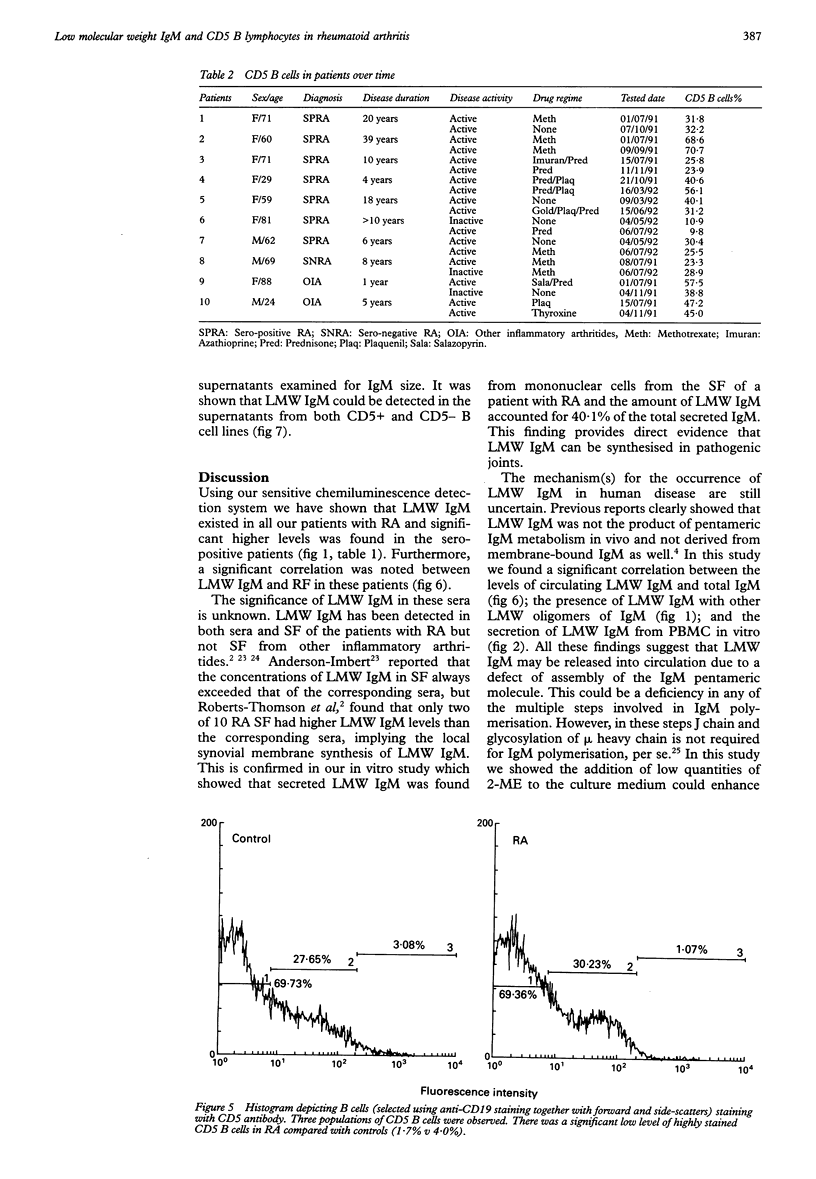
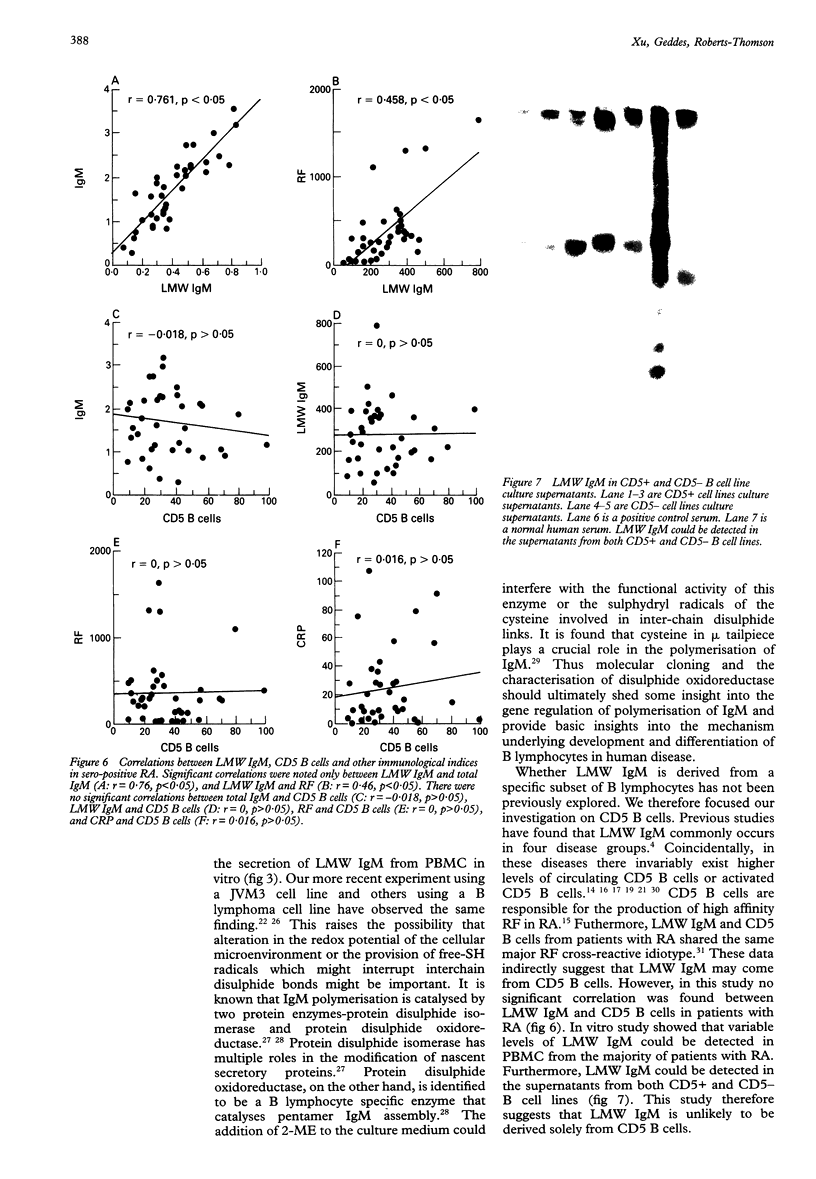
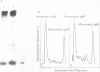Abstract
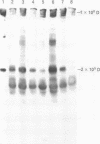
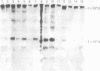
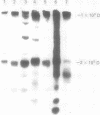
OBJECTIVES--To evaluate the role of low molecular weight (LMW) IgM and CD5 B cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to explore the possibility that LMW IgM is derived selectively from this subset of B cells. METHODS--LMW IgM in sera and culture supernatants was detected by a sensitive immunoblot technique with an enhanced chemiluminescence detection system. CD5 B cells were determined by FACScan cytometry. In vitro studies were established in culture plates containing pokeweed mitogen with or without 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME). Supernatants were obtained from CD5 positive hybridomas and CD5 negative hybridomas. Other immunological indices were measured by laser nephelometry. RESULTS--Circulating LMW IgM was detected in all rheumatoid patients with significantly higher levels being observed in sero-positive patients. LMW IgM correlated significantly with total IgM and RF. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from the majority of the patients with RA secreted LMW IgM in vitro as did mononuclear cells from a synovial fluid sample. The addition of low concentrations of 2-ME to the culture medium enhanced the proportions of secreted monomeric IgM. In contrast, PBMC from healthy subjects secreted only trace quantities of LMW IgM. In RA no significant correlations were observed between CD5 B cells and LMW IgM and RF. LMW IgM could be detected in the supernatants from both CD5+ and CD5- B cell lines. Finally, CD5 B cells were not significantly elevated in RA and levels remained constant over time. CONCLUSION--LMW IgM exists in high concentrations in RA sera and synovial fluid. Serum level correlates with RF and IgM. In vitro studies have suggested that the occurrence of LMW IgM may be due to an intrinsic defect(s) in the assembly of the IgM pentameric molecule. LMW IgM is unlikely to be derived solely from CD5 B cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberini C. M., Bet P., Milstein C., Sitia R. Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):485–487. doi: 10.1038/347485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antin J. H., Emerson S. G., Martin P., Gadol N., Ault K. A. Leu-1+ (CD5+) B cells. A major lymphoid subpopulation in human fetal spleen: phenotypic and functional studies. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bofill M., Janossy G., Janossa M., Burford G. D., Seymour G. J., Wernet P., Kelemen E. Human B cell development. II. Subpopulations in the human fetus. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1531–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonagura V. R., Pernis B., Agostino N., Ilowite N. T., Hatam L., Wedgwood J. F. The major rheumatoid factor cross-reactive idiotype in rheumatic disease. Int Rev Immunol. 1989;5(2):139–151. doi: 10.3109/08830188909061980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burastero S. E., Casali P., Wilder R. L., Notkins A. L. Monoreactive high affinity and polyreactive low affinity rheumatoid factors are produced by CD5+ B cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):1979–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Burastero S. E., Balow J. E., Notkins A. L. High-affinity antibodies to ssDNA are produced by CD-B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3476–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Burastero S. E., Nakamura M., Inghirami G., Notkins A. L. Human lymphocytes making rheumatoid factor and antibody to ssDNA belong to Leu-1+ B-cell subset. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):77–81. doi: 10.1126/science.3105056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. Probing the human B-cell repertoire with EBV: polyreactive antibodies and CD5+ B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:513–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauphinée M., Tovar Z., Talal N. B cells expressing CD5 are increased in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 May;31(5):642–647. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. C., Shulman M. J. IgM--molecular requirements for its assembly and function. Immunol Today. 1989 Apr;10(4):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki I., Shingu M., Nobunaga M., Otsuka E. Detection of low molecular weight IgM by immunoblot analysis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;14(4):674–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K. Development and physiology of Ly-1 B and its human homolog, Leu-1 B. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:53–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Shimizu M., Yamasaki K., Kishimoto T. Rheumatoid factor secretion from human Leu-1+ B cells. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3105057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harisdangkul V., Barnes T. Y., Songcharoen S., Pennebaker J. B. Clinical significance of low molecular weight IgM in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):638–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries R., Beckman I., Roberts-Thomson P. Low molecular weight IgM. Detection using immunoblotting. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 3;88(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J. The CD5 B cell. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:117–185. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Vaughan J. H. Genetic influence on the levels of circulating CD5 B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1060–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh L. Y., Jones D. N., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Appearance of low molecular weight IgM during course of infective endocarditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):471–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwitko A. O., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Shearman D. J. Low molecular weight IgM in selective IgA deficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):198–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. Surface phenotype and function of tonsillar germinal center and mantle zone B cell subsets. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jan;15(1):30–43. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Plater-Zyberk C., Andrew E. Autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. An approach via a study of B lymphocytes. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):319–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini A., Massa M., De Benedetti F., Viola S., Neirotti G., Burgio R. G. CD5 positive B lymphocytes in seronegative juvenile arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jul;17(7):932–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plater-Zyberk C., Maini R. N., Lam K., Kennedy T. D., Janossy G. A rheumatoid arthritis B cell subset expresses a phenotype similar to that in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Sep;28(9):971–976. