Abstract
Background and Aims
The prevalence of chronic liver disease in adults exceeds 30% in some countries and there is significant interest in developing tests and treatments to help control disease progression and reduce healthcare burden. Breath is a rich sampling matrix that offers non-invasive solutions suitable for early-stage detection and disease monitoring. Having previously investigated targeted analysis of a single biomarker, here we investigated a multiparametric approach to breath testing that would provide more robust and reliable results for clinical use.
Methods
To identify candidate biomarkers we compared 46 breath samples from cirrhosis patients and 42 from controls. Collection and analysis used Breath Biopsy OMNI™, maximizing signal and contrast to background to provide high confidence biomarker detection based upon gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Blank samples were also analyzed to provide detailed information on background volatile organic compounds (VOCs) levels.
Results
A set of 29 breath VOCs differed significantly between cirrhosis and controls. A classification model based on these VOCs had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.95±0.04 in cross-validated test sets. The seven best performing VOCs were sufficient to maximize classification performance. A subset of 11 VOCs was correlated with blood metrics of liver function (bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time) and separated patients by cirrhosis severity using principal component analysis.
Conclusions
A set of seven VOCs consisting of previously reported and novel candidates show promise as a panel for liver disease detection and monitoring, showing correlation to disease severity and serum biomarkers at late stage.
Keywords: Breath Biopsy, Non-invasive, Biomarker, Cirrhosis, Liver function test
Introduction
Progression of chronic liver diseases to cirrhosis is often asymptomatic, with more than 50% of the cases diagnosed at advanced stages with clinical decompensation, when therapeutic interventions are often ineffective for preserving liver function.1,2 Early detection is still limited by available diagnostic tests, which are inadequate for population screening or lack the required sensitivity or specificity. The gold standard remains liver biopsy despite the proliferation of non-invasive surrogate imaging techniques and serological markers.3 These tests also rely on anatomical alterations rather than hepatic function and are mainly effective at advanced stages.2–4 Additionally, absence of non-invasive functional tests represents a hurdle for clinical outcome evaluation of therapeutic interventions.
Analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath represents an emerging diagnostic approach with the potential to develop functional, non-invasive tests for early detection based on the reduced hepatic function associated with chronic liver diseases, especially clearance and protein synthesis capacity.5–8 Impaired hepatic function shifts the spectrum of compounds detoxified by the liver. A subset of these can be measured in breath as VOCs and are potential biomarkers.8–13 In our previous study,8 limonene, an exogenous VOC taken-up mainly through the diet, was elevated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis and had diagnostic potential in agreement with previous exploratory studies.10,14 This compound is metabolized in the liver by the enzymes CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 to trans-carveol and perillyl alcohol.15 In the cirrhotic liver, reduced activity of these enzymes impairs hepatic clearance, resulting in extended limonene half-life in the bloodstream, which in turn, raises its abundance in the breath.10 We additionally showed that limonene correlated with blood metrics that reflect hepatic clearance and protein synthesis capacity, indicating that a limonene breath test could be applied as functional means for chronic liver disease detection.8
Nonetheless, the complexity of hepatic metabolic pathways does not allow a comprehensive evaluation of liver function from a single biomarker. Thus, combination of multiple VOCs generated by alterations of different metabolic pathways provides a more exhaustive picture of the liver condition, improving diagnostic performances of a breath test and providing the potential to detect early-stage liver disease. To these purposes, we used Breath Biopsy OMNI global VOC analysis to discover differentially abundant VOCs in patients with cirrhosis, compared to controls in order to identify potential disease-related biomarkers that could be used to diagnose patients with progressive liver disease, from early to end stage, in large-scale cohorts.
Methods
Study design and subjects
This cross-sectional case-control study was part of the Owlstone Medical (Cambridge, UK) and Cancer Research UK (CRUK) funded PAN-study (NCT03756597, US National Library of Medicine), and was approved by the ethics committee of the East of England–Cambridge East Research Ethics Committee (REC reference: 18/EE/0041. IRAS ID: 237560). All participants provided written informed consent. A total of 46 subjects with cirrhosis, and 42 controls were enrolled with random recruitment. Subjects >30 years of age were recruited from the clinical research facility at Addenbrooke’s Hospital (Cambridge) or through the Cambridge BioResource. Patients had an established histological or radiological diagnosis of cirrhosis according to European Association for the Study of the Liver and American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases guidelines.16,17 Disease severity was classified using the Child-Pugh (CP) scoring system.18 Per-protocol only patients with CP class A or B were eligible for the study regardless of disease etiology. Patients who developed hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the context of cirrhosis were not receiving any anticancer treatment at the time of sampling. Control subjects had no known liver disease and were excluded if they were under medical investigation or had a history of non-skin malignancy in the last 2 years. No dietary restrictions were applied to any participant. Data about the participants are reported in Table 1.
Table 1. Subject characteristics.
| Characteristic | Control | Cirrhosis | p-values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 42 | 46 (14 with HCC) | |
| Age in years, median (range) | 62 (34–81) | 58.5 (35–79) | 0.61 |
| Male/female sex | 21/21 | 29/17 | |
| Height median, cm (range) | 170 (157–191) | 173 (150–197) | 0.67 |
| Weight median, kg (range) | 76 (51–149) | 85 (48–165) | 0.03 |
| BMI median, kg/m2 (range) | 25.5 (18.9–46.0) | 29.7 (18.0–43.4) | 0.01 |
| Child-Pugh class A/B/C/na* | – | 30/12/1/3 | |
| MELD median (range) | – | 8 (7–19) | |
| UKELD median (range) | – | 48.1 (44.7–60.5) | |
| Total bilirubin median, µmol/L (range) | – | 17 (7–86) | |
| Serum albumin median, g/L (range) | – | 35 (24–45) | |
| INR median, % (range) | – | 1.07 (0.82–1.78) | |
| ALT median, IU/L (range) | – | 27 (14–105) | |
| ALP median, IU/L (range) | – | 100 (40–440) | |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | – | 67 (38–147) | |
| Sodium, mM | – | 139 (126–144) |
*Some blood metrics were not available for three patients. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; BMI, body mass index; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease; UKELD, the United Kingdom model for end-stage liver disease; INR, international normalized ratio; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
Breath sampling
Acquisition of Breath Biopsy samples was performed by using the ReCIVA® Breath Sampler (Owlstone Medical) as previously reported.8,19 Detailed methods are available in the Supplementary File 1.
