Abstract
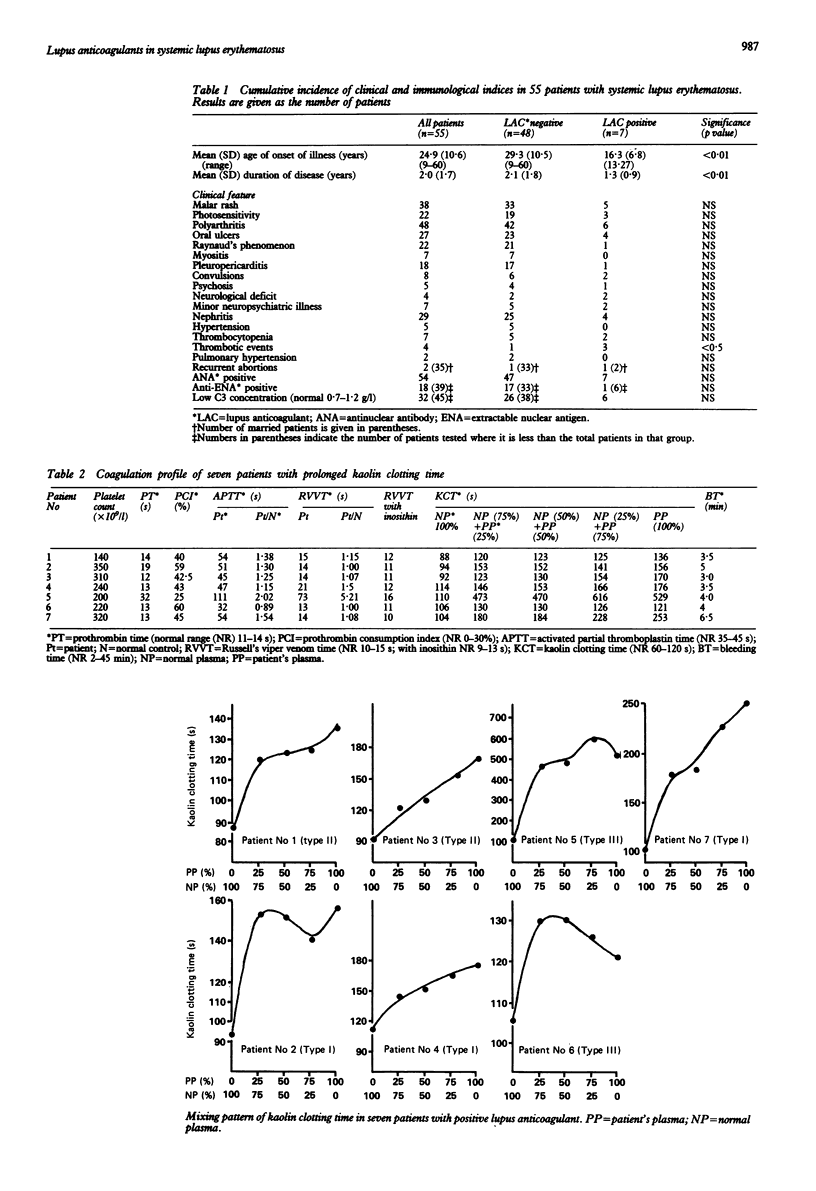
The prevalence of lupus anticoagulant (LAC) and its relation with reported clinical associations has been determined in 55 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) from northern India who were studied prospectively. Kaolin clotting time was used to screen for LAC, which was detected in seven (13%) of the patients. Significant associations were found between LAC and thrombotic events, onset of disease at an early age, and disease of shorter duration. No statistically significant association could be found between LAC and recurrent abortions, pulmonary hypertension, thrombocytopenia, and neurological manifestations. It is concluded that LAC is a useful marker for a subset of patients with SLE at risk of thromboembolic events.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boey M. L., Colaco C. B., Gharavi A. E., Elkon K. B., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: striking association with the presence of circulating lupus anticoagulant. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Oct 8;287(6398):1021–1023. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6398.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Scott J. R., Kochenour N. K., Hershgold E. Obstetric complications associated with the lupus anticoagulant. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 21;313(21):1322–1326. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511213132104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen R. H., Bouma B. N., Kater L. The prevalence and clinical associations of the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. 1987;16(3):185–192. doi: 10.3109/03009748709165272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen R. H., Kater L. Lupus anticoagulant: revival of an old phenomenon. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Oct-Dec;3(4):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias M., Eldor A. Thromboembolism in patients with the 'lupus'-type circulating anticoagulant. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Mar;144(3):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Rickard K. A., Kronenberg H. A sensitive test demonstrating lupus anticoagulant and its behavioural patterns. Br J Haematol. 1978 Sep;40(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein D. I., Rapaport S. I. Acquired inhibitors of blood coagulation. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1972;1:75–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):132–138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner K., Pabinger-Fasching I. Lupus anticoagulants and thrombosis. A study of 25 cases and review of the literature. Haemostasis. 1985;15(4):254–262. doi: 10.1159/000215157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Druzin M. L., Goei S., Qamar T., Magid M. S., Jovanovic L., Ferenc M. Antibody to cardiolipin as a predictor of fetal distress or death in pregnant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):152–156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507183130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubbe W. F., Butler W. S., Palmer S. J., Liggins G. C. Fetal survival after prednisone suppression of maternal lupus-anticoagulant. Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1361–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Canciani M. T., Mari D., Meucci P. The varied sensitivity of partial thromboplastin and prothrombin time reagents in the demonstration of the lupus-like anticoagulant. Scand J Haematol. 1979 May;22(5):423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C. H., Jr, Kaneshiro M. M., Maher I. A., Weiner J. M., Rapaport S. I. The standardized normal Ivy bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueh J. R., Herbst K. D., Rapaport S. I. Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):156–159. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri M., Rheinschmidt M., Whiting-O'Keefe Q., Hellmann D., Corash L. The frequency of lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus. A study of sixty consecutive patients by activated partial thromboplastin time, Russell viper venom time, and anticardiolipin antibody level. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):524–531. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosove M. H., Ismail M., Koziol B. J., Runge A., Kasper C. K. Lupus anticoagulants: improved diagnosis with a kaolin clotting time using rabbit brain phospholipid in standard and high concentrations. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):472–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleider M. A., Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A., Coleman M. A clinical study of the lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1976 Oct;48(4):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A., Brandt J. T., Kaczor D., Schaeffer J. Laboratory diagnosis of lupus inhibitors: a comparison of the tissue thromboplastin inhibition procedure with a new platelet neutralization procedure. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;79(6):678–682. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.6.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


