Abstract
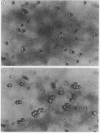
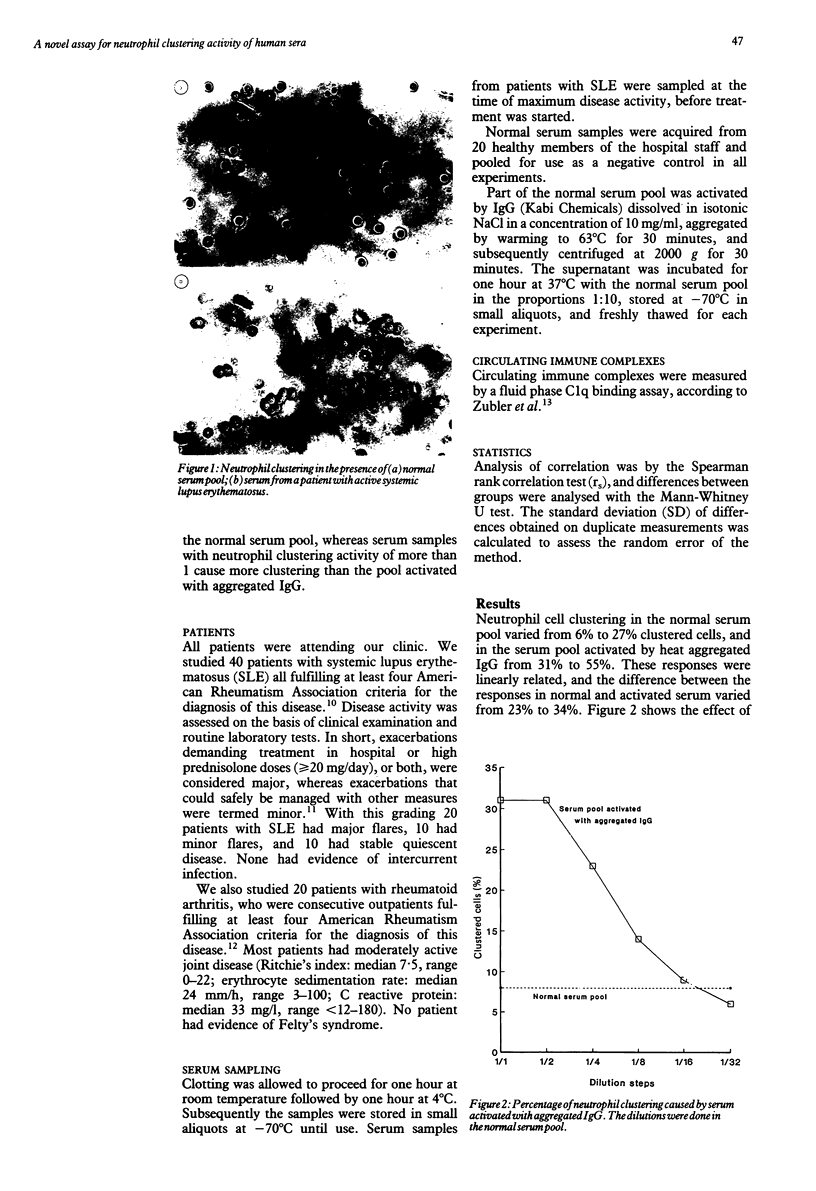
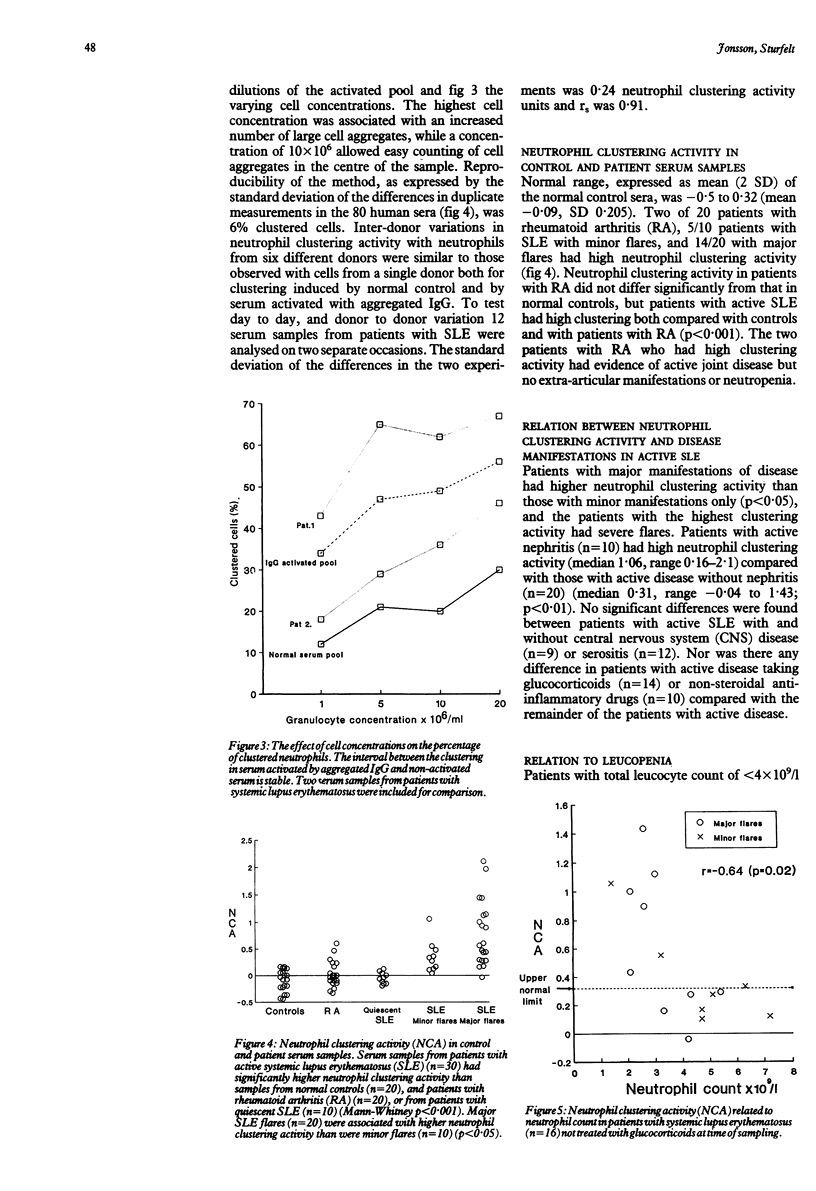
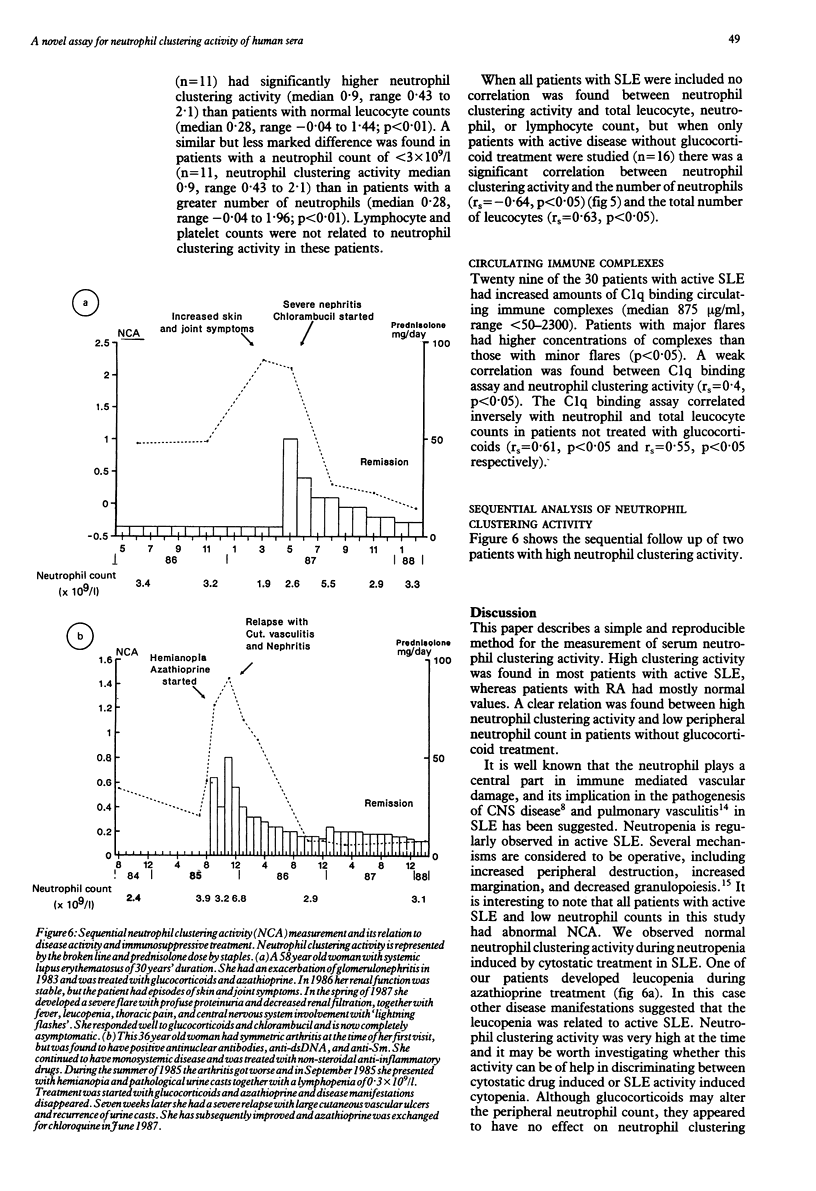
A simple and reproducible method for the measurement of serum neutrophil clustering activity was developed. High clustering activity was found in 19/30 patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and 14/20 of those with severe disease flares. In contrast, 0/10 patients with quiescent SLE and 2/20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis had high neutrophil clustering activity. Particularly high clustering activity was found in patients with SLE with lupus glomerulonephritis and in certain patients with central nervous system disease. An inverse correlation was found between neutrophil clustering activity and peripheral blood neutrophil count in patients with SLE not treated with glucocorticoids, and clustering activity was high in all patients with low neutrophil counts in this group. A moderate correlation was found between neutrophil clustering activity and C1q binding circulating immune complexes. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoids had little direct effect on neutrophil clustering activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S. B., Given W. P., Edelson H. S., Weissmann G. Neutrophil aggregation induced by sera from patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 May;26(5):630–636. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner S., Abramovitz M., Kariv N., Weinberger A., Yaron M., Lavie G., Pinkhas J., Aronson M. The leukergy test in rheumatic diseases. New implications for an old test. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):899–903. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg A., Franklin W., Chan K. L., Kopp E., Carrington C. B. Pulmonary hemorrhage and immune-complex deposition in the lung. Complications in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Jul;104(7):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Weaver L. J., Hudson L. D., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Association of complement activation and elevated plasma-C5a with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Pathophysiological relevance and possible prognostic value. Lancet. 1980 May 3;1(8175):947–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Ziff M., Hurd E. R. Increased endothelial cell adherence, aggregation, and superoxide generation by neutrophils incubated in systemic lupus erythematosus and Felty's syndrome sera. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Dec;25(12):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. S. Neutrophil activation as a mechanism of tissue injury. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;13(1 Suppl 1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(83)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Edelson H. S., Friedman R., Weissmann G. The roles of degranulation and superoxide anion generation in neutrophil aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 13;721(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturfelt G., Sjöholm A. G. Complement components, complement activation, and acute phase response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;75(1):75–83. doi: 10.1159/000233593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B., Sturfelt G. Monocyte in vitro function in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). II. Glass adherence and spreading in presence of SLE-sera. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1980;31:43–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Ward P. A. Lung injury secondary to chemotactic factor-induced leukocyte activation. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;12:383–396. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9352-7_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Niho Y., Yanase T. Granulopoiesis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Apr;26(4):516–521. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]