Analytical measurements
Breath samples were analyzed using Breath Biopsy OMNI global VOC analysis as previously described.8 Detailed methods are available in the Supplementary File 1.
Feature extraction
Raw data files, collected in profile mode, were centroided using the peak picking vendor algorithm of the ProteoWizard-MSConvert application.20 The centroid data were imported into MZmine 2.53 to proceed with feature extraction workflow.21 ADAP chromatogram builder module was used to detect the peak with the a minimum highest intensity of 1.0E5 and m/z tolerance of 5 PPM.22 Detected features were deconvoluted using the Wavelet ADAP algorithm with the parameters S/N of 3, S/N estimator wavelet coefficient. SN; coefficient/area threshold of 100, peak duration range of 0–1.0 m, and RT wavelet range of 0–0.15 m. Hierarchical clustering was used to combine peaks into analytes and construct fragmentation spectra for each analyte as described by Smirnov, et al.23 ADAP Aligner (GC) was used for retention time alignment, with a minimum confidence of 0.1, an RT tolerance of 0.5 m, an m/z tolerance of 5 ppm, score threshold of 0.75, and a score weight of 0.1. Retention time similarity was calculated using the retention time difference (fast) method. Compounds were tentatively identified using the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) library and in-house high resolution accurate mass (HRAM) library (https://www.owlstonemedical.com/about/blog/2022/may/30/biomarker-analysis-breath-hram-library/). Database hits were filtered according to their structure relevance to standard compounds. Identity of compounds was validated by standards injection (R)-(+)-Limonene,9–12,14,24,25 (183164, (Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, UK), 2-pentanone,9,10,24,26 (471194; Sigma Aldrich), dimethyl selenide,9,26 (41572; Sigma Aldrich), Indole (I3408; Sigma Aldrich), and eucalyptol (29210; Sigma Aldrich).
Data handling and statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by the Python and R programming languages (Python Software Foundation, Python Language Reference, version 2.7. http://www.python.org and R Core Team, 2021, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org). Data visualization was performed with matplotlib,27 seaborn,28 and ggplot2,29 libraries.
Intensity of VOCs (count/m), median, and range were compared between groups using the Mann-Whitney U-test for non-parametric data, and p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant unless stated otherwise. A total of 11 VOCs with a Benjamin-Hochberg adjusted p<0.1 advanced to investigation for correlation with blood metrics of liver function. Data was pre-processed as described below and breath-sample assay results were averaged. Correction for instrument fluctuation was obtained by probabilistic quotient normalization.30 Log transformation was performed to bring VOC intensity closer to a normal distribution.
To build a classification model, first dimensionality reduction was performed by considering as candidate biomarkers only features identified as statistically significant in the univariate analysis (p<0.05) between cirrhosis and controls. This selection reduced the feature space that any model needs to search, and thus the likelihood of unstable results, or overfitting.31 The top VOCs for classification were identified by stability selection and LASSO logistic regression.32 Model performance was validated by five-fold cross validation, with VOC selection performed within each fold training set. Only features above a certain stability score were selected in the model. The importance of each feature for classification was expressed as the resulting average stability score across the five-fold cross validation.
Stability selection chooses the features that behave consistently through permutations of a dataset. In the context of a clinical test, it may be important to reduce the number of features/VOCs required for further measurement. To this end, an analysis was conducted to observe how few features with similar AUCs could be obtained compared with the stable model. Step-forward feature selection,33 with a simple five-fold cross validation was used to obtain the best performing models with one or two features, or so on, minimizing the number of VOCs necessary for a potential breath test. Starting from a feature set size of one, classification performance of combinations of candidate biomarkers expressed as AUCs was measured by adding one new VOC at a time to the model.
Within the cirrhosis group, the relationship between blood bilirubin, albumin and international normalized ratio (INR), and breath metrics was assessed by canonical correlation analysis (CCA).34 CCA finds the relationship between two multivariate sets of variables measured for the same set of samples and was considered as the extension of bivariate correlations. The identified new bases (new directions) for each data set were a linear combination of the original parameters. The new bases (i.e., canonical variates) represented maximized correlations of the original parameters in two datasets (i.e., VOCs and blood metrics). The resulting CCA score plot was generated using statistically significant canonical variates. In the score plot, each point corresponded to the combined information from breath and blood samples collected from the same patient. The shape of the projected data point indicates the correlation between two blocks of data, which were VOCs in breath and blood metrics. The contribution of the original parameters to the correlation between the two blocks of variables was estimated by calculating the canonical loadings, which expressed the correlation between the original variable and the canonical variate. Variance of selected features in relation to severity of cirrhosis was assessed by principal component analysis (PCA).
Results
Subject characteristics
Breath samples were collected from 42 controls, mean 62 (range 34–81) years of age, 21 men and 21 women, and 46 patients with cirrhosis (14 complicated by HCC, mean 58.5 (range 35–79) years of age, 29 men and 17 women. Subject characteristics are shown in Table 1, and in Ferrandino et al.8 An unbalanced sex ratio was observed in the cirrhosis group, consistent with the known male preponderance of liver disease. However, no sex-linked differences in exhaled VOCs were identified (Supplementary Fig. 1) or have been previously described.8,25,35 Significant differences in body weight (p=0.03) and body mass index (BMI, p=0.01) were observed between the study groups.
