Abstract
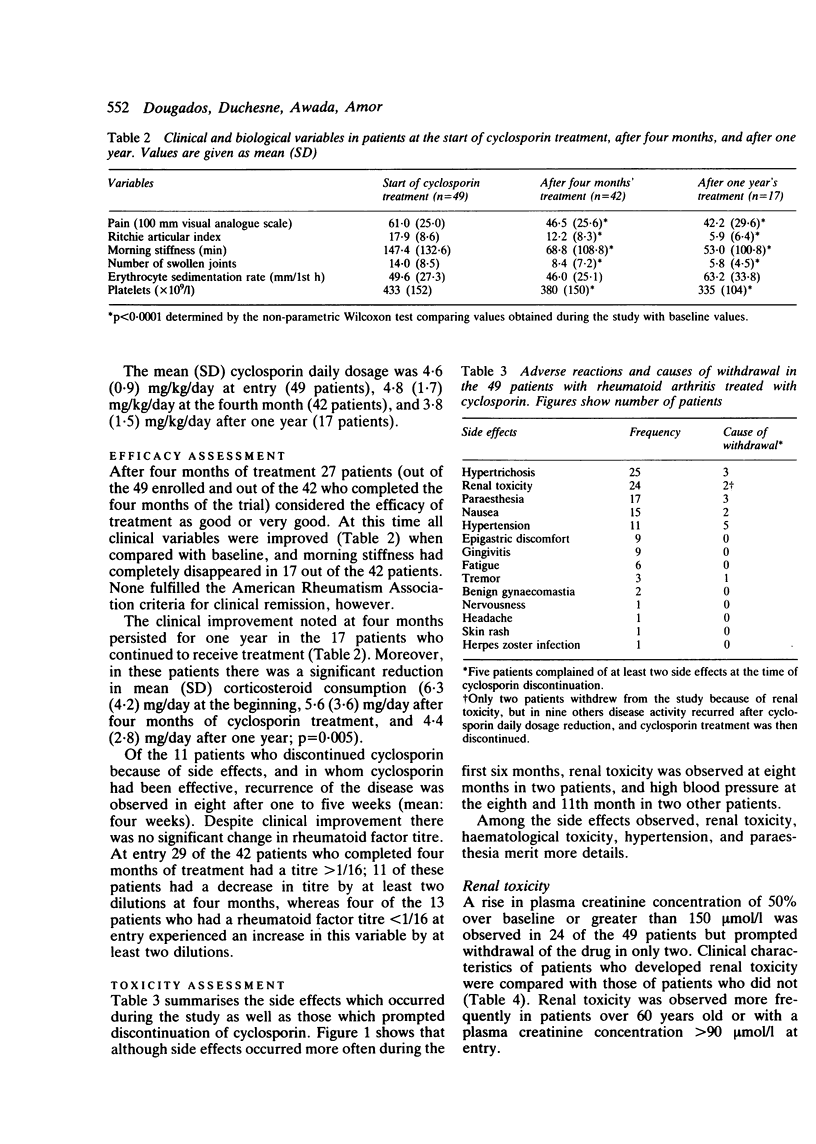
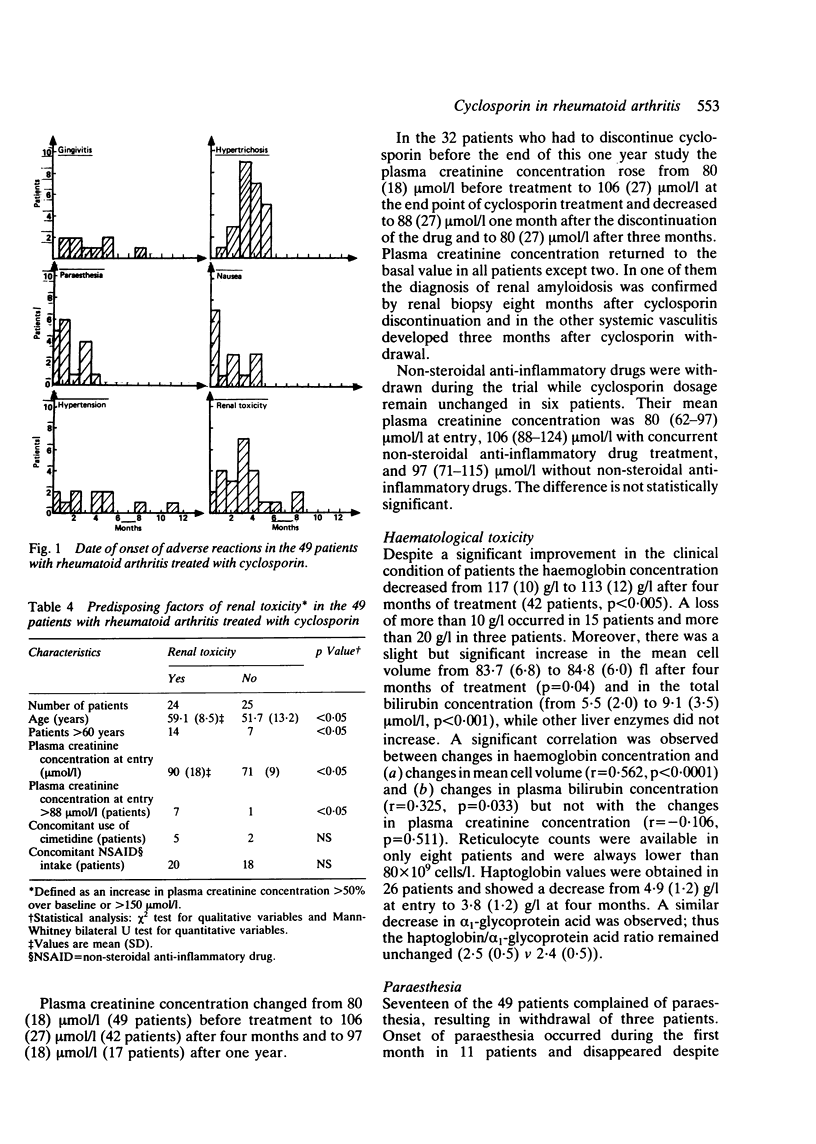
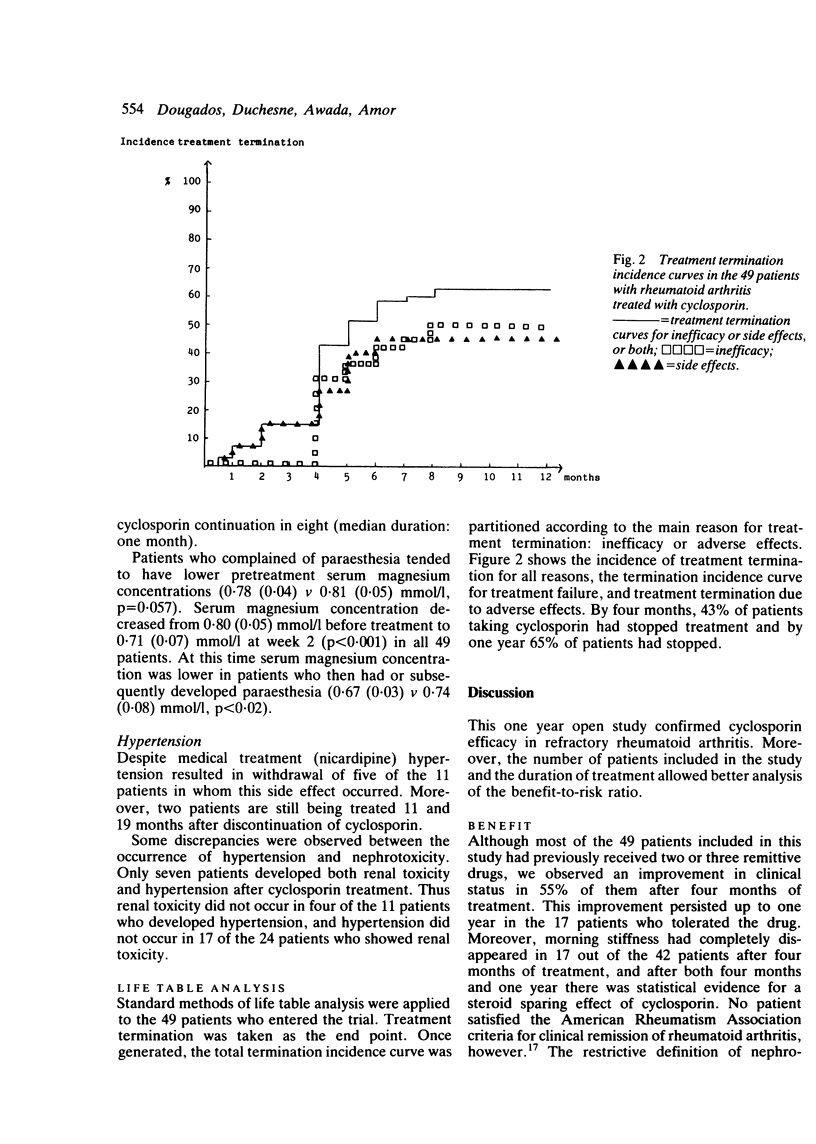
The efficacy of cyclosporin in a double blind, placebo controlled trial of four months' duration has previously been reported by us. To assess the benefit-to-risk of cyclosporin this study was followed by a one year open trial including 49 of the previous 52 patients. Cyclosporin was given at an initial dosage of 5 mg/kg/day and then modulated on the basis of efficacy and renal toxicity. During the study the drug had to be discontinued in 32 patients: because of inefficacy in 10, side effects in 11, both in nine, and in two because of unrelated events. The significant clinical improvement noted at four months persisted through one year in the 17 patients who continued to receive treatment. Nephrotoxicity of the drug (24 patients) required constant and close monitoring as well as modulation of daily drug dosage during the trial. This study indicated that cyclosporin might be valuable in the treatment of patients with advanced rheumatoid arthritis, in whom other second line agents have failed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breedveld F. C., Valentijn R. M., Westedt M. L., Weening J. J. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis with glomerular crescent formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1985 Sep;4(3):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF02031622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAGNOSTIC criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 1958 revision by a committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Mar;18(1):49–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Amor B. Cyclosporin A in rheumatoid arthritis: preliminary clinical results of an open trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):83–87. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Awada H., Amor B. Cyclosporin in rheumatoid arthritis: a double blind, placebo controlled study in 52 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Feb;47(2):127–133. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Nguyen M., Duchesne L., Benjelloun M., Amor B. Appreéciation de l'utilité des traitements de fond de la polyarthrite rhumatoïde par l'analyse du taux de maintenance theérapeutique. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1989 Jan;56(1):89–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O., Bjerkhoel F., Salvesen C. F., Berg K. J., Rugstad H. E., Saelid G., Mellbye O. J., Kåss E. An open, controlled, randomized comparison of cyclosporine and azathioprine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a preliminary report. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):88–92. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf U., Marbet U., Müller W., Thiel G. Cyclosporin A--Wirkungen und Nebenwirkungen bei der Behandlung der chronischen Polyarthritis und der Psoriasisarthritis. Immun Infekt. 1981 Mar;9(1):20–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keown P. A., Essery G. L., Stiller C. R., Sinclair N. R., Mullen R., Ulan R. A. Mechanisms of immunosuppression by cyclosporin. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 1):386–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Jasani M. K., Dick W. C., Buchanan W. W. Evaluation of a functional index in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1973;2(2):71–77. doi: 10.3109/03009747309098820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Palestine A. G., Chan C. C., Mochizuki M., Yancey K. Effectiveness of cyclosporin therapy for Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jun;28(6):671–679. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palestine A. G., Nussenblatt R. B., Chan C. C. Side effects of systemic cyclosporine in patients not undergoing transplantation. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):652–656. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinals R. S., Masi A. T., Larsen R. A. Preliminary criteria for clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1308–1315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller C. R., Dupré J., Gent M., Jenner M. R., Keown P. A., Laupacis A., Martell R., Rodger N. W., von Graffenried B., Wolfe B. M. Effects of cyclosporine immunosuppression in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1362–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.6367043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., June C. H., Sullivan K. M., Thomas E. D. Association between cyclosporin neurotoxicity and hypomagnesaemia. Lancet. 1984 Nov 17;2(8412):1116–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91556-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Coblyn J. S., Fraser P. A., Anderson R. J., Spragg J., Trentham D. E., Austen K. F. Cyclosporin A treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):11–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijthoven A. W., Dijkmans B. A., Goei The H. S., Hermans J., Montnor-Beckers Z. L., Jacobs P. C., Cats A. Cyclosporin treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: a placebo controlled, double blind, multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):726–731. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


