ABSTRACT
“Radiation uses and ubiquitousness: The good, bad, and limits” an earlier review was published before launch of 5th Generation (5G) mobile networks technology. Now with 5G technology’s upcoming use, its advantages need to be used for advancing healthcare. All this for best applications possible and as safely as possible. The review update aims at reviewing the 5G technology benefits, risks, and its reduction. All this is important for rationale use. We searched the MedLine database and relevant statutory government recommendations. Results are discussed and put in proper perspective. Advantages are higher data transmission rates, lower latency and better quality of service. 5G technology will be beneficial for health services with shortened time and space. It will aid overcoming some of the current challenges to healthcare. The advantageous applications are elaborated for (1) proper assessment, (2) pertinent treatment, (3) progress monitoring, (4) prevention applications, and (5) professional standards. The concerns about possible adverse effects to human health needs to be addressed. The health effects of frequencies in the range 450 to 6,000 MHz are cautioned. There is a need of studies on nonthermal effects of the higher frequencies. In our present state of understanding and evidence, the useful strategies suggested are the “3Rs”: (1) risk-reducing devices, (2) risk-reduction necessarily, and (3) risk-reduction engineering and environment. Balancing risks and rewards are the best strategy forward. Robust communication will make excellent healthcare reach all, always and especially in times of need.
Keywords: 5G technology, adverse effects, non-thermal, radiation, risks, robotic surgery, telemedicine, telesurgery, the internet of things
Introduction
The upcoming deployment of 5th Generation (5G) mobile networks has many advantages and should be used for advancing healthcare. The technology needs to be understood for best applications possible, and as safely as possible. Most healthcare providers are unaware of the extraordinary opportunities 5G provides for implementation of healthcare impactfully.[1] The concerns about possible adverse effects to human health needs to be addressed.
We have aimed at reviewing the 5G technology benefits, risks and its reduction. All this is important for rationale use. Primary care physicians and family physicians can contribute immensely in reaching all, for health benefits of all and reducing risks.
Methodology
A search of the literature using MedLine database, for 5G technology uses and risks.
Analyze worldwide statutory government recommendations on 5G. These included (i) National Institute of Health, National Cancer Institute,[2] (ii) European Parliamentary Research Service,[3] and (iii) International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP).[4] Present findings in proper perspective.
The technology progress
Why 5G technology? Growing demand for higher data transmission rates, lower latency, and better quality of service are the reasons. 5G can accommodate a much higher number of devices than 4G. A comparison of 3G/4G/5G/6G is given in Table 1. Sixth generation (6G) will be even higher, in terabits range.
Table 1.
Comparison
| Characteristic | 3G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth (maximum amount of data that can be handled at any moment) | 2 mbps | 200 mbps | >1 gbps |
| Average Speed (rate of data transmission) | 144 kbps | 25 mbps | 200-400 mbps |
| Latency | 100-500 ms | 20-30 ms | <10 ms |
k - kilo; m - mega; g - giga; b - bits; p - per; s - seconds
5G pioneer bands identified at EU level have frequencies of 700 MHz, 3.6 GHz (3.4–3.8 GHz), and 26 GHz (24.25–27.5 GHz). In India, the proposed frequencies are 600–900 MHz, 1.8–3.3 GHz, and 26 GHz Bands. The first two frequencies are similar to those used for 2G–4G technologies. The “millimeter wave” range is 30 GHz frequency and above.
A conceptual framework of rewards and risks is given at Figure 1 and elaborated below.
Figure 1.

5G technology and Health – a conceptual framework
The technology promoting healthcare
5G technology will lead to greatly shortened time and space for health services. Reaching all, rightly, timely, and robustly will become a reality with 5G technology. It will aid in overcoming some of the current challenges to healthcare. The data sharing and managing diseases become faster and easier by using 5G.[5]
1.Proper assessment
Clear communications with clear images will aid proper diagnosis, assessment, and diligence. Faster reliable communication without time lag will make popular the teleconsultation and tele-assessment.
2.Pertinent treatment
Faster communication and favorable computation, all at increased scale and volume, comprehensively, precisely, perfectly will get a boost with 5G technology. Clinical data access and interpretations for actual diligent treatment decisions will be easier than ever before.
