Abstract
Background
Pimecrolimus was developed as an alternative to topical corticosteroids for treating eczema (atopic dermatitis) but its efficacy and safety compared with existing treatments remains unclear.
Objectives
To assess the effects of topical pimecrolimus for treating eczema.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register (to October 2006), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library Issue 3, 2006), MEDLINE (from 2003 to October 2006), and EMBASE (from 2005 to October 2006). We also contacted researchers and manufacturers in the field.
Selection criteria
Randomised controlled trials of 1.0% topical pimecrolimus used twice daily compared against other topical comparators for treating eczema.
Data collection and analysis
Two authors independently examined each retrieved study for eligibility and extracted data for efficacy, tolerability and safety. A random‐effects model was used to estimate the pooled risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
Main results
We included 31 trials (8019 participants) in the analysis. In short‐term (≤ 6 weeks) trials, pimecrolimus cream was significantly more effective and well‐tolerated than vehicle (cream base, but not containing pimecrolimus). In long‐term trials (≥ 6 months), pimecrolimus was significantly better than vehicle in preventing flares (9 trials, 3091 participants, RR 1.47, 95% CI 1.32 to 1.64 at six months) and in improving quality of life. Pimecrolimus was significantly less effective than two topical corticosteroids, i.e. 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide for investigators' global assessment (1 trial, 658 participants, RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.83) and 0.1% betamethasone valerate for participants' global assessment (1 trial, 87 participants, RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.81) at three weeks. Pimecrolimus was also associated with significantly more overall withdrawals and skin burning. None of the trials reported on key adverse effects such as thinning of skin.
Pimecrolimus was significantly less effective than 0.1% tacrolimus for investigators' global assessment at 6 weeks (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.74) and led to more withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 2.37, 95% CI 1.10 to 5.08) based on 2 trials involving 639 participants, but there was no significant difference in proportions of participants experiencing any adverse events.
Authors' conclusions
Topical pimecrolimus is less effective than moderate and potent corticosteroids and 0.1% tacrolimus. The therapeutic role of topical pimecrolimus is uncertain due to the absence of key comparisons with mild corticosteroids.
Plain language summary
Topical pimecrolimus for eczema
This review of clinical trials aimed to find out whether topical pimecrolimus is better than topical corticosteroids or tacrolimus for treating eczema in infants, children and adults by assessing the improvement of eczema and adverse events associated with treatments.
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a very common and long‐lasting skin disease caused by both genetic and environmental factors, and most often begins in infancy and childhood. Corticosteroid creams have been used to treat eczema but may cause unwanted side effects, including thinning of the skin. Pimecrolimus cream was developed as an alternative to topical corticosteroids, but it is much more expensive than corticosteroids. It is also not clear whether pimecrolimus is more effective or better tolerated than corticosteroids or a similar drug called tacrolimus.
This review included data from 31 clinical trials involving 8019 participants. In the short‐term (less than six weeks) treatment of eczema, we found pimecrolimus was more effective and well‐tolerated when compared against vehicle (cream base not containing any pimecrolimus). Likewise, pimecrolimus was better than vehicle cream in preventing deterioration in eczema based on data from 9 trials involving 3091 participants. However, we found that 3 weeks treatment with pimecrolimus was less effective than a moderate (triamcinolone acetonide, data from 1 trial with 658 participants) and a potent topical corticosteroid (betamethasone valerate, data from 1 trial with 87 participants). Furthermore, 6‐weeks treatment with pimecrolimus was less effective and caused more participants to drop out of treatment due to lack of efficacy than tacrolimus based on 2 trials involving 639 participants.
Pimecrolimus caused a similar rate of adverse events to vehicle cream but had a lower overall dropout rate. In contrast, pimecrolimus had higher dropout rates and caused more skin burning than topical corticosteroids. None of the trials reported on key adverse effects, such as thinning of skin. Pimecrolimus caused a similar rate of adverse events to tacrolimus. There were no cancer‐related events reported in any of the 31 clinical trials.
This review did not find evidence to support the notion that pimecrolimus was better than moderate or potent corticosteroids or tacrolimus in treating eczema. However, there is a distinct lack of trials comparing pimecrolimus against mild‐potency corticosteroids.
Background
Description of the condition
Prevalence and causes
Eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) is a chronic, relapsing, intensely itchy, inflammatory skin disease, which typically involves the folds of the elbows or behind the knees (Williams 1994; Johansson 2004). The cause of eczema is unknown but evidence suggests a role for both genetic and environmental factors in determining disease expression. The causes of eczema are probably due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors (Cookson 2002). Eczema is often present with, or exacerbated by, food allergies, aeroallergens (e.g. house dust mites, moulds, animal danders) and skin colonisation by Staphylococcus aureus, which is present in 90% of eczema lesions (Leung 2003). However, up to 60% of individuals with eczema may not have specific immunoglobulin E production in response to allergens, which is associated with "atopic dermatitis", i.e. eczema with allergic reaction (Flohr 2004). To clarify the confusion on diagnosis and treatment, the world allergy association revised nomenclature for allergy and recommended using "eczema" to refer this specific disease (Johansson 2004). Symptoms of eczema may appear in infants as young as one month old, and in most cases usually appear before the age of two years. Around 60% of cases have cleared (or gone into remission) by early adolescence, although some people will experience continuing eczema into, or relapse in adult life. The prevalence of eczema varies considerably from one country to another, and also within countries (Williams 1999). In the UK there has been a steady increase in prevalence, and the condition now affects around 15% of schoolchildren (Emerson 1998; Kay 1994; Neame 1995) and 1% to 3% of adults. Most children who have eczema experience mild or moderate disease. A survey of 1760 children aged one to five years in England found that 84% of cases were mild, 14% moderate and 2% severe (Emerson 1998).
Impact of the disease
The social and economic impact of eczema is considerable, especially when the disease is severe, with sufferers experiencing significant limitations of normal social functions. It has a profound impact on the quality of life of both children (Kiebert 2002; Lewis‐Jones 2001) and adults (Kiebert 2002). People with eczema experience itch, sleep loss, bleeding from the skin and interference with nearly all aspects of daily life (Herd 2000). The emotional impact of visible eczema lesions can be considerable, especially in children, and may contribute to psychological distress. The school or work time interruption caused by sleep loss and the need to take time off work for visits to health care professionals result in considerable family disturbance. (Herd 2000). In the US, the annual cost of illness for eczema has been estimated to range from $0.9 billion to $3.8 billion when projected across the total number of people younger than 65 years insured by private insurers and Medicaid (Ellis 2002). Likewise, in the UK, it has been estimated that the annual cost of eczema in children aged one to five years is £47 million, with £30 million spent by the National Health Service and £17 million spent by the families of affected children (Emerson 2001). On the basis of an estimated 1.5 million people with eczema in Germany, it has been suggested that the total annual costs to society are as high as US$325 billion (Gieler 1999).
Management of the disease
Traditionally, the treatment of mild‐to‐moderate eczema has included the frequent use of emollients, and intermittent use of topical corticosteroids to control acute 'flares'. Corticosteroids, though effective, may be associated with a number of local and systemic adverse events, such as skin thinning and suppression of the adrenal glands (Williams 2005). To minimise these rare but possible side effects, topical corticosteroids are generally only used to treat flares and occasionally to prevent them (Ellis 2003). Fears about the safety profile of topical corticosteroids, compounded by inconsistent advice from health professionals, have important implications for adherence to treatment. Parental knowledge on differentiating weak from strong preparations is poor (Beattie 2003; Charman (b) 2000). Systemic treatment, with immunosuppressant drugs such as ciclosporin, may be associated with potentially serious adverse effects and is generally reserved for severe cases that prove resistant to conventional treatment with topical agents.
Description of the intervention
Topical pimecrolimus
Since eczema is an immune‐mediated inflammatory skin disorder, it has been considered as a good target for the immunosuppressant properties of substances called macrolides (such as cyclosporin, tacrolimus, and pimecrolimus). Pimecrolimus is a non‐steroidal immunosuppressant derived from one type of the naturally occurring antimicrobial (macrolactam), called ascomycin. Laboratory experiments have shown that pimecrolimus inhibits the production of inflammatory substances in the body (such as the synthesis and release of inflammatory cytokines from T‐lymphocytes, and the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells) that are thought to be important in causing skin lesions (Stuetz 2001), and hence pimecrolimus is used in treating severe eczema.
Why it is important to do this review
In recent years, a number of clinical trials have studied the use of topical pimecrolimus in the treatment of eczema (Hoare 2000). Most studies have compared topical pimecrolimus against placebo controls. Although the placebo‐controlled studies show that topical pimecrolimus clearly has a beneficial effect on eczema, it is not clear how they compare to existing treatments, and doctors and patients are sometimes confused how topical pimecrolimus should be used in relation to other existing therapies such as topical corticosteroids. It is also unclear whether topical pimecrolimus is best used as treatment of second choice after first line treatment has failed and whether it should be used for short‐term or long‐term control of eczema, or whether it should only be used for "sensitive sites" such as the face or armpits where skin thinning can more easily develop after using topical corticosteroids.
Recently, reports from both US and EU post‐marketing surveillance signalled a potential risk of skin cancer and lymphoma associated with pimecrolimus and tacrolimus. In December 2004, the US FDA had received 10 cases (four children and six adults) of cancer‐related adverse events associated with pimecrolimus, including lymphoma, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and granulomatous lymphadenitis. The median exposure time of pimecrolimus in these cases was 90 days, with a range from one week and 300 days (FDA 2005). These alerts on the potential risk of rare dermatological malignancies associated with pimecrolimus have raised concerns about the long‐term safety of pimecrolimus. (FDA 2005).
Objectives
To assess the effects of topical pimecrolimus compared with other topical treatments for the treatment of eczema.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs; including cross‐over trials and within‐participant studies)
Types of participants
Anyone diagnosed with eczema by a medical practitioner using standardised diagnostic criteria such as the Hanifin and Rajka definition (Hanifin 1980), the UK modification (Williams 1994), or by a dermatologist using the terms 'atopic eczema' or 'eczema'. The term 'eczema' will only be acceptable when referring to children prior to the revised World Allergy nomenclature of 2003. Following the recommendations of the World Allergy Organisation Nomenclature Review Committee, we have used the term 'eczema' throughout this systematic review (Johansson 2004).
Types of interventions
Trials comparing topical pimecrolimus at a licensed therapeutic dose (1.0%) twice daily with vehicle (cream base, but not containing pimecrolimus) or another active treatment, such as topical corticosteroids or topical tacrolimus. We also included trials that allowed concomitant use of emollients.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
The primary outcome was efficacy of treatment measured as global degree of improvement in symptoms and/or signs rated by the participants (participants' global assessments; PGA) or medical practitioners (investigators' global assessment; IGA), which are defined as following:
Investigator‐rated clinical response
The proportion of participants whose eczema were rated by the investigator as clear or almost clear (IGA score 0 or 1)
Participant‐ or carer‐rated clinical response
The proportion of participants who rated their eczema as well‐controlled or completely‐controlled (PGA)
The proportion of participants who rated their eczema as better or much better
Secondary outcomes
Safety and tolerability outcomes included:
Withdrawal from treatment
The proportion of participants who withdraw from treatment for any reason
The proportion of participants who withdraw from treatment due to lack of efficacy
The proportion of participants who withdraw from treatment due to adverse events
Adverse events
The proportions of participants experiencing any adverse events
The proportions of participants experiencing any skin infections, bacterial skin infections, viral skin infections, skin burning and skin thinning
Tertiary outcome measures
Imrovement in pruritus
The proportion of participants experiencing mild or absent pruritus (itch; pruritus score 0 or 1)
No flare of eczema
The proportion of participants not experiencing flares of eczema during treatment
No rescue medication
The proportion of participants not using topical corticosteroids as rescue medications during treatment
Improvement in quality of life (QoL)
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
We searched the following electronic databases:
Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register (to October 2006) using the search strategy in Appendix 1.
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library (Issue 3, 2006) using the search strategy in Appendix 2.
MEDLINE (OVID) from 2003 to October 2006 using the search strategy in Appendix 3.
EMBASE from 2005 to October 2006 using the search strategy in Appendix 4.
Searching other resources
References from published studies
We searched the references of the included and excluded studies in an attempt to identify any additional trials.
Unpublished literature
Unpublished and on‐going trials were identified by checking the following websites: European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products (EMEA, http://www.emea.europa.eu/, accessed 1st November 2006); The US Food and Drug administration (FDA, http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/index.htm, accessed 1st November 2006); The manufacturer of pimecrolimus (Novartis) clinical trial results (http://www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp, accessed 1st November 2006); The meta Register of Current Controlled trials (www.controlled‐trials.com, www.clinicaltrials.gov, accessed October 2006); The Cochrane Skin Group Ongoing Skin Trials Register (www.nottingham.ac.uk/ongoingskintrials/, accessed October 2006).
Language
We did not impose any language restrictions when searching for publications.
Adverse Effects
We searched for the adverse effects of pimecrolimus in MEDLINE (OVID) from 1966 to October 2006 using the search strategy in Appendix 5.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Trial eligibility was determined by two authors (LC, DMA). Any disagreement was resolved by discussion between the authors.
Data extraction and management
Two authors (LC, DMA) independently extracted dichotomous outcome data (numbers of event and intended‐to‐treat) and trial characteristics. The denominators related to all participants who were randomised to treatment (intention‐to‐treat), whereas the numerator related to the number of participants who were reported to have experienced the outcomes of interests. The authors were not blinded to the names of trialists, journal or institutions.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Assessment of methodological quality
Quality assessment included an evaluation of the following components for each included study, since there is some evidence that these are associated with biased estimates of treatment effect (Juni 2001). Each component was categorised as adequate, unclear, or inadequate.
Randomisation
Methods of generation and concealment of allocation: (a) Allocation generation: adequate when the allocation sequence protects against biased allocation to the comparison groups (b) Allocation concealment: adequate in any sequence where the assignment cannot be foreseen
Blinding
Blinding of outcome assessors, participants and clinicians was adequate when they are unaware of the allocation
Loss to follow up
Presence of dropouts and withdrawals, and the analysis of these; adequate when more than 80% of participants are followed up, then analysed in the groups to which they were originally randomised (intention to treat)
In addition, the quality assessment also included:
Degree of certainty that participants had atopic dermatitis.
Baseline comparison of severity of disease.
Assessment of heterogeneity
Heterogeneity statistics (I2) were calculated to test the agreement of the individual trial results with the combined meta‐analytical summary (Deeks 2001; Higgins 2003). All analyses were carried out using RevMan version 4.2.6.
Data synthesis
Analysis
The primary outcome measures were investigator‐rated and participant‐rated efficacy, and were stratified by treatment comparators and the duration of treatment. We summarised the dichotomous results as rate ratios (relative risks) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) using a random‐effects model (DerSimonian 1986) and compared topical pimecrolimus 1% against vehicle, topical corticosteroids (i.e. betamethasone valerate 0.1% and triamcinolone acetonide 0.1%) or topical tacrolimus (i.e. 0.03% or 0.1%), or different application regimens of 1.0% pimecrolimus. In addition, we separately analysed trials that allowed topical corticosteroids as rescue medication (i.e. flare‐preventing trials), trials that involved participants responding or not responding to previous topical corticosteroids or pimecrolimus, and within‐participant trials. We also described quality of life data from relevant studies.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
Sixty‐one trials were identified by electronic database searches (164 publications) and supplementary searches of other data sources. Overall, we identified 31 RCTs including 8019 participants with eczema that met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1).
1.
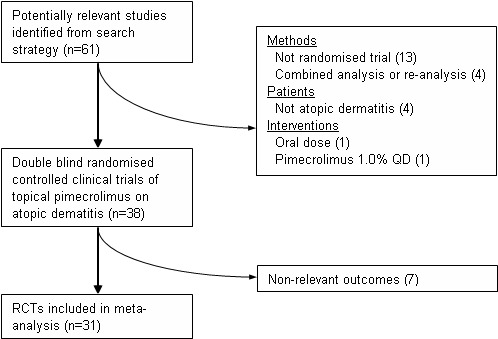
Flow diagram outlining the inclusion of studies
Included studies
(a) Design, sample sizes and participants
Of these, four trials were conducted on infants (< 24 months, n = 822), two trials on both infants and children (n = 383), 11 trials on children and adolescents (2 to 19 years, n = 3074), six trials on both children and adults (n = 1383), and eight trials on adults (> 20 years, n = 2357). Given the broad range of ages of participants included in the trials, we did not attempt to undertake subgroup analysis based on age bands.
The severity of participants' eczema varied from mild to very severe based on IGA scores in 30 trials, the majority of participants had mild to moderate (IGA 2 to 3, 15 trials, n = 3315), moderate to severe (IGA 3 to 4, 5 trials, n=1385), mild or severe (IGA 2 to 4, 3 trials, n = 807) or mild to very severe (IGA ≥ 2, 3 trials, n = 1049) eczema. In addition, two trials were conducted on participants with mild eczema (n = 1137), one trial on moderate eczema (n = 141) and one trial one severe eczema (n = 185). One trial (CASM981C2442 2006) involved 200 participants with mild to moderate facial eczema; the results from this trial are presented separately.
Four trials included participants whose response to previous treatments had been assessed prior to evaluation in the trials. One trial (CASM981C2314 2006) involved 268 participants that had already been shown to respond to 1.0% pimecrolimus twice daily. One trial (ASM981C2402 2005) involved 73 participants who had poor response to topical prednicarbate (a medium strength corticosteroid). Two trials (CASM981C2436 2006; ASM981CDE10 2005) involved 252 participants that had been shown to respond to topical corticosteroids. The results from these four trials were considered separately.
