Abstract
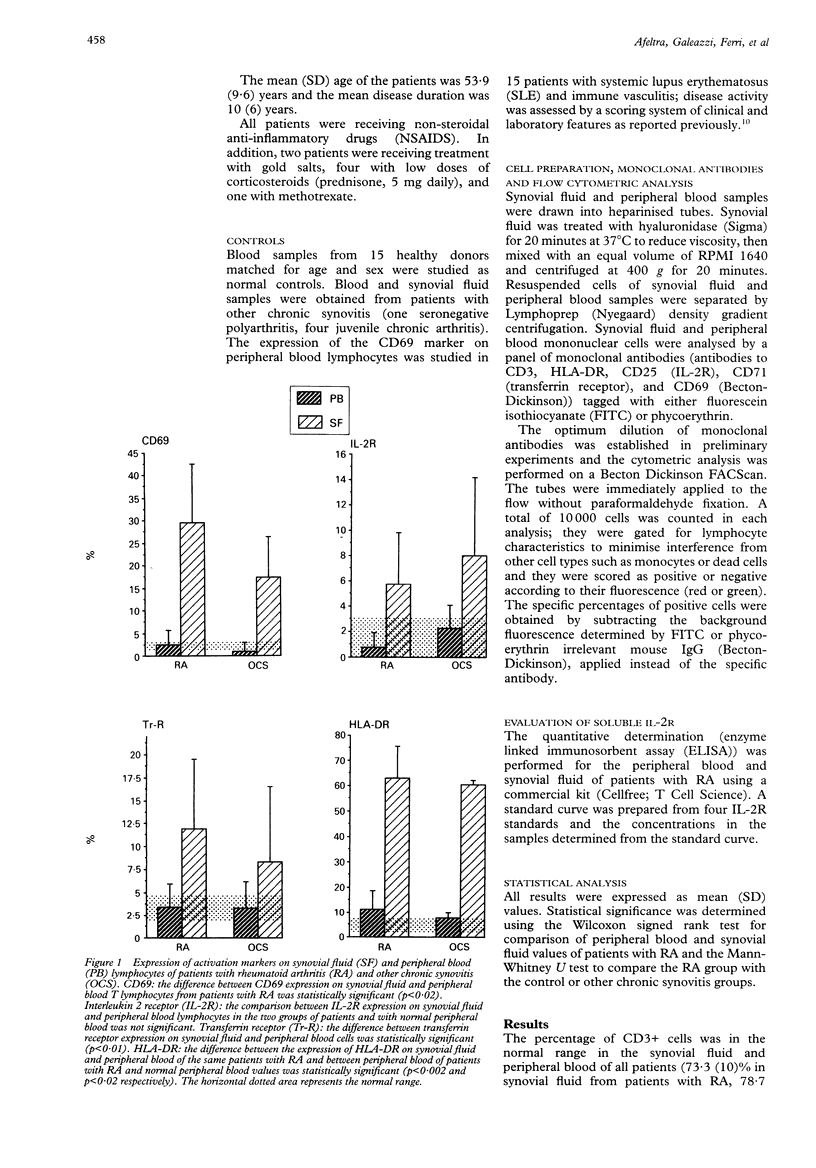
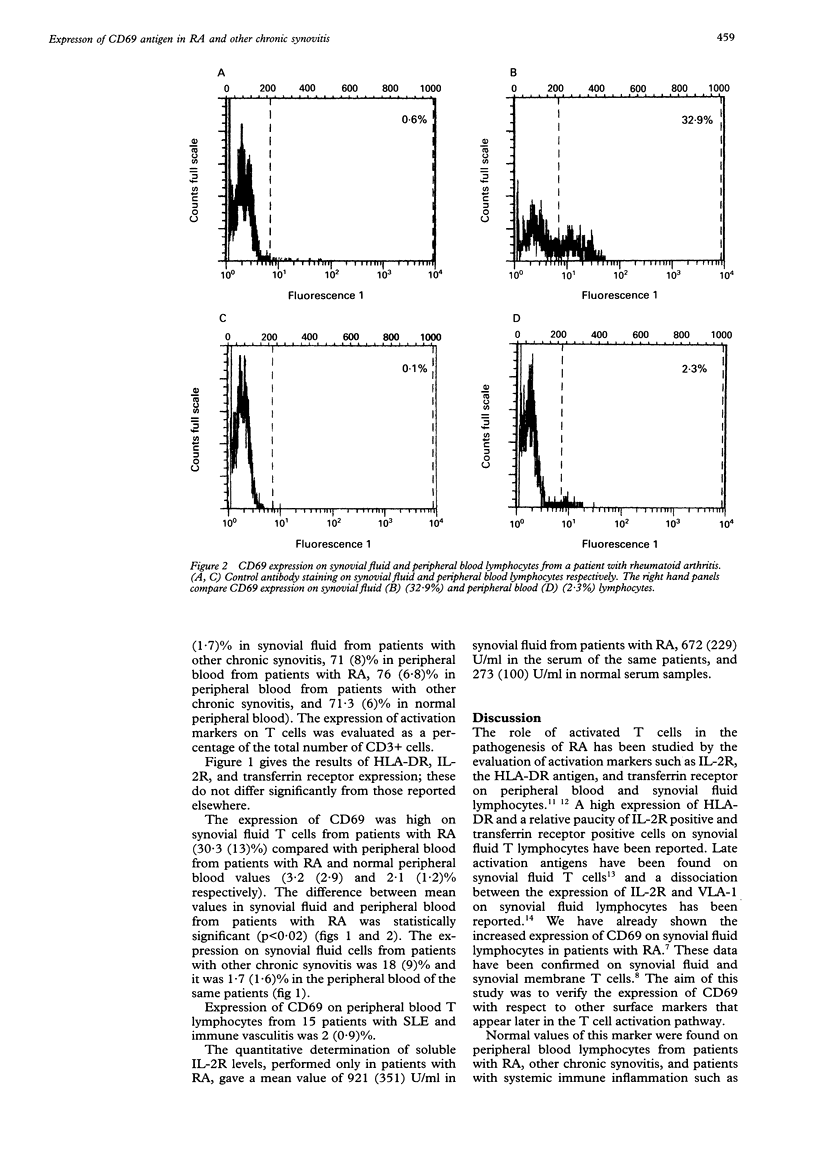
OBJECTIVES--The expression of the CD69 antigen on synovial fluid and peripheral blood lymphocytes was studied in 12 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), five subjects with other forms of chronic synovitis, and on the peripheral blood lymphocytes of 15 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and immune vasculitis. METHODS--The CD69 antigen and other activation markers (HLA-DR, interleukin 2 receptor (IL-2R), transferrin receptor) were measured by cytometric analysis. In patients with RA soluble IL-2R was determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS--The percentage of T cells bearing CD69 was significantly increased in synovial fluid from patients with RA (30.3 (13)%) and other chronic synovitis (18 (9)%). The expression of CD69 on peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with RA, other chronic synovitis, and SLE and immune vasculitis was within the normal range 2.1 (1.2)%. According to previously published work, a high proportion of synovial fluid T cells are HLA-DR positive (64.2 (12.4)% in synovial fluid from patients with RA and 61 (1.2)% in synovial fluid from patients with other chronic synovitis). Transferrin receptor expression on synovial fluid was up-regulated compared with that on peripheral blood. The increase of IL-2R expression on synovial fluid lymphocytes v peripheral blood was not significant; the quantitative determination of soluble IL-2R levels gave a mean value of 921 (351) U/ml in synovial fluid of patients with RA, 672 (229) U/ml in the serum of the same patients, and 273 (100) U/ml in serum from normal subjects. CONCLUSIONS--Synovial fluid lymphocytes are in a different functional state than peripheral blood lymphocytes. CD69 antigen is an interesting cellular marker which should be studied in patients with chronic synovitis. The unusual expression of the activation antigens and the sequence of their appearance require further study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afeltra A., Galeazzi M., Basso P., Pietrucci A., De Pità O., Ferri G. M., Porzio F., Bonomo L. Immune imbalance in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients: effects of intra-articular injection of thymopentin. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1991 Apr-Jun;5(2):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biselli R., Matricardi P. M., D'Amelio R., Fattorossi A. Multiparametric flow cytometric analysis of the kinetics of surface molecule expression after polyclonal activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Apr;35(4):439–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb02879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Yu D. T., Irani A. M., Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J. Ia+ T cells in synovial fluid and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1370–1376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián M., Yagüe E., Rincón M., López-Botet M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Triggering