The tele-operation takes place at a great distance for the needy, supervised by experts from anywhere. This will increase advantageously with use of 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.[6] Robotic surgery with the advantage of greatly reduced time lag will be possible remotely. No time lag ensures immediate corrective actions, life-saving and enhancing.
3.Progress monitoring
Monitoring of patients in hospitals and health monitoring of people with wearable smart medical devices will all be improved with 5G technology. All this can be done continuously and ubiquitously.
Emergency monitoring and excellent management require no time lag or longing talent. Real-time monitoring remotely is possible with 5G Technology for actual advanced decisions. Massive transmissions will all lead to required experience for meticulousness.
5G is powerful, and will support thousands of medical devices simultaneously, from sensors to mobiles, medical equipment, and video cameras, all for comprehensive monitoring for holistic care.[7] Enhancing connectivity of devices to server and central cloud computing platforms without any traffic congestions can provide alerts to doctors and the affected for real time actions.
4.Prevention applications
Knowing current state, comprehensively and timely, will enhance active prevention with faster communication for focused care with favorable actions.
5.Professional standards
Medical resources scarcity and imbalances along with inefficient healthcare systems administration are detrimental and lead to inconvenient medical experiences. Maintaining overall professional standards is likely to be energized with increasing efficiency of required processes with efficient communication with 5G technology. Virtual Reality can streamline whole hospitals for highest standards.
Virtual interactions energized for vital interpretations exemplary will be all the new norm with 5G Technology. Attending worldwide webinars, virtual conferences, teleconferences by many and majorly will all lead to expertise excellently.
5G technology with excellent connectivity will reduce the problems faced, including connectivity issues and audio/voice issues.[8]
Dangers and diligence
Frequencies less than 3.8 GHz are similar to those used for 2G to 4G technologies and have been investigated in both epidemiological and experimental studies for different end points (including carcinogenicity and reproductive/developmental effects). Frequencies of 26 GHz and higher have not been adequately studied for the same.
An earlier publication, before 5G technology, had stated “IARC has classified radiofrequency EM fields (RF EMF) as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B)”.[9] Further, research has highlighted Reproductive/developmental effects. The effects of frequencies in the range 450 to 6,000 MHz are (i) clearly affect male fertility, (ii) possibly affect female fertility, and (iii) possibly have adverse effects on the development of embryos, fetuses, and newborns.[3] Studies on nonthermal effects of the higher frequencies are needed.
The scientific safe aspect is that radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF EMF) penetration into body tissue decreases with increasing frequency. The depth of penetration above 6 GHz is relatively short, and the predominant effect is surface heating.[10]
The ICNIRP has recently remarked that the only substantiated adverse health effects caused by exposure to RF EMFs (up to 300 GHz) are nerve stimulation, changes in the permeability of cell membranes, and effects due to temperature elevation.[4]
RF radiation is a new form of environmental pollution.[11] Epidemiological studies should be energized with data from regions using 5G compared with regions not using 5G as control population. Future epidemiological studies should continue to monitor long-term health effects.[10]
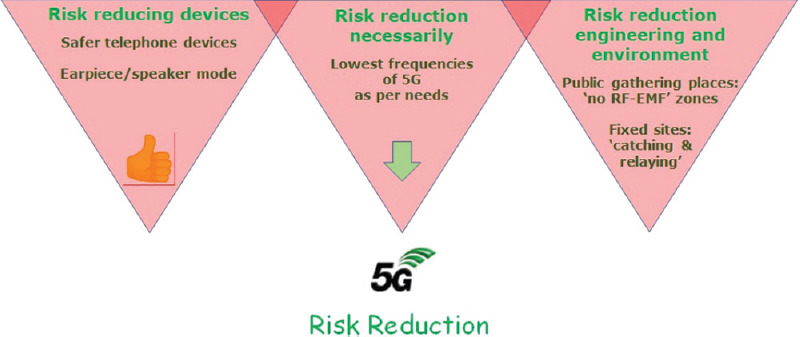
In our present state of understanding and evidence, the useful strategies suggested are the “3Rs”:
1.Risk-reducing devices
Lowering radiation exposure as much as possible is useful whatever the frequencies being used, from 1G to 5G.
