Abstract
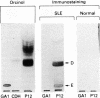
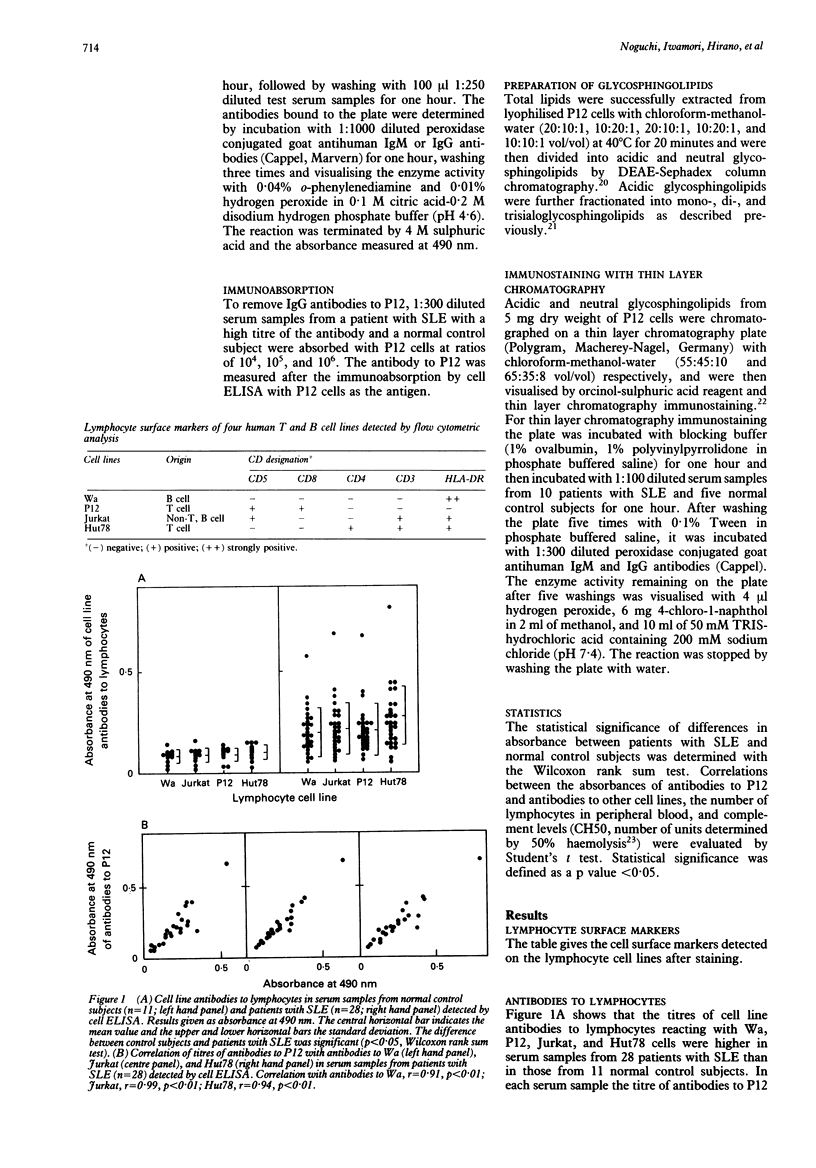
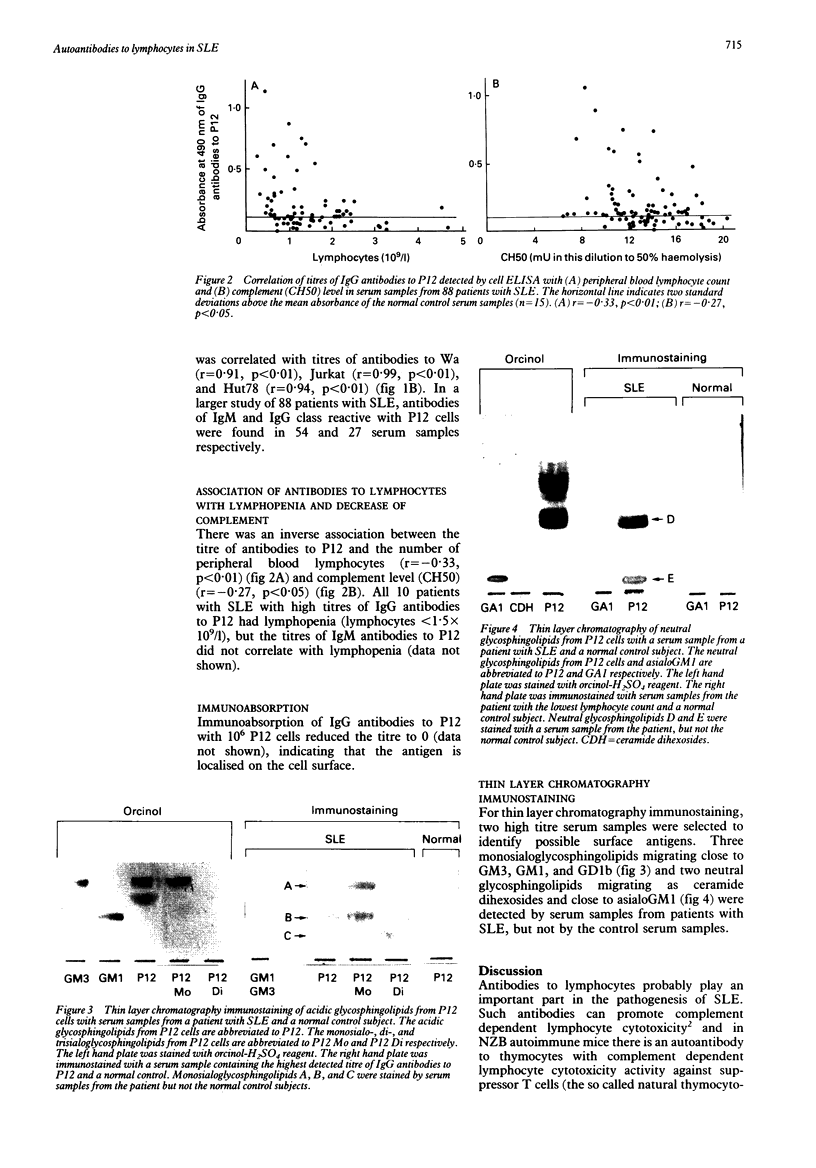
Antibodies to lymphocytes in serum samples from 88 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and 15 normal control subjects were examined by a cell enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with four human T and B cell lines as antigens. The antibodies reacted with the Wa B cell line and the T cell lines P12 (CD4-, CD8+), Jurkat (CD4-, CD8-), and Hut78 (CD4+, CD8-). Antibody titres in serum samples from patients with SLE were higher than in those from normal control subjects. Titres of antibodies to P12 were correlated with titres of antibodies to Wa, Jurkat, and Hut78 in serum samples from patients with SLE. IgG antibodies to P12 were associated with lymphopenia and reduced haemolytic complement. By thin layer chromatography immunostaining, the antibodies in serum samples from two of 10 patients with SLE with high titres of IgG antibodies to P12 and lymphopenia were shown to react with three monosialoglycosphingolipids and two neutral glycosphingolipids from P12 cells. Antibodies to lymphocytes in serum samples from patients with SLE react with T and B cell lines, recognise a series of cell membrane glycosphingolipids and are associated with the lymphopenia and hypocomplementaemia typical of active disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocchieri M. H. An ELISA for anti-thymocyte autoantibody in NZB mice. Comparison with the cytotoxic assay. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Aug 3;101(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Scott D. D., Stewart S. S., Kundu S. K., Marcus D. M. Antibodies to glycosphingolipids in patients with multiple sclerosis and SLE. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1793–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. S., Bresnihan B., Hughes G. R. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for reactivity with i antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Mar;31(3):443–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Hashimoto H., Shiokawa Y., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Kasai M., Ochiai Y., Okumura K. Antiglycolipid autoantibody detected in the sera from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1437–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Sakayori M., Nozawa S., Yamamoto T., Yago M., Noguchi M., Nagai Y. Monoclonal antibody-defined antigen of human uterine endometrial carcinomas is Leb. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):718–722. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Sawada K., Hara Y., Nishio M., Fujisawa T., Imura H., Nagai Y. Neutral glycosphingolipids and gangliosides of bovine thyroid. J Biochem. 1982 Jun;91(6):1875–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Lety M. A., Bach J. F., Louvard D. Human systemic lupus erythematosus sera contain antibodies against cell-surface protein(s) that share(s) epitope(s) with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara T. Establishment of a human leukemia cell line in nude mice and its application to the screening system of antileukemic agents. Nihon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1980 Dec;43(6):1034–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., De Horatius R., Ferrone S. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus patients and their relatives: reactivity with the HLA antigenic molecular complex. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):265–272. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minota S., Winfield J. B. Identification of three major target molecules of IgM antilymphocyte autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3644–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minota S., Winfield J. B. IgG anti-lymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus react with surface molecules shared by peripheral T cells and a primitive T cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1750–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi T., Ando S., Magai Y. High resolution preparative column chromatographic system for gangliosides using DEAE-Sephadex and a new porus silica, Iatrobeads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;441(3):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Distaso J. A., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus T cell subsets, anti-T cell antibodies, and T cell functions. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):689–700. doi: 10.1172/JCI111261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Kumagai S., Namiuchi S., Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Maeda M., Takatsuki K., Suginoshita T., Imura H. Systemic lupus erythematosus sera antilymphocyte reactivity: detection of antibodies to Tac-antigen positive T cell lines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jan;63(1):8–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Maeda H., Mukai R., Yabe T., Hamaguchi H. Identification of the MT3 molecule using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and alloantisera. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(6):575–583. doi: 10.1007/BF00345965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi O., Miyajima H., Hirano T., Noguchi M., Ueda A., Hashimoto H., Hirose S., Okumura K. The Leu-1 B-cell subpopulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Nov;7(6):441–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00915053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Peterlin B. M. Methylation patterns of HLA-DR alpha genes in six mononuclear cell lines. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(5):298–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00395534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Cohen P. L., Winfield J. B. Subset specificity of antilymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Preferential reactivity with cells bearing the T4 and autologous erythrocyte receptor phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Mar;28(3):262–270. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Shaw M., Winfield J. B. Surface antigen specificity of cold-reactive IgM antilymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jan;28(1):44–51. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]