For full details, please see Characteristics of included studies.
(b) Interventions
(i) Vehicle controlled trials
Fourteen trials (2214 participants) compared 1% pimecrolimus cream applied twice daily against a vehicle control. Of these, three trials were undertaken in specific subgroups of participants, including those who had facial eczema (CASM981C2442 2006, n = 200), those who had responded to topical corticosteroids (CASM981C2436 2006, n = 67), and those who responded poorly to topical corticosteroids (ASM981C2402 2005, n = 73).
Ten trials (3364 participants) allowed the concomitant use of topical corticosteroids to control flares of eczema during treatment. Of the 10 flare‐preventing trials, one trial (ASM981CDE10 2005) involved 185 children who had previously responded to topical corticosteroids.
(ii) Active controlled trials
Six of the 31 included trials compared 1% pimecrolimus cream applied twice daily against an active treatment, including 0.1% betamethasone valerate (Luger 2001), 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide (Luger 2004), 0.03% tacrolimus cream (Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005) and 0.1% tacrolimus cream (Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005) applied twice daily for the treatment of eczema.
(iii) Treatment schedule trials
Three trials compared different regimens of 1% pimecrolimus cream. One trial (Ling 2005, n = 49) compared 1% pimecrolimus cream twice daily against the same strength applied four times daily, and one trial compared 1% pimecrolimus cream applied twice daily against the same strength applied once daily on participants who had previously been shown to respond to pimecrolimus (CASM981C2314 2006, n = 268).
(iv) Treatment duration
Treatment durations of the 31 included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) ranged from 1 week to 1 year; for 20 trials, the treatment durations were no more than 6 weeks, 1 trial lasted for 4 months, 8 trials lasted for 6 months and 4 trials lasted for 12 months.
Excluded studies
Thirty‐three trials were excluded from this systematic review (please see 'Characteristics of excluded studies') . Three abstracts of RCTs were excluded as they duplicated data contained in full publications. We also excluded 13 (non‐randomised) open‐label trials which were extended from RCTs and four combined or re‐analysis studies. Four excluded trials were conducted on patients with vitiligo, intertriginous psoriasis, chronic hand dermatitis and head and neck dermatitis. One trial included oral pimecrolimus and one included topical pimecrolimus 1.0% administrated once a day which were excluded. Seven trials which did not report the outcomes measures defined in this meta‐analysis were also excluded.
Risk of bias in included studies
The quality of the included trials is summarised in Table 1.
1. Summary of methodological quality.
| Name of study | Allocat'n generation | Allocat'n concealed | Blinding | Loss to follow up | Attrition rate | Certainty of AD | Comparable severity |
| ASM981C2315 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 15.36% | Unclear | Adequate |
| ASM981C2316 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 18.42% | Unclear | Unclear |
| ASM981C2322 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 10.12% | Unclear | Unclear |
| ASM981C2402 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 23.29% | Unclear | Unclear |
| Barba 2003 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 7.55% | Unclear | Unclear |
| CASM981C1301 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 13.75% | Adequate | Unclear |
| CASM981C1303 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 15.61% | Unclear | Unclear |
| CASM981C2413 2006 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 27.24% | Unclear | Unclear |
| CASM981C2436 2006 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 16.87% | Adequate | Unclear |
| CASM981C2442 2006 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 43.5% | Adequate | Unclear |
| CASM981CDE10 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 15.76% | Adequate | Unclear |
| CASM981CUS03 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 26.89% | Unclear | Unclear |
| Eichenfield (a) 2002 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 18.18% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Eichenfield (b) 2002 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 13.66% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Ho 2003 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 23.66% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Kapp 2002 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 27.09% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Kaufmann 2006 | Adequate | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 5.56% | Unclear | Adequate |
| Kempers 2004 | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | 11.35% | Unclear | Adequate |
| Leo 2004 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 0.00% | Adequate | Unclear |
| Ling 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 16.33% | Adequate | Unclear |
| Luger 2001 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 22.31% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Luger 2004 | Adequate | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 41.19% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Meurer 2002 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 30.21% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Paller (a) 2005 | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | 24.18% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Paller (b) 2005 | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | Inadequate | 34.96% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Paller (c) 2005 | Adequate | Adequate | Adequate | Inadequate | 21.79% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Staab 2005 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Adequate | 19.39% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Seigfried 2006 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 21.45% | Adequate | Unclear |
| Thaci 2003 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 28.72% | Unclear | Adequate |
| Wahn 2002 | Adequate | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 38.26% | Adequate | Adequate |
| Whalley 2002 | Unclear | Unclear | Adequate | Inadequate | 36.10% | Adequate | Unclear |
Allocation
Five out of the 31 included trials (16.1%) reported an adequate allocation concealment (Kaufmann 2006; Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005; Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005), but the other 26 trials (83.9%) did not clearly describe the allocation generation and concealment. Most of the included RCTs did not report on the method of randomisation. Only seven trials described using a computerised system (Luger 2004; Wahn 2002) or telephoning a controlled randomisation system (Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005; Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005) to automate the assignment of treatment, and reported the ratio or blocks of allocation.
Blinding
Of the 31 included trials, four (Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005; Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005) were investigator‐blind, and other 27 trials were both investigator and participant‐blind (double‐blind). Only nine of the 27 double‐blind trials reported on the methods used to ensure the blinding of outcome assessment.
Incomplete outcome data
Follow‐up and exclusions
The loss to follow up rate (attrition rate) of the included RCTs ranged from 0% to 44%. In 15 trials, the withdrawal rate was more than 20%. The attrition rate was correlated with the treatment duration (Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.38; P = 0.032). The dropouts and reasons for dropouts were recorded and analysed, with the exception of one trial which did not specify reasons for withdrawals (Whalley 2002)
Selective reporting
Only 16 trials reported the criteria used for diagnosing eczema, and 21 trials stated that the baseline severities of eczema were comparable between the different treatment groups.
Effects of interventions
1. Efficacy and quality of life
We have summarised the efficacy results for the different treatment comparisons separately. The efficacy results include Investigator‐rated clinical response (IGA), participant‐ or carer‐rated clinical response (PGA) and improvement in pruritus. Global changes in composite rating scales (e.g. Atopic Dermatitis Area Severity Index [ADASI]) or the duration of remission were not routinely reported in the included trials. Of the 31 trials only 2 trials (Eichenfield (a) 2002; Eichenfield (b) 2002) reported on the clinical signs of eczema (erythema, induration or papulation, excoriation, and lichenification) assessed by a physician as mild or absent. The impact of treatment on QoL is reported separately due to marked differences in the QoL instruments used and the timing of QoL assessments.
(a) Pimecrolimus versus vehicle
(i) Investigator‐rated clinical response as clear or almost clear eczema (eight studies)
One trial (CASM981C2322 2005) involving 336 children who had mild to moderate eczema found that pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear eczema following 1 and 2 weeks of therapy; the pooled rate ratios (RRs) were 2.00 (95% CI 1.06 to 3.76; Analysis 1.1) and 1.58 (95% CI 1.00 to 2.52; Analysis 1.1) respectively. Likewise, the pooled results from 5 trials (783 participants) found that pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle (RR 2.72, 95% CI 1.84 to 4.03; Analysis 1.1) on the same outcome at 3 weeks. Pimecrolimus also remained significantly more effective than vehicle following 6 weeks treatment (RR 2.03, 95% CI 1.50 to 2.74; Analysis 1.1) based on the pooled results from 3 trials involving 589 participants.
1.1. Analysis.
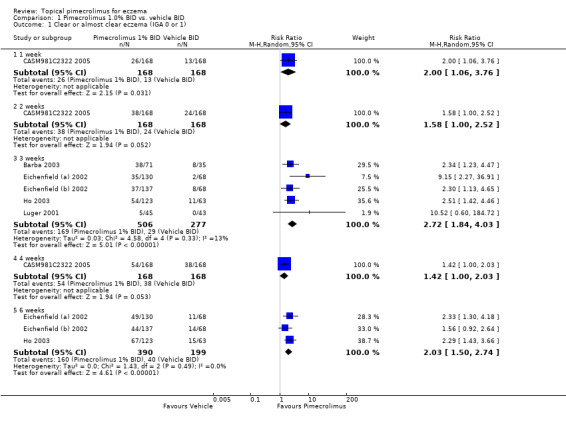
Comparison 1 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
One trial (CASM981C2442 2006) that involved 200 participants with mild to moderate facial eczema found that pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear facial eczema following 1, 3, and 6 weeks of treatment. The pooled RRs were 2.94 (95% CI 1.31 to 6.61; Analysis 2.1), 3.02 (95% CI 1.72 to 5.29; Analysis 2.1) and 2.88 (95% CI 1.76 to 4.72; Analysis 2.1). A further trial (ASM981C2402 2005) involving 73 children and adults with mild to moderate eczema who had not responded to a 2‐week treatment of prednicarbate (a medium‐strength corticosteroid) cream showed that there was no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema at 6 weeks (RR 6.19, 95% CI 0.36 to 107.66; Analysis 4.1).
2.1. Analysis.
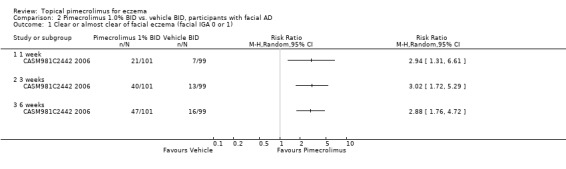
Comparison 2 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants with facial AD, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear of facial eczema (facial IGA 0 or 1).
4.1. Analysis.
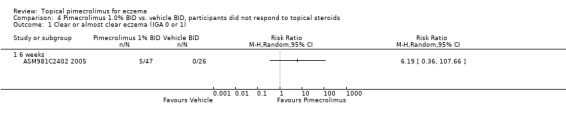
Comparison 4 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
(ii) Participant‐ or carer‐rated clinical response as complete or well controlled eczema (three studies)
One trial (Barba 2003) involving 106 infants and children reported that 1.0% pimecrolimus resulted in significantly more participants achieving complete or well controlled eczema than vehicle following 3 weeks of treatment (RR 1.88, 95% CI 1.33 to 2.67;Analysis 1.2). Likewise, 1 trial (Ho 2003) involving 186 participants found pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle on the same outcome at 6 weeks (RR 2.65, 95% CI 1.74 to 4.04; Analysis 1.2 comparison 01‐01). However, the trial involving 73 participants who did not respond to a pre‐trial treatment of prednicarbate found no significant difference in achieving complete or well controlled eczema at 6 weeks (RR 1.29, 95% CI 0.56 to 2.95; Analysis 4.2).
1.2. Analysis.
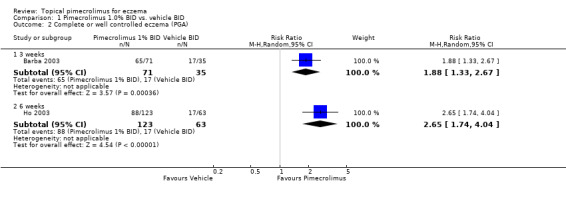
Comparison 1 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, Outcome 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA).
4.2. Analysis.
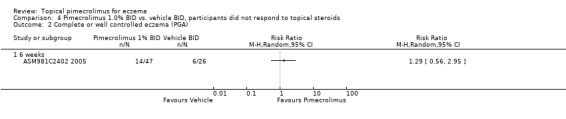
Comparison 4 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids, Outcome 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA).
(iii) Mild or absent pruritus (eight studies)
Pimecrolimus resulted in significantly more participants achieving mild or absent pruritus at one week (RR 1.89, 95% CI 1.51 to 2.35; Analysis 1.3), 3 weeks (RR 2.02, 95% CI 1.69 to 2.42; Analysis 1.3) and 6 week (RR 1.82, 95% CI 1.48 to 2.25; Analysis 1.3) compared against vehicle, based on pooled results from 3 trials (472 participants), 5 trials (783 participants) and 3 trials (589 participants) respectively.
1.3. Analysis.
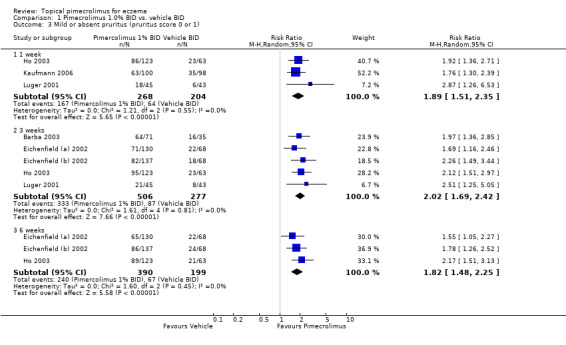
Comparison 1 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, Outcome 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
Likewise, pimecrolimus resulted in significantly more participants with facial eczema achieving mild or absent pruritus following 1, 3, and 6 weeks of treatment based on results from 200 participants, the pooled RRs were 1.81 (95% CI 1.32 to 2.50; Analysis 2.2), 1.85 (95% CI 1.39 to 2.47; Analysis 2.2) and 2.02 (95% CI 1.49 to 2.73; Analysis 2.2). However, the trial involving 73 participants who did not respond to a pre‐trial of prednicarbate found no significant difference in achieving mild or absent pruritus at six weeks (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.47 to 2.60; Analysis 4.3).
2.2. Analysis.
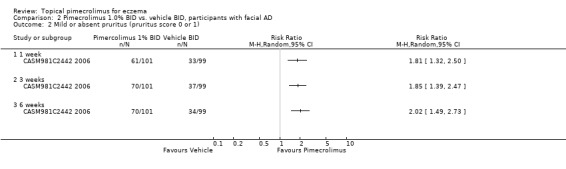
Comparison 2 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants with facial AD, Outcome 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
4.3. Analysis.
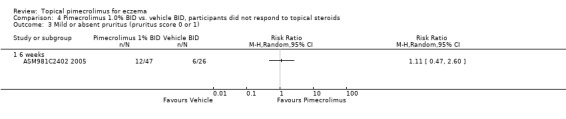
Comparison 4 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids, Outcome 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
(iv) Improvement in quality of life (three studies)
Information on quality of life (QoL) was patchy, with a lack of common outcome measures (Table 2). Only six of the 31 included RCTs reported quality of life outcomes. Three trials (Leo 2004; Staab 2005; Whalley 2002) compared pimecrolimus against vehicle and the other three trials (Kapp 2002; Meurer 2002; Wahn 2002) were flare‐preventing trials.
2. Quality of life measures.
| Population | QoL measure | Scale of measure | Study |
| Adults | Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) | 10 items, maximum score: 30 (score 0 to 3 for each item) | Meurer 2002, |
| Quality of Life Index‐ Atopic Dermatitis (QoLI‐AD) | 25 items, maximum score: 25 (yes, no scored 1, 0) | Meurer 2002, | |
| Children | Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI) | 10 items, maximum score: 30 (score 0 to 3 for each item) | Leo 2004, Wahan 2002 |
| Carers | Parent's Index of Quality of Life‐ Atopic Dermatitis (PIQoL‐AD) | 28 items, maximum score: 28 (yes, no scored 1, 0) | Whalley 2002, Kappa 2002, Wahn 2002 |
| Parents' Quality of Life Index‐ Atopic Dermatitis (PQoL‐AD) | 26 items in 5 sub‐scales (each items scored 1 to 5 in 5‐point Likert Scale) | Staab 2005 |
One vehicle‐controlled trial (Whalley 2002) involving 403 children with mild to moderate eczema used the Parent's Index of Quality of Life in Atopic Dermatitis (PIQoL‐AD) score to measure QoL. This study included a 6‐week RCT period and a 20‐week open‐label trial period. The PIQoL‐AD scores were completed by the parents of a subset of participants (children aged 2 to 8 years) at baseline (241 cases), 6 weeks (193 cases) and 6 months (161 cases) of treatment. At six weeks, those children who received pimecrolimus were judged by their parents to have a significantly improved quality of life compared with those receiving vehicle (P = 0.023). The least‐square mean change was 3.20 for the pimecrolimus group and 1.63 for the vehicle group, with an estimated treatment difference of 1.57 (95% CI 0.22 to 2.92). At six months (end of open‐label phase), both treatment groups showed a significant within‐group improvement (P < 0.001) compared with baseline, but the mean PIQoL‐AD scores were similar between the two treatment groups. A reduction of 10% or more in PIQoL‐AD score between baseline and 6 months was found in 76.1% of parents of children who had been initiated with pimecrolimus and 77.1% of parents of children who had started with vehicle.
One vehicle‐controlled trial (Leo 2004) involving 19 children with mild to moderate eczema reported a trend towards lower Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI) score (a validated measure consisting of 10 questions that inquire about the effect of eczema on a child's QoL, lower score indicates improved QoL) at 2 weeks in the pimecrolimus group, but there was no significant difference detected from baseline (P = 0.12). The mean CDLQI score changed from 7.44 to 3.8 for pimecrolimus 1.0% and from 7.72 to 5.4 for vehicle treatment.
Likewise, another trial (Staab 2005) involving 190 infants with mild to severe eczema used the Parents' Quality of Life Index Atopic Dermatitis (PQoL‐AD) to measure QoL. At four weeks (end of the double‐blind treatment), participants receiving pimecrolimus were judged by their parents to have a significantly improved quality of life from baseline in all five sub‐scales of PQoL‐AD compared against vehicle (P < 0.05); the mean percentage changes from baseline for all five sub‐scales were: psychosomatic well‐being 14.6% vs. 6.2%; effects on social life 6.7% vs. 2.3%; confidence in medical treatment 10.0% vs. 3.7%; emotional coping 16.1% vs. 6.5%; acceptance of disease 19.6% vs. 7.0%.