of T cell proliferation through AIM, an activation inducer molecule expressed on activated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1621–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Jung L. K., Bjorndahl J. M., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. III. Rapid induction of a phosphorylated 28 kD/32 kD disulfide-linked early activation antigen (EA 1) by 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate, mitogens, and antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1988–2005. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Glass D., Coblyn J. S., Jacobson J. G. Very late activation antigens on rheumatoid synovial fluid T lymphocytes. Association with stages of T cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):696–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI112629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffon A., Sánchez-Madrid F., Ortíz de Landázuri M., Jiménez Cuesta A., Ariza A., Ossorio C., Sabando P. Very late activation antigen on synovial fluid T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Apr;32(4):386–392. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffón A., García-Vicuña R., Humbría A., Postigo A. A., Corbí A. L., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Upregulated expression and function of VLA-4 fibronectin receptors on human activated T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):546–552. doi: 10.1172/JCI115338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Buck D. W., Rhodes L., Ding A., Evans E., Barney C., Phillips J. H. Interleukin 2 activation of natural killer cells rapidly induces the expression and phosphorylation of the Leu-23 activation antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1572–1585. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Haskard D., Panayi G. The preferential accumulation of helper-inducer T lymphocytes in inflammatory lesions: evidence for regulation by selective endothelial and homotypic adhesion. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Sep;18(9):1397–1404. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon M., Bacon P. A., Symmons D. P., Blann A. D. Transferrin receptor bearing cells in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):346–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastiani G. D., Passiu G., Galeazzi M., Porzio F., Carcassi U. Prevalence and clinical associations of anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study. Clin Rheumatol. 1991 Sep;10(3):289–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02208692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Leu 23 induction as an early marker of functional CD3/T cell antigen receptor triggering. Requirement for receptor cross-linking, prolonged elevation of intracellular [Ca++] and stimulation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1854–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. T cell activation via Leu-23 (CD69). J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1123–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


