Abstract
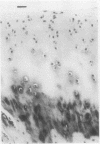
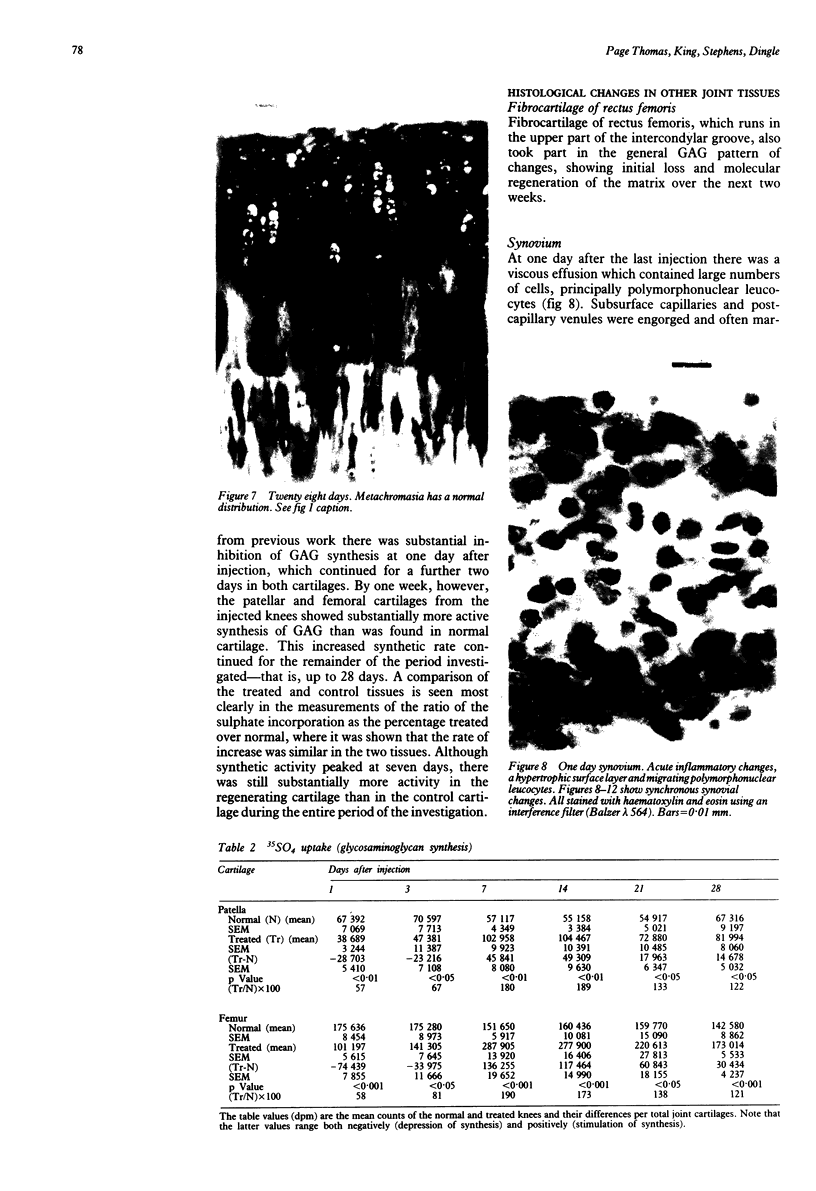
The response of the rabbit knee joint to a brief episode of cytokine induced damage is described. After three intra-articular injections of catabolin/interleukin-1 all joint cartilages showed an immediate extensive loss of proteoglycan (glycosaminoglycan), which was gradually replaced over three to four weeks. Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis (measured by 35SO4 uptake) was initially depressed, but at one week had almost doubled its rate as compared with the normal side. This increased synthetic activity was further maintained throughout the duration of the experiment (28 days), though the rate gradually fell. Histological cartilage metachromasia to toluidine blue mirrored the glycosaminoglycan changes. No disturbance of the articular cartilage collagen network was found. It is considered, therefore, that during treatment for arthritis the indigenous chondrocyte must continue to be capable of carrying out regenerative matrix repair and that antiarthritic agents should first be screened for interference with that process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton H. P., Tyler J. A. Inhibition of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by interleukin I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T., Page Thomas D. P., King B., Bard D. R. In vivo studies of articular tissue damage mediated by catabolin/interleukin 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jul;46(7):527–533. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.7.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T. The effect of synovial catabolin on cartilage synthetic activity. Connect Tissue Res. 1984;12(3-4):277–286. doi: 10.3109/03008208409013690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettipher E. R., Higgs G. A., Henderson B. Interleukin 1 induces leukocyte infiltration and cartilage proteoglycan degradation in the synovial joint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8749–8753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. Reversible collapse of rabbit ears after intravenous papain, and prevention of recovery by cortisone. J Exp Med. 1956 Aug 1;104(2):245–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A. Articular cartilage cultured with catabolin (pig interleukin 1) synthesizes a decreased number of normal proteoglycan molecules. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2270869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]