(b) Pimecrolimus versus vehicle, plus topical corticosteroids to treat flares
(i) Investigator‐rated clinical response as clear or almost clear eczema (two studies)
Two trials (Kapp 2002; Siegfried 2006) involving 526 participants found that 1.0% pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving clear or almost clear eczema at 1 week (RR 3.45, 95% CI 1.66 to 7.14; Analysis 5.1). However, results from a 12‐month trial (Kapp 2002) involving 251 infants found no significant difference between pimecrolimus 1% and vehicle on the same outcome at 3 weeks (RR 1.43, 95% CI 0.98 to 2.10; Analysis 5.1), 6 months (RR 1.46, 95% CI 0.98 to 2.19; Analysis 5.1) and 12 months (RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.60; Analysis 5.1).
5.1. Analysis.
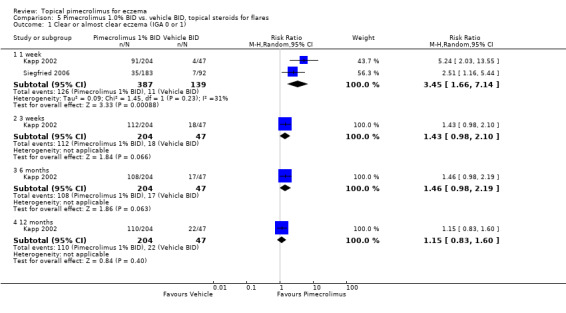
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
(ii) Participant‐ or carer‐rated clinical response as complete or well controlled eczema (two studies)
Kapp (et al.) (2002) found that 1.0% pimecrolimus resulted in significantly more participants achieving complete or well controlled eczema than vehicle at 6 weeks (RR 1.40, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.85; Analysis 5.2), 9 months (RR 1.33; 95% CI 1.01 to 1.74; Analysis 5.2), but not at 12 months (RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.47; Analysis 5.2). Pooled results from two trials (Kapp 2002; Meurer 2002) involving 443 participants also showed that pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving complete or well controlled eczema at 6 months (RR 1.62, 95% CI 1.29 to 2.04; Analysis 5.2).
5.2. Analysis.
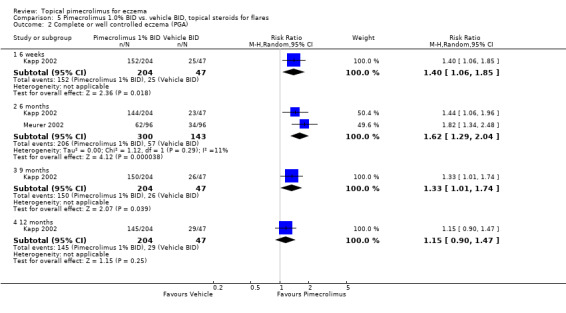
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA).
(iii) Mild or absent pruritus (one study)
Similarly, Kapp (et al.) (2002) found that pimecrolimus was significantly more effective than vehicle in achieving mild or absent pruritus at 6 weeks (RR 1.33, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.72; Analysis 5.3), 6 months (RR 1.37, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.82; Analysis 5.3), 9 months (RR 1.36, 95% CI 1.04 to 1.79; Analysis 5.3), but not at 12 months (RR 1.25, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.58; Analysis 5.3).
5.3. Analysis.
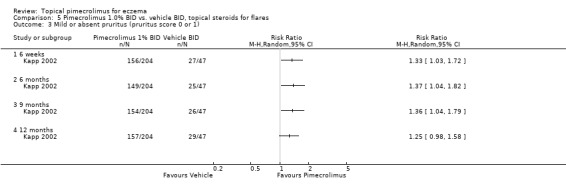
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
(iv) No flare of eczema during treatment (nine studies)
Nine trials (3091 participants) reported on the proportion of participants who did not experience a flare of eczema at six months, and pimecrolimus resulted in significantly more participants without flares compared against vehicle (RR 1.47, 95% CI 1.32 to 1.64). Likewise, pimecrolimus was also significantly more effective than vehicle at preventing flares of eczema at 12 months (RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.45 to 1.96) based on data from 2 trials (Kapp 2002; Wahn 2002) involving 962 participants.
(v) No use of topical corticosteroids as rescue medication (three studies)
Data from one trial (Meurer 2002) involving 192 participants showed pimecrolimus was found to have significantly lower rates of corticosteroid use than vehicle at 6 months (RR 2.24, 95% CI 1.46 to 3.44; Analysis 5.5). In the 2 trials (Kapp 2002; Wahn 2002) which allowed the use of moderately potent topical corticosteroids as 'rescue' medication for treating flares of eczema, pimecrolimus was found to have significantly lower rates of corticosteroid use at 12 months (RR 1.76, 95% CI 1.50 to 2.08; Analysis 5.5) compared against vehicle based on results from 962 participants.
5.5. Analysis.
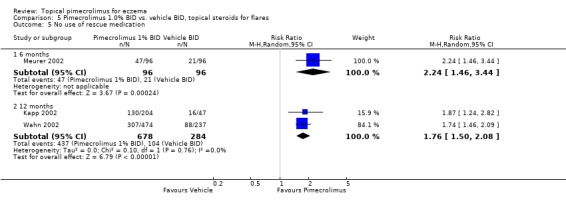
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 5 No use of rescue medication.
(vi) Improvement in quality of life (three studies)
Three flare prevention studies (McKenna 2006; Meurer 2002) reported on quality of life assessments. A 24‐week RCT (Meurer 2002) involving 192 adults with moderate to severe eczema assessed QoL using both the Quality of Life Index AD (QoLI‐AD) and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Participants receiving pimecrolimus had a significantly improved quality of life at 6 months compared with those receiving vehicle. The mean decreases (i.e. improvement) in the QoLI‐AD score were 25.6% and 7.4% comparing pimecrolimus against vehicle (P = 0.002), and the mean decreases (i.e. improvement) in the DLQI score were 22.0% and 6.7% (P = 0.01).
McKenna 2006 reported on the QoL and health‐related quality of life (HRQL) data from two 12‐month flare‐preventing trials, involving 251 infants with mild to very severe eczema (Kapp 2002) and 713 children with mild eczema (Wahn 2002). The Parent's Index of Quality of Life‐ eczema (PIQoL‐AD) was used in both trials and the Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI) was used in the children trial to assess QoL at baseline, 6 weeks, 6 months and 12 months. Comparing change from baseline in PIQoL‐AD scores, 1.0% pimecrolimus cream treatment resulted in significantly better improvement of eczema than vehicle in both trials at 6 months (P = 0.002 and 0.001 for infant and children trials) and 12 months (P = 0.016 and 0.015 for infant and children trials) of treatment, and also in the children trial at 6 weeks of treatment (P = 0.017). In the infant trial, the odds of giving an unfavourable answer to the PIQoL‐AD questions were 41%, 87% and 80% higher for members of the control group at 6 weeks, 6 months and 12 months, respectively. The equivalent odds in the children trial were 34%, 59% and 46%. In addition, pimecrolimus was significantly superior to vehicle in the improvement of CDLQI score in the children trial at 6 weeks (P < 0.001), 6 months (P = 0.001) and 12 months (P = 0.10) of treatment; the mean CDLQI scores were 8.1 vs. 7.4, 4.9 vs. 7.1, 5.4 vs. 7.8 and 5.7 vs. 7.4, respectively (lower score indicates improved QoL).
(c) Pimecrolimus versus topical corticosteroids
(i) Investigator‐rated clinical response as clear or almost clear eczema (one study)
A 12 month trial (Luger 2004) which compared 1.0% pimecrolimus against 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide (a mid‐potency topical corticosteroid) in 658 adults with moderate to severe eczema found pimecrolimus to be significantly less effective than triamcinolone acetonide in achieving clear or almost clear of eczema after 1 week (RR: 0.52, 95%CI 0.45 to 0.61; Analysis 7.1), 3 weeks (RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.83; Analysis 7.1), 6 months (RR 0.89, 95%CI 0.83 to 0.96; Analysis 7.1) and 12 months (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.86 to 0.98; Analysis 7.1) of treatment.
7.1. Analysis.
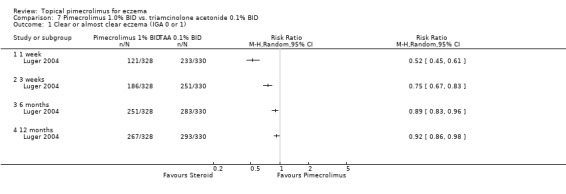
Comparison 7 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
(ii) Participant‐rated clinical response as complete or well controlled eczema (one study)
One trial (Luger 2001) compared 1% pimecrolimus against 0.1% betamethasone valerate (a potent topical corticosteroid) in 87 adults with moderate to severe eczema for 3 weeks. Pimecrolimus was found to be significantly less effective than betamethasone valerate in achieving moderately clear or better eczema (i.e. 50% improvement from baseline) at 3 weeks (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.81; Analysis 8.1).
8.1. Analysis.
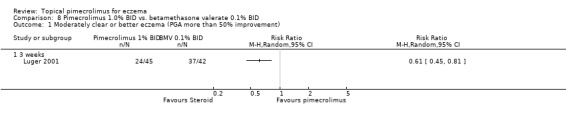
Comparison 8 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID, Outcome 1 Moderately clear or better eczema (PGA more than 50% improvement).
(iii) Mild or absent pruritus (2 studies)
Luger 2001 also reported that pimecrolimus resulted in significantly fewer participants achieving mild or absent pruritus compared against 0.1% betamethasone valerate following 1 week (RR 0.51, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.75; Analysis 8.2) and 3 weeks (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.81; Analysis 8.2) of treatment. Likewise, the 12‐month trial (Luger 2004) found pimecrolimus resulted in significantly fewer participants achieving mild or absent pruritus than 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide at 12 months of treatment (RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.58; Analysis 7.2).
8.2. Analysis.
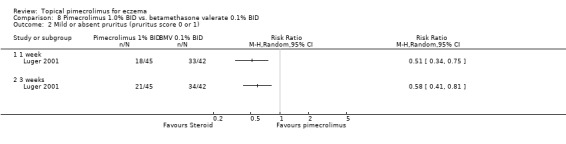
Comparison 8 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID, Outcome 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
7.2. Analysis.
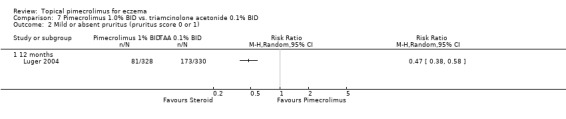
Comparison 7 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID, Outcome 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
(iv) Improvement in quality of life (No studies)
We did not identify any quality of life assessments in trials that compared pimecrolimus against topical corticosteroids directly.
(d) Pimecrolimus versus tacrolimus
(i) Investigator‐rated clinical response as clear or almost clear eczema (four studies)
Two trials (Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005) involving 567 children compared 1.0% pimecrolimus against 0.03% tacrolimus directly. The pooled results found no statistically significant difference between 1.0% pimecrolimus and 0.03% tacrolimus in achieving clear or almost clear of eczema following 1 week (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.31; Analysis 9.1), 3 weeks (RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.15; Analysis 9.1) and 6 weeks (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.69 to 1.02; Analysis 9.1) of treatment.
9.1. Analysis.
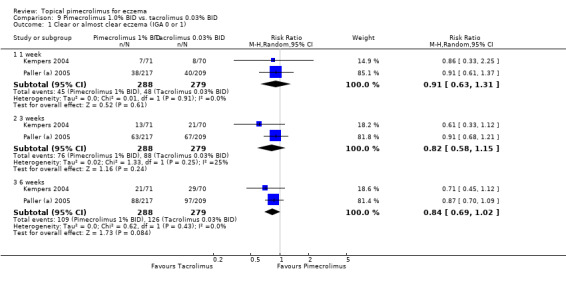
Comparison 9 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
Paller 2005 also reported on 2 trials (Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005) involving 639 participants that compared 1% pimecrolimus against 0.1% tacrolimus directly. The pooled results found no significant difference in achieving clear or almost clear eczema following 1 week of treatment (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.34; Analysis 10.1); however, 1.0% pimecrolimus was significantly less effective than 0.1% tacrolimus in achieving clear or almost clear eczema following 3 weeks (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.77; Analysis 10.1) and 6 weeks (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.74; Analysis 10.1) of treatment.
10.1. Analysis.
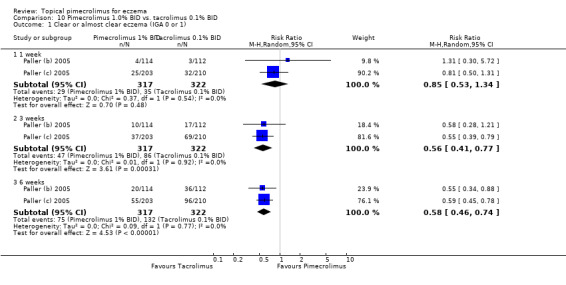
Comparison 10 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
(ii) Mild or absent pruritus (two studies)
The results from 1 trial (Kempers 2004) involving 141 participants that compared 1.0% pimecrolimus against 0.03% tacrolimus found no statistically significant difference in achieving mild or absent pruritus following 1 week (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.04; Analysis 9.2) and 6 weeks (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.17; Analysis 9.2) of treatment, but 1.0% pimecrolimus was significantly less effective in achieving mild or absent pruritus at 3 weeks (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.61 to 0.99; Analysis 9.2).
9.2. Analysis.
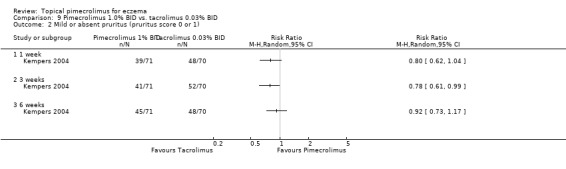
Comparison 9 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID, Outcome 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
(iii) Impact on quality of life (No studies)
We did not identify any quality of life assessments in trials that compared pimecrolimus against tacrolimus directly.
(e) Different treatment schedules of pimecrolimus
(i) Investigator‐rated clinical response as clear or almost clear eczema (two studies)
One trial (Ling 2005) involving 49 children and adults compared 1.0% pimecrolimus applied twice daily against 4r times daily. There were no significant differences between the 2 treatment schedules in achieving clear or almost clear eczema following 3 weeks of treatment (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.43 to 2.52; Analysis 11.1). One trial (CASM981C2314 2006) involving 268 children who responded to a pre‐trial 1% pimecrolimus twice daily treatment found no significant difference between twice daily and once daily schedules in achieving clear or almost clear eczema at 8 weeks (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.31; Analysis 12.1) and 16 weeks (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.28; Analysis 12.1).
11.1. Analysis.
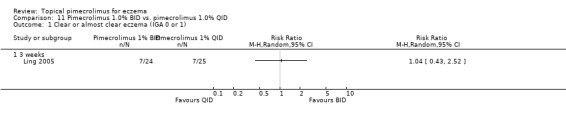
Comparison 11 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
12.1. Analysis.
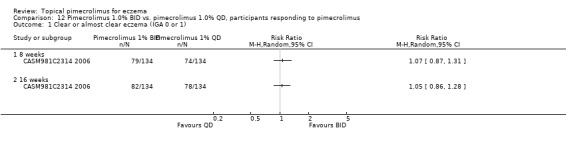
Comparison 12 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD, participants responding to pimecrolimus, Outcome 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1).
(ii) Participant‐ or carer‐rated clinical response as complete or well controlled eczema (No studies)
Ling 2005 also found that there were no significant differences between twice and four times daily regimens of pimecrolimus in achieving complete or well controlled eczema following three weeks of treatment (RR 1.33, 95% CI 0.76 to 2.31Analysis 11.1).
(iii) Mild or absent pruritus (one study)
Likewise, Ling 2005 reported no significant differences between twice and 4 times daily regimens of pimecrolimus in the proportion of participants achieving mild or absent of pruritus at 3 weeks (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.56, 1.67; Analysis 11.3).
11.3. Analysis.
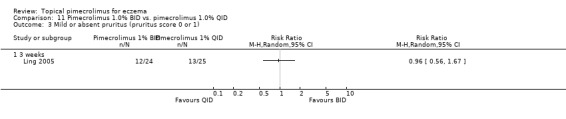
Comparison 11 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID, Outcome 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1).
(iv) No flare of eczema during treatment (one study)
One trial (CASM981C2314 2006) involving 268 children who responded to a pre‐trial 1% pimecrolimus twice daily treatment found no significant difference between twice daily and once daily schedules in achieving no flare of eczema at 16 weeks (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.96 to 1.15; Analysis 12.2).
12.2. Analysis.
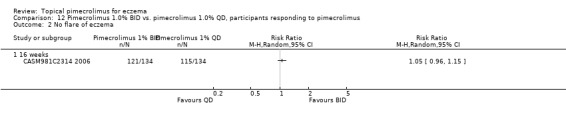
Comparison 12 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD, participants responding to pimecrolimus, Outcome 2 No flare of eczema.
(v) Improvement in quality of life (No studies)
We did not identify any quality of life assessments in trials that compared between different treatment schedules of pimecrolimus.
2. Safety and tolerability
The tolerability results include total withdrawals, withdrawals due to lack of efficacy and withdrawals due to adverse events. The adverse events reported in the 31 included trials were generally mild. We did not identify any skin and internal cancers reported in the RCTs; likewise, there was no data on skin thinning. The most commonly reported adverse events were skin infection or application site reactions. We report the pooled results of proportions of participants experiencing any skin infections, bacterial skin infection, viral skin infections and local application site skin burning.
