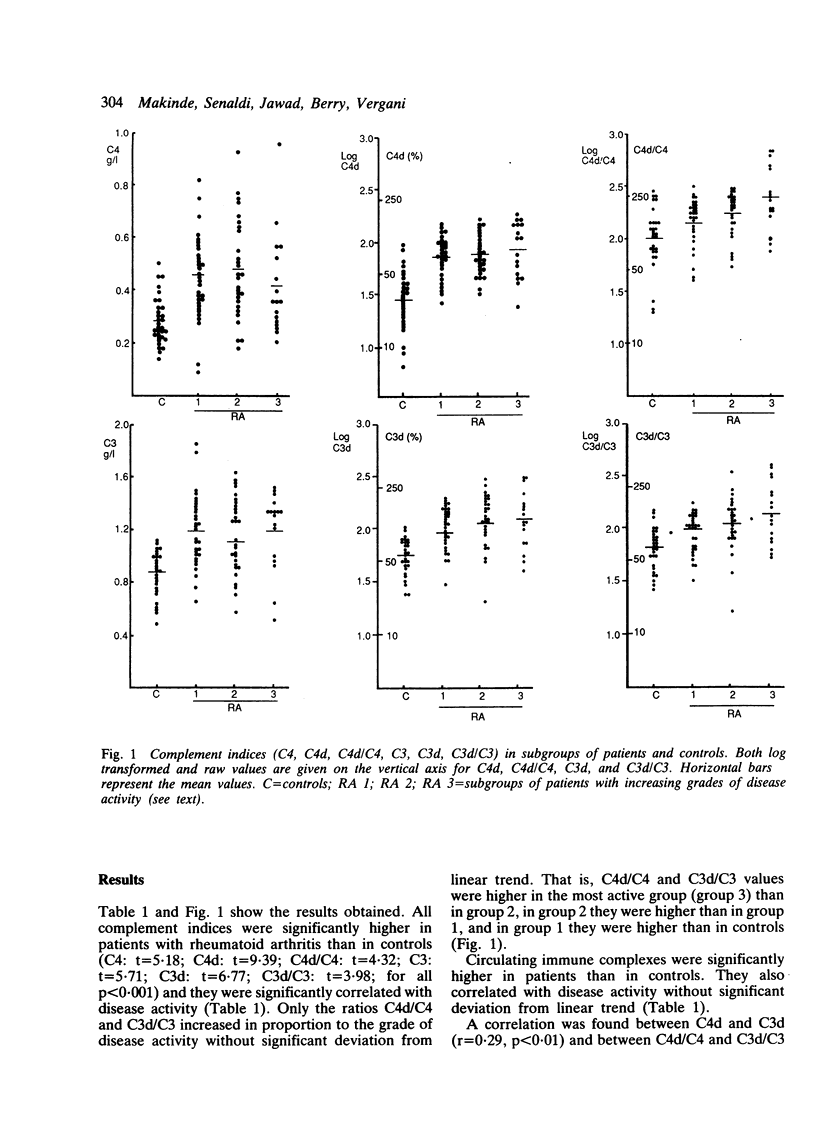
Abstract
Levels of C4d, a fragment of C4 generated during activation of the classical complement pathway, were measured in the plasma of 77 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and 30 healthy subjects. Disease activity was judged according to Ritchie's articular index to be mildly active in 31 (group 1), moderately active in 29 (group 2), and severely active in 17 patients (group 3). Plasma levels of C3d, a fragment of C3, and serum levels of C4, C3, and immune complexes were also measured. The ratios C4d/C4 and C3d/C3 were calculated. The C4d/C4 and C3d/C3 ratios and the levels of circulating immune complexes correlated with the degree of disease activity without significantly departing from linear trend and discriminated between patients with different grades of disease activity. C4d, C3d, C4, and C3 also correlated with disease activity but in a non-linear relationship. A significant correlation was found between C4d and C3d, and between C4d/C4 and C3d/C3. C4d and C4d/C4 also correlated with circulating immune complexes. These results indicate that indices of C4 and C3 activation, in particular the ratios C3d/C3 and C4d/C4, provide a sensitive assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis, and confirm the major part played by the classical complement pathway in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowicz A., Kappelgaard E., Petersen J., Nielsen H., Ingemann-Hansen T., Halkjaer-Kristensen J., Sørensen H. Complement C3c and C3d in plasma and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1983 Dec;91(6):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies E. T., Nasaruddin B. A., Alhaq A., Senaldi G., Vergani D. Clinical application of new technique that measures C4d for assessment of activation of classical complement pathway. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Feb;41(2):143–147. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay R., Micheli A., Fallet G. H. Behaviour of synovial complement C3 and C4 components in inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases, before and after synoviorthesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Apr;34(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levamisole in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomised double-blind study comparing two dosage regimens of levamisole with placebo. Multicentre study group. Lancet. 1978 Nov 11;2(8098):1007–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., Vergani D., Tee D. E., Bevis L., de Beer F. C., Berry H., Hamilton E. D., Mace B. E., Pepys M. B. Correlation in rheumatoid arthritis of concentrations of plasma C3d, serum rheumatoid factor, immune complexes and C-reactive protein with each other and with clinical features of disease activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):747–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom H., Curd J. G., Kaplan R. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Vaughan J. H. Activation of the fourth component of complement (C4): assessment by rocket immunoelectrophoresis and correlation with the metabolism of C4. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2780–2785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lea T., Mellbye O. J., Pahle J., Grand O., Harboe M. Complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by C3dg and the terminal complement complex. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):715–721. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow W. J., Williams D. J., Ferec C., Casburn-Budd R., Isenberg D. A., Paice E., Snaith M. L., Youinou P., Le Goff P. The use of C3d as a means of monitoring clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Dec;42(6):668–671. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.6.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Zubler R. H., Gabay R., Joliat G., Karagevrekis C. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating complement breakdown products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation between plasma C3d, circulating immune complexes, and clinical activity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):862–868. doi: 10.1172/JCI108708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Depressed synovial fluid levels of properdin and properdin factor B in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):289–295. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubart A. F., Ewald R. W., Schroeder W. C., Rothschild H. J., Bhatavadekar D. N., Pullen P. K. Serum complement levels in rheumatoid arthritis. A longitudinal study of 43 cases with correlation of clinical and serological data including rheumatoid factor and thermolabile inhibitor of the F-II L.P. test. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Sep;24(5):439–450. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.5.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., van Rooyen A., Vogelaar C., Pillay M., Hack E. Complement (C3) metabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus in relation to the disease course. Rheumatol Int. 1986;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00541371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., BAYLES T. B., FAVOUR C. B. Serum complement in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med Sci. 1951 Aug;222(2):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Bevis L., Nasaruddin B. A., Mieli-Vergani G., Tee D. E. Clinical application of a new nephelometric technique to measure complement activation. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;36(7):793–797. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.7.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


