Abstract
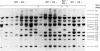
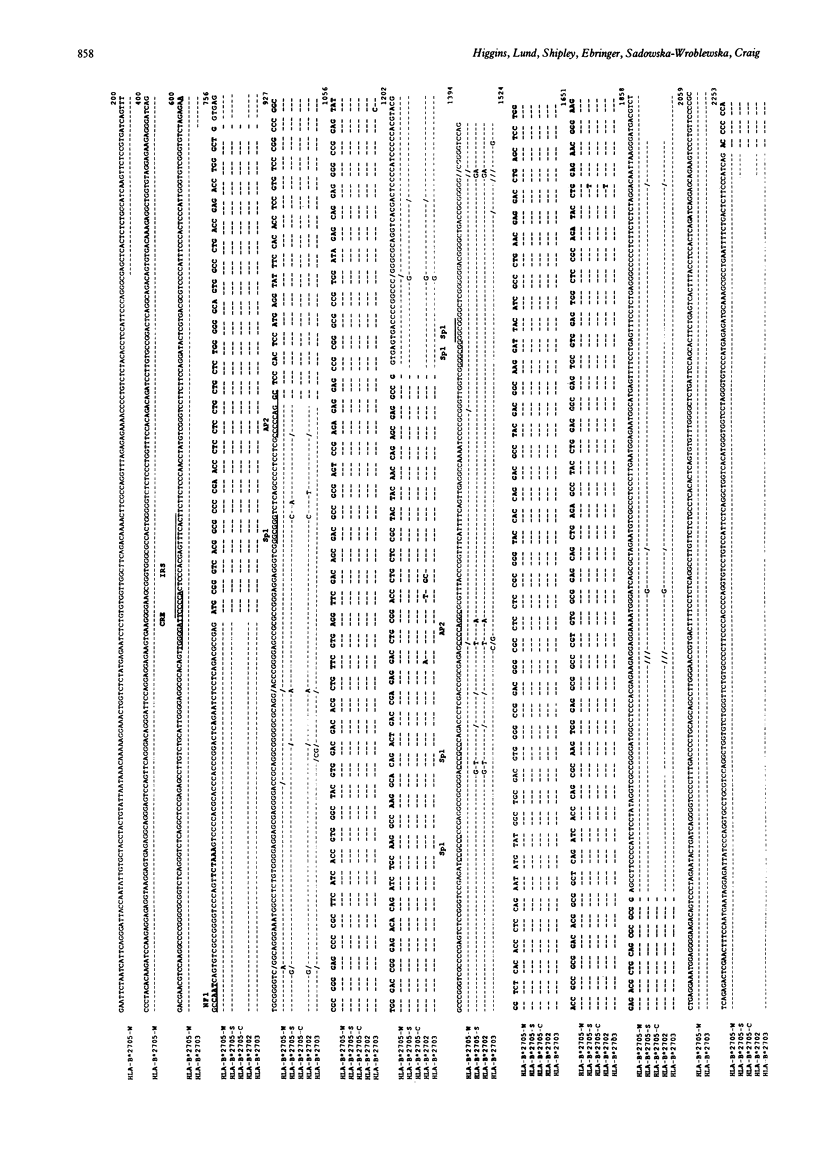
Two groups of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) from England and Poland were examined for restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) associated with the disease. No preferential association was found between the 9.2 kb PvuII fragment in HLA-B27 positive patients with AS compared with HLA-B27 healthy subjects as had been previously reported. In the English group, however, a 14 kb PvuII fragment was more common in HLA-B27 positive subjects with AS than in normal controls. Also 4.6 and 3.7 kb PvuII fragments were more prevalent in subjects without AS than in the group with AS, but these results were confined to the English group. Furthermore, the sequence of an HLA-B*2705 gene isolated from a patient with AS was examined, and no significant differences were found compared with the sequence isolated from a healthy subject. There do not seem to be significant genetic differences in the coding or in the regulatory region in HLA-B27 alleles, in subjects with or without AS.