(a) Vehicle controlled and flare‐preventing studies
(i) Withdrawal from treatment (22 studies)
Pimecrolimus was associated with significantly fewer overall withdrawals (RR 0.40, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.58; Analysis 1.4), withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.21 95% CI 0.11 to 0.41; Analysis 1.4), and withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 0.43, 95%CI 0.19 to 0.97; Analysis 1.4) than vehicle from the pooled results of 10 (1785 participants), 8 (1657 participants) and 5 (1025 participants) vehicle‐controlled trials, respectively.
1.4. Analysis.
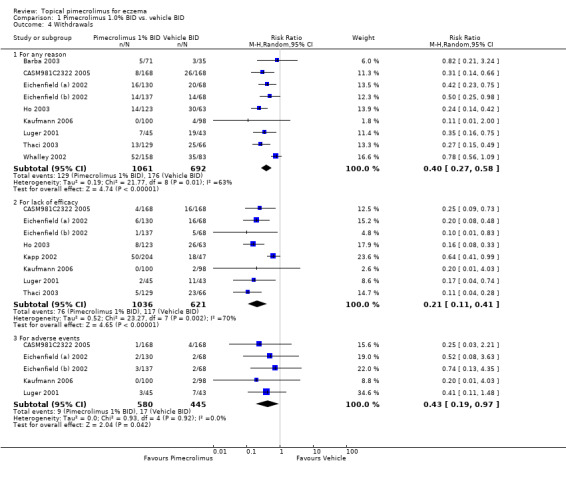
Comparison 1 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, Outcome 4 Withdrawals.
One trial (CASM981C2442 2006) involving 200 participants with facial eczema found pimecrolimus resulted in fewer overall withdrawals (RR 0.44, 95%CI 0.31 to 0.63; Analysis 2.3) and withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.27, 95%CI 0.15 to 0.48; Analysis 2.3) than vehicle, but no significant difference was detected in withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 0.82, 95%CI 0.26 to 2.59; Analysis 2.3). Similarly, results from 1 trial (CASM981C2436 2006) involving 67 participants who responded to topical corticosteroid treatment found pimecrolimus resulted in fewer overall withdrawals (RR 0.28, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.76; Analysis 3.1) and withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.28, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.76; Analysis 3.1) than vehicle; but no withdrawals due to adverse events were reported. One further trial (ASM981C2402 2005) involving 73 participants who did not respond to topical corticosteroid treatment found no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in overall withdrawals (RR 0.62, 95% CI 0.27 to 1.42; Analysis 4.4), withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.41, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.71; Analysis 4.4), or adverse events (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.15 to 4.65; Analysis 4.4).
2.3. Analysis.
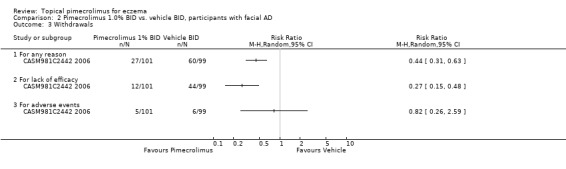
Comparison 2 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants with facial AD, Outcome 3 Withdrawals.
3.1. Analysis.
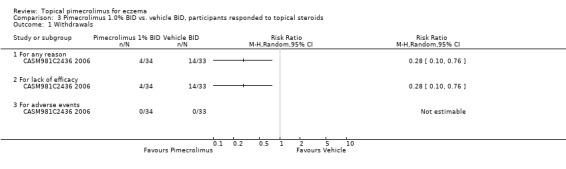
Comparison 3 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants responded to topical steroids, Outcome 1 Withdrawals.
4.4. Analysis.
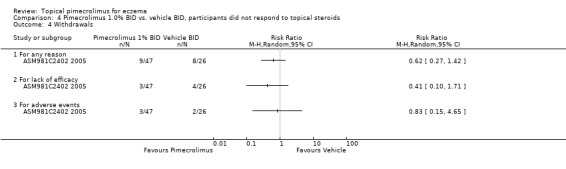
Comparison 4 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids, Outcome 4 Withdrawals.
Pimecrolimus was associated with significantly fewer overall withdrawals (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.54 to 0.76; Analysis 5.6) and withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.51; Analysis 5.6) than vehicle from the pooled results of 9 flare‐preventing trials involving 3091 participants. However, no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle was detected in withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.28 to 1.27; Analysis 5.6) from the pooled results of 8 flare‐preventing trials involving 2380 participants. One flare‐preventing trial (ASM981CDE10 2005) involving 184 participant who responded to topical corticosteroids also found no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in overall withdrawals (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.29 to 1.14; Analysis 6.1) and withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.17 to 1.09; Analysis 6.1) than vehicle; and no withdrawals due to adverse events were reported in this trial.
5.6. Analysis.
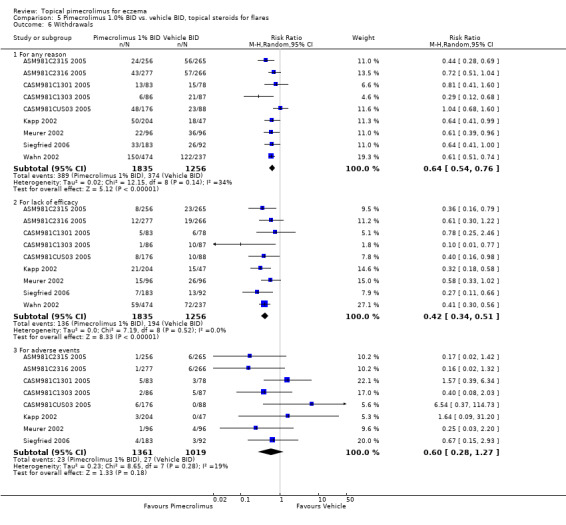
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 6 Withdrawals.
6.1. Analysis.
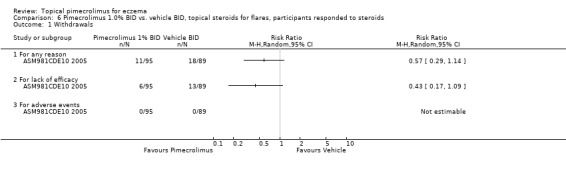
Comparison 6 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, participants responded to steroids, Outcome 1 Withdrawals.
(ii) Adverse events (17 studies)
We found no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in the proportions of participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.02; Analysis 1.5), bacterial skin infections (RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.12; Analysis 1.5) and skin burning (RR 1.40, 95% CI 0.90 to 2.18; Analysis 1.5) from the pooled results of four (827 participants), 1 (186 participants) and 5 (914 participants) vehicle‐controlled trials, respectively.
1.5. Analysis.
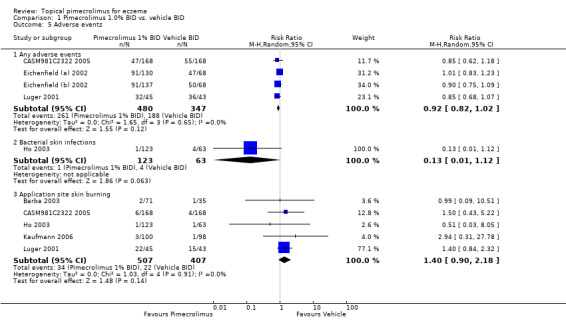
Comparison 1 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, Outcome 5 Adverse events.
The vehicle‐controlled trial (CASM981C2442 2006) involving 200 participants with facial eczema did not report any relevant adverse event data. One trial (CASM981C2436 2006) involving 67 participants who responded to topical corticosteroids found no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in any adverse events (RR 1.70, 95% CI 0.82 to 3.51; Analysis 3.2). One trial (ASM981C2402 2005) involving 73 participants who did not respond to topical corticosteroids found no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle in any adverse events (RR 1.19, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.87; Analysis 4.5), any skin infections (RR 1.66, 95% CI 0.18 to 15.16; Analysis 4.5), viral skin infections (RR 2.81, 95% CI 0.14 to 56.46; Analysis 4.5), and skin burning (RR 0.55, 95% CI 0.08 to 3.70; Analysis 4.5).
3.2. Analysis.
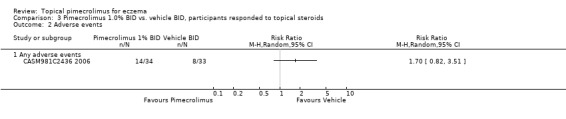
Comparison 3 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants responded to topical steroids, Outcome 2 Adverse events.
4.5. Analysis.
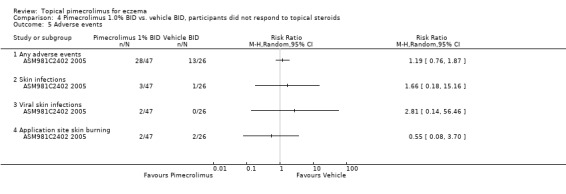
Comparison 4 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids, Outcome 5 Adverse events.
We found pimecrolimus was associated with significantly more participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.07, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.16; Analysis 5.7) and skin burning (RR 4.36, 95% CI 1.75 to 10.85; Analysis 5.7) than vehicle from the pooled results of four (1398 participants) and three (999 participants) flare‐preventing trials. However, no significant difference between pimecrolimus and vehicle was detected in participants experiencing any skin infections (RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.72; Analysis 5.7), bacterial skin infections (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.51 to 1.39; Analysis 5.7) and viral skin infections (RR 1.79, 95% CI 0.89 to 3.61; Analysis 5.7) from the pooled results of 3 (718 participants), 3 (718 participants) and 4 (982 participants) flare‐preventing trials, respectively. The flare‐preventing trial (ASM981CDE10 2005) involving participants who responded to topical corticosteroids did not report relevant safety outcomes.
5.7. Analysis.
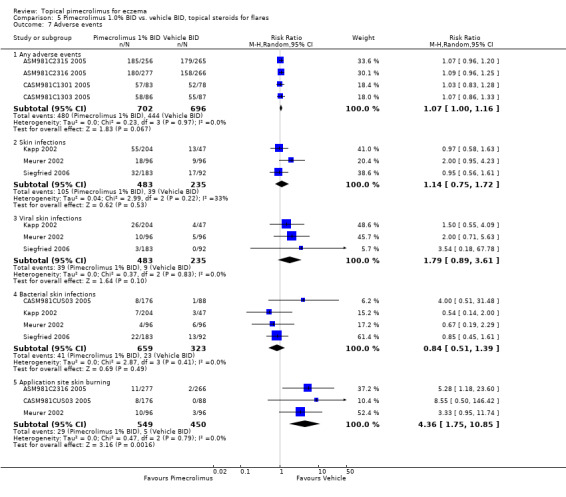
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 7 Adverse events.
(b) Pimecrolimus versus topical corticosteroids
(i) Withdrawal from treatment (two studies)
One 52‐week trial (Luger 2004) involving 658 participants found that 1% pimecrolimus was associated with significantly more overall withdrawals (RR 2.45, 95% CI 1.98 to 3.03; Analysis 7.3), withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 4.43, 95% CI 3.01 to 6.54; Analysis 7.3) and withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 5.63, 95% CI 2.20 to 14.41; Analysis 7.3) than 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide.
7.3. Analysis.
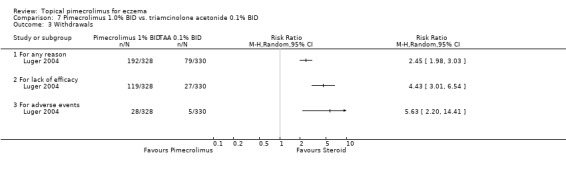
Comparison 7 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID, Outcome 3 Withdrawals.
However, one three‐week trial (Luger 2001) involving 87 participants found no significant difference between 1% pimecrolimus and 0.1% betamethasone valerate for the overall withdrawals (RR 2.18, 95% CI 0.60 to 7.88; Analysis 8.3), or withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 4.67, 95% CI 0.23 to 94.61; Analysis 8.3) and withdrawals due to adverse effects (RR 2.80, 95% CI 0.30 to 25.88; Analysis 8.3).
8.3. Analysis.
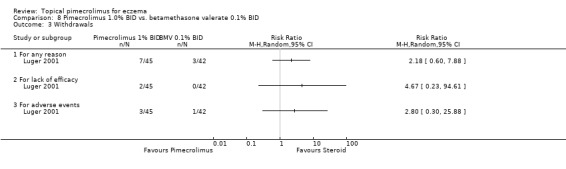
Comparison 8 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID, Outcome 3 Withdrawals.
(ii) Adverse events (two studies)
Luger 2004 found no significant difference between 1% pimecrolimus and 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide in the proportion of participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.17; Analysis 7.4), any skin infections (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.15; Analysis 7.4), viral skin infections (RR 0.62, 95% CI 0.34 to 1.13; Analysis 7.4) or bacterial skin infections (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.61 to 1.37; Analysis 7.4), but 1% pimecrolimus was associated with a significantly higher rate of skin burning (RR 2.38, 95% CI 1.66 to 3.40; Analysis 7.4) than 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide.
7.4. Analysis.
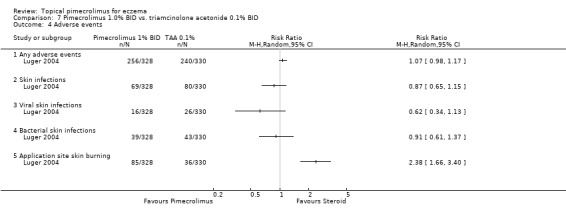
Comparison 7 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID, Outcome 4 Adverse events.
However, Luger 2001 reported that 1% pimecrolimus was associated with a significantly higher rate than 0.1% betamethasone valerate of participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.57, 95% CI 1.07 to 2.30) or skin burning (RR 5.13, 95% CI 1.93 to 13.66; Analysis 7.4; there was no other relevant safety outcomes reported in this trial.
None of the included trials reported on changes in skin thickness.
(c) Pimecrolimus versus tacrolimus
(i) Withdrawal from treatment (four studies)
Two trials (Kempers 2004; Paller (a) 2005) involving 567 participants found no significant difference between 1% pimecrolimus and 0.03% tacrolimus in the overall withdrawal rate (RR 1.94, 95% CI 0.54 to 6.98; Analysis 9.3), but 1% pimecrolimus was associated with significantly higher withdrawal rates due to lack of efficacy (RR 3.45, 95% CI 1.23 to 9.71; Analysis 9.3) and adverse events (RR 8.19, 95% CI 1.50 to 44.73; Analysis 9.3) than 0.03% tacrolimus.
9.3. Analysis.
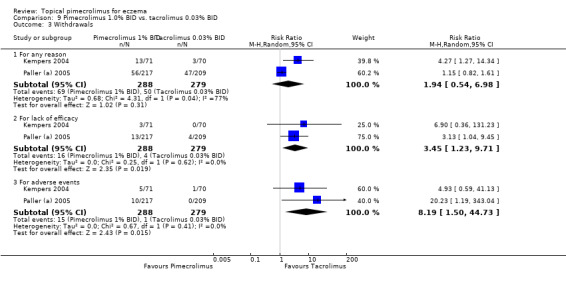
Comparison 9 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID, Outcome 3 Withdrawals.
Pooled results from 2 trials (Paller (b) 2005; Paller (c) 2005) involving 639 participants found no significant difference in the overall withdrawals (RR 1.18, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.52; Analysis 10.1) and withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.43 to 2.41; Analysis 10.2), but 1% pimecrolimus was associated with significantly a higher withdrawal rate due to lack of efficacy (RR 2.37, 95% CI 1.10 to 5.08; Analysis 10.2) than 0.1% tacrolimus.
10.2. Analysis.
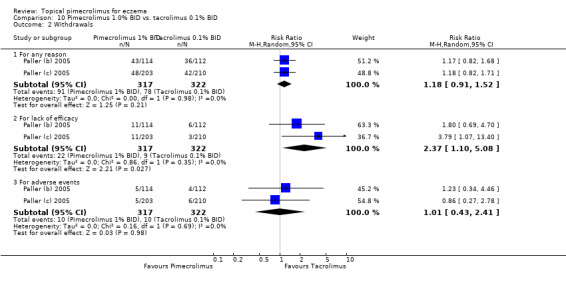
Comparison 10 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID, Outcome 2 Withdrawals.
(ii) Adverse events (four studies)
We found no significant differences between the head‐to‐head comparisons of 1.0% pimecrolimus against 0.03% tacrolimus in participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.17; Analysis 9.4), skin infections (RR 1.65, 95% CI 0.12 to 22.75; Analysis 9.4), bacterial skin infections (RR 6.90, 95% CI 0.36 to 131.23; Analysis 9.4), viral skin infections (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.15 to 6.96; Analysis 9.4) and skin burning (RR 1.17, 95% CI 0.55 to 2.49; Analysis 9.4).
9.4. Analysis.
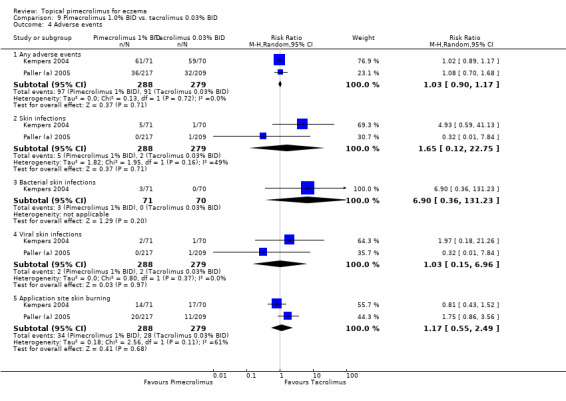
Comparison 9 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID, Outcome 4 Adverse events.