Generation of the discovery dataset
Automated feature extraction performed on a total of 478 ion chromatograms, 176 breath samples measured in duplicate, 123 calibration standards, 109 quality checks, and 70 blanks, resulted in a data frame of 2,593 molecular features (MFs). Of these, 768 had <50% missing values. Discriminatory potential between study groups of environmental contaminants may originate from spurious correlations between variables generated by data normalization.36 To exclude those contaminants, we compared the intensity of each MF with those measured in blanks. A total of 196 MFs referred to as VOCs were significantly elevated in breath compared with blanks (p<0.1, Mann-Whitney U-test, and positive fold change in breath) and were used to generate the discovery dataset. An initial quality control based on these VOCs was constructed by PCA and separated breath samples from blanks over the first two principal components, and explained 24.1% and 14.4 % of data variance, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 2)
Identification of VOCs associated with cirrhosis
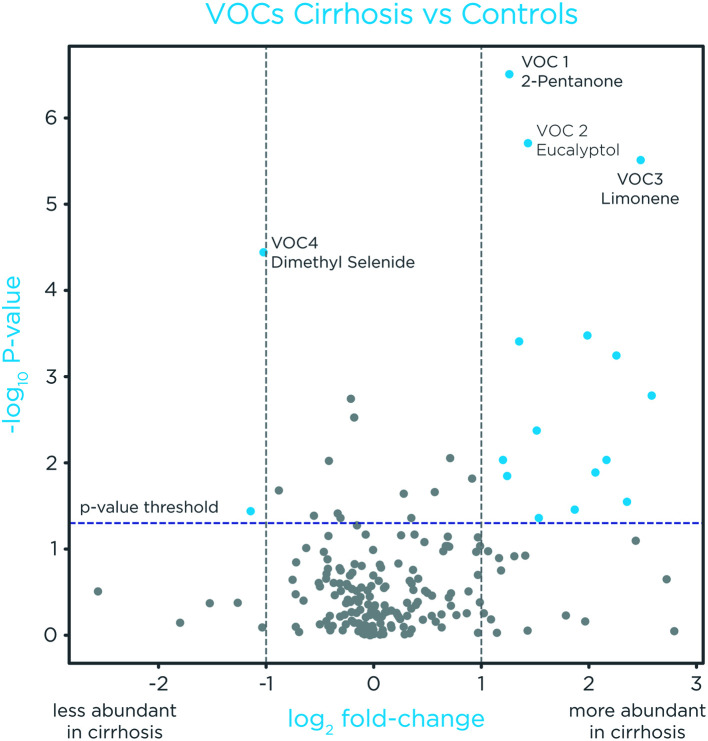
An exploratory, cirrhosis-associated VOC profile generated by univariate analysis with uncorrected p-values of <0.05 (Mann-Whitney U-test) and log fold-change ≥ 2, resulted in 15 upregulated and 2 downregulated VOCs in the breath of cirrhosis patients compared with controls (Fig. 1). As expected, limonene (m/z 91.05, RT ∼11 m), and 2-pentanone (m/z 71.04, RT ∼5 m) were upregulated, and dimethyl selenide (m/z 109.96, RT ∼3 min), was downregulated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis (Fig. 1) as previously reported.9–12,14,24–26
Fig. 1. Volcano plot of exhaled VOCs.
The X-axis represents the log2 mean ratio fold-change of the relative abundance of each VOC between cirrhosis and controls. The Y-axis represents the p-value of each VOC. Compounds with fold-change >2 and p<0.05 are highlighted in blue. Limonene and 2-pentanone were elevated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis and dimethyl selenide was reduced, as expected. VOC, volatile organic compound.
Estimation of classification performance
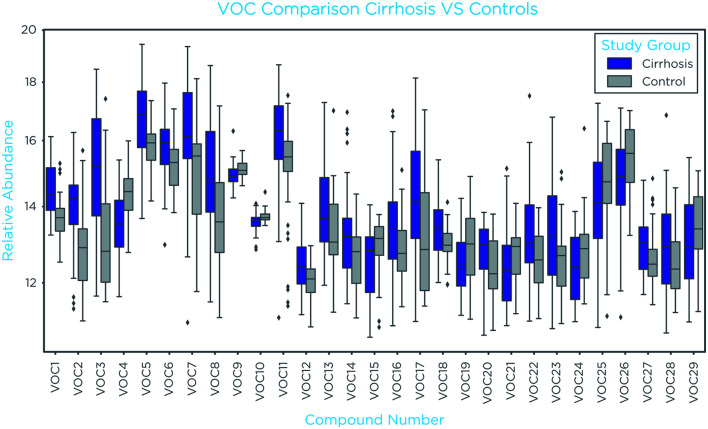
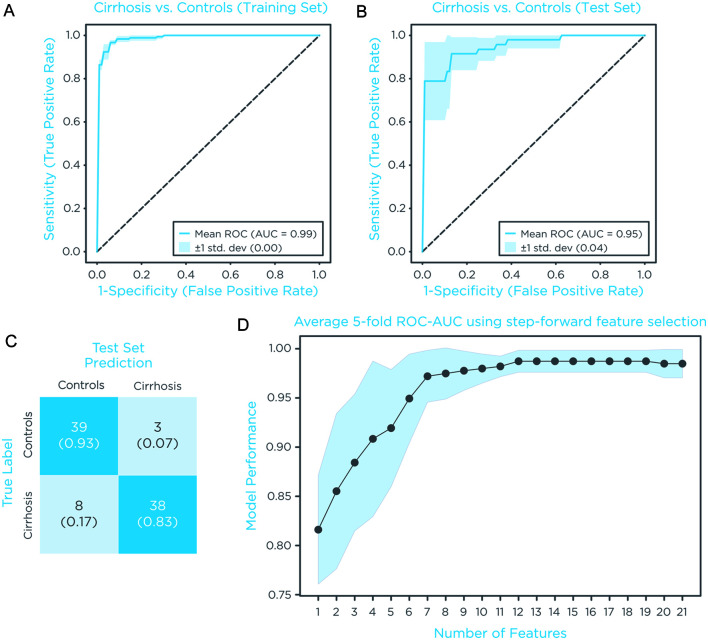
A total of 29 on-breath VOCs were differentially abundant (unadjusted p-value <0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test) between controls and cirrhosis groups (Fig. 2) and were first used to generate individual receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plots to estimate individual diagnostic performance predicting the presence of cirrhosis. The top four compounds with AUC of 0.82, 0.80, 0.79, and 0.76 are shown in Figure 3. Subsequently, the performance of combinations of VOCs was explored. A stratified five-fold cross validation train/test split of 70%/30% was performed to build a classification model. In the training sets, the model returned an average AUC of 0.99±0.00 (Fig. 4A), and in the test sets, an average AUC of 0.95±0.04 (Fig. 4B). The corresponding confusion matrix generated by cross-validated predictions (Fig. 4C) had three false positives (7%) that were misclassified because of elevated levels of limonene or 2-pentanone. Of the eight false negatives (17%), six were CP class A, two were CP class B, and three had HCC with CP class A.
Fig. 2. Box plots of discriminatory VOCs between cirrhosis and controls.
A total of 29 on-breath VOCs were found significantly different (p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test) between control and cirrhosis groups. VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
Fig. 3. Receiver operating characteristic plots of the four top single VOCs comparing cirrhosis vs. controls.
