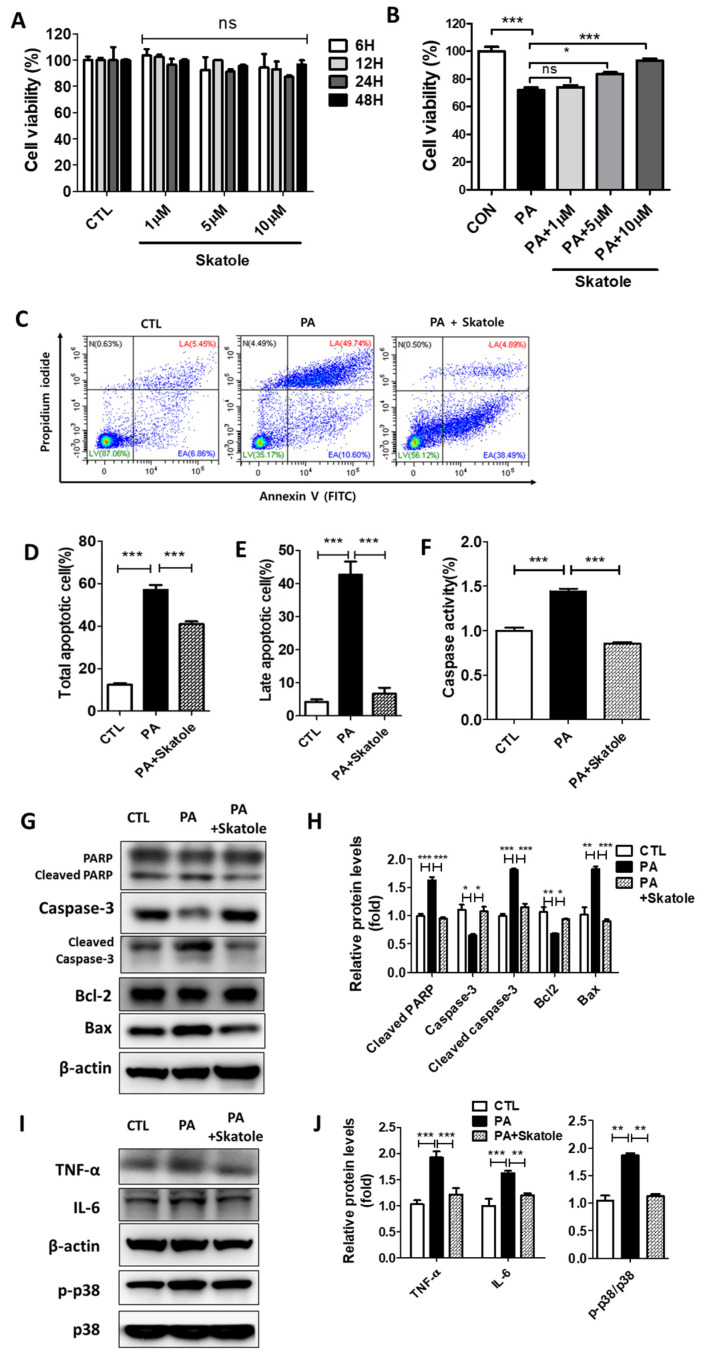
Figure 3.
Skatole is non-toxic and inhibits PA-induced apoptosis, caspase activity, and inflammation in HepG2 cells. (A) HepG2 cells were treated with different concentrations (1–10 μM) of skatole for different times (6–48 h) and cell viability was analyzed. (B) HepG2 cells were exposed to skatole with 0.25 mM PA for 24 h and cell viability was analyzed. (C) HepG2 cells were treated with 0.25 mM PA and 5 μM skatole for 24 h. The apoptotic cell population was detected by flow cytometry (FCM) assay of Annexin V and PI staining detected the apoptotic cell population. (D) The total apoptotic cell population (Annexin V+) was calculated based on (C). (E) The late apoptotic cell population (Annexin V+/PI+) was calculated based on (C). (F) HepG2 cells were treated with the same conditions as (C). The caspase activity in HepG2 cells was measured using the fluorometric assay. (G) The expression levels of apoptotic proteins were estimated by Western blotting of the PA and skatole-treated HepG2 cells. (H) Relative apoptotic proteins were normalized with β-actin. (I) Inflammatory proteins were estimated by Western blot in the treated HepG2 cells. (J) Relative inflammatory proteins (TNF-α and IL-6) were normalized with β-actin, and phosphor-p38 was normalized with total p38. Three independent samples were performed for all experiments, and the values are shown as mean ± SD, analyzed by one-way ANOVA. (n = 3–5, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, ns: not significant. CTL: control, LV: live cells, EA: Early apoptotic cells, LA: Late apoptotic cells, N: Necrotic cells).