Abstract
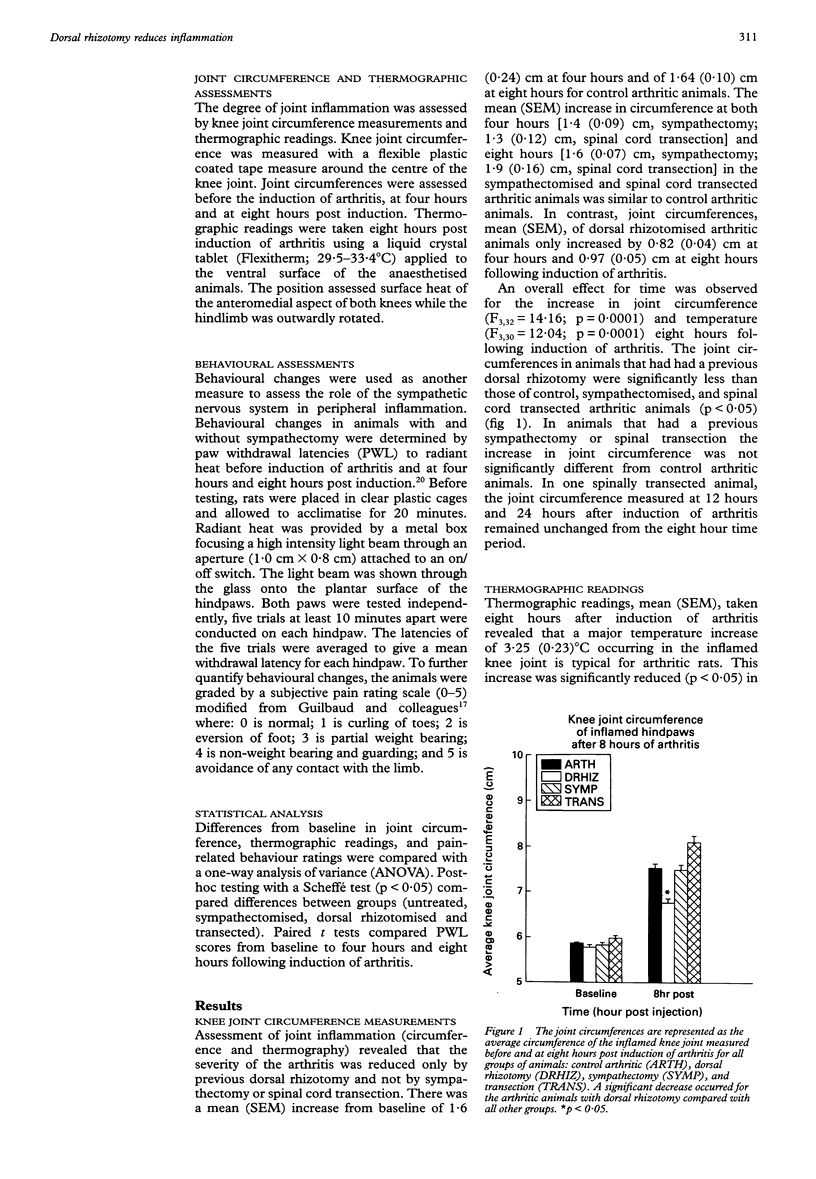
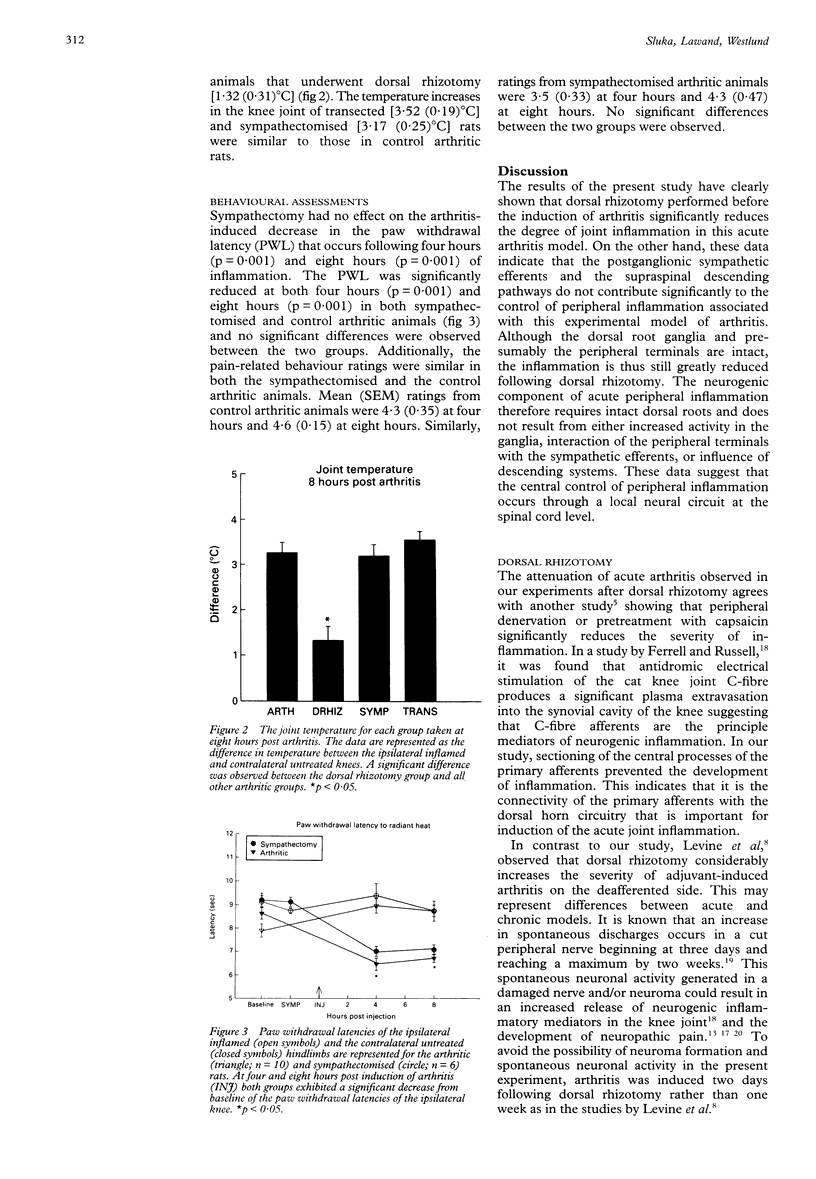
OBJECTIVES--To investigate the role of primary afferents, sympathetic postganglionic efferents and descending systems on the central control of peripheral inflammation. METHODS--Acute inflammation was induced by intra-articular injection of kaolin and carrageenan into the knee joint cavity of the rat. Before the induction of the arthritis, a unilateral dorsal rhizotomy, a chemical (phentolamine) and/or surgical sympathectomy, or a spinal transection was performed. Joint inflammation (joint circumference and thermographic readings) and behavioural signs were assessed. RESULTS--Only arthritic animals with a dorsal rhizotomy showed a significant reduction of the inflammatory response compared with control arthritic animals. No significant differences in the inflammatory response occurred following sympathectomy or spinal transection. The animals who received sympathectomy showed similar behavioural manifestations to the arthritic animals. CONCLUSIONS--The central terminals of primary afferents are important in the development of acute joint inflammation since dorsal rhizotomy attenuated the inflammatory response in the knee joint. The sympathetic nervous system is not involved in the acute inflammatory phase of this arthritis model. The central processes controlling acute inflammation involve a local spinal circuit since spinal cord transection at T9 has no effect on the inflammation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Tuveri M. A., Levi-Montalcini R. Studies on carrageenan-induced arthritis in adult rats: presence of nerve growth factor and role of sympathetic innervation. Rheumatol Int. 1992;12(5):213–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00302155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attal N., Jazat F., Kayser V., Guilbaud G. Further evidence for 'pain-related' behaviours in a model of unilateral peripheral mononeuropathy. Pain. 1990 May;41(2):235–251. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. J., Xie Y. K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988 Apr;33(1):87–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Tonic descending inhibition of spinal cord neurones driven by joint afferents in normal cats and in cats with an inflamed knee joint. Exp Brain Res. 1991;83(3):675–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00229846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colpaert F. C., Donnerer J., Lembeck F. Effects of capsaicin on inflammation and on the substance P content of nervous tissues in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Life Sci. 1983 Apr 18;32(16):1827–1834. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R., Russell N. J. Extravasation in the knee induced by antidromic stimulation of articular C fibre afferents of the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:407–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govrin-Lippmann R., Devor M. Ongoing activity in severed nerves: source and variation with time. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 29;159(2):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Na H. S., Sheen K., Chung J. M. Effects of sympathectomy on a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Pain. 1993 Oct;55(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90187-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Capsaicin suppresses substance P-induced joint inflammation in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Inhibition of carrageenan induced inflammation in the rat knee joint by substance P antagonist. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Nov;48(11):928–932. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.11.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Neurogenic component of different models of acute inflammation in the rat knee joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Nov;50(11):747–751. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.11.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Clark R., Devor M., Helms C., Moskowitz M. A., Basbaum A. I. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6208609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Dardick S. J., Roizen M. F., Helms C., Basbaum A. I. Contribution of sensory afferents and sympathetic efferents to joint injury in experimental arthritis. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3423–3429. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03423.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Taiwo Y. O., Collins S. D., Tam J. K. Noradrenaline hyperalgesia is mediated through interaction with sympathetic postganglionic neurone terminals rather than activation of primary afferent nociceptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):158–160. doi: 10.1038/323158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu M., Sugimura K., Aoki S., Takahashi A. Morphometric analysis of the sural nerve in experimental dorsal rhizotomy in rats. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Jun;116(2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Neugebauer V., Cervero F., Schmidt R. F. Changes in tonic descending inhibition of spinal neurons with articular input during the development of acute arthritis in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Sep;66(3):1021–1032. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.3.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka K. A., Westlund K. N. Centrally administered non-NMDA but not NMDA receptor antagonists block peripheral knee joint inflammation. Pain. 1993 Nov;55(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90150-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka K. A., Willis W. D., Westlund K. N. Joint inflammation and hyperalgesia are reduced by spinal bicuculline. Neuroreport. 1993 Nov 18;5(2):109–112. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199311180-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonussi C. R., Ferreira S. H. Rat knee-joint carrageenin incapacitation test: an objective screen for central and peripheral analgesics. Pain. 1992 Mar;48(3):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90095-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