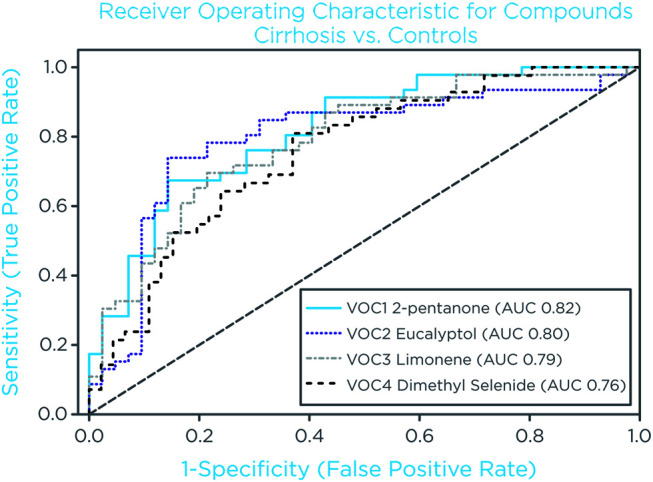
The top 4 ROC plots for on-breath VOCs were calculated to explore their discriminatory performance. 2-pentanone, limonene, and dimethyl selenide were found among them. ROC, receiver operating characteristic; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
Fig. 4. Classification performance of combined VOCs.
(A) ROC plot and confidence interval obtained for the training set. (B) ROC plot and confidence interval obtained for the test set. (C) Corresponding confusion matrix generated using the Youden index as threshold. (D) Improvements of classification performance by addition of VOCs to the model. ROC, receiver operating characteristic; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
To estimate a trade-off between the number of features to measure, and classification performance in a potential breath test, we used step-forward feature selection. Average AUC plateaus after the first seven features (Table 2) were added to the model (Fig. 4D). Identity of these top performing VOCs is reported in Table 2 and their detailed fragmentation pattern is reported in Supplementary Table 1. Additionally, potential effects of cirrhosis comorbidities, namely, obesity (BMI>30), type 2 diabetes, HCC, and portal hypertension on these seven top performing VOCs were explored. Significantly increased limonene and 2-pentanone were found in patients with portal hypertension (n=7), and significantly increased indole with obesity (n=23, Supplementary Table 2). No significant differences were found for the other comorbidities.
Table 2. Best performing VOCs.
| VOC | Compound ID | RT | m/z | Average stability score | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOC1 | 2-Pentanone | 5.30598 | 71.04919 | 0.916 | HRAM, Standard |
| VOC12 | 1-pentene, 4-methyl, or 1-hexene | 7.62411 | 42.03163 | 0.890 | NIST |
| VOC17 | Indole | 17.13762 | 116.90607 | 0.886 | HRAM, Standard |
| VOC4 | Dimethyl selenide | 3.30723 | 109.963 | 0.762 | HRAM, Standard |
| VOC3 | Limonene | 11.00585 | 91.05427 | 0.734 | HRAM, Standard |
| VOC2 | Eucalyptol | 11.34312 | 139.11181 | 0.732 | HRAM, Standard |
| VOC29 | Benzene, (1-propylnonyl)- | 20.9004 | 133.19707 | 0.6 | NIST |
HRAM, breath biopsy high resolution accurate mass library; VOC, volatile organic compound; RT, retention time.
Identification of breath compounds correlated with hepatic function in subjects with cirrhosis
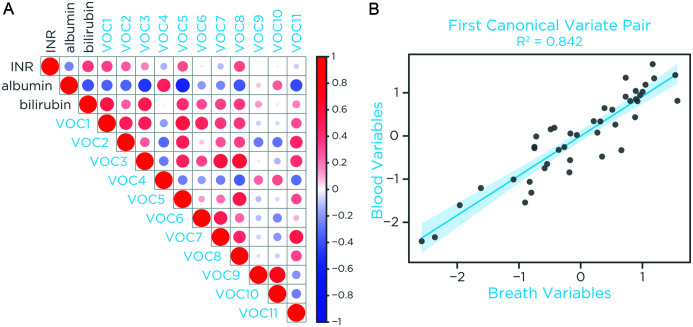
A correction for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) method returned a subset of 11 VOCs with an adjusted p<0.1. Correlations between these selected breath compounds and blood metrics of liver function within the cirrhosis group, namely bilirubin, albumin, and prothrombin time expressed as INR, were first investigated by generating a Pearson correlation matrix visualized in Figure 5A and Table 3. As expected, limonene (VOC3) had a positive correlation with bilirubin and INR and a negative correlation with albumin, as previously reported.8 Other MFs with retention time of ∼11 m had a similar pattern. Consistently, dimethyl selenide (VOC4) and VOC10 that were downregulated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis (Fig. 2), had a positive correlation with albumin. No correlations were observed between VOCs and markers of hepatic inflammation, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), or markers of advanced portal hypertension, such as serum sodium, and creatinine (Supplementary Fig. 3). Interestingly, none of the compounds identified as background contaminants were correlated with blood metrics (data not shown).
Fig. 5. Correlation of breath VOCs with blood metrics of liver function in cirrhosis subjects.
(A) Correlation plot of identified VOCs and serum bilirubin, albumin, and INR. Blue indicates a negative and red a positive correlation. Circle size and color intensity show the magnitude of the correlation. (B) CCA score plot using the first canonical variates of selected sets of VOCs and blood metrics of liver function. Each projected data point represents the combined information of breath VOCs and blood metrics of one cirrhotic patient. The CCA analysis revealed significant correlations, with R2=0.842. CCA, canonical correlation analysis; INR, international normalized ratio; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
Table 3. Area under the curve (AUC) and correlation of VOCs with blood metrics.