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P. J., Wernick R. M., Ziff M. Low molecular weight IgM in rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jun;24(6):795–802. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Koshland M. E. Identification of a lymphocyte enzyme that catalyzes pentamer immunoglobulin M assembly. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4633–4639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Neuberger M., Alberini C., Bet P., Fra A., Valetti C., Williams G., Milstein C. Developmental regulation of IgM secretion: the role of the carboxy-terminal cysteine. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):781–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90092-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley H. B., Todd J., Barnes R. M., Thompson R. N., Abraham G. N., Johnson P. M. Estimation of serum V kappa IIIb light chains in rheumatoid arthritis and correlation with CD5-positive B-cells. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Oct;29(5):325–330. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.5.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowden J. A., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Zola H. Evaluation of CD5-positive B cells in blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7(6):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00270525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Sakane T., Engleman E. G. Anti-DNA antibody production by CD5+ and CD5- B cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):238–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI114418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. J., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J., Zola H. Comparative evaluation of CD5 B cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and essential mixed cryoimmunoglobulinemia using FACS analyzer and FACSCAN flow cytometer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 May 4;651:594–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb24673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. J., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Low molecular weight IgM in the sera of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Pathology. 1993 Jan;25(1):52–56. doi: 10.3109/00313029309068902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. J., Umapathysivam K., McNeilage J., Gordon T. P., Roberts-Thomson P. J. An enhanced chemiluminescence detection system combined with a modified immunoblot technique for the detection of low molecular weight IgM in sera from healthy adults and neonates. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 5;146(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90233-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Circulating low molecular weight IgM--a disease marker in autoimmune, infective, immunodeficient and B cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Dis Markers. 1992 May-Jun;10(3):115–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youinou P., Mackenzie L., Katsikis P., Merdrignac G., Isenberg D. A., Tuaillon N., Lamour A., Le Goff P., Jouquan J., Drogou A. The relationship between CD5-expressing B lymphocytes and serologic abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis patients and their relatives. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Mar;33(3):339–348. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]