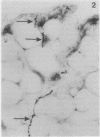
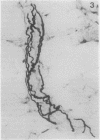
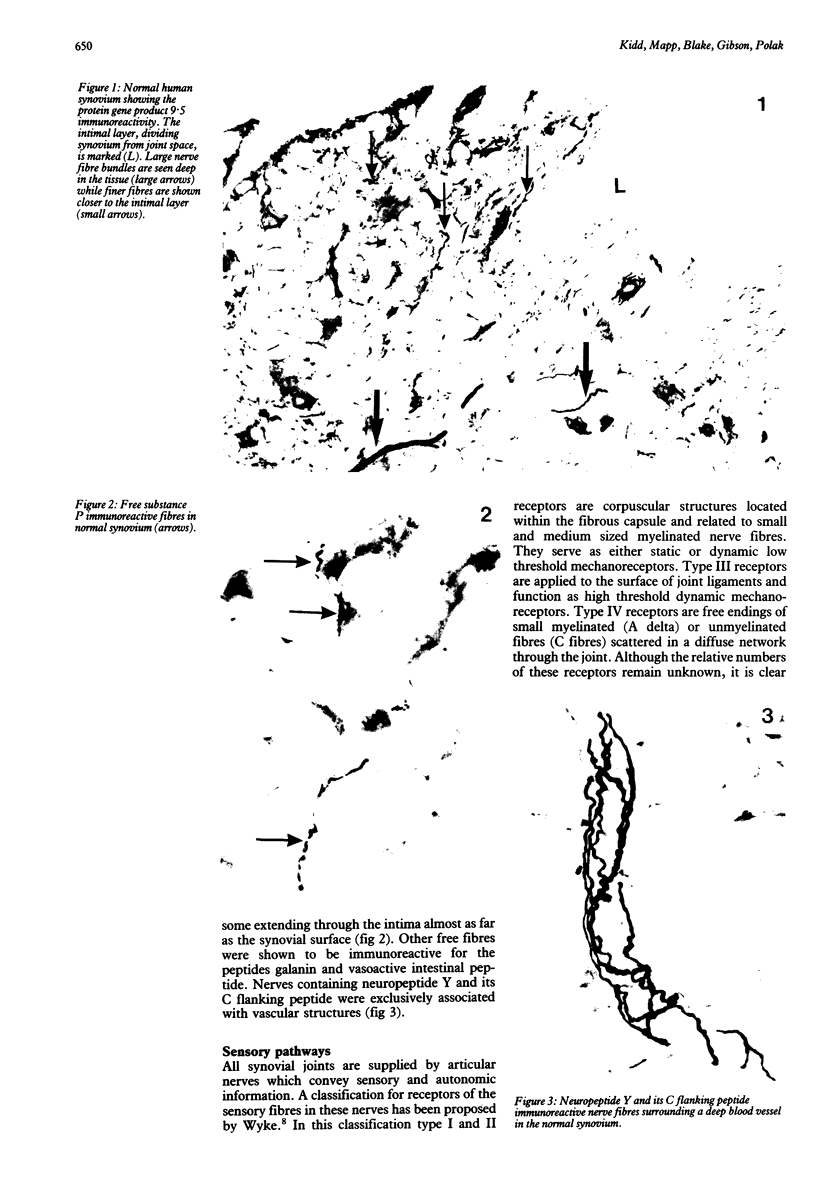
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coderre T. J., Basbaum A. I., Levine J. D. Neural control of vascular permeability: interactions between primary afferents, mast cells, and sympathetic efferents. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jul;62(1):48–58. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtright L. J., Kuzell W. C. Sparing effect of neurological deficit and trauma on the course of adjuvant arthritis in the rat. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Jul;24(4):360–368. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. V. Anatomy and Physiology of Diarthrodial Joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1945 Dec;5(2):29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R., Russell N. J. Extravasation in the knee induced by antidromic stimulation of articular C fibre afferents of the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:407–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A., Wyke B. The innervation of the knee joint. An anatomical and histological study in the cat. J Anat. 1967 Jun;101(Pt 3):505–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick E. N. Asymmetrical rheumatoid arthritis after poliomyelitis. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 1;3(5556):26–28. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5556.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg P., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Mechanical sensitivity of group III and IV afferents from posterior articular nerve in normal and inflamed cat knee. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;55(4):635–643. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad M., Konttinen Y. T., Korkala O., Liesi P., Hukkanen M., Polak J. M. Neuropeptides in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;15(12):1807–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):739–768. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd B. L., Mapp P. I., Gibson S. J., Polak J. M., O'Higgins F., Buckland-Wright J. C., Blake D. R. A neurogenic mechanism for symmetrical arthritis. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1128–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Inhibition of carrageenan induced inflammation in the rat knee joint by substance P antagonist. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Nov;48(11):928–932. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.11.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford L. A., Schmidt R. F. Afferent and efferent axons in the medial and posterior articular nerves of the cat. Anat Rec. 1983 May;206(1):71–78. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092060109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Clark R., Devor M., Helms C., Moskowitz M. A., Basbaum A. I. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6208609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Substance P activation of rheumatoid synoviocytes: neural pathway in pathogenesis of arthritis. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.2433770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani R., Cooper C., Kidd B. L., Cole J. D., Cawley M. I. Use of laser Doppler flowmetry and transcutaneous oxygen tension electrodes to assess local autonomic dysfunction in patients with frozen shoulder. J R Soc Med. 1989 Sep;82(9):536–538. doi: 10.1177/014107688908200910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massardo L., Watt I., Cushnaghan J., Dieppe P. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint: an eight year prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Nov;48(11):893–897. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.11.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON H. J., 3rd, MILLER M. R., KASAHARA M. Nerve endings in human fasciae, tendons, ligaments, periosteum, and joint synovial membrane. Anat Rec. 1960 Feb;136:137–147. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091360208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON M., BYWATERS E. G. Unilateral rheumatoid arthritis following hemiplegia. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962 Dec;21:370–377. doi: 10.1136/ard.21.4.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihe E., Nohr D., Millan M. J., Stein C., Müller S., Gramsch C., Herz A. Peptide neuroanatomy of adjuvant-induced arthritic inflammation in rat. Agents Actions. 1988 Dec;25(3-4):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01965027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Lopez-Belmonte J., Rees D. D. Modulation of the vasodepressor actions of acetylcholine, bradykinin, substance P and endothelin in the rat by a specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):646–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12639.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf C. J., Wall P. D. Relative effectiveness of C primary afferent fibers of different origins in evoking a prolonged facilitation of the flexor reflex in the rat. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1433–1442. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01433.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L. Substance P release from knee joint afferent terminals: modulation by opioids. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 23;458(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90474-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]