| VOC | Identity | AUC | Correlation (coefficient r, p-value) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilirubin | Albumin | PT-INR | |||
| VOC1 | 2-pentanone | 0.82 | 0.548, 0.01 | −0.346, 0.014 | 0.347, 0.013 |
| VOC2 | Eucalyptol | 0.80 | 0.258, 0.07 | −0.348, 0.013 | 0.264, 0.064 |
| VOC3 | Limonene | 0.79 | 0.516, 0.01 | −0.487, 0.01 | 0.178, 0.216 |
| VOC4 | Dimethyl selenide | 0.76 | −0.012, 0.936 | 0.492, 0.01 | −0.135, 0.352 |
| VOC5 | Terpene | 0.72 | 0.415, 0.003 | −0.552, 0.01 | 0.309, 0.029 |
| VOC6 | 2-Pentanone (m/z 43.02369) | 0.72 | 0.308, 0.03 | −0.196, 0.173 | −0.022, 0.881 |
| VOC7 | Terpene | 0.71 | 0.344, 0.014 | −0.236, 0.098 | −0.112, 0.441 |
| VOC8 | Terpene | 0.70 | 0.368, 0.009 | −0.388, 0.005 | 0.338, 0.016 |
| VOC9 | Unknown | 0.69 | 0.136, 0.346 | 0.067, 0.642 | 0.0, 1.0 |
| VOC10 | Unknown | 0.68 | 0.028, 0.845 | 0.267, 0.061 | −0.014, 0.921 |
| VOC11 | Terpene | 0.67 | 0.177, 0.22 | −0.412, 0.003 | −0.077, 0.594 |
VOC, volatile organic compound; AUC, area under the curve; PT-INR, prothrombin time-international normalized ratio.
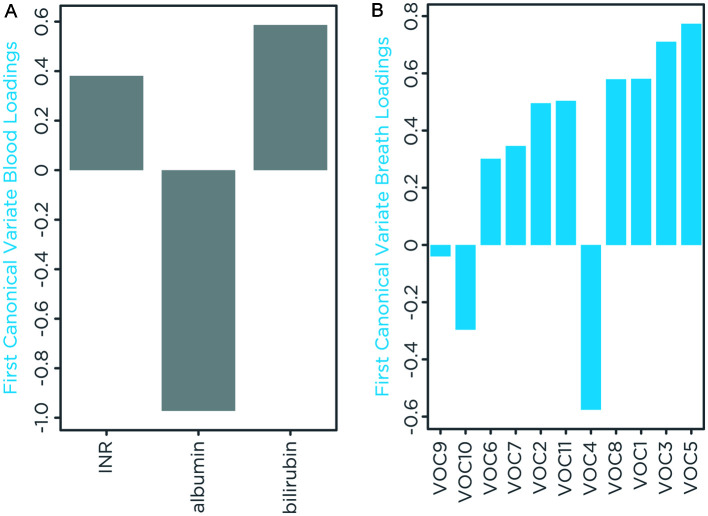
Collective correlations between breath and blood metrics of subjects with cirrhosis were further investigated by using the CCA.34 The resulting CCA score plot of the first canonical variates showed that the set of variables measured in blood significantly correlated with the set of variables measured in breath (R2=0.842, Fig. 5B). Inter-relation between individual exhaled VOCs and blood metrics of liver function was investigated by computing the canonical loadings. These parameters represent the correlation between each variable and its resulting canonical variate, reflecting the contribution of the variable to the overall correlation. Among the set of blood metrics, albumin had a correlation that was the reverse of bilirubin and INR, as expected. Albumin contributed the most to the overall correlation, while INR had the smallest contribution (Fig. 6A). Among the set of breath metrics, eight upregulated VOCs, including limonene (VOC3) and 2-pentanone (VOC1), showed positive loading, while dimethyl selenide (VOC4) and VOC10, which were found downregulated (Fig. 2) had a negative loading, and VOC9 had a loading near zero (Fig. 6B).
Fig. 6. Canonical loadings of set of variables.
Canonical loadings represent the correlation between a variable and its canonical variate and express the contribution of each variable to the overall correlation. (A) Loadings for blood variables, albumin has opposite correlation than bilirubin and INR, as expected. (B) Loadings for breath VOCs, limonene and 2-pentanone had a positive contribution. Dimethyl selenide (VOC4), which was downregulated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis, had a negative correlation. INR, international normalized ratio; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
Effect of cirrhosis severity on exhaled VOCs
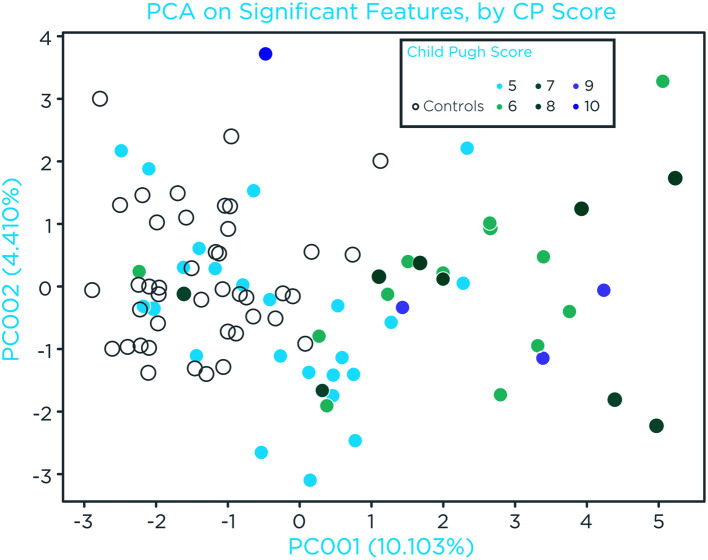
Given that bilirubin, albumin, and INR are used to calculate the CP score, as a readout of hepatic function impairment associated with cirrhosis,18 we investigated the relation of the identified VOCs and this scoring system. The subset of 11 VOCs reported in Table 2 were used to perform PCA and projected data points for each patient were colored by CP score (Fig. 7). PC1 explained 10.1%, and PC2 explained 4.4% of variance and distinguished patients with CP scores >5 from controls. Conversely, ∼50% of the patients with CP score of five overlapped with controls. Two patients with a CP score of >5 overlapped with controls (PC1<0 and PC2<1, Fig. 7). Of those, one had a score of seven points due to the presence of moderate ascites, and the other had an albumin of <35 g/L (34 g/L).
Fig. 7. VOC alterations in relation to cirrhosis severity.
Projected data points of the first two components of a PCA calculated using breath variables with a BH adjusted p<0.1. PC1 explains 10.1% and PC2 4.4% of variance and shows that separation of cirrhotic patients based on their CP score. About 50% of the patients with a CP=5 cluster with controls. BH, Benjamin-Hochberg; CP, Child-Pugh; PCA, principal component analysis; VOC, volatile organic compound.
