Abstract
The case is presented of a 70 year old woman with mild hypercholesterolaemia and hypertension who was readmitted to hospital six months after a previous admission for angina pectoris. The patient was treated with verapamil, nifedipine, and aspirin, and had been receiving bezafibrate (400 mg every 12 hours) for the previous 40 days. Twenty four hours after admission she developed podagra, which was treated with indomethacin (100 mg daily). Eight days after admission myocardial infarction was suspected, and the next day she presented with symptoms of rhabdomyolysis, which was confirmed by laboratory tests. Bezafibrate was withdrawn and the patient became asymptomatic after seven days. It is recommended that doctors should be aware of the possibility of patients, especially those with impaired renal function, developing rhabdomyolysis while being treated with bezafibrate.
Full text
PDF
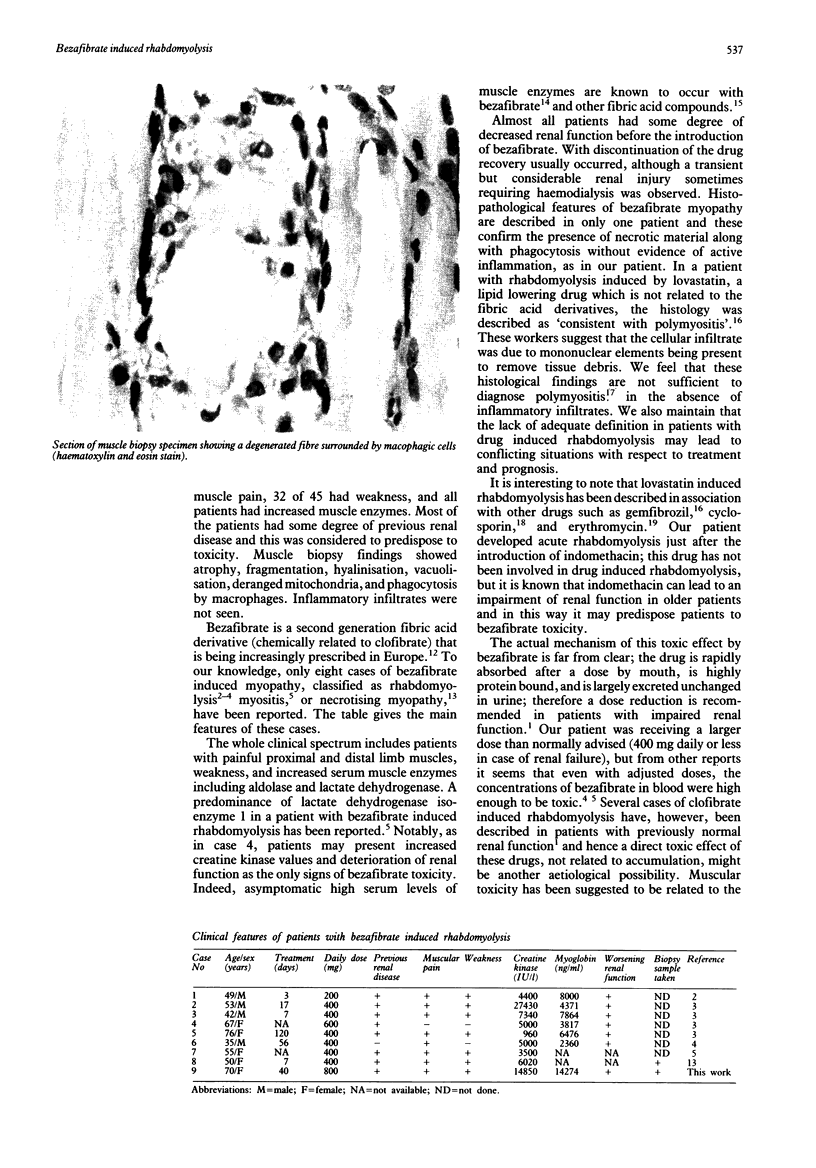

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayanian J. Z., Fuchs C. S., Stone R. M. Lovastatin and rhabdomyolysis. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Oct 15;109(8):682–683. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-8-682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blane G. F. Comparative toxicity and safety profile of fenofibrate and other fibric acid derivatives. Am J Med. 1987 Nov 27;83(5B):26–36. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90868-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpier C. L., Jones P. H., Suki W. N., Lederer E. D., Quinones M. A., Schmidt S. W., Young J. B. Rhabdomyolysis and renal injury with lovastatin use. Report of two cases in cardiac transplant recipients. JAMA. 1988 Jul 8;260(2):239–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabow P. A., Kaehny W. D., Kelleher S. P. The spectrum of rhabdomyolysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 May;61(3):141–152. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198205000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Manzano C., Fueyo J., Pedro-Botet Montoya J., Fernández-Solá J. Miopatía necrosante inducida por bezafibrato. Med Clin (Barc) 1991 Mar 23;96(11):439–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubenstock A., Schröcksnadel W., Bauer K., Schmidt P., Gabl F. Predominance of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme 1 in a patient with bezafibrate-induced rhabdomyolysis. Clin Chem. 1984 Sep;30(9):1587–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann H., Bock K. D. Briefe an die Redaktion. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Apr 15;59(8):413–414. doi: 10.1007/BF01698522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsilambros N., Braaten J., Ferguson B. D., Bradley R. F. Muscular syndrome after clofibrate. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 18;286(20):1110–1111. doi: 10.1056/nejm197205182862014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köppel C. Clinical features, pathogenesis and management of drug-induced rhabdomyolysis. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp. 1989 Mar-Apr;4(2):108–126. doi: 10.1007/BF03259907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Levy R. I. Acute muscular syndrome associated with administration of clofibrate. N Engl J Med. 1968 Oct 17;279(16):856–858. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196810172791604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk J. P., Todd P. A. Bezafibrate. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in hyperlipidaemia. Drugs. 1987 Jun;33(6):539–576. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198733060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf K. W., Albers R., Scheler F. Letter: Clofibrate-induced myopathy syndrome. Lancet. 1976 Jan 31;1(7953):249–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush P., Baron M., Kapusta M. Clofibrate myopathy: a case report and a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;15(3):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(86)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teräväinen H., Larsen A., Hillbom M. Clofibrate-induced myopathy in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Aug 16;39(2):135–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00703319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbano-Márquez A., Casademont J., Grau J. M. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis: the current position. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Mar;50(3):191–195. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J., Baker F., Walls J. The short term effects of bezafibrate on the hypertriglyceridaemia of moderate to severe uraemia. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;18(3):361–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeshurun D., Dakak N., Khoury K., Daher E. [Acute severe myositis due to bezafibrate treatment]. Harefuah. 1989 Mar 1;116(5):261–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]