Likewise, no significant differences between 1.0% pimecrolimus and 0.1% tacrolimus in participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.47 to 2.26; Analysis 10.3), skin infections (RR 1.60, 95% CI 0.37 to 6.99; Analysis 10.3), viral skin infections (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.43; Analysis 10.3) and skin burning (RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.36 to 1.62; Analysis 10.3, comparison 10‐10) were detected.
10.3. Analysis.
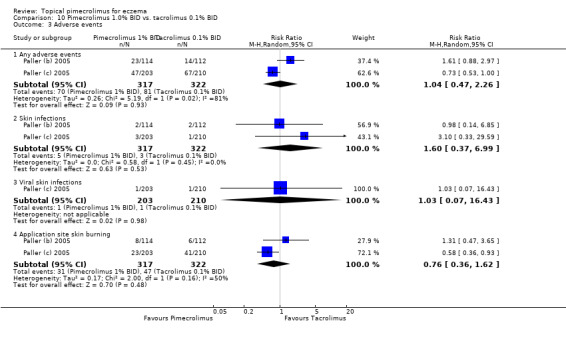
Comparison 10 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID, Outcome 3 Adverse events.
(d) Different regimens of pimecrolimus
(i) Withdrawal from treatment (two studies)
We found no significant differences between 1% pimecrolimus applied twice daily compared against the same strength applied 4 times daily in overall withdrawals (RR 0.15, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.12; Analysis 11.4), withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.62; Analysis 11.4) and withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 3.12, 95% CI 0.13 to 73.04; Analysis 11.4) based on the results of 1 trial involving 49 participants (Ling 2005).
11.4. Analysis.
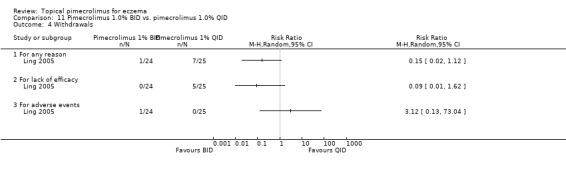
Comparison 11 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID, Outcome 4 Withdrawals.
One trial (CASM981C2314 2006) involving 268 participants who responded to a pre‐trial pimecrolimus treatment compared 1% pimecrolimus twice daily against the same strength applied once daily found that the twice daily schedule was associated with significantly fewer overall withdrawals (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.67; Analysis 12.3) and withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.88; Analysis 12.3) than once daily schedule; but we found no significant difference in withdrawals due to adverse events (RR 0.67, 95% CI 0.19 to 2.31; Analysis 12.3).
12.3. Analysis.
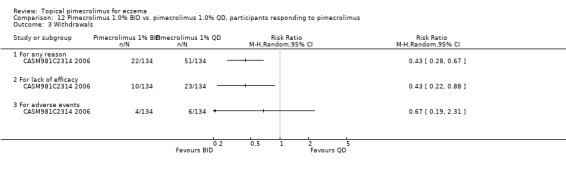
Comparison 12 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD, participants responding to pimecrolimus, Outcome 3 Withdrawals.
(ii) Adverse events (two studies)
Ling 2005 found no significant differences between the direct comparisons of 1% pimecrolimus twice daily against the same strength applied once or 4 times daily in 49 participants experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.35 to 5.57; Analysis 11.5) and skin burning (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.23 to 4.66; Analysis 11.5).
11.5. Analysis.
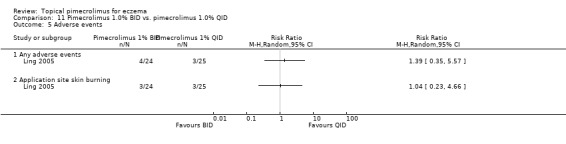
Comparison 11 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID, Outcome 5 Adverse events.
One trial (CASM981C2314 2006) found no significant differences between the direct comparisons of 1% pimecrolimus twice daily against the same strength applied once daily for 268 participants who responded to pimecrolimus treatment in experiencing any adverse events (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.19; Analysis 12.4) or skin infections (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.18 to 21.79; Analysis 12.4).
12.4. Analysis.
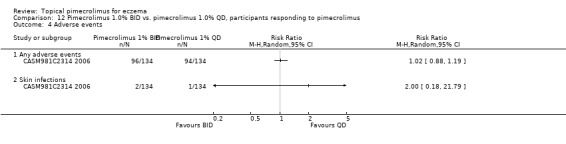
Comparison 12 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD, participants responding to pimecrolimus, Outcome 4 Adverse events.
(e) Potential serious adverse events
In our review, we found no cancer‐related events reported in RCTs and a lack of long‐term observational studies to examine the risk of skin cancers and lymphoma. Therefore, the risk of cancer‐related events associated with pimecrolimus remains uncertain. We only found a nested case‐control study that used an automated database to evaluate the association between topical immunosuppressants and lymphoma in a cohort of participants with eczema. This study identified 294 cases of lymphoma in 293253 participants, but did not find an increased risk of lymphoma in participants treated with topical corticosteroids and topical calcineurin inhibitors. The odds ratios were (1.2, 95% CI 0.8 to 1.8) for "super potent" topical steroids, (1.1, 95% CI 0.7 to 1.6) for "low potency" topical steroids, (0.8, 95% CI 0.4 to 1.6) for pimecrolimus and (0.8, 95% CI 0.4 to 1.7) for tacrolimus (Arellano 2006).
Discussion
Summary of main results
Principal findings
Evidence from short‐term (no more than six weeks) vehicle‐controlled trials has shown that topical pimecrolimus is effective in controlling the signs and symptoms of eczema or facial eczema with acceptable tolerability and safety profiles. Evidence from long‐term (more than six months) flare‐preventing trials showed that pimecrolimus is effective in controlling the signs and symptoms of eczema. The long‐term quality of life measures gathered from adults, carers of infants and children also suggests that pimecrolimus also improves quality of life more than vehicle alone. It is not surprising that an active treatment shows better efficacy outcomes than vehicle only in eczema. The vehicle controlled studies have been helpful in establishing that short‐term efficacy and capability of preventing flares does exist and that the tolerability and short‐term adverse effect profile of topical pimecrolimus is acceptable. More vehicle controlled studies are not needed (Freeman 2006) and may even be considered unethical, especially if children with severe eczema are included (Williams 2003).
Current evidence for the head‐to‐head comparisons of topical immunosuppressants (i.e. pimecrolimus vs. tacrolimus) are limited, yet we found some evidence in four trials that 1% pimecrolimus is as effective as 0.03% tacrolimus and less effective than 0.1% tacrolimus in treating eczema. Pimecrolimus presented similar tolerability and safety profiles to both 0.03% and 0.1% tacrolimus, but more participants withdrew from pimecrolimus treatment due to the lack of efficacy.
Strengths and limitations of the review
We comprehensively searched for randomised controlled trials from a wide range of databases in order to avoid the risk of publication bias, used clinically relevant outcome measures, and included direct comparisons with other active treatments, rather than making indirect inferences from placebo controlled trials. However, there are several limitations of this review:
(1) Participants
One limitation of our systematic review is that we failed to analyse the outcome data according to participants' age groups and the severity of eczema due to the enormous discrepancies of definitions for these subgroups within the included trials. Therefore, some caution is needed for the interpretation of results as applied to particular age groups.
We acknowledge the high drop‐out (attrition) rates of included trials. Seventeen of the 31 trials have more than 20% dropouts. Although the attrition rate is related to treatment duration, 11 of the 17 trials with inadequate attrition rates are short‐term trials (no more than 6 weeks). Participants' severity of eczema and efficacy of treatment may also influence the attrition rates. Therefore, we explored the reasons for attrition in terms of withdrawals due to lack of efficacy or adverse events and found the majority of participants withdrew from the trials due to lack of efficacy.
(2) Comparisons
There are very limited data available for the active comparisons (pimecrolimus vs. topical corticosteroids) and head‐to‐head comparisons of pimecrolimus against topical tacrolimus.
As 1.0 % pimecrolimus is licensed for acute treatment of mild to moderate eczema (including flares), in practice, 1% hydrocortisone acetate (a mild topical corticosteroid) licensed for the same indication is the most relevant comparator to pimecrolimus. However, the comparison of pimecrolimus with existing therapy for such a group is currently not available. Perhaps this is not surprising as 1% hydrocortisone is much less expensive than topical pimecrolimus and topical pimecrolimus would need to be much more effective (or have much fewer adverse effects) than 1% hydrocortisone in order to become cost‐effective. Both scenarios seem unlikely given the performance of topical pimecrolimus against stronger topical corticosteroid preparations. Although we found pimecrolimus is more effective in preventing flares than vehicle, the comparative efficacy of pimecrolimus against the early use of mild topical corticosteroids is not known. In the absence of such key comparisons, the therapeutic role of pimecrolimus in treating mild to moderate eczema is unclear.
In addition, there is also a lack of crucial outcome data for other active and head‐to‐head comparisons. Although topical immunosuppressants (i.e. pimecrolimus and tacrolimus) were developed as an alternative to topical corticosteroids to overcome possible adverse effects of corticosteroids (such as thinning of the skin or adrenal gland suppression), we found no clear evidence that these newer, more expensive products offer better tolerability and safety profiles compared with existing standard practice. Crucially, we found no evidence to show that use of topical pimecrolimus was associated with less skin thinning than topical corticosteroids in long term studies, perhaps because such skin thinning is very rare when topical corticosteroids are used appropriately (Williams 2005). One preliminary randomised controlled trial of pimecrolimus applied to normal skin for four weeks found no thinning of the skin (Queille‐Roussel 2001), however, the results are difficult to generalise to people with eczema who apply preparations over the course of a year.
One obvious area of potential use for a new and more expensive product like topical pimecrolimus is in the treatment of eczema that has become "resistant" or that has failed to respond to topical corticosteroids. Only one small‐scale study has evaluated such a use, and failed to demonstrate any greater efficacy than vehicle. Another area where topical pimecrolimus might have an important niche is in the treatment of eczema at "sensitive" sites such as the face in people who might have become dependent on inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids at such sites, and therefore at high risk of skin thinning. Although four trials have shown efficacy of topical pimecrolimus when compared with vehicle for facial eczema, we are not aware of any studies that have shown any advantage in terms of less skin thinning when compared against topical corticosteroids for such sensitive site eczema. Nor are we aware of any studies that have shown that pimecrolimus might work when topical corticosteroids have stopped working on facial eczema or in people who have developed topical corticosteroid‐related skin thinning. So we have a lot of data on pimecrolimus where it is not needed, and very little to none on the clinical situations where it might be useful.
(3) Outcomes
There are various outcome measures reported relating to different timings from the included trials. No trial reported on QoL data comparing pimecrolimus against tacrolimus. We failed to analyse the global changes in composite rating scales (e.g. ADASI or eczema area and severity index [EASI]) presented in mean or median percentages of improvement from baseline. The use of investigators' global assessments of response to treatment also causes some concern. Despite the fact that these assessments of response to treatment are widely used as outcome measures in clinical trials of eczema further research is needed to fully determine their validity, reliability, and sensitivity to change (Charman (a) 2000; Charman 2003). Likewise, it is possible that blinding in placebo controlled trials may have been compromised due to relatively high proportions of participants receiving pimecrolimus experiencing skin burning.
One limitation of our systematic review is that our analyses of withdrawal rates and adverse events were based on data pooled from trials of different durations. We did not find any rare or severe adverse events reported in the included trials. However, in response to the warning from U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA 2006) and European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products (EMEA 2006) in 2006 on the potential risks of skin cancer and lymphoma associated with pimecrolimus and tacrolimus, further population‐based, long‐term epidemiological studies are needed to assess rare and severe adverse events of topical immunosuppressants. One study has already emerged which suggests that topical pimecrolimus is not associated with a higher risk of lymphoma, but further long term studies are needed (Arellano 2006).
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Our systematic review shows that pimecrolimus is effective when compared against vehicle with short bursts of topical corticosteroids for flare‐ups of eczema. However, there is limited evidence on the comparative efficacy, tolerability, and adverse events associated with pimecrolimus compared against existing optimal treatments, such as mild topical corticosteroids and tacrolimus. The clinical role of pimecrolimus is therefore uncertain owing to a lack of relevant comparative data. There is no evidence at present to suggest that pimecrolimus is effective in people who fail to respond to topical corticosteroids. Whilst topical pimecrolimus might have a useful role in treating eczema at sensitive sites such as the face where skin thinning may become a problem, no comparative studies have addressed this issue and demonstrated any advantage over existing therapy. Whilst short‐term studies on drug safety are reassuring, more long term studies evaluating the possible risks associated with skin immunosuppression are needed.
Implications for research.
More vehicle controlled studies are not needed and may even be considered as unethical. Pragmatic randomised controlled trials lasting at least 12 months are needed to compare topical pimecrolimus and 1% hydrocortisone acetate in children and adults with mild to moderate eczema. More trials are needed to see if topical pimecrolimus works in people who fail to respond adequately to topical corticosteroids. Trials are needed that evaluate topical pimecrolimus in sensitive sites such as the face. Outcome data should include clearing capacity, relapse, quality of life, adverse events (including skin thinning), and costs. Although several trials have been undertaken on participants who responded poorly to topical corticosteroids, current evidence is insufficient to support using pimecrolimus as a second line treatment of eczema despite recommendation by the UK National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE 2004) and the US Food and Drug Administration to use it in such circumstances (FDA 2005). Experience of long term use of topical pimecrolimus is limited and the risk of rare but more serious adverse effects remains a concern. Further long term surveillance of these agents is needed (Williams 2002).
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 22 June 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 4, 2005 Review first published: Issue 4, 2007
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20 August 2007 | New search has been performed | Minor update |
| 13 August 2007 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Substantive amendment |
Acknowledgements
The review team would like to thank the following people Sarah Garner (lead editor) and Jonathon Brown (consumer).
The editorial base would like to thank the following people who were external referees for this review: Adelaide Herbert and David Paige (content experts) and Shirley Manknell (consumer).
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategy for the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register
We searched the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register (to October 2006) using the search terms:
(((atopic OR childhood OR infantile) AND (dermatitis OR eczema)) OR neurodermatitis OR (besniers AND prurigo)) AND (pimecrolimus OR elidel or SDZASM981)
Appendix 2. Search strategy for the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library (Issue 3, 2006):
#1(atopic next dermatitis) or (atopic next eczema) or neurodermatitis in All Fields, from 1800 to 2005 in all products #2(infantile next eczema) or (childhood next eczema) or (besniers next prurigo) in All Fields in all products #3MeSH descriptor Dermatitis, Atopic explode all trees in MeSH products #4MeSH descriptor Neurodermatitis explode all trees in MeSH products #5(#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4) #6(pimecrolimus):ti,ab,kw or (ELIDEL):ti,ab,kw or (SDZ ASM 981):ti,ab,kw #7(#5 AND #6) #8SR‐SKIN #9(#7 AND NOT #8)
Appendix 3. Search strategy for MEDLINE (OVID)
We searched MEDLINE (OVID) from 2003 to October 2006 using the following search strategy:
1. RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL.pt. 2. CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL.pt. 3. RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS.sh. 4. RANDOM ALLOCATION.sh. 5. DOUBLE BLIND METHOD.sh. 6. SINGLE‐BLIND METHOD.sh. 7. or/1‐6 8. animal/ not human/ 9. 7 not 8 10. CLINICAL TRIAL.pt. 11. exp CLINICAL TRIALS/ 12. (clin$ adj25 trial$).ti,ab. 13. ((singl$ or doubl$ or trebl$ or tripl$) adj25 (blind$ or mask$)).ti,ab. 14. PLACEBOS.sh. 15. placebo$.ti,ab. 16. random$.ti,ab. 17. RESEARCH DESIGN.sh. 18. or/10‐17 19. 18 not 8 20. 19 not 9 21. COMPARATIVE STUDY.sh. 22. exp EVALUATION STUDIES/ 23. FOLLOW UP STUDIES.sh. 24. PROSPECTIVE STUDIES.sh. 25. (control$ or prospectiv$ or volunteer$).ti,ab. 26. or/21‐25 27. 26 not 8 28. 27 not (9 or 20) 29. 9 or 20 or 28 30. exp Dermatitis, Atopic/ 31. atopic dermatitis.mp. 32. atopic eczema.mp. 33. exp NEURODERMATITIS/ 34. neurodermatitis.mp. 35. infantile eczema.mp. 36. childhood eczema.mp. 37. Besniers' Prurigo.mp. 38. 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 39. pimecrolimus.mp. 40. ELIDEL.mp. 41. SDZ ASM 981.mp. 42. 39 or 40 or 41 43. 29 and 38 and 42 44. limit 43 to yr="2003 ‐ 2006"1. RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL.pt.