Discussion
This pilot study demonstrated that a panel of exhaled VOCs discriminated cirrhosis patients from controls with no known liver diseases. The AUC of the test set was 0.95, which was better than the AUC of 0.78 measured when using limonene alone.8 The spectrum of alterations of the exhaled VOCs reflects disease-associated hepatic impairment as demonstrated by correlations with blood biomarkers of clearance and the protein synthesis capacity of the liver. Our data point toward the use of these VOCs as potential biomarkers for functional, non-invasive detection of chronic liver disease. Several studies have identified breath VOCs associated with different stages of liver disease.4,37,38 However, only few of them attempted to explore correlations of VOCs with blood biomarkers of liver function.8,11,14 In this study, comprehensive analysis projected the entire set of discriminant exhaled VOCs into the set of blood metrics of liver function, measured in subjects with cirrhosis, demonstrating a significant collective correlation between the two sets of variables and quantifying the contribution of each single variable to the overall correlation. Additionally, lower-dimensional data, obtained by projection of discriminatory features onto the first two components, revealed a separation of subjects with more advanced cirrhosis estimated by CP score. This innovation in the data analysis workflow contributed one additional layer of confidence to the validity of the identified discriminatory features and demonstrated that alterations of VOCs in breath depend on the extent of disease-associated liver dysfunction. The results expand our previous finding that limonene was correlated with albumin, bilirubin, and INR.8
Taken together, the correlation data provide a novel mechanistic understanding. Alteration of serum bilirubin, albumin, and INR are considered a consequence of reduced clearance and protein synthesis by the liver. Therefore, we speculate that alterations of the identified VOCs are consequence of impaired liver function and can be used to monitor the progression of chronic liver disease. VOC9 was significantly elevated in the breath of patients with cirrhosis and had a poor correlation with blood metrics, indicating that it may be correlated with other alterations associated with chronic liver disease such as inflammation and/or fibrosis. In validation studies, potential correlations of these VOCs with liver biopsy histopathology would pave the way to replacing invasive procedures by breath collection for prognosis following therapeutic interventions.
The results reported here are consistent with existing literature. For example, Dadamio et al. 2011,9 Fernandez Del Rio et al. 2015,10 and Pijls et al. 2016,12 also found a spectrum of cirrhosis-associated compounds in breath. As in those studies, we observed elevated signals of limonene,9–12,14,24,25 2-pentanone,9,10,24,26 and an alkene (1-pentene, 4-methyl or 1-hexene),9 and reduced signals of dimethyl selenide9,26 in the breath of patients with cirrhosis. In contrast, we found an elevated indole signal, which Dadamio et al. 2011 found to be reduced in the breath of patients with cirrhosis.9 In that study, eucalyptol was detected but with no significant differences in the study groups. We found it was elevated in the breath of subjects with cirrhosis. The discrepancies may be explained by different dietary habits that determine the ingestion of foods from which the VOCs originated.
A study strength is the procedures used for breath collection, which are a substantial advance over prior studies. Firstly, we ensured the inhaled air was purified to minimize environmental contribution to the signal. Secondly, the volume of sampled breath or blanks was standardized and closely monitored. Finally, multiple blanks were collected during each session, allowing experimental discrimination of contaminants from exhaled VOCs. Taken together they provided a high degree of confidence in our ability to discern on-breath VOCs from environmental contaminants and use only the former for classification. The detailed clinical characterization of cases adds to the strength of the study, allowing us to evaluate the impact of disease severity on exhaled VOCs and classification performance.
A study limitation is the reduced characterization of subjects allocated to the control group, with no laboratory blood data available. The subjects may have been affected by a liver disease at a preclinical stage and misclassified as false positives, influencing the classification performance. However, establishing the accuracy of a breath test for cirrhosis requires a large population and goes beyond the exploratory nature of this study. Another limitation is the unstandardized dietary intake and exposure to exogenous compounds before testing. On one hand, this represents clinical reality; on the other hand, it could have impacted the discriminatory performance of these compounds. Limonene is a monoterpene isolated from a variety of plant sources.39 2-pentanone has been found in cheddar cheese40 and ripe bananas.41 Selenium, in its different forms, is a micronutrient essential for cellular function and is abundant in plant-based foods.42 Although these compounds accumulate in the body when liver function is impaired,10 subjects at earlier stage cirrhosis, and with random exposure lower than hepatic clearance, may be misclassified as false negative and affect test sensitivity. On the other hand, control subjects exposed to these compounds shortly before testing may result as false positive and impair test specificity. Consistent with this hypothesis, the three false positives allocated by our model in the test set were above the 75th percentile for limonene or 2-pentanone, indicating that they probably ingested these compounds shortly before breath collection. These observations suggest that standardizing compound exposure would be vital to increasing the performance of a breath test so that it can be extended to earlier stage liver diseases such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).5
Classification with combined VOCs outperformed that measured with single compounds, indicating that multiple compounds better represent the complexity of hepatic metabolic pathways. Terpenes, and terpenoids such as limonene and eucalyptol, are mainly metabolized by the CYP system,15,43 which is well established to be downregulated in chronic hepatic conditions including NASH.44–46 2-pentanone and other ketones may be converted to 2-pentanol,47 by αα-alcohol dehydrogenase (αα-ADH),48 and to a lesser extent to 3-Hydroxy-2-pentanone and 2,3-pentanediol.47 Consistent with those observations, liver samples obtained from patients with NASH had reduced ADH and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity.49 Elevated breath levels of alkenes may derive from lipid peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids as a consequence of persistent inflammation and oxidative stress affecting the cirrhotic liver.37 Indole is generated by the catabolism of tryptophan mediated by gut bacteria.37 Impaired hepatic clearance may explain elevated levels of indole in cirrhosis. Alkylbenzenes with a long alkyl group may be oxidized to the corresponding carboxylic acids and undergo β-oxidation to form benzoic acid, which is then converted to hippuric acid. This metabolic pathway was found downregulated in subjects with cirrhosis.50 Dimethyl selenide is an excretion product of selenium metabolism.42 Impaired organic and inorganic selenium biotransformation explains downregulation of dimethyl selenide in the breath of cirrhotic patients. Consistent with this hypothesis, plasma selenium concentration was reduced in patients with cirrhosis to an extent related to disease severity.51 Cirrhosis comorbidities may also influence the amount of exhaled VOCs. Increased levels of limonene and 2-pentanone in subjects with cirrhosis and portal hypertension compared to those without portal hypertension, suggest that altered blood flow to the liver contributes to reduce the hepatic ability to clear these compounds. Similarly, obese patients with increased levels of indole, may have alterations of gut bacteria leading to increased production of this compound. That, coupled with reduced hepatic clearance leads to greater elevation of levels in the breath. Although, information on comorbidities was collected, the study design was not optimal to address those questions.