Greatest burden of exposure in humans generally derives from their own mobile phones, rather than transmitting installations. Hence, the need for safer telephone devices. These should be emitting low energy and if possible only working when at a certain distance from the body. The cable earpiece/speaker mode solves much of the problem. Strict mobile phone SAR (Specific Absorption Rate: a measure of the rate at which energy is absorbed per unit mass by a human body when exposed to a RF electromagnetic field) limits need to be enforced.
2. Risk-reduction necessarily
Using lowest frequencies of 5G based on need. Precautionary exposure limits need to be adopted.
3. Risk-reduction engineering and environment
Fast transmission from 5G network can be caught centrally and relayed by optic-fiber cables. Optic-fiber cables are as good as lower frequency 5G. This strategy should be used whenever connections are needed in fixed sites, like schools, libraries, workplaces, hospitals, houses, public buildings, and all new buildings etc.
A good idea is making public gathering places as “no RF EMF” areas (similar to no-smoking areas). This will avoid the passive exposure of people not using a mobile phone. This will protect many vulnerable elderly or immune-compromised people, children, etc.
The “3Rs” have to be promoted and popularized, Figure 2. Primary care and Family physicians should take these responsible things to the masses.
Figure 2.
Rationale use 5G
Conclusion
5G Technology has potential to revolutionize healthcare and overcome the current challenges to healthcare. Healthcare requires a multitude of aspects as health is multi-dimensional. All aspects can be energized for excellence with use of 5G technology. Robust communication rightly will make excellent healthcare reach all, always and especially in times of need. Right necessary use along with risk reduction strategies suggested will ensure safety and success.
Key messages
5G technology will be beneficial for health services with greatly shortened time and space.
Telemedicine benefits with faster reliable communication without time lag.
No time lag ensures emergency excellence.
Data management enhanced for advances.
In our present state of understanding and evidence the useful strategies for rationale use and risk reduction are the ‘3Rs’.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
Thankful to all the authors of references quoted.
References
- 1.Georgiou KE, Georgiou E, Satava RM. 5G use in healthcare:The future is present. JSLS. 2021;25:e2021.00064. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2021.00064. doi:10.4293/JSLS.2021.00064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. [Last accessed on 2022 Aug 21];National Institute of Health, National Cancer Institute. Cell phones and cancer risk. 2022 Mar 10; Available from:https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/radiation/cell-phones-fact-sheet. [reviewed . [Google Scholar]
- 3.Belpoggi F for Panel for the Future of Science and Technology (STOA) Scientific Foresight Unit Directorate-General for Parliamentary Research Services (EPRS) the Secretariat of the European Parliament Health impact of 5G Brussels ©European Union. 2021 ISBN:978-92-846-8030-6. doi:10.2861/657478. [Google Scholar]
- 4.International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz) Health Phys. 2020;118:483–524. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mishra L, Vikash , Varma S. Seamless health monitoring using 5G NR for internet of medical things. Wirel Pers Commun. 2021;120:2259–89. doi: 10.1007/s11277-021-08730-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cepolina F, Razzoli RP. An introductory review of robotically assisted surgical systems. Int J Med Robot. 2022;18:e2409. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2409. doi:10.1002/rcs. 2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li D. 5G and intelligence medicine-how the next generation of wireless technology will reconstruct healthcare?Precis Clin Med. 2019;2:205–8. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbz020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mishra D, Nair AG, Verma L, Grover AK, Mathur S, Srivastav T. The perceived impact of webinars during the COVID.19 pandemic:A survey of ophthalmology trainees from India. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2021;14:78–84. doi: 10.4103/ojo.ojo_87_21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jain S. Radiation in medical practice and health effects of radiation:Rationale, risks, and rewards. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021;10:1520–4. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2292_20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Karipidis K, Mate R, Urban D, Tinker R, Wood A. 5G mobile networks and health-a state-of-the-science review of the research into low-level RF fields above 6 GHz. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2021;31:585–605. doi: 10.1038/s41370-021-00297-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Russell CL. 5G wireless telecommunications expansion:Public health and environmental implications. Environ Res. 2018;165:484–95. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


