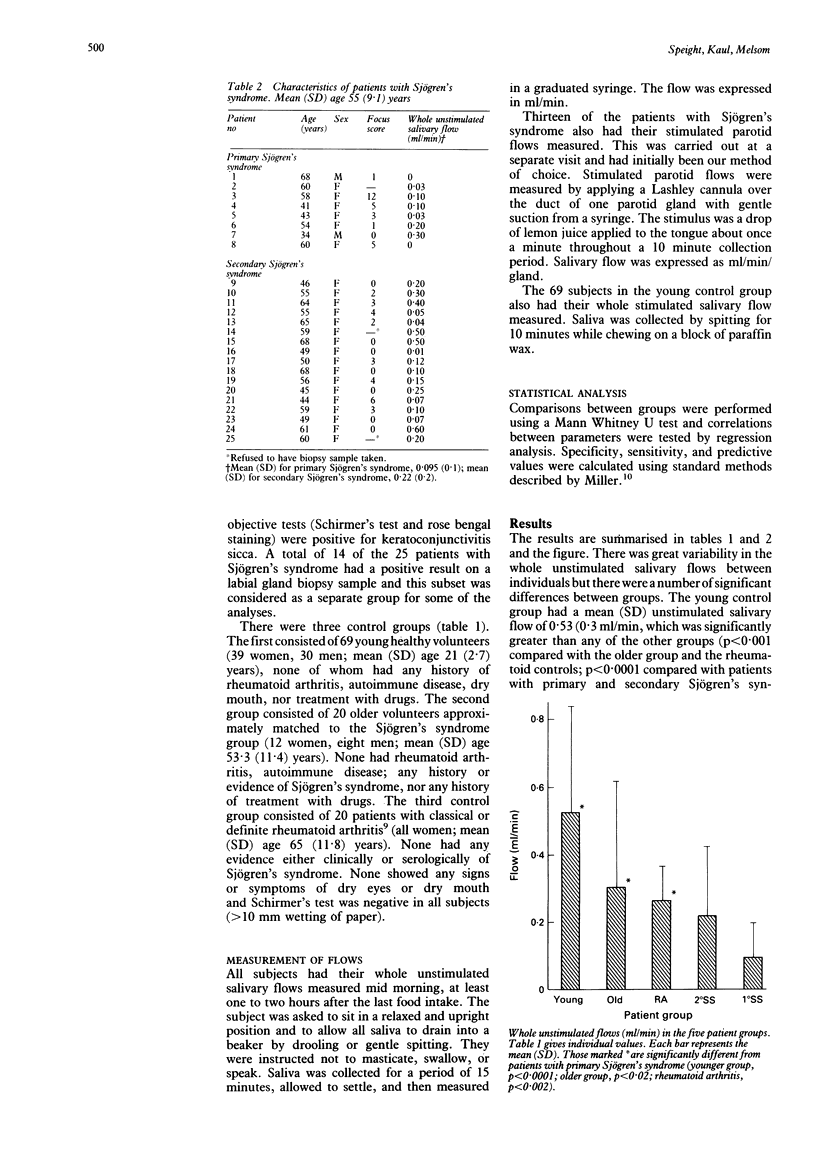
Abstract
The criteria for a clinical diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome remain controversial and vary widely from study to study. With respect to the oral component it is considered necessary to use some form of objective test, but many of those available are not suitable for use in a busy clinical situation. The purpose of this study was to evaluate a simple method for measuring the whole unstimulated salivary flow. Twenty five patients with Sjögren's syndrome, 69 young control subjects, 20 age matched normal older control subjects and 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis without Sjögren's syndrome had their salivary flows measured. Whole unstimulated salivary flows in the young control subjects were higher than in all other groups. Patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome had lower flows than either the older controls or the rheumatoid patients. Among the patients with Sjögren's syndrome 52% had a flow of 0.1 ml/min or less compared with only 8% of age matched controls. The positive predictive value of this low flow was 81%. It is concluded that whole unstimulated salivary flows of 0.1 ml/min or less are highly specific for xerostomia. When interpreted in the context of all the clinical findings whole unstimulated salivary flows are useful for diagnosing the oral component of Sjögren's syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Aryeh H., Miron D., Szargel R., Gutman D. Whole-saliva secretion rates in old and young healthy subjects. J Dent Res. 1984 Sep;63(9):1147–1148. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630091001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels T. E., Silverman S., Jr, Michalski J. P., Greenspan J. S., Sylvester R. A., Talal N. The oral component of Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1975 Jun;39(6):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(75)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Robinson C. A., Curd J. G., Kozin F., Howell F. V. Sjögren's syndrome. Proposed criteria for classification. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):577–585. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman D., Ben-Aryeh H. The influence of age on salivary content and rate of flow. Int J Oral Surg. 1974;3(5):314–317. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(74)80069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heft M. W., Baum B. J. Unstimulated and stimulated parotid salivary flow rate in individuals of different ages. J Dent Res. 1984 Oct;63(10):1182–1185. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthorpe R., Oxholm P., Prause J. U., Schiødt M. The Copenhagen criteria for Sjögren's syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1986;61:19–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvinen T., Larmas M. The relation of stimulated salivary flow rate and pH to Lactobacillus and yeast concentrations in saliva. J Dent Res. 1981 Dec;60(12):1929–1935. doi: 10.1177/00220345810600120201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully C. Oral parameters in the diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Mar-Apr;7(2):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopouli F. N., Siouna-Fatourou H. I., Ziciadis C., Moutsopoulos H. M. Evaluation of unstimulated whole saliva flow rate and stimulated parotid flow as confirmatory tests for xerostomia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Mar-Apr;7(2):127–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreebny L. M., Valdini A. Xerostomia. Part I: Relationship to other oral symptoms and salivary gland hypofunction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988 Oct;66(4):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(88)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreebny L. M., Valdini A., Yu A. Xerostomia. Part II: Relationship to nonoral symptoms, drugs, and diseases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989 Oct;68(4):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(89)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


