Abstract
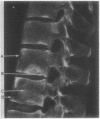
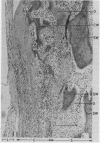
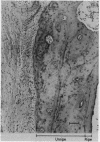
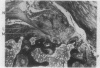
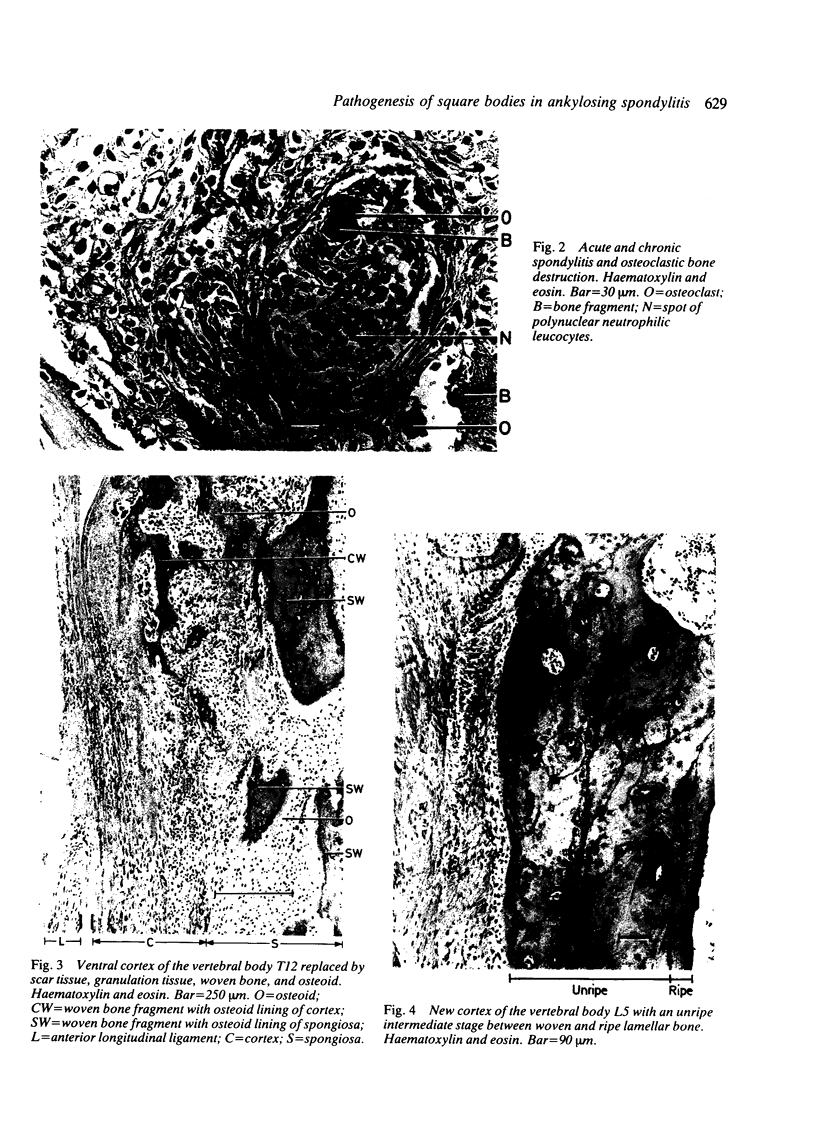
The pathogenesis of squaring of the vertebral bodies is analysed in a 25 year old patient with ankylosing spondylitis. The squaring derives from a straightening of the anterior contour. The disease was diagnosed five years before the patient's death. The remodelling of bone that explains squaring of the vertebral bodies is described for the first time. Histologically, an acute and chronic spondylitis with destruction and simultaneous rebuilding of the cortex and the spongiosa of the vertebral bodies has been found. The development of square vertebral bodies is shown to be based on a combination of a destructive osteitis and repair.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufdermaur M., Spycher M. Pathogenesis of osteochondrosis juvenilis Scheuermann. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(4):452–457. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100040408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. Enthesopathy of rheumatoid and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):213–223. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley M. I., Chalmers T. M., Kellgren J. H., Ball J. Destructive lesions of vertebral bodies in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Sep;31(5):345–358. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGFELDT B., ROMANUS R., YDEN S. Histological studies of pelvo-spondylitis ossificans (ankylosing spondylitis) correlated with clinical and radiological findings. Ann Rheum Dis. 1954 Sep;13(3):219–228. doi: 10.1136/ard.13.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANUS R., YDEN S. Destructive and ossifying spondylitic changes in rheumatoid ankylosing spondylitis (pelvo-spondylitis ossificans). Acta Orthop Scand. 1952;22(2):88–99. doi: 10.3109/17453675208988998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WURM H. Zur pathologischen Anatomie und Pathologie der entzündlichen Wirbelsäulenversteifung (Bechterew-Marie-Strümpell). Z Rheumaforsch. 1955 Dec;14(11-12):337–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]