Appendix 4. Search strategy for EMBASE (OVID)
1. random$.mp. 2. factorial$.mp. 3. crossover$.mp. 4. placebo$.mp. or PLACEBO/ 5. (doubl$ adj blind$).mp. [mp=title, abstract, subject headings, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer name] 6. (singl$ adj blind$).mp. [mp=title, abstract, subject headings, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer name] 7. assign$.mp. 8. volunteer$.mp. or VOLUNTEER/ 9. Crossover Procedure/ 10. Double Blind Procedure/ 11. Randomized Controlled Trial/ 12. Single Blind Procedure/ 13. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 14. atopic dermatitis.mp. or exp Atopic Dermatitis/ 15. atopic eczema.mp. 16. eczema.mp. or exp ECZEMA/ 17. neurodermatitis.mp. or exp NEURODERMATITIS/ 18. child$ eczema.mp. 19. infant$ eczema.mp. 20. besniers prurigo.mp. 21. 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 22. pimecrolimus.mp. or exp PIMECROLIMUS/ 23. ELIDEL.mp. 24. SDZ ASM 981.mp. 25. 22 or 23 or 24 26. 13 and 21 and 25 27. limit 26 to yr="2005 ‐ 2006"
Appendix 5. Search strategy for adverse effects MEDLINE (OVID)
1. exp product surveillance, postmarketing/ or exp adverse drug reaction reporting systems/ or exp clinical trials, phase iv/ 2. adverse events.mp. 3. adverse effects.mp. 4. exp hypersensitivity/ or exp drug hypersensitivity/ or exp drug eruptions/ or exp hypersensitivity, delayed/ or exp hypersensitivity, immediate/ 5. exp hypersensitivity, immediate/ or exp anaphylaxis/ or exp conjunctivitis, allergic/ or exp dermatitis, atopic/ or exp food hypersensitivity/ or exp respiratory hypersensitivity/ or exp urticaria/ 6. side effect$.mp. 7. exp Poisoning/ 8. exp hepatitis, toxic/ or exp hepatitis, chronic, drug‐induced/ 9. exp Substance‐Related Disorders/ 10. exp Drug Toxicity/ 11. exp Abnormalities, Drug‐Induced/ 12. exp Teratogens/ 13. exp Mutagens/ 14. exp Carcinogens/ 15. metabolites.mp. 16. exp dermatitis, contact/ or exp dermatitis, allergic contact/ or exp dermatitis, irritant/ or exp dermatitis, phototoxic/ 17. photoallergic reactions.mp. 18. exp dermatitis, allergic contact/ or exp dermatitis, photoallergic/ 19. phototoxicity.mp. 20. sensitization.mp. 21. exp Burning Mouth Syndrome/ 22. stinging.mp. 23. burning.mp. 24. fetal abnormalities.mp. 25. exp Drug Monitoring/ 26. harm$ effects.mp. 27. (toxic effects or drug effects).mp. 28. Sleep Apnea, Obstructive/ 29. ARRHYTHMIA/ 30. undesirable effect$.mp. 31. (safe or safety).mp. [mp=title, original title, abstract, name of substance word, subject heading word] 32. toxicity.mp. 33. noxious.mp. 34. serious reaction$.mp. 35. complication$.mp. 36. treatment emergent.mp. 37. tolerability.mp. 38. (adverse adj3 (effect$ or reaction$ or event$ or outcome$)).mp. [mp=title, original title, abstract, name of substance word, subject heading word] 39. rebound.mp. 40. Hypercalcemia/ci [Chemically Induced] 41. Urinary Calculi/ci [Chemically Induced] 42. Tachyphylaxis/ci, de [Chemically Induced, Drug Effects] 43. Substance Withdrawal Syndrome/ci, de [Chemically Induced, Drug Effects] 44. ATROPHY/ci [Chemically Induced] 45. TELANGIECTASIS/ci [Chemically Induced] 46. skin thinning.mp. 47. Liver Diseases/ci [Chemically Induced] 48. Kidney Diseases/ci [Chemically Induced] 49. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation/ci [Chemically Induced] 50. Multiple Organ Failure/ci [Chemically Induced] 51. Stevens‐Johnson Syndrome/ci [Chemically Induced] 52. Epidermal Necrolysis, Toxic/ci [Chemically Induced] 53. Heart Block/ci [Chemically Induced] 54. COMA/ci [Chemically Induced] 55. PARALYSIS/ci [Chemically Induced] 56. exp Nausea/dt [Drug Therapy] 57. exp Vomiting/dt [Drug Therapy] 58. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 51 or 52 or 53 or 54 or 55 or 56 or 57 59. pimecrolimus.mp. 60. elidel.mp. 61. SDZ ASM 981.mp. 62. 59 or 60 or 61 63. 58 and 62 64. mortality.mp. or MORTALITY/ 65. 58 or 64 66. 62 and 65
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 1 week | 1 | 336 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [1.06, 3.76] |
| 1.2 2 weeks | 1 | 336 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.58 [1.00, 2.52] |
| 1.3 3 weeks | 5 | 783 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.72 [1.84, 4.03] |
| 1.4 4 weeks | 1 | 336 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.42 [1.00, 2.03] |
| 1.5 6 weeks | 3 | 589 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.03 [1.50, 2.74] |
| 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 3 weeks | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.88 [1.33, 2.67] |
| 2.2 6 weeks | 1 | 186 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.65 [1.74, 4.04] |
| 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 1 week | 3 | 472 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.89 [1.51, 2.35] |
| 3.2 3 weeks | 5 | 783 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.02 [1.69, 2.42] |
| 3.3 6 weeks | 3 | 589 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.82 [1.48, 2.25] |
| 4 Withdrawals | 10 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 For any reason | 9 | 1753 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.27, 0.58] |
| 4.2 For lack of efficacy | 8 | 1657 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.11, 0.41] |
| 4.3 For adverse events | 5 | 1025 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.19, 0.97] |
| 5 Adverse events | 7 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5.1 Any adverse events | 4 | 827 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.82, 1.02] |
| 5.2 Bacterial skin infections | 1 | 186 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.01, 1.12] |
| 5.3 Application site skin burning | 5 | 914 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.90, 2.18] |
Comparison 2. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants with facial AD.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear of facial eczema (facial IGA 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 1 week | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 1 week | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 3. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants responded to topical steroids.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 4. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, participants did not respond to topical steroids.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 Skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.3 Viral skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.4 Application site skin burning | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 5. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 1 week | 2 | 526 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.45 [1.66, 7.14] |
| 1.2 3 weeks | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.43 [0.98, 2.10] |
| 1.3 6 months | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [0.98, 2.19] |
| 1.4 12 months | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.83, 1.60] |
| 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 6 weeks | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.40 [1.06, 1.85] |
| 2.2 6 months | 2 | 443 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.62 [1.29, 2.04] |
| 2.3 9 months | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.33 [1.01, 1.74] |
| 2.4 12 months | 1 | 251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.90, 1.47] |
| 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 9 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.4 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 No flare of eczema | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 6 months | 9 | 3091 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.47 [1.32, 1.64] |
| 4.2 12 months | 2 | 962 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.69 [1.45, 1.96] |
| 5 No use of rescue medication | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5.1 6 months | 1 | 192 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.24 [1.46, 3.44] |
| 5.2 12 months | 2 | 962 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.76 [1.50, 2.08] |
| 6 Withdrawals | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 6.1 For any reason | 9 | 3091 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.54, 0.76] |
| 6.2 For lack of efficacy | 9 | 3091 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.34, 0.51] |
| 6.3 For adverse events | 8 | 2380 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.60 [0.28, 1.27] |
| 7 Adverse events | 8 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 7.1 Any adverse events | 4 | 1398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.07 [1.00, 1.16] |
| 7.2 Skin infections | 3 | 718 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.75, 1.72] |
| 7.3 Viral skin infections | 3 | 718 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.79 [0.89, 3.61] |
| 7.4 Bacterial skin infections | 4 | 982 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.51, 1.39] |
| 7.5 Application site skin burning | 3 | 999 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.36 [1.75, 10.85] |
5.4. Analysis.
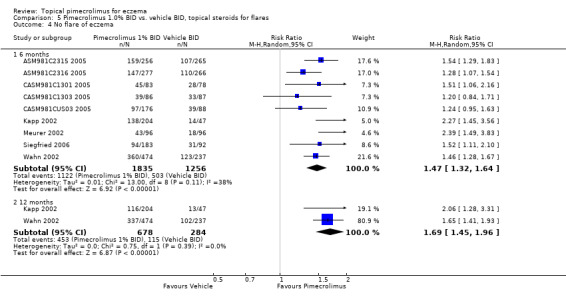
Comparison 5 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, Outcome 4 No flare of eczema.
Comparison 6. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. vehicle BID, topical steroids for flares, participants responded to steroids.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 7. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 1 week | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.4 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 Skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.3 Viral skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.4 Bacterial skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.5 Application site skin burning | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 8. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Moderately clear or better eczema (PGA more than 50% improvement) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 1 week | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 Application site skin burning | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
8.4. Analysis.
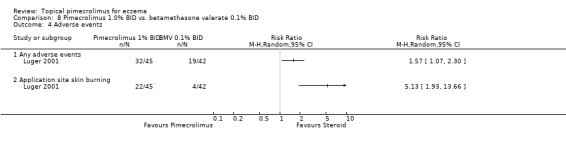
Comparison 8 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID, Outcome 4 Adverse events.
Comparison 9. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 1 week | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.63, 1.31] |
| 1.2 3 weeks | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.58, 1.15] |
| 1.3 6 weeks | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.69, 1.02] |
| 2 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 1 week | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 6 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Withdrawals | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 For any reason | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.94 [0.54, 6.98] |
| 3.2 For lack of efficacy | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.45 [1.23, 9.71] |
| 3.3 For adverse events | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 8.19 [1.50, 44.73] |
| 4 Adverse events | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 Any adverse events | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.90, 1.17] |
| 4.2 Skin infections | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.65 [0.12, 22.75] |
| 4.3 Bacterial skin infections | 1 | 141 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 6.90 [0.36, 131.23] |
| 4.4 Viral skin infections | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.15, 6.96] |
| 4.5 Application site skin burning | 2 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.55, 2.49] |
Comparison 10. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 1 week | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.53, 1.34] |
| 1.2 3 weeks | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.41, 0.77] |
| 1.3 6 weeks | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.46, 0.74] |
| 2 Withdrawals | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 For any reason | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.18 [0.91, 1.52] |
| 2.2 For lack of efficacy | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.37 [1.10, 5.08] |
| 2.3 For adverse events | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.43, 2.41] |
| 3 Adverse events | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Any adverse events | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.47, 2.26] |
| 3.2 Skin infections | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.60 [0.37, 6.99] |
| 3.3 Viral skin infections | 1 | 413 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 3.4 Application site skin burning | 2 | 639 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.36, 1.62] |
Comparison 11. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Mild or absent pruritus (pruritus score 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 3 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 Application site skin burning | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
11.2. Analysis.
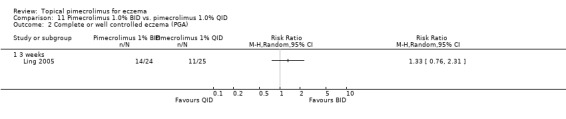
Comparison 11 Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID, Outcome 2 Complete or well controlled eczema (PGA).
Comparison 12. Pimecrolimus 1.0% BID vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD, participants responding to pimecrolimus.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clear or almost clear eczema (IGA 0 or 1) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 8 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 16 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 No flare of eczema | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 16 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Withdrawals | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 For any reason | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 For lack of efficacy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 For adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Any adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 Skin infections | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
ASM981C2315 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre randomised controlled trial (flare prevention study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 521), mild to moderate eczema, age: 2 to 17 years, requiring treatment with topical corticosteroids, pimecrolimus or tacrolimus at least twice in the six months proceeding randomisation, IGA=1. Exclusion criteria: medical history or concomitant illness and treatment could interfere with study, history of malignancy, inadequate response to tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, immunocompromised, current skin status that could interfere with study evaluation, and active infections. Wash out period: corticosteroids, immunosupressants, phototherapy: one month; topical tacrolimus or pimecrolimus: four weeks; systemic antibiotics: two weeks; topical therapy: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n=256) vs. vehicle BID (n=265) for 26 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with medium potency topical corticosteroids. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving no flare; mean number of flares; mean duration of not using TS (days). 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
ASM981C2316 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare prevention study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 543), mild to moderate eczema, age: >=18 years, IGA 2 to 3, requiring topical corticosteroid. Exclusion criteria: history of malignancy, inadequate response to tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, immunocompromised, concurrent skin disease, active viral, bacterial or fungal infections, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: pimecrolimus or tacrolimus: six months; systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, cytostatics or phototherapy: one month; topical tacrolimus: four weeks, systemic antibiotics: two weeks; topical therapy: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n=277) vs. vehicle BID (n=266) for 26 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with medium potency topical corticosteroids. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving no flare; mean number of flares; mean duration (days) of not using TS. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
ASM981C2402 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children and adults (N = 73), mild to moderate eczema, age: 2 to 50 years, BSA >=5%, poor response to treatment with prednicarbate emollient cream. Exclusion criteria: concurrent skin diseases, systemic malignancy, active lymph proliferation, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: phototherapy, systemic or topical therapy: four weeks, systemic retinoid or investigational drugs: eight weeks, systemic or topical antibiotics: two weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n=47) vs. vehicle BID (n=26) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA), achieving complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus; mean reduction in EASI from baseline; number of participants' eczema improved by at least one IGA score 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, viral skin infections, application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. This study involved participants who had poor response to topical corticosteroid treatment. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
ASM981CDE10 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare prevention study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N =185), severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Rajka & Langeland), age: 2 to 17 years, eczema score 8 or 9, responded to 21 days of treatment with prednicarbate cream 0.25%. Exclusion criteria: phototherapy, systemic or topical therapy or systemic corticosteroid prior to study entry which could have an effect on eczema. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0 % BID (n=95) vs. vehicle BID (n=89) for 24 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with topical prednicarbate cream 0.25% BID. | |
| Outcomes | Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. This study involved participants who responded to topical corticosteroid treatment. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Barba 2003.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants and children (N = 106), mild to moderate eczema, age: 3 months to 18 years, IGA score 2 to 3. Exclusion criteria: not stated. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n=71) vs. vehicle BID (n = 35) for three weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA), achieving complete or well controlled eczema (PGA), and achieving mild or absent pruritus; median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs; number of participants experiencing application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Abstract only, we did not include data for the 24‐week, open‐label, noncomparative trial period. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C1301 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 240), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Williams et al.), age: 2 to 16 years, TBSA >= 5%, IGA >= 2. Exclusion criteria: history of malignant disease, active skin infections, other systemic infections, other skin conditions. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy: four weeks, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal therapy: two weeks, topical therapy or systemic antiallergic drugs: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 83) vs. vehicle BID (n =7 8) for 26 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with hydrocortisone butyrate on body/limbs, clobetasone butyrate on face/neck, prednisolone valerate acetate lotion on scalp. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving no flare. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C1303 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 173), mild to moderate eczema, age: 16 to 65 years, TBSA <= 5%, IGA >= 2. Exclusion criteria: history of malignant, active skin infection, systemic infections, other skin conditions. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy: four weeks, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal therapy: two weeks, topical therapy or systemic antiallergic therapy: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 86) vs. vehicle BID (n = 87) for 26 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with topical corticosteroids and/or tacrolimus hydrate ointment BID. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving no flare; median duration (days) to first flare of eczema. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C2314 2006.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 268), mild to severe eczema, age: 2 to 17 years, TBSA >= 5%, being pre‐treated pimecrolimus 1% BID to remission during 6‐week run‐in period. Exclusion criteria: pregnant or breast‐feeding women, immunocompromised, open skin infection, head lice or scabies, relapse during the run‐in period, active skin infection. Wash out period: topical therapy: two weeks; phototherapy: four weeks; systemic immunosuppressant or steroids: four weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 134) vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QD (n = 13) for 16 weeks. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving no flare and achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA); median duration (days) to first eczema flare, EASI. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy,; WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs skin infections. | |
| Notes | This study involved participants whose AD was treated by pimecrolimus 1.0% BID to remission. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C2322 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 336), mild to moderate eczema, age: 2 to 17 years, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: females of childbearing potential using inadequate contraception or who were pregnant or breastfeeding, HIV, immunocompromised, skin conditions that interfere with study evaluation, investigational therapy, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: topical therapy: seven days; systemic corticosteroid or leukotriene antagonist: one month; phototherapy or immunosuppressants or cell growth inhibitors: one month. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 168) vs. vehicle BID (n = 168) for 4 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA). 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C2436 2006.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 67), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka, prick‐test and/or elevated IgE background), age >= 20 years, >= 3 year history of AD, whole body IGA of 2 or 3, localized EASI of 1 to 8, affecting bilateral arms and/or legs >= 10 cm, after topical corticosteroids treatment for 2 weeks, localized EASI <=1. Exclusion criteria: immunocompromised, concurrent skin diseases, active skin infections, history of rheumatic fever, prosthetic constituents, poor response to study drugs, hypersensitivity, serious reactions to anaesthetics, topical therapy. Wash out period: phototherapy, systemic corticosteroids or other systemic therapy known or suspected to have an effect on AD: four weeks, antihistamines: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 34) vs. vehicle BID (n = 33) for 3 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. This study involved participants who responded to topical corticosteroid treatment. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981C2442 2006.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children and adults (N = 200), mild to moderate facial eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka), age: >= 12 years, facial IGA 2 to 3 based on assessment on the face only and excluding the ears and the neck. Exclusion criteria: <= 30% BSA, pregnant or breast‐feeding women, concurrent skin disease, immunocompromised, poor response, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy: four weeks, investigational drugs: eight weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 101) vs. vehicle BID (n = 99) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear facial eczema (IGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, incident rate of ADEs of different organ systems (events/days). | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website. We did not include data for the 6‐week, open‐label period. The numbers of participants experiencing ADEs are not available. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CASM981CUS03 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 264), mild to severe eczema, age: 18 to 65 years, IGA >= 2, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: not stated. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 176) vs. vehicle BID (n = 88) for 24 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with topical corticosteroids (not specified). | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving no flares; mean number of flares; mean duration (days) of participants using TS. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, bacterial skin infections and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Eichenfield (a) 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 198), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Williams et al.), age: 1 to 17 years, diagnostic criteria of Williams, TBSA >5%, IGA score 2 or 3, receiving emollient for at least 7 days before baseline. Exclusion criteria: significant concurrent disease, pregnancy or breast nursing. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy within one month from baseline, topical therapy with seven days, systematic antibiotics within two weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 130) vs. vehicle BID (n = 68) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | This is a report of two trials combined ‐ separate data were extractable with the use of the data gathered from the FDA website regulatory submissions http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/nda/2001/21‐302_Elidel.htm (accessed 24/03/04) We could not separate the ADEs of the two studies because only the combined analysis of ADEs is available from both published results and FDA website. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Eichenfield (b) 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 205), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Williams et al.), age: 1 to 17 years,diagnostic criteria of Williams, TBSA > 5%, IGA score 2 or 3, receiving emollient for at least 7 days before baseline. Exclusion criteria: significant concurrent disease, pregnancy or breast nursing Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy within one month from baseline, topical therapy with seven days, systematic antibiotics within two weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 137) vs. vehicle BID (n = 68) or 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs. | |
| Notes | This is a report of two trials combined ‐ separate data were extractable with the use of the data gathered from the FDA website regulatory submissions http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/nda/2001/21‐302_Elidel.htm (accessed 24/03/04) We could not separate the ADEs of the two studies because only the combined analysis of ADEs is available from both published results and FDA website. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Ho 2003.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants (N = 186), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Seymour et al.), age: 3 to 23 months, TBSA >= 5%, IGA 2 or 3. Exclusion criteria: immunocompromised, concurrent or active skin diseases or viral skin infections, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic treatments: one month, topical therapy: one week, sedative antihistamines to treat pruritus: one week. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 123) vs. vehicle BID (n = 63) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA), achieving complete or well controlled of eczema (PGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus; median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, bacterial skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Used additional data from the FDA report to supplement data extracted from the paper. We did not included data for the 20‐week, open‐label, noncomparative trial period. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Kapp 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants (N = 251), mild to very severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Seymour et al.), age: 3 to 23 months, IGA >= 2, BSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: immunocompromised, malignant history, active skin infection, treated with medicines affecting eczema, skin condition could affect the evaluation of study drug. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic therapy: one month; topical therapy: seven days; systemic antibiotics: two weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 204) vs vehicle BID (n = 47) for 52 weeks. Short‐term acute flares (IGA >= 4) were treated with moderately potent topical corticosteroids (0.02% difluprednate, 0.1% hydrocortisone butyrate, 0.05% clobetasone butyrate, 0.02% triamcilonone acetonide, 0.2% hydrocortisone valerate). | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA); median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline; mean percentage (%) of reduction in BSA; ; mean decrease in DLQI score; mean PIQoL‐AD score. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Kaufmann 2006.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 198), mild to moderate eczema, age: 18 to 81 years, IGA 2 or 3, BSA >= 5%, moderate to severe pruritus (pruritus score 2 or 3). Exclusion criteria: skin diseases, allergy, infections, poor response to topical tacrolimus, immunocompromised, malignant history, breast‐feeding, pregnant, not use medically approved contraception. Wash out period: topical medication for pruritus relief or antibiotic therapy < seven days, anti‐pruritus or sedatives medications < two weeks, systemic or phototherapy for eczema < one month. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0%BID (n = 100) vs. emollients BID (n = 98) for 1 week | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving mild or absent pruritus, number of participants improved by at least one pruritus score 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any skin infections and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | The total duration was six weeks, but we did not include data for the five‐week open‐label trial. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Kempers 2004.