Full text
PDF

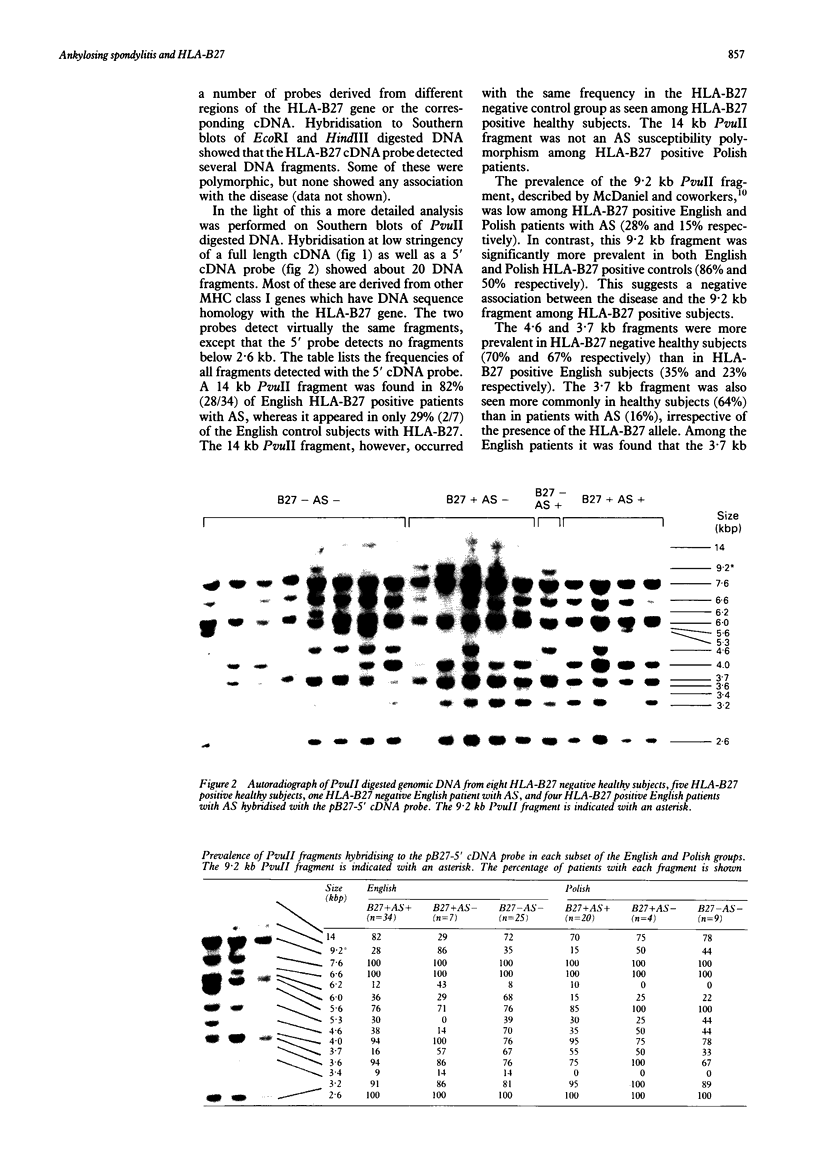
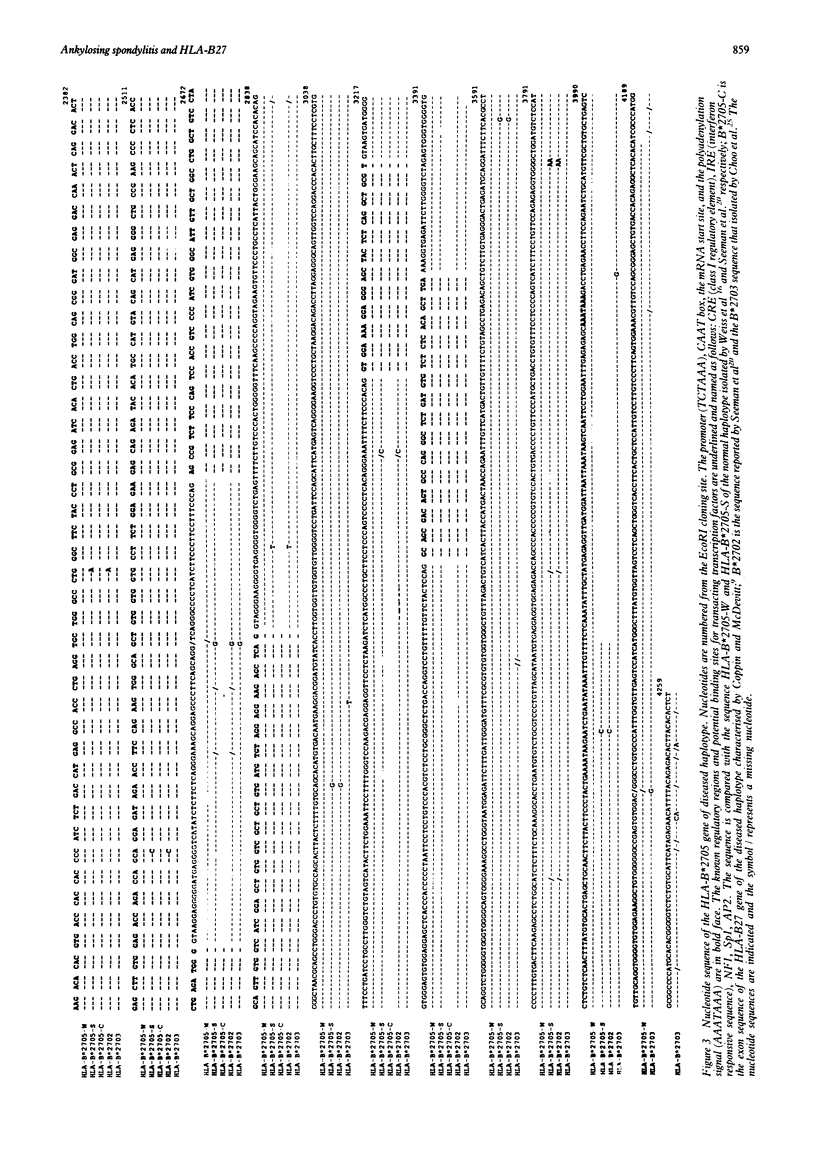



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Calomiris J. J., Wigley F. M., Jabs D. A., Bias W. B., Hochberg M. C. Characterization of the class I HLA 9.2-kb PVU II restriction fragment length polymorphism. Linkage to HLA-A and lack of disease association. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):870–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R., Parham P. Guilt by association: HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90051-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo S. Y., St John T., Orr H. T., Hansen J. A. Molecular analysis of the variant alloantigen HLA-B27d (HLA-B*2703) identifies a unique single amino acid substitution. Hum Immunol. 1988 Mar;21(3):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(88)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin H. L., McDevitt H. O. Absence of polymorphism between HLA-B27 genomic exon sequences isolated from normal donors and ankylosing spondylitis patients. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2168–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand J. P., Taurog J. D. Association between ankylosing spondylitis and a 9.2 kb Pvu II class I HLA DNA restriction fragment: a reassessment. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jul;15(7):1119–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastmond C. J., Woodrow J. C. Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Aug;36(4):360–364. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer A. The cross-tolerance hypothesis, HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1983 Nov;22(4 Suppl 2):53–66. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxii.suppl_2.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer A. The relationship between Klebsiella infection and ankylosing spondylitis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;3(2):321–338. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(89)80024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer R., Cooke D., Cawdell D. R., Cowling P., Ebringer A. Ankylosing spondylitis: klebsiella and HL-A B27. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1977 Aug;16(3):190–196. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/16.3.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing C., Ebringer R., Tribbick G., Geysen H. M. Antibody activity in ankylosing spondylitis sera to two sites on HLA B27.1 at the MHC groove region (within sequence 65-85), and to a Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase reductase peptide (within sequence 181-199). J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1635–1647. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel D. O., Acton R. T., Barger B. O., Koopman W. J., Reveille J. D. Association of a 9.2-kilobase Pvu II class I major histocompatibility complex restriction fragment length polymorphism with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Aug;30(8):894–900. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo S., Aparicio P., Choo S. Y., Hansen J. A., López de Castro J. A. Structural analysis of an HLA-B27 population variant, B27f. Multiple patterns of amino acid changes within a single polypeptide segment generate polymorphism in HLA-B27. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):831–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo S., Aparicio P., Hansen J. A., Choo S. Y., López de Castro J. A. Structural analysis of an HLA-B27 functional variant, B27d, detected in American blacks. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann G. H., Rein R. S., Brown C. S., Ploegh H. L. Gene conversion-like mechanisms may generate polymorphism in human class I genes. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szöts H., Riethmüller G., Weiss E., Meo T. Complete sequence of HLA-B27 cDNA identified through the characterization of structural markers unique to the HLA-A, -B, and -C allelic series. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1428–1432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Leino R., Ståhlberg T., Vuento R. Pathogenesis of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: immunological, microbiological and clinical aspects. Immunol Rev. 1985 Aug;86:47–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trull A., Ebringer A., Panayi G., Ebringer R., James D. C. HLA-B27 and the immune response to enterobacterial antigens in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):74–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Buchwald M., Barker D., Braman J. C., Knowlton R., Schumm J. W., Eiberg H., Mohr J., Kennedy D., Plavsic N. Cystic fibrosis locus defined by a genetically linked polymorphic DNA marker. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1054–1057. doi: 10.1126/science.2997931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. A., Bragado R., Iványi P., Peláez J. L., López de Castro J. A. Molecular analysis of a functional subtype of HLA-B27. A possible evolutionary pathway for HLA-B27 polymorphism. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3557–3565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Bloemer K., Doerner C., Kuon W., Lang M., Pohla H., Schattenkirchner M., Riethmüller G. Molecular biology of the HLA-B27 locus. Br J Rheumatol. 1988;27 (Suppl 2):12–18. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxvii.suppl_2.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Kuon W., Dörner C., Lang M., Riethmüller G. Organization, sequence and expression of the HLA-B27 gene: a molecular approach to analyze HLA and disease associations. Immunobiology. 1985 Dec;170(5):367–380. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(85)80061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow J. C., Nichol F. E., Whitehouse G. H. Genetic studies in ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1983 Nov;22(4 Suppl 2):12–17. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/xxii.suppl_2.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]