Collectively, the evidence indicates that breath analysis looking at specific VOCs has potential to assess functional alterations of specific metabolic pathways associated with chronic liver diseases. Although there is no clinical need for an additional diagnostic test for cirrhosis, current diagnostic modalities have limitations as screening tools. Consistently, more than 50% of the subjects receive a diagnosis after suffering decompensating events.1,2,52 A breath-based test could be used as a screening tool either in primary care, or for at home self-testing, such that lifestyle changes and therapeutic interventions could be implemented before the first episode of decompensation.
In summary, this study identified a set of exhaled VOCs with alterations that seem to be driven primarily by functional impairment of the liver. The results underpin earlier observations that downregulation of different hepatic metabolic pathways occurring in cirrhosis and early stages of liver disease may be the underlying mechanism. Interestingly, most of the VOCs were of exogenous origin. Further investigation will establish if adjustment of the exposure to these VOCs allows detection of more subtle metabolic alterations that occur in earlier stages of liver diseases such as NASH.
Supporting information
PCA dimensionality reduction using on-breath VOCs. Projected data points on the first two principal components were colored by sex. PC1 explains ∼10% and PC2 ∼7% of the variance. PCA, principal component analysis; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
PCA of breath samples and blanks. Projected data points in different types of samples are shown by different colors. PC1 explains ∼24% and PC2 ∼14% of variance and show separation of breath from blanks. PCA, principal component analysis.
Blue indicates a negative and red a positive correlation. Circle size and intensity of color show the magnitude of the correlation. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the selfless contributions of all subjects who partook in this study. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Abbreviations
- ADH
alcohol dehydrogenase
- ALDH
aldehyde dehydrogenase
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AUC
area under the curve
- BH
Benjamin-Hochberg
- BMI
body mass index
- CCA
canonical correlation analysis
- CP
Child-Pugh
- GC-MS
gas chromatography mass spectrometry
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HRAM
high resolution accurate mass
- INR
international normalized ratio
- MFs
molecular features
- PCA
principal component analysis
- ROC
receiver operating characteristic
- RT
retention time
- VOCs
volatile organic compounds
Ethical statement
This cross-sectional case-control study was part of Owlstone Medical and Cancer Research UK (CRUK) PAN-study (NCT03756597 U.S. National Library of Medicine), which was approved by the ethics committee of the East of England – Cambridge East Research Ethics Committee (REC reference: 18/EE/0041. IRAS ID: 237560) and all participants provided written informed consent.
Data sharing statement
The supplementary tables, figures, and methods used to support the findings of this study are included within the supplementary information files.
References
- 1.Holzhutter HG, Wuensch T, Gajowski R, Berndt N, Bulik S, Meierhofer D, et al. A novel variant of the (13)C-methacetin liver function breath test that eliminates the confounding effect of individual differences in systemic CO2 kinetics. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94(2):401–415. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02654-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2014;383(9930):1749–1761. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Soresi M, Giannitrapani L, Cervello M, Licata A, Montalto G. Non invasive tools for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(48):18131–18150. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Murgia A, Ahmed Y, Sweeney K, Nicholson-Scott L, Arthur K, Allsworth M, et al. Breath-Taking Perspectives and Preliminary Data toward Early Detection of Chronic Liver Diseases. Biomedicines. 2021;9(11):1563. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gaude E, Nakhleh MK, Patassini S, Boschmans J, Allsworth M, Boyle B, et al. Targeted breath analysis: exogenous volatile organic compounds (EVOC) as metabolic pathway-specific probes. J Breath Res. 2019;13(3):032001. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ab1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fisher CD, Lickteig AJ, Augustine LM, Ranger-Moore J, Jackson JP, Ferguson SS, et al. Hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme alterations in humans with progressive stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(10):2087–2094. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.027466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Woolsey SJ, Mansell SE, Kim RB, Tirona RG, Beaton MD. CYP3A Activity and Expression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015;43(10):1484–1490. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.065979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferrandino G, Orf I, Smith R, Calcagno M, Thind AK, Debiram-Beecham I, et al. Breath Biopsy Assessment of Liver Disease Using an Exogenous Volatile Organic Compound-Toward Improved Detection of Liver Impairment. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020;11(9):e00239. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dadamio J, Van den Velde S, Laleman W, Van Hee P, Coucke W, Nevens F, et al. Breath biomarkers of liver cirrhosis. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012;905:17–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fernandez Del Rio R, O’Hara ME, Holt A, Pemberton P, Shah T, Whitehouse T, et al. Volatile Biomarkers in Breath Associated With Liver Cirrhosis - Comparisons of Pre- and Post-liver Transplant Breath Samples. EBioMedicine. 2015;2(9):1243–1250. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Friedman MI, Preti G, Deems RO, Friedman LS, Munoz SJ, Maddrey WC. Limonene in expired lung air of patients with liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39(8):1672–1676. doi: 10.1007/bf02087774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pijls KE, Smolinska A, Jonkers DM, Dallinga JW, Masclee AA, Koek GH, et al. A profile of volatile organic compounds in exhaled air as a potential non-invasive biomarker for liver cirrhosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19903. doi: 10.1038/srep19903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Thomas JN, Roopkumar J, Patel T. Machine learning analysis of volatolomic profiles in breath can identify non-invasive biomarkers of liver disease: A pilot study. PLoS One. 2021;16(11):e0260098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sinha R, Lockman KA, Homer NZM, Bower E, Brinkman P, Knobel HH, et al. Volatomic analysis identifies compounds that can stratify non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JHEP Reports. 2020;2(5):100137. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miyazawa M, Shindo M, Shimada T. Metabolism of (+)- and (-)-limonenes to respective carveols and perillyl alcohols by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30(5):602–607. doi: 10.1124/dmd.30.5.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–943. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.European Association for the Study of the Liver EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69(1):182–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Markar SR, Brodie B, Chin ST, Romano A, Spalding D, Hanna GB. Profile of exhaled-breath volatile organic compounds to diagnose pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg. 2018;105(11):1493–1500. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chambers MC, Maclean B, Burke R, Amodei D, Ruderman DL, Neumann S, et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):918–920. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pluskal T, Castillo S, Villar-Briones A, Oresic M. MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:395. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Myers OD, Sumner SJ, Li S, Barnes S, Du X. One Step Forward for Reducing False Positive and False Negative Compound Identifications from Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Data: New Algorithms for Constructing Extracted Ion Chromatograms and Detecting Chromatographic Peaks. Anal Chem. 2017;89(17):8696–8703. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smirnov A, Jia W, Walker DI, Jones DP, Du X. ADAP-GC 3.2: Graphical Software Tool for Efficient Spectral Deconvolution of Gas Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Data. J Proteome Res. 2018;17(1):470–478. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Morisco F, Aprea E, Lembo V, Fogliano V, Vitaglione P, Mazzone G, et al. Rapid “breath-print” of liver cirrhosis by proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry. A pilot study. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O’Hara ME, Fernandez Del Rio R, Holt A, Pemberton P, Shah T, Whitehouse T, et al. Limonene in exhaled breath is elevated in hepatic encephalopathy. J Breath Res. 2016;10(4):046010. doi: 10.1088/1752-7155/10/4/046010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Van den Velde S, Nevens F, Van Hee P, van Steenberghe D, Quirynen M. GC-MS analysis of breath odor compounds in liver patients. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008;875(2):344–348. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hunter JD. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Computing in Science and Engineering. 2007;9(3):90–95. doi: 10.1109/MCSE.2007.55. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Waskom ML. Seaborn: statistical data visualization. Journal of Open Source Software. 2021;6(60):1–4. doi: 10.21105/joss.03021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag; [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dieterle F, Ross A, Schlotterbeck G, Senn H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Anal Chem. 2006;78(13):4281–4290. doi: 10.1021/ac051632c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Spratt HM, Ju H. Statistical Approaches to Candidate Biomarker Panel Selection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:463–492. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41448-5_22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meinshausen N, Bühlmann P. Stability selection. J R Statist SocB. 2010;74(4):417–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2010.00740.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hocking RR. A Biometrics Invited Paper. The Analysis and Selection of Variables in Linear Regression. Biometrics. 1976;32(1):1–49. doi: 10.2307/2529336. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Smolinska A, Tedjo DI, Blanchet L, Bodelier A, Pierik MJ, Masclee AAM, et al. Volatile metabolites in breath strongly correlate with gut microbiome in CD patients. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1025:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kwak J, Preti G. Volatile disease biomarkers in breath: a critique. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(7):1067–1074. doi: 10.2174/138920111795909050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Filzmoser P, Walczak B. What can go wrong at the data normalization step for identification of biomarkers? J Chromatogr A. 2014;1362:194–205. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stavropoulos G, van Munster K, Ferrandino G, Sauca M, Ponsioen C, van Schooten FJ, et al. Liver Impairment-The Potential Application of Volatile Organic Compounds in Hepatology. Metabolites. 2021;11(9):618. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Haworth JJ, Pitcher CK, Ferrandino G, Hobson AR, Pappan KL, Lawson JLD. Breathing new life into clinical testing and diagnostics: perspectives on volatile biomarkers from breath. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2022;59(5):353–372. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2022.2038075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Eggersdorfer M. Terpenes. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 40.van den Velde S, Quirynen M, van Hee P, van Steenberghe D. Halitosis associated volatiles in breath of healthy subjects. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;853(1-2):54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.02.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kelling FJ, Ialenti F, Den Otter CJ. Background odour induces adaptation and sensitization of olfactory receptors in the antennae of houseflies. Med Vet Entomol. 2002;16(2):161–169. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2915.2002.00359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Burk RF, Hill KE. Regulation of Selenium Metabolism and Transport. Annu Rev Nutr. 2015;35:109–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071714-034250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Duisken M, Sandner F, Blomeke B, Hollender J. Metabolism of 1,8-cineole by human cytochrome P450 enzymes: identification of a new hydroxylated metabolite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1722(3):304–311. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dietrich CG, Gotze O, Geier A. Molecular changes in hepatic metabolism and transport in cirrhosis and their functional importance. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(1):72–88. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Elbekai RH, Korashy HM, El-Kadi AO. The effect of liver cirrhosis on the regulation and expression of drug metabolizing enzymes. Curr Drug Metab. 2004;5(2):157–167. doi: 10.2174/1389200043489054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jamwal R, Barlock BJ. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Hepatic Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020;13(9):222. doi: 10.3390/ph13090222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dietz FK, Rodriguez-Giaxola M, Traiger GJ, Stella VJ, Himmelstein KJ. Pharmacokinetics of 2-butanol and its metabolites in the rat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981;9(5):553–576. doi: 10.1007/BF01061026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morey TE, Booth M, Wasdo S, Wishin J, Quinn B, Gonzalez D, et al. Oral adherence monitoring using a breath test to supplement highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Behav. 2013;17(1):298–306. doi: 10.1007/s10461-012-0318-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Li H, Toth E, Cherrington NJ. Alcohol Metabolism in the Progression of Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Toxicol Sci. 2018;164(2):428–438. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Saltzman A, Caraway WT. Cinnamic acid as a test substance in the evaluation of liver function. J Clin Invest. 1953;32(8):711–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI102785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Burk RF, Early DS, Hill KE, Palmer IS, Boeglin ME. Plasma selenium in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27(3):794–798. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Labenz C, Arslanow A, Nguyen-Tat M, Nagel M, Worns MA, Reichert MC, et al. Structured Early detection of Asymptomatic Liver Cirrhosis: Results of the population-based liver screening program SEAL. J Hepatol. 2022;77(3):695–701. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
PCA dimensionality reduction using on-breath VOCs. Projected data points on the first two principal components were colored by sex. PC1 explains ∼10% and PC2 ∼7% of the variance. PCA, principal component analysis; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.
PCA of breath samples and blanks. Projected data points in different types of samples are shown by different colors. PC1 explains ∼24% and PC2 ∼14% of variance and show separation of breath from blanks. PCA, principal component analysis.
Blue indicates a negative and red a positive correlation. Circle size and intensity of color show the magnitude of the correlation. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; VOCs, volatile organic compounds.