| Methods | Parallel group, investigator blind, active control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 141), moderate eczema, age: 2 to 17 years. Exclusion criteria: not stated. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 71) vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID (n = 70) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, bacterial skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | We did not include data for the 20‐week open‐label uncontrolled extension period. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Leo 2004.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, single centre, placebo control, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 19), mild to moderate eczema, age: 7 to 17 years. Exclusion criteria: patients treated with any topical medicaiton in the previous four weeks. Wash out period: one week. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 9) vs. vehicle BID (n = 10) for 2 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: mean EASI score (95% CI); CDLQI score | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Ling 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children or adults (N = 49), moderate to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Raijka), age >= 11 years, >= 30% TBSA, IGA >= 2, pruritus score >= 2. Exclusion criteria: immunocompromised, concurrent skin diseased could interfere with evaluation. Wash out period: phototherapy or systemic corticosteroid therapy: one month, systemic antibiotics: two week, topical therapy: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 24) vs. pimecrolimus 1.0% QID (n = 25) for 3 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA), achieving complete or well controlled eczema (PGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus; number of participants have improved at least one IGA score; mean percentage (%) of reduction in total BSA. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | Data from poster presented at EADV 2002 conference (http://www.prous.com/webcaster/ elidel/contents/articles/Ling_ASm55b_poster.pdf and http://www.prous.com/webcaster/elidel/contents/articles/Ling_ASm55a_poster.pdf accessed 24/03/04) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Luger 2001.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, active control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 260), moderate to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka, Rajka and Lengelend), age >= 18 years, TBSA 5 to 30%. Exclusion criteria: concomitant medical condition that would interfere with treatment evaluation, pregnancy, lactation, women not using medically approved contraception if child‐bearing potential. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 45) vs. vehicle BID (n = 43) vs. betamethasone valerate 0.1% BID (n = 42) vs. pimecrolimus 0.05% (n = 42), 0.2% (n = 46), 0.6% (n = 42) BID for 3 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving moderately clear or better controlled eczema (PGA >= 50% improvement) and achieving mild or absent pruritus; median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, number of participants experiencing any ADEs and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | We did not include data from 130 participants treated on non‐licensed doses of pimecrolimus. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Luger 2004.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, active control, international multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 658), moderate to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Rajka and Langeland), age >= 18 years, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: Malignancy, acute or chronic bacterial viral or fungal diseases, child‐bearing women not using approved contraception, pregnant or breast feeding, hypersensitivity, drug or alcohol abuse. Wash out period: phototherapy or systematic therapy: 1 month, topical therapy (excluding tar shampoo for scalp treatment): 24 hours. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 328) vs. triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% BID (n = 330) for 52 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA) and achieving mild or absent pruritus, not using topical TS; have improved by at least one IGA score; median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI; mean EASI score (95% CI). 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; number of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, bacterial skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Meurer 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 192), moderate to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Rajka et al.), IGA score 3 or 4, TBSA >5%. Exclusion criteria: pregnancy, lactation, women of gestational age not using reliable contraception, patient requiring potent topical corticosteroids, severe concurrent allergic disease associated to malignancies or immunocompromised states. Wash out period: phototherapy or systematic corticosteroid: three months, topical therapies or systematic antibiotics: two weeks, systematic steroids for non‐AD indications: one month. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 96) vs. vehicle BID (n = 96) for 24 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving complete or well controlled eczema (PGA), achieving no flare, not using TS; mean number of flares; mean duration (days) of participants not using TS; mean number of flares; median percentage (%) reduction in EASI; EASI score (95% CI); mean percentage of (%) reduction in total BSA; number of participants improved by at least one IGA score; mean decrease in QoLIAD score; mean decrease in DLQI score 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, bacterial skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | This study allowed the concomitant use of cetirizine. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Paller (a) 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, investigator blind, active control, multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 426), mild eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka), age: 2 to 15 years, IGA = 2, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: use of nonsteroidal immunosuppressants, light therapy, systemic and topical corticosteroids, topical H1 & H2 antihistamines, topical antimicrobials. Wash out period: four weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 217) vs. tacrolimus 0.03% BID (n = 209) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA); median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline; mean percentage (%) of reduction in BSA. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, bacterial skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | This paper reports separate data for three trials. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Paller (b) 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, investigator blind, active control, multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 226), moderate to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka), age: 2 to 15 years, IGA 3 to 4, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: use nonsteroidal immunosuppressants, light therapy, systemic and topical corticosteroids, topical H1 & H2 antihistamines, topical antimicrobials. Wash out period: four weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 114) vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID (n = 112) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA); median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline; mean percentage (%) of reduction in BSA. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, viral skin infections, and application site skin burning. | |
| Notes | This paper reports separate data for three trials. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Paller (c) 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, investigator blind, active control, multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: adults (N = 413), mild to very severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Hanifin and Rajka), age >= 16 years, IGA 2 to 5, TBSA >= 5%. Exclusion criteria: use nonsteroidal immunosuppressants, light therapy, systemic and topical corticosteroids, topical H1 & H2 antihistamines, topical antimicrobials. Wash out period: four weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 203) vs. tacrolimus 0.1% BID (n = 210) for 6 weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA); median percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline; mean percentage (%) of reduction in BSA 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs; WDs due to lack of efficacy; WDs due to ADEs; numbers of participants have: any adverse event, skin infection, bacterial skin infection, viral skin infection, and skin burning | |
| Notes | This paper reports separate data for three trials. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Siegfried 2006.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants and children (N = 275), mild to severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Sampson, Williams et al.), age: 3 months to 11 years. Exclusion criteria: female patients of childbearing potential if pregnant, breastfeeding or not using approval contraception up to four weeks after treatment, immunocompromised, active infection or concurrent skin condition. Wash out period: systemic therapy: one month; topical therapy: seven days. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 189) vs. vehicle BID (n = 92) for 24 weeks. Short‐term acute flares were treated with topical corticosteroids (fluticasone propionate 0.05% cream for all participants, mometasone furate 0.1% cream for participants older than two years of age). | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA), achieving complete or well controlled eczema (PGA), and achieving no flare; mean number of flares; mean duration (days) of using TS 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy, WDs due to ADEs, numbers of participants experiencing any ADEs, skin infections, bacterial skin infections, and viral skin infections. | |
| Notes | Report from Novartis clinical trial results website | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Staab 2005.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants (N = 190), mild to very severe eczema (diagnosis criteria: Seymour et al.), age: 3 to 23 months. Exclusion criteria: immunocompromised, concomitant diseases, hypersensitivity. Wash out period: systemic corticosteroids and phototherapy: one month, antibiotics: two weeks; topical steroids or therapies: one week. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 130) vs. vehicle BID (n = 60) for 4 weeks. | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: number of participants achieving clear or almost clear eczema (IGA) 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs; WDs due to lack of efficacy; number of participants have any adverse event; mean percentage (%) of reduction in EASI from baseline; mean score PIQoL‐AD | |
| Notes | Only quality of life results were presented in the publication. We did not include data for the 12‐week open label noncomparative trial period. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Thaci 2003.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants (N = 195), mild to very severe eczema, IGA >= 2, TBSA >= 5% Exclusion criteria: not stated. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 129) vs. vehicle BID (n = 66) for 4 weeks | |
| Outcomes | Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy | |
| Notes | Abstract only | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Wahn 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, international multi‐centre, randomised controlled trial (flare‐preventing study) | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 711), mild eczema (diagnosis criteria: Williams et al.), age: 2 to 17 years, TBSA >= 5%, IGA >= 2. Exclusion criteria: infections that required prohibited medication or that could affect evaluation of skin. Wash out period: phototherapy or systematic therapy: one month, topical therapy: seven days, systematic antibiotics: two weeks. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n = 474) vs. emollients BID (n = 237) for 52 weeks and followed up to 53 weeks. Short‐term flares were treated with moderately potent topical steroids (0.02% difluprednate, 0.25% prednicarbate, 0.1% hydrocortisone butyrate, 0.05% clobetasone butyrate, 0.02% triamcinolone acetonide, 0.1% hydrocortisone valerate). | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: numbers of participants achieving no flare and not using TS; percentage (%) of mean duration for TS use; number of participants using antihistamine; mean decrease in DLQI score; mean PIQoL‐AD score. 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs, WDs due to lack of efficacy. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Whalley 2002.
| Methods | Parallel group, double blind, placebo control, multi‐centre, randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children (N = 241), mild to moderate eczema (diagnosis criteria: Williams et al.), IGA score 2 or 3, TBSA > 5%, age 2 to 17 years, total 430 patients, only patients over than 8 years were included, QoL score available for 241 of 278 participants. Exclusion criteria: not stated. Wash out period: not stated. | |
| Interventions | pimecrolimus 1.0% BID (n=158) vs. vehicle BID (n=83) for six weeks | |
| Outcomes | 1. Efficacy: mean PIQoL‐AD score 2. Safety and tolerability: total WDs | |
| Notes | We did not include data for the six‐month, open‐label trial period. This study assessed parents of those aged two to eight years to obtain the QoL data. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
AD: atopic dermatitis; IGA: investigators' global assessment; PGA: participants' global assessment; WDs: withdrawals; BID: twice daily; QID: four times daily; QD: once a day; EASI: eczema area and severity index. Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores is a method to characterize the extent of eczema. It is generally an indicator for the severity of eczema, such as IGA score, and may also be used to follow up the treatment effect. An EASI score of 15 to 20 indicates approximately a 10% to 15% body involvement of eczema (atopic dermatitis). Mild AD is defined by areas of scaling, papulation, erythema, and lichenification of 5 to 10 cm involving less than 15% total body surface area. Typical areas of involvement would include the wrists, antecubital fossa, knees, popliteal fossa, and ankles.; TS: topical corticosteroids; TBSA: total body surface area; ADSI: Atopic Dermatitis Severity Index, uses a 4‐point (0‐3) scale for erythema, pruritus, exudation, excoriation, and lichenification, and calculates the sum of these 5 ratings (range, 0 to 15); RCT: randomised controlled trial; ADEs: adverse drug events; flare‐free days: the numbers of days on study without topical corticosteroid use; achieving clear or almost clear AD: IGA score 0‐1; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; DLQI: Dermatology Life Quality Index; QoLI‐AD: Quality of Life Index‐ Atopic Dermatitis; CDLQI: Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index; PIQoL‐AD: Parent's Index of Quality of Life‐ Atopic Dermatitis; PQoL‐AD: Parents' Quality of Life Index‐ Atopic Dermatitis
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Ball 2002 | Interventions: Compared pimecrolimus 1% QD vs. vehicle QD |
| Belsito 2004 | Participants: patients with chronic hand dermatitis |
| CASM9819315E1 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C1302 2006 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C1304 2006 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C2405 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C2405‐ext.200 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C2420 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981C2421 2005 | Participants: patients with vitiligo |
| CASM981C2434 2005 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcomes |
| CASM981C2434E1 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981CEG01 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981CES01 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981CJP01 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981CPI01 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981CUS05 2005 | Participants: patients with intertriginous psoriasis |
| CASM981CUS08 2005 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcomes |
| CASM981CZA01 2006 | Methods: non‐randomised trial |
| CASM981DE06 2005 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcome measures (atopy patch test) |
| CASM981M2301 2006 | Participants: patients with chronic hand dermatitis |
| McKenna 2006 | Methods: combined analysis of QoL data based on Kapp A 2002 and Wahn U 2002 |
| Meads 2005 | Methods: combined analysis of QoL data based on 4 trial (trials remain unspecified) |
| Meurer 2004 | Methods and participants: a re‐analysis on patients with moderate AD (IGA=3) from Meurer 2002 |
| Papp 2004 | Methods: combined analysis based on data from Kapp A 2002 (infant) and Wahn U 2002 (children) |
| Papp 2005 | Methods: non‐randomised trial (extended from Kapp A 2002) |
| Queille‐Roussel 2001 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcome measures |
| Rappersberger 2002 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcome measures |
| Van Leent 1998 | Outcomes: non‐relevant outcomes |
| Weissenbacher 2006 | Participants: to investigate the effect of pre‐treatment with 1% pimecrolimus cream on the atopy patch test and skin prick test |
| Wolff 2005 | Interventions: oral pimecrolimus used |
Contributions of authors
DMA, RG and LC undertook the literature searches, identified the studies, and conducted the data extraction and quality assessment. DMA and LC also undertook the statistical analyses. DMA and LC prepared the first draft of the review. RG, KS and HCW commented and edited subsequent drafts.
Sources of support
Internal sources
School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Manchester, UK.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
None known.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
ASM981C2315 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2315). A 26‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the incidence of atopic dermatitis flares when pimecrolimus cream 1% is used at the first signs and/or symptoms of atopic dermatitis and its safety and tolerability in children and adolescents 2‐17 years of age. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981C2316 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2316). A 26‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the incidence of atopic dermatitis flares when pimecrolimus cream 1% is used at the first signs and/or symptoms of atopic dermatitis and its safety and tolerability in adults 18 years of age and older. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981C2402 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol ASM981C2402). An exploratory, randomized, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled, multicenter, parallel dose study investigating the use of pimecrolimus cream 1% in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis patients who demonstrate a clinical insensitivity to topical glucocorticoids. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
ASM981CDE10 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol ASM981CDE10). A 24‐week, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study on pimecrolimus cream 1% assessing the steroid‐sparing effect in the long term management of pediatric patients with severe atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
Barba 2003 {published data only}
- Barba JF, Beirana A, Cohen V, Dominguez L, Duran C, Leon G, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1% is effective, well tolerated and safe in infants and children with atopic eczema of the face. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2003; Vol. 17, issue Suppl 3:P2.35.
CASM981C1301 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis CASM981C1301 Norvatis (protocol CASM981C1301) Norvatis CASM981C1301. Confirmatory study in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis‐ multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, vehicle‐controlled study with a 26‐weeks treatment phase to determine the efficacy, safety of pimecrolimus cream for long‐term treatment of pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C1303 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1303). Confirmatory study in adult patients with atopic dermatitis‐ multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, vehicle‐controlled study with a 26‐week treatment phase to determine the efficacy, safety of pimecrolimus cream for long‐term treatment of adult patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2314 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2314). A 22‐week randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind study to compare a pimecrolimus cream 1% twice daily (BID) maintenance dosing regimen to a once daily (OD) maintenance dosing regimen in the management of atopic dermatitis in pediatric subjects. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 31th October 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2322 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2322). A 4‐week, randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled, parallel‐group clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in the short‐term treatment of patients with mild to moderate Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema). www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2436 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2436). A multicenter, 5‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, parallel group study exploring the effects of pimecrolimus cream 1% (twice daily application) vs. placebo control (twice daily application) on the molecular and cellular profile of adult male patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2442 2006 {published data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2442). A 12 week multicenter study consisting of a 6 week double blind, randomized, vehicle controlled, parallel group phase, followed by a 6 week open label phase, to assess the safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in mild to moderate head and neck atopic dermatitis of patients intolerant of topical corticosteroid. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 31th October 2006) 2006.
CASM981CUS03 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS03). A 6‐month, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus 1% cream twice daily vs. standard of care in the management of mild to severe atopic dermatitis in adults. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
Eichenfield (a) 2002 {published and unpublished data}
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, Langley RG, Cherill R, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/index.htm) 2002 (accessed 1st November 2003);46(4):495‐504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eichenfield (b) 2002 {published and unpublished data}
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, Langley RG, Cherill R, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/index.htm) 2002 (accessed 1st November 2003);46(4):495‐504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ho 2003 {published data only}
- Ho VC, Gupta A, Kaufmann R, Todd G, Vanaclocha F, Takaoka R, Folster‐Holst R, Potter P, Marshall K, et al. Safety and efficacy of nonsteroid pimecrolimus cream 1% in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2003;142(2):155‐62. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kapp 2002 {published data only}
- Kapp A, Papp K, Bingham A, Folster‐Holst R, Ortonne JP, Potter PC, Gulliver W, Paul C, Molloy S, Barbier N, Thurston M, Prost Y, Flare Reduction in Eczema with Elidel (infants) multicenter investigator study group. Long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in infants with topical pimecrolimus, a nonsteroid anti‐inflammatory drug. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;110(2):277‐84. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kaufmann 2006 {published data only}
- Kaufmann R, Bieber T, Helgesen AL, Andersen BL, Luger T, Poulin Y, et al. Onset of pruritus relief with pimecrolimus cream 1% in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: a randomized trial. Allergy 2006;61(3):375‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kempers 2004 {published data only}
- Kempers S, Boguniewicz M, Carter E, Jarrat M, Pariser D, Stewart D. Comparison of pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% in paediatric patients with atopic eczema. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2003;17:41. [Google Scholar]
- Kempers S, Boguniewicz M, Carter E, Jarratt M, Pariser D, Stewart D, et al. A randomized investigator‐blinded study comparing pimecrolimus cream 1% with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% in the treatment of pediatric patients with moderate atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2004;51(4):515‐25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Leo 2004 {published data only}
- Leo HL, Bender BG, Leung SB, Tran ZV, Leung DY. Effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% on skin condition and sleep disturbance in children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;114(3):691‐93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ling 2005 {published data only}
- Ling M, Gottlieb A, Pariser D, Caro I, Stewart D, Scott G, et al. A randomized study of the safety, absorption and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% applied twice or four times daily in patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2005;16(3):142‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling M, Gottlieb AB, Abrams K. Ling M, Gottlieb AB, Abrams K. Pimecrolimus cream 1%; bid and qid application were equally effective and well tolerated. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2002; Vol. 16:27.
Luger 2001 {published data only}
- Luger T, Leent EJM, Graeber M, Hedgecock S, Thurston M, Kandra A, et al. SDZ ASM 981: An emerging safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144(4):788‐94. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Luger 2004 {published data only}
- Luger TA, Lahfa M, Folster‐Holst R, Gulliver WP, Allen R, Molloy S, et al. Long‐term safety and tolerability of pimecrolimus cream 1% and topical corticosteroids in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2004;15(3):169‐78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meurer 2002 {published data only}
- Meurer M, Folster‐Holst R, Wozel G, Weidinger G, Junger M, Brautigam M, et al. Pimecrolimus cream in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in adults: a six‐month study. Dermatology 2002;205(3):271‐77. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Paller (a) 2005 {published data only}
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Paller (b) 2005 {published data only}
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Paller (c) 2005 {published data only}
- Paller AS, Lebwohl M, Fleischer AB Jr, Antaya R, Langley RG, Kirsner RS, et al. Tacrolimus ointment is more effective than pimecrolimus cream with a similar safety profile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: results from 3 randomized, comparative studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(5):810‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Siegfried 2006 {published data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS04). A 6‐month, randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1 % twice daily vs. standard of care in the management of mild to severe atopic dermatitis in children 3 months to 11 years. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
- Siegfried E, Korman N, Molina C, Kianifard F, Abrams K. Safety and efficacy of early intervention with pimecrolimus cream 1% combined with corticosteroids for major flares in infants and children with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2006;17(3):143‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Staab 2005 {published data only}
- Staab D, Kaufmann R, Brautigam M, Wahn U. Treatment of infants with atopic eczema with pimecrolimus cream 1% improves parents' quality of life: a multicenter, randomized trial. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 2005;16(6):527‐33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thaci 2003 {published data only}
- Thaci D, Folster‐Holst R, Hoger P, Kaufmann R, Brautigam M, Weidinger G, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1% is effective in the treatment of atopic eczema in infants irrespective of clinical score. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2003; Vol. 17, issue Suppl 3:P2.37.
Wahn 2002 {published data only}
- Wahn U, Bos JD, Goodfield M, Caputo R, Papp K, Manjra A, et al. Flare Reduction in Eczema with Elidel (Children) Multicenter Investigator Study Group. Efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in children. Pediatrics 2002;110(1:Pt 1):e2. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Whalley 2002 {published data only}
- Whalley D, Huels J, McKenna S P, Assche D. The benefit of pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) on parents' quality of life in the treatment of pediatric atopic dermatitis. Pediatrics 2002;110(6):1133‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Ball 2002 {unpublished data only}
- Ball C, Mason T. A double‐blind, randomized, parallel‐group, multi‐center study to compare 1% SDZ ASM 981 cream and vehicle in their ability to maintain remission of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adults, for up to one year (Novartis protocol CASM981GB01). Novartis Clinical Study Report 2002.
Belsito 2004 {published data only}
- Belsito DV, Fowler JF Jr, Marks JG Jr, Pariser DM, Hanifin J, Duarte IA, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1%: a potential new treatment for chronic hand dermatitis. Cutis 2004;73(1):31‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
CASM9819315E1 2005 {published data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM9810315E1). A 12‐month open‐label noncontrolled extension to a randomized, multicenter parallel group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in the long‐term management of atopic dermatitis in children from 3 months to 23 months of age. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C1302 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1302). Extension study following confirmatory study in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C1304 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C1304). Extension study following confirmatory study in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981C2405 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2405). A 6‐month open‐label, multinational, effectiveness, and safety study of pimecrolimus cream 1% in subjects with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2405‐ext.200 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2405‐ext). A open‐label effectiveness and safety study of pimecrolimus cream 1% in subjects with atopic dermatitis (AD) who completed study CASM981C2405. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2420 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2420). Naturalistic, open‐label, multicenter study of long‐term management in patients = 3 months of age with mild or moderate atopic dermatitis using pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2421 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CAS981C2421). A double‐blind, randomized, intra–patient comparison of Pimecrolimus 1% Cream vs. placebo in the treatment of vitiligo.. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2434 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2434). A randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the time to onset of pruritus improvement during the first week of Pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment in adult patients (=18 years old) with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981C2434E1 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981C2434E1). A 5‐week open label, multicenter, non‐comparative extension study in patients (>= 18 years old) with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis to provide patients who completed the core study, CASM981C2434, access to pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CEG01 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CEG01). A multicentre, single‐arm prospective, open‐label study to assess the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in patients with atopic dermatitis in daily practice settings. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CES01 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CES01). A 6‐month randomized multi‐center vehicle‐controlled parallel‐group study of 3 double‐blind weeks followed by a 23‐week open‐label phase to study the safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis on the face. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CJP01 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (CASM981CJP01). Assessment of blood concentrations, tolerability, and efficacy of pimecrolimus cream 1% in Japanese pediatric patients. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CPI01 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CPI01). Naturalistic, open‐label, multicenter study of short‐term management in early school‐aged (6‐10 years old) children with mild or moderate atopic dermatitis using pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CUS05 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS05). An 8‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled multicenter study in adults to assess the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus 1% cream twice daily in the treatment of inverse psoriasis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CUS08 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CUS08). A randomized, multicenter, parallel‐group, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled study to evaluate the time of pruritus improvement during the first week of pimecrolimus cream 1% treatment in patients =2 years old with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981CZA01 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981CZA01). A 3‐month open label, national, quality of life , and safety study with pimecrolimus cream, 1% in children (age 2‐12 years ) with atopic dermatitis. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
CASM981DE06 2005 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981DE06). A single‐center, randomized, double‐blind, intraindividual, experimental vehicle‐controlled investigation of the protective effect of Pimecolimus cream 1% on the development of atopic eczema by the atopy patch test (APT). www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2005.
CASM981M2301 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Novartis (protocol CASM981M2301). A 6‐week randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study to investigate the efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in patients with mild to moderate chronic hand dermatitis, followed by a 6‐week open‐label phase to assess the safety of pimecrolimus cream 1%. www.novartisclinicaltrials.com/clinicaltrialrepository/public/login.jsp?target=%2Fclinicaltrialrepository%2Fpublic%2Fmain.jsp (accessed 1st August 2006) 2006.
McKenna 2006 {published data only}
- McKenna SP, Whalley D, Prost Y, Staab D, Huels J, Paul CF, et al. Treatment of paediatric atopic dermatitis with pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981): impact on quality of life and health‐related quality of life. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2006;20(3):248‐54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meads 2005 {published data only}
- Meads DM, McKenna SP, Kahler K. The quality of life of parents of children with atopic dermatitis: interpretation of PIQoL‐AD scores. Quality of Life Research 2005;14(10):2235‐45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meurer 2004 {published data only}
- Meurer M, Fartasch M, Albrecht G, Vogt T, Worm M, Ruzicka T, et al. Long‐term efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in adults with moderate atopic dermatitis. Dermatology 2004;208(4):365‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Papp 2004 {published data only}
- Papp K, Staab D, Harper J, Potter P, Puig L, Ortonne JP, et al. Effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% on the long‐term course of pediatric atopic dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology 2004;43(12):978‐83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Papp 2005 {published data only}
- Papp KA, Werfel T, Folster‐Holst R, Ortonne JP, Potter PC, Prost Y, et al. Long‐term control of atopic dermatitis with pimecrolimus cream 1% in infants and young children: a two‐year study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(2):240‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Queille‐Roussel 2001 {published data only}
- Queille‐Roussel C, Paul C, Duteil L, Lefebvre MC, Rapatz G, Zagula M, et al. The new topical ascomycin derivative SDZ ASM 981 does not induce skin atrophy when applied to normal skin for 4 weeks: a randomized, double‐blind controlled study. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144(3):507‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rappersberger 2002 {published data only}
- Rappersberger K, Komar M, Ebelin ME, Scott G, Burtin P, Greig G, et al. Pimecrolimus identifies a common genomic anti‐inflammatory profile, is clinically highly effective in psoriasis and is well tolerated. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2002;119(4):876‐87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Van Leent 1998 {published data only}
- Leent EJ, Graber M, Thurston M, Wagenaar A, Spuls PI, Bos JD. Effectiveness of the ascomycin macrolactam SDZ ASM 981 in the topical treatment of atopic dermatitis. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(7):805‐9. [MEDLINE: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Weissenbacher 2006 {published data only}
- Weissenbacher S, Traidl‐Hoffmann C, Eyerich K, Katzer K, Braeutigam M, Loeffler H, et al. Modulation of atopy patch test and skin prick test by pretreatment with 1% pimecrolimus cream. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 2006;140(3):239‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wolff 2005 {published data only}
- Wolff K, Fleming C, Hanifin J, Papp K, Reitamo S, Rustin M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of three different doses of oral pimecrolimus in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(6):1296‐1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Arellano 2006
Beattie 2003
- Beattie PE, Lewis‐Jones MS. Parental knowledge of topical therapies in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2003;28:549‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Charman (a) 2000
- Charman C, Williams H. Outcome measures of disease severity in atopic eczema. Archives of Dermatology 2002;136(6):763‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Charman (b) 2000
- Charman CR, Morris AD, Williams HC. Topical corticosteroid phobia in patients with atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142:931‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Charman 2003
- Charman C, Chambers C, Williams H. Measuring atopic dermatitis severity in randomized controlled clinical trials: what exactly are we measuring?. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2003;120(6):932‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cookson 2002
- Cookson W. Genetics and genomics of asthma and allergic diseases. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;113(5):832‐6. [Google Scholar]
Deeks 2001
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combing results form several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic reviews in health care: meta‐analysis in context. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2001:385‐12. [072791488X] [Google Scholar]
DerSimonian 1986
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ellis 2002
- Ellis CN, Drake LA, Prendergast MM, Abramovits W, Boguniewicz M, Daniel CR, et al. Cost of atopic dermatitis and eczema in the United States. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;46(3):361‐70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ellis 2003
- Ellis C, Luger T, on behalf of the ICCAD II Faculty. International Consensus Conference on Atopic Dermatitis II (ICCAD II): clinical update and current treatment strategies. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;148(Suppl. 63):3‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
EMEA 2006
- European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products. Questions and answers on Protopic/Protopy and Elidel. http://www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/general/direct/pr/8027006en.pdf (accessed 31th March 2006) 2006.
Emerson 1998
- Emerson RM, Williams HC, Allen BR. Severity distribution of atopic dermatitis in the community and its relationship to secondary referrals. British Journal of Dermatology 1998;139:73‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Emerson 2001
- Emerson RM, Williams HC, Allen BR. What is the cost of atopic dermatitis in preschool children?. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;143:514‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
FDA 2005
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. FDA Public Health Advisory: Elidel (pimecrolimus) Cream and Protopic (tacrolimus) Ointment. http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/advisory/elidel_protopic.htm (Accessed 4th January 2007) 2005.
FDA 2006
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Alert for Healthcare Professionals: Pimecrolimus (marketed as Elidel). http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/InfoSheets/HCP/ElidelHCP.pdf (accessed 1st July 2006) 2006.
Flohr 2004
- Flohr C, Johansson SG, Wahlgren CF, Williams H. How atopic is atopic dermatitis?. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2004;114(1):150‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Freeman 2006
- Freeman SR, Williams HC, Dellavalle RP. The increasing importance of systematic reviews in clinical dermatology research and publication. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(111):2357‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gieler 1999
- Gieler U, Hohmann M, Niemeler V, Kupfer J. Cost evaluation of atopic eczema. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1999;10:S15‐20. [Google Scholar]
Hanifin 1980
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic eczema. Acta Dermato Venerologica (Stockholm) 1980;92:44‐7. [Google Scholar]
Herd 2000
- Herd RM. The morbidity and cost of atopic dermatitis. In: Williams HC editor(s). Atopic dermatitis. Vol. 85‐95, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000. [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. British Medical Journal 2003;327(7414):557‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hoare 2000
- Hoare C, Li Wan Po A, Williams HC. Systematic review of treatments of atopic dermatitis. Health Technology Assessment 2000;4(37):141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Johansson 2004
- Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;113(5):832‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Juni 2001
- Juni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. British Medical Journal 2001;323:42‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kay 1994
- Kay J, Gawkroger DJ, Mortimer MJ, Jaron AG. The prevalence of childhood atopic eczema in a general population. Journal of American Academy of Dermatology 1994;30:35‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kiebert 2002
- Kiebert G, Sorensen SV, Revicki D, Fagan SC, Doyle JJ, Cohen J, et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a decrement in health‐related quality of life. International Journal of Dermatology 2002;41:151‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Leung 2003
- Leung DYM, Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2003;361:151‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lewis‐Jones 2001
- Lewis‐Jones MS, Finlay AY, Dykes PJ. The Infants' Dermatitis Quality of Life Index. British Journal of Dermatology 2001;144:104‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Neame 1995
- Neame RL, Berth‐Jones J, Kurinczuk JJ, Graham‐Brown RAC. Prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Leicester: a study of methodology and examination of possible ethnic variations. British Journal of Dermatology 1995;132:772‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NICE 2004
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Technology appraisal guidance 82: tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for atopic eczema. http://www.nice.org.uk/download.aspx?o=TA082guidance&template=download.aspx (accessed 26th August 2004) 2004; Vol. London.
Stuetz 2001
- Stuetz A, Grassberger M, Meingassner JG. Pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) ‐ preclinical pharmacologic profile and skin sensitivity. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2001;20(4):233‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 1994
- Williams HC, Burney PGJ, Pembroke AC, Hay RH. The UK Working Party's diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 1994;131(3):383‐96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 1999
- Williams H, Robertson C, Stewart A, Ait‐Khaled N, Anabwani G, Anderson R, et al. Worldwide variations in the prevalence of symptoms of atopic eczema in the international study of asthma and allergies in childhood. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1999;103(1):125‐38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 2002
- Williams H. New treatments for atopic dermatitis.. British Medical Journal 2002;324(7353):1533‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 2003
- Williams H. 1% Pimecrolimus Cream for Atopic Dermatitis‐‐Reply. Archives of Dermatology Archives of Dermatology 2003;139(10):1370‐1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 2005
- Williams HC. Clinical practice. Atopic dermatